Most people have difficulty understanding the concept of Debit and Credit. If you are a business owner, it will be useful that you learn the basic terminology of Debit and Credit so that you can keep accurate records for your business.
For every transaction, you will need to record it in your business accounting books in two accounts: the Debit and Credit accounts.
The recorded transactions will have an impact on the company's financial statement. Hence, it is essential to keep a precise record so that there will not be any error to balance the accounts.
What is a debit account?
A Debit account is an accounting entry that increases the assets or expense accounts or decreases the liabilities or equity accounts.
The type of accounts that follow this rule is the asset, expenses, and dividend account. The Debit account is placed on the left side of the accounting entry.
What is a credit account?
A Credit account is an accounting entry that increases the liabilities or equity accounts or decreases the assets or expense accounts.
The type of accounts that follow this rule is the liabilities, revenue, and equity accounts. The Credit account is placed on the right side of the accounting entry.
Example of debit and credit usage
Here is an example to have a clearer understanding of record keeping:
Jackson Corporation buys a machine with a cost of $20,000 on credit to run their business.
We will need to record the equipment in the fixed asset account as Debit and Credit the account payable (liability) account.
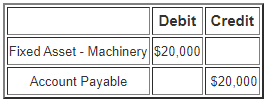
The reason we Debit the fixed asset is that any purchase of fixed assets such as machinery, plant, land, office equipment, furniture, and computers increases the company's asset account.
Thus, we record the fixed asset under the debit column.
The company purchased the machine under credit terms and not fully paid. Therefore, this increases the liability account, and we Credit the account payable.

