Industry
Industrial Manufacturing
High Tech & Electronics
Footwear Manufacturing
Apparel & Textiles
Food & Beverage
Rubber & Plastics
Metal Fabrication
Industrial Machinery & Equipment
Construction & Engineering
Furnitures & Fixtures
Medical Device Manufacturing
Automotive Manufacturing
Aerospace And Defence
Screw Shop Manufacturing
Spring Shop Manufacturing
Solutions
Pricing
Resources
Company
What is MRP?
Deskera MRP helps you optimize your entire manufacturing process - from production planing and process scheduling, to quality and compliance - while reducing total manufacturing cost. All while being integrated to your Accounting, CRM, and HR systems.

What Is Material Requirements Planning (MRP)?
In order to streamline production and ensure that materials are available when they are needed, businesses use material requirements planning (MRP). MRP is a computer-based inventory management system that determines when raw materials should be ordered and delivered to the production floor. The goal of MRP is to avoid stock outs, which can disrupt production and lead to lost sales.
MRP systems begin with a forecast of customer demand. This demand forecast is then used to create a production plan that outlines the specific quantities of materials and components that will be needed to produce the forecasted number of finished goods. The production plan is then used to generate purchase orders for raw materials.
MRP systems take into account the lead time for each component. Lead time is the amount of time that passes between the placement of an order and the receipt of the goods. In order to ensure that materials are available when they are needed, the MRP system must account for the lead time of each component in the production process.
MRP systems are also capable of handling production constraints. A production constraint is any factor that limits the amount of product that can be produced. For example, a business might have a limited number of machines that can be used to produce a product.
How Material Requirements Planning Works
The MRP system is based on three important concepts:
The bill of materials (BOM)
The production schedule
The inventory records
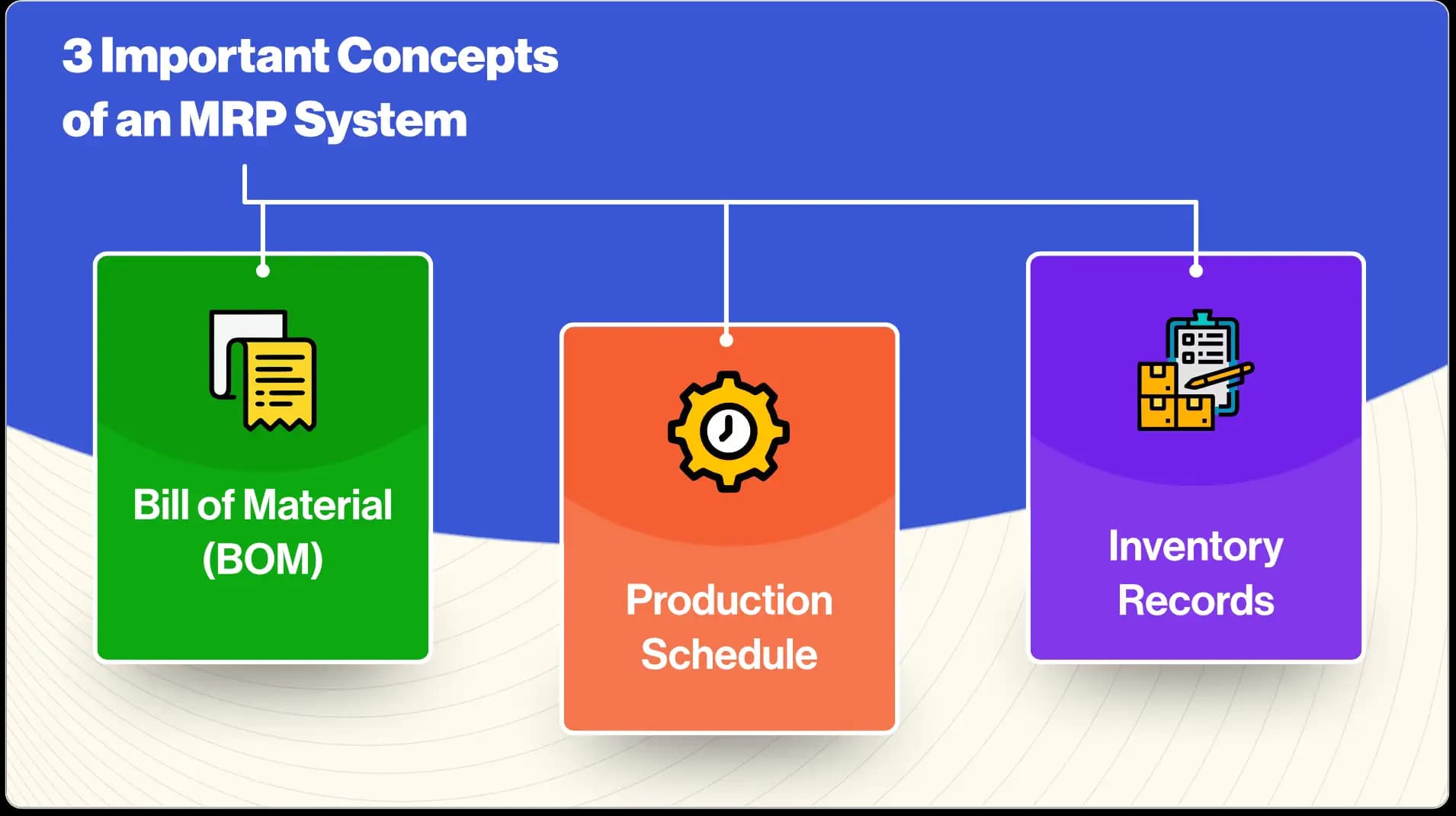
The bill of materials is a list of all the materials needed to produce a product. It includes the quantity of each material required and the order in which they are used. The production schedule is a plan that indicates when each product is to be made and in what quantity. The inventory records show how much of each material is on hand at any given time. MRP brings these three concepts together to create a master production schedule. This schedule is used to produce the materials needed for each product in the correct quantities and at the right time.
The Role of MRP In Manufacturing
MRP software gives manufacturers the ability to make better-informed decisions about production planning, scheduling, and inventory management. It ensures that the correct materials are available when needed, and that production schedules are adhered to.
MRP also provides visibility into the manufacturing process, so that issues can be identified and resolved quickly. This visibility into the manufacturing process helps to identify issues quickly and resolve them before they cause delays. Without MRP, it would be very difficult to manage the manufacturing process effectively. MRP ensures that production schedules are followed, and that the correct materials are available when needed.
What are the differences between MRP and ERP?
In the business world, the terms MRP and ERP are often used interchangeably, but there is a big difference between the two. MRP is focused on materials, while ERP is focused on all resources. MRP systems are typically used by manufacturing businesses, while ERP systems are used by businesses of all types.
There are four primary differences between MRP and ERP systems:
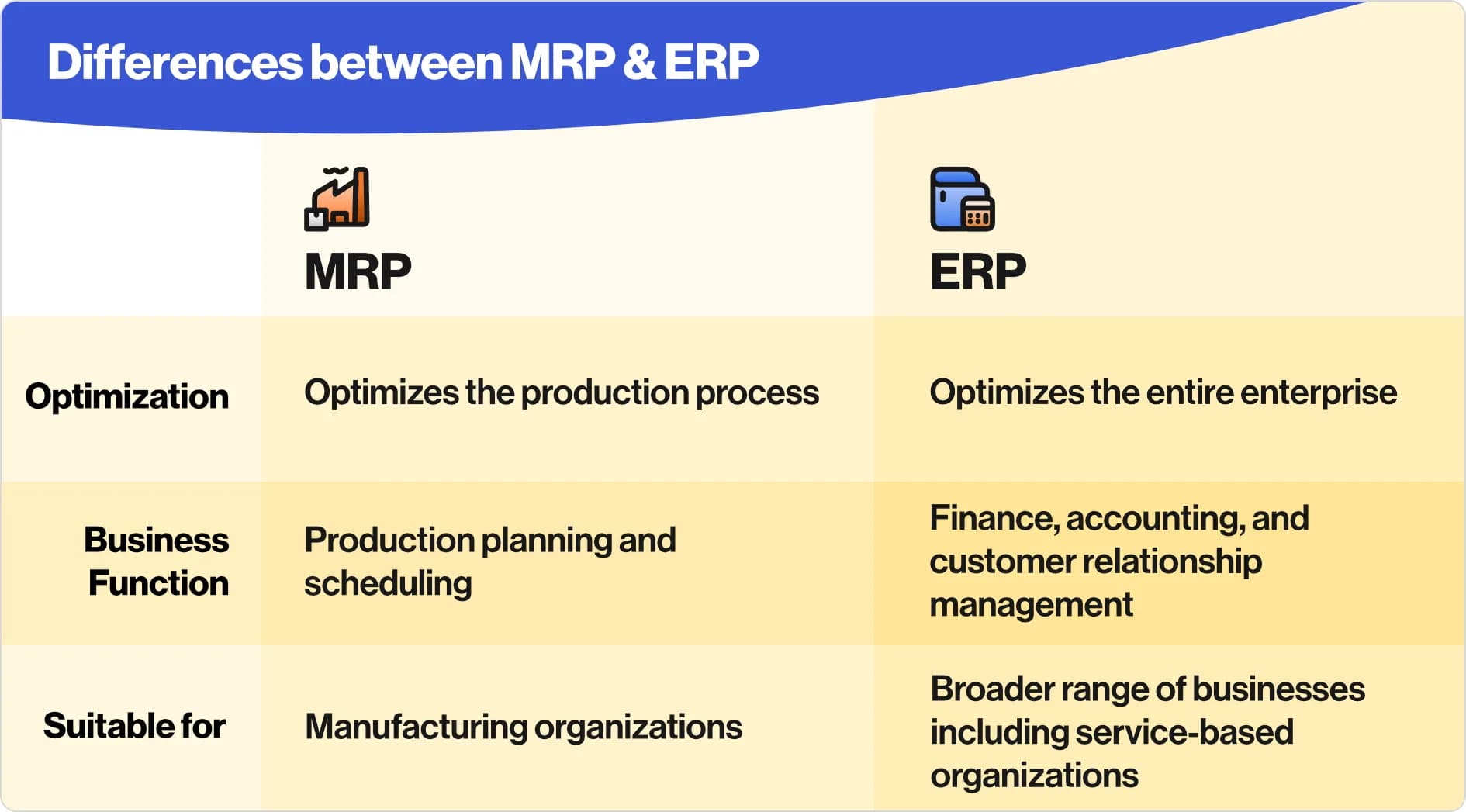
MRP systems are designed to optimize the production process, while ERP systems are designed to optimize the entire enterprise.
MRP systems focus on production planning and scheduling, while ERP systems encompass a wider range of business functions including finance, accounting, and customer relationship management.
MRP systems are typically used by manufacturing organizations, while ERP systems are used by a broader range of businesses including service-based organizations.
MRP systems are typically deployed on-premise, while ERP systems are available as both on-premise and cloud-based solutions.
Benefits of an MRP system
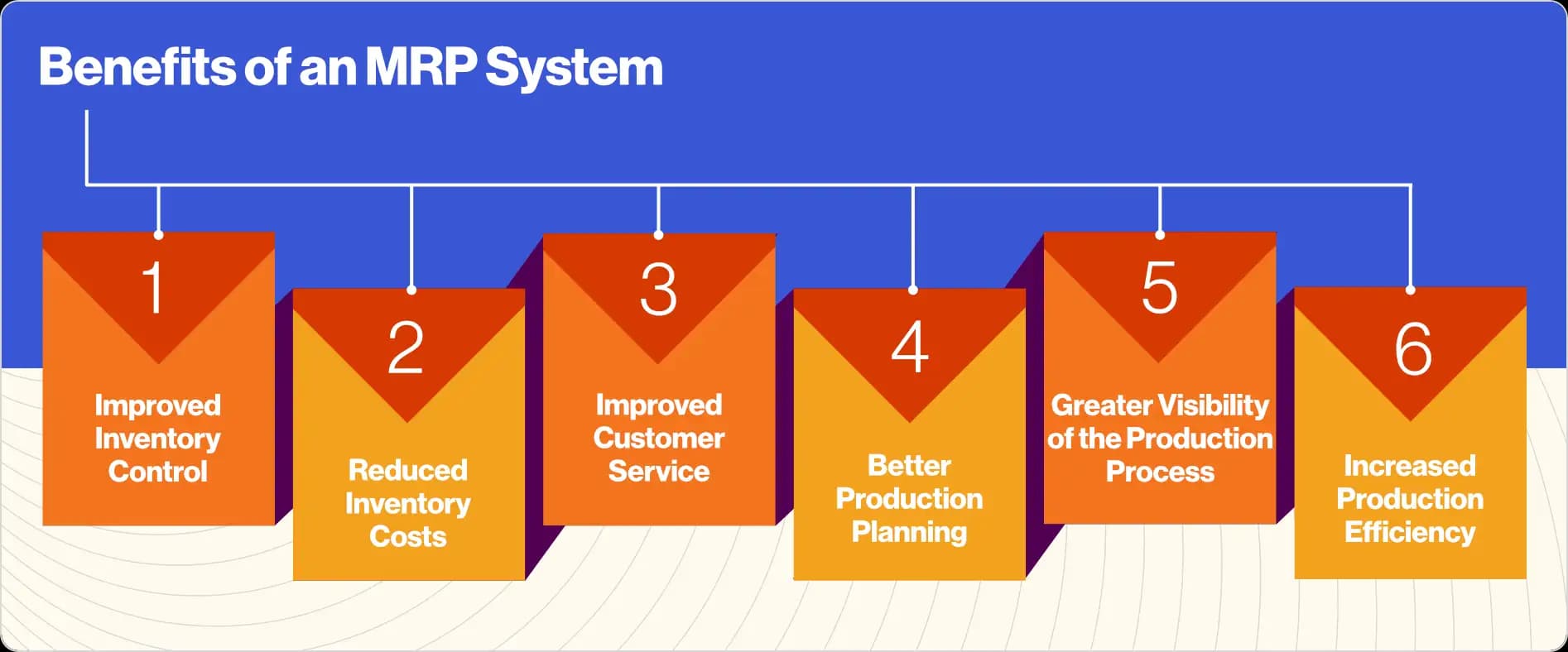
There are many benefits of using MRP, including:
Improved inventory control:
MRP ensures that the right materials and components are on hand when needed, and that inventory levels are kept at optimal levels. This can help to reduce stock-outs and excess inventory, both of which can lead to lost sales and increased costs.
Reduced inventory costs:
An MRP system can help manufacturers reduce inventory costs by ensuring that materials are only purchased and produced when they are required. This “just in time” production approach can help to avoid the need for expensive inventory storage and can minimize the risk of materials becoming obsolete.
Improved customer service:
An MRP system can help manufacturers to improve customer service by ensuring that products are available when they are needed. This can be particularly important for companies that produce products to customer order, or that operate in industries with seasonal demand.
Better production planning:
MRP can help to improve production planning by providing accurate information on lead times and material availability. This can help to avoid production delays and disruptions.
Greater visibility of the production process:
An MRP system can provide manufacturers with greater visibility of the production process, by tracking progress and identifying potential problems. This information can be used to improve the efficiency of the production process and to avoid delays or disruptions.
Increased production efficiency:
An MRP system enables manufacturers to plan production more efficiently and effectively, by considering all of the resources required to produce a product. This includes material requirements, as well as production capacity and availability. By planning production in advance, manufacturers can avoid delays and disruptions caused by last-minute changes or unexpected shortages.
How To Plan Your MRP System
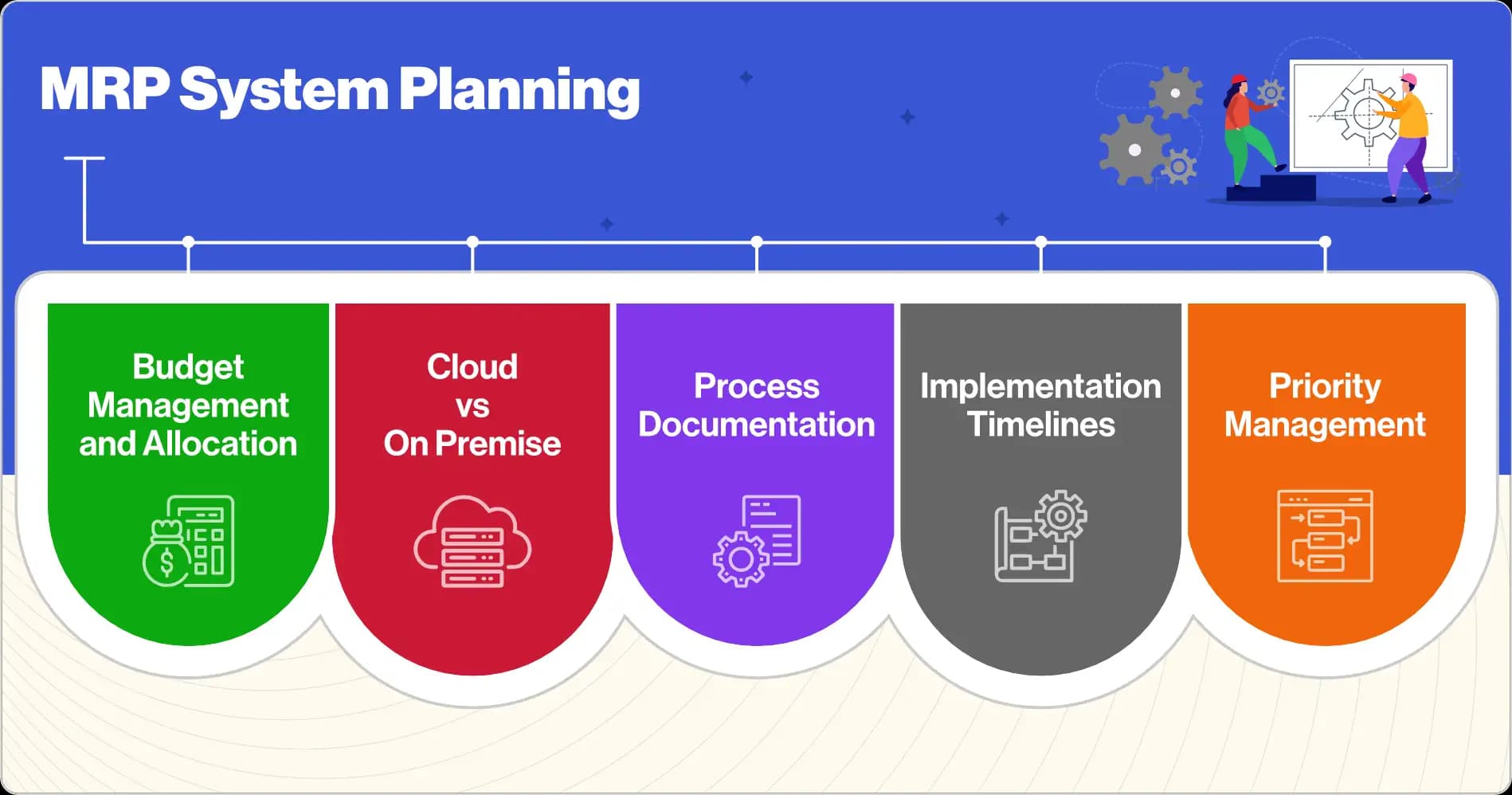
Budget Management and Allocation
Budget management is an important part of any business, but it is especially important when implementing new software. A properly managed budget will help ensure that your business has the funds it needs to cover the costs of the software, as well as any other associated costs.
When it comes to budgeting for MRP, there are a few things to keep in mind. First, you will need to consider the one-time cost of purchasing MRP.
In addition to the purchase price, you will also need to consider the cost of training your staff to use the software. This can be done in-house or through a third-party provider. Finally, you will need to consider the ongoing costs of using the software. These can include things like subscription fees, support costs, and upgrades.
Cloud vs On Premise
Cloud-based MRP software is hosted by the software provider and is accessed via the internet. Some advantages of cloud based MRP software:
Quick and easy set up
No hardware or software to install
No maintenance costs
Accessible from anywhere with an internet connection
Scalable - you can add or remove users as your business needs change
Automatically backed up
Regular software updates included in the subscription fee
On-premise MRP software is installed on a company’s own servers and is managed internally. Some advantages of on-premise MRP software:
You own the software so there are no monthly subscription fees
You have full control over the software and can customize it to your specific needs
You can host the software on your own servers so it's not reliant on a good internet connection
Both cloud and on premise MRP have their disadvantages. Using a cloud MRP requires a good internet connection and requires a monthly subscription fee. Using an on premise MRP requires significant upfront investment, IT resources to install and maintain the software, and may not be able to keep up with the latest software updates.
Process documentation
Documenting internal processes is critical to the success of any Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP) implementation. By documenting and analyzing current processes, organizations can identify areas in which MRP can be used to improve efficiencies and effectiveness. Additionally, documenting processes can help to ensure that all stakeholders are aware of the steps involved in manufacturing and can provide a clear understanding of how MRP will impact each stage of production.
There are a few key areas that should be addressed when documenting internal processes:
Production process flow:
The first step is to map out the current production process flow. This will help to identify any bottlenecks or inefficiencies in the current process. Additionally, it is important to document the specific tasks that are performed at each stage of production.
Materials and components:
Another key area to document is the materials and components that are used in the production process. This includes both raw materials and finished goods. It is important to track the movement of materials and components throughout the production process to identify any potential issues with inventory levels.
Capacity and utilization:
Another key factor to consider is the capacity and utilization of the existing production facilities. This information will help to determine if the current facilities are adequate to support the projected production volume. Additionally, it can help to identify any areas where additional capacity may be required.
Scheduling:
The current scheduling process should also be documented. This includes the methods that are used to create the production schedule as well as the methods that are used to track progress and revise the schedule as necessary.
Quality:
The final key area to address is quality. The current quality control procedures should be documented. Additionally, any issues that have been identified with the current quality control process should be addressed.
Once the internal processes have been documented, the next step is to analyze the information to identify areas where MRP can be used to improve the process.
Implementation Timelines
Implementation timelines are critical to the success of any manufacturing resource planning (MRP) system. By finalizing the implementation timeline before starting the MRP project, you can avoid many of the pitfalls that can occur during an MRP implementation.
There are a few key steps to finalizing the implementation timeline:
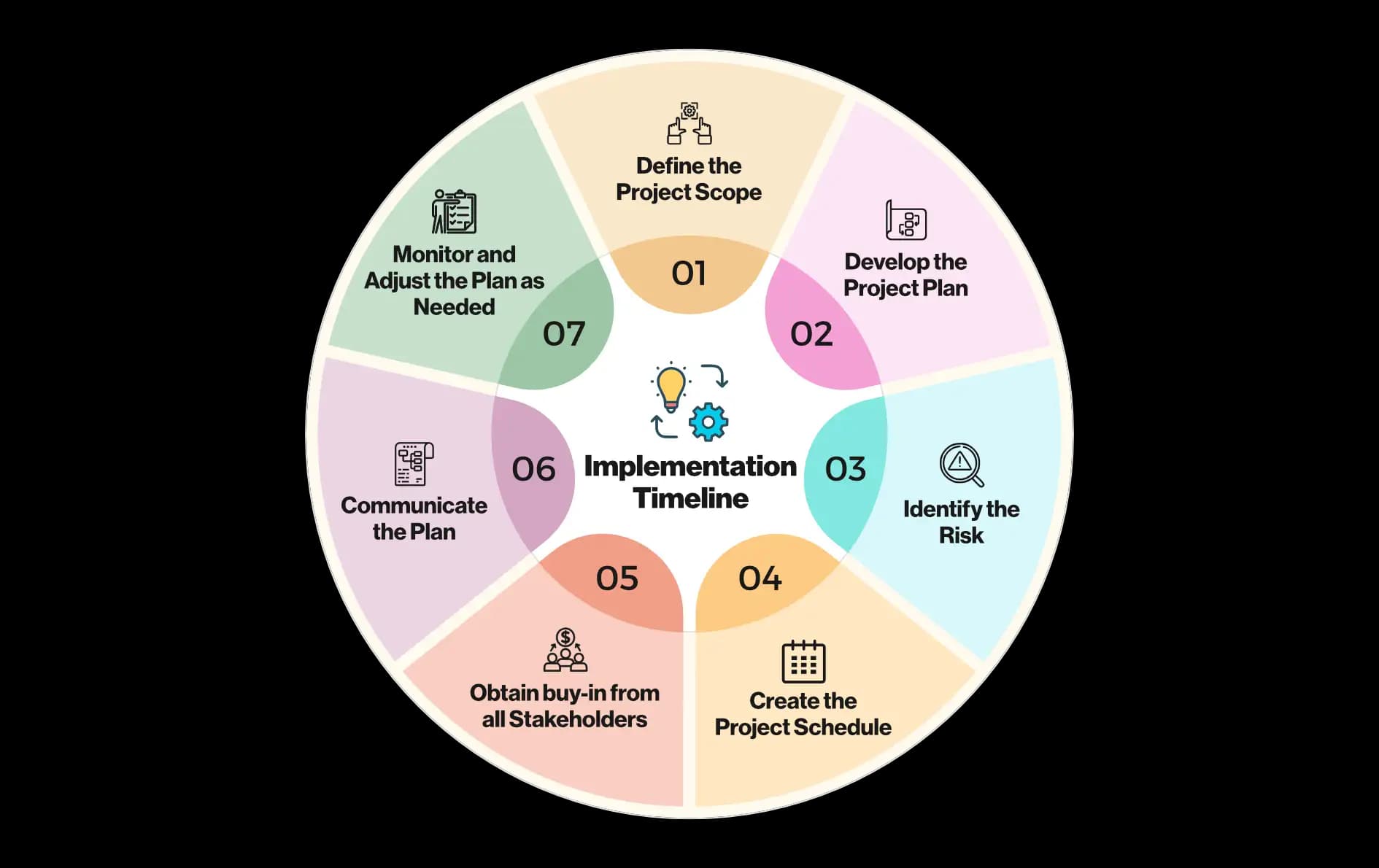
Define the project scope.
The first step is to define the project scope. This includes understanding the current state of the manufacturing operation, the desired state of the operation after MRP is implemented, and the specific goals and objectives of the MRP project.
Develop the project plan.
The next step is to develop the project plan. This plan should include a detailed description of the tasks that need to be completed, the resources required, the timeline for each task, and the dependencies between tasks.
Identify the risks.
As with any project, there are always risks associated with an MRP implementation. It is important to identify these risks upfront and develop plans to mitigate them.
Create the project schedule.
The project schedule is a critical component of the project plan. It should include the start and end dates for each task, the dependencies between tasks, and the resources required for each task.
Obtain buy-in from all stakeholders.
Once the project plan is complete, it is important to obtain buy-in from all stakeholders. This includes executive management, the project team, and any other individuals who will be affected by the MRP implementation.
Communicate the plan.
After the project plan is finalized, it is important to communicate the plan to all stakeholders. This includes providing them with a copy of the project schedule and ensuring that they understand their role in the project.
Monitor and adjust the plan as needed.
As the project progresses, it is important to monitor the project schedule and make adjustments as needed. This includes adding or removing tasks, changing the resources assigned to tasks, and adjusting the timeline.
Monitor and adjust the plan as needed.
As the project progresses, it is important to monitor the project schedule and make adjustments as needed. This includes adding or removing tasks, changing the resources assigned to tasks, and adjusting the timeline.
By following these steps, you can develop a detailed and accurate implementation timeline that will help ensure the success of your MRP project.
Priority Management
An important step in any MRP implementation is to develop a clear understanding of the priorities of the organization. What are the most important things that the organization wants to achieve? What are the timeframes in which these things need to be accomplished? What are the risks and potential rewards associated with each priority? Once these questions have been answered, the organization can develop a clear plan for how MRP will be used to achieve its goals.
One of the most important aspects of priority management is setting realistic goals. It is important to remember that MRP is a tool, and not a magic bullet. It can help to streamline production and make it more efficient, but it cannot do everything. Organizations need to set realistic goals for what they want to achieve with MRP, and then develop a plan for how to best utilize the tool to achieve those goals.
What is a good MRP system?
An effective MRP system comprises of a few key components:
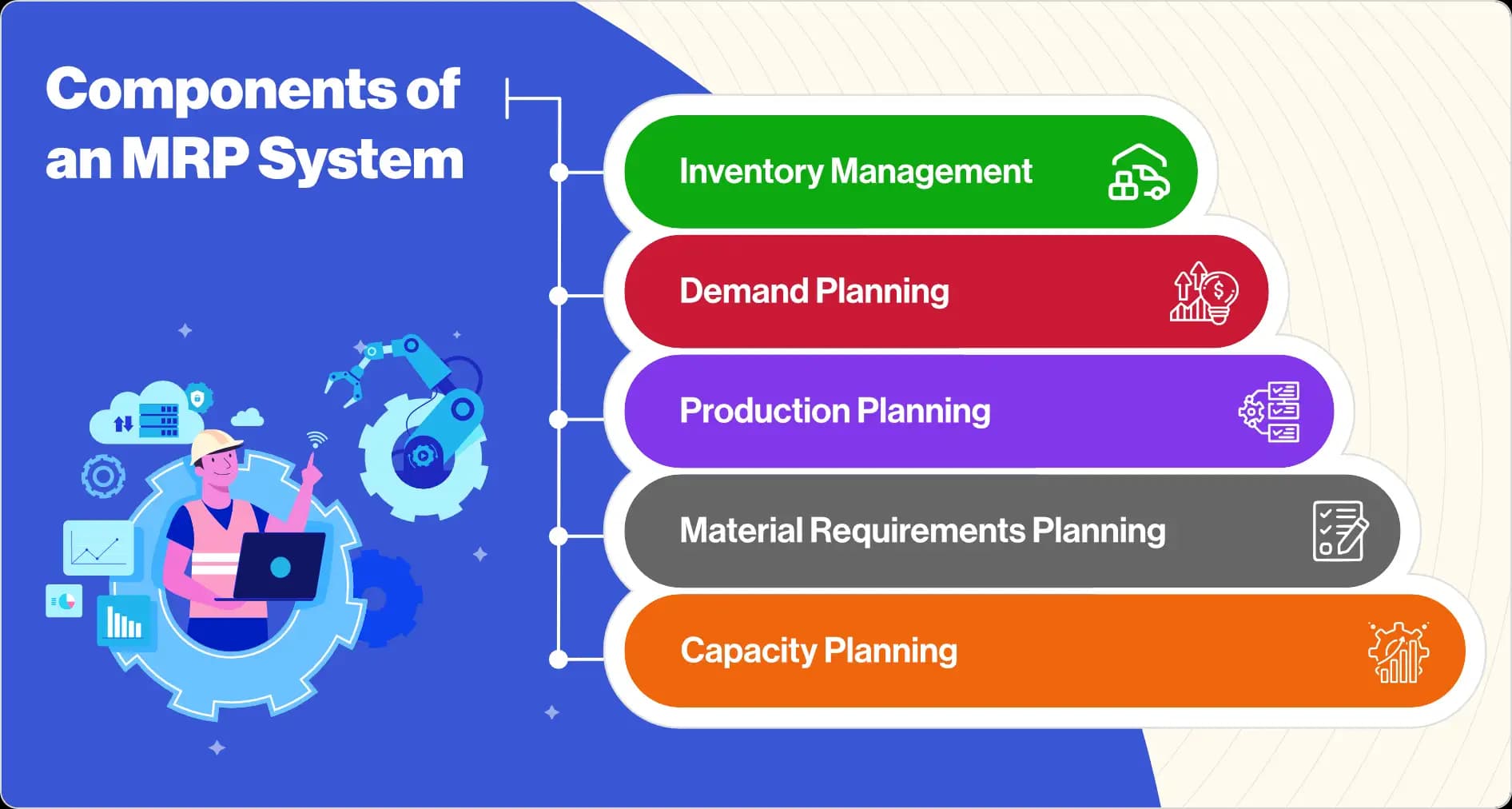
Inventory management:
This module is responsible for managing inventory levels, and ensuring that there is enough stock on hand to meet customer demand. It tracks inventory levels, reorder points, and lead times to help ensure that materials are available when needed.
Demand planning:
This module forecasts future demand for a product or service, and is used to create production plans that meet this demand. It takes into account factors such as seasonality, customer trends, and historical data to generate accurate predictions.
Production planning:
This module creates production plans that detail when and how much of a product needs to be produced. It takes into account inventory levels, demand forecasts, and lead times to ensure that finished goods are available when needed.
Material requirements planning:
This module is responsible for ensuring that the necessary materials are available to support production. It creates detailed plans that specify what materials are needed, when they are needed, and how much is needed.
Capacity planning:
This module ensures that the necessary resources are available to support production. It takes into account factors such as machine utilization, crew availability, and downtime to create a production plan that can be executed without issue.
These are just a few of the key components that make up a successful MRP system. When all of these components are working together, they can help create a well-oiled machine that runs smoothly and efficiently.
Why is MRP important?
Here are five reasons why MRP is important:
MRP ensures that the right materials are available when needed.
MRP reduces the overall cost of inventory.
MRP eliminates the need for keeping excess inventory.
MRP increases production efficiency.
MRP facilitates decision making regarding production planning.
Who uses an MRP system?
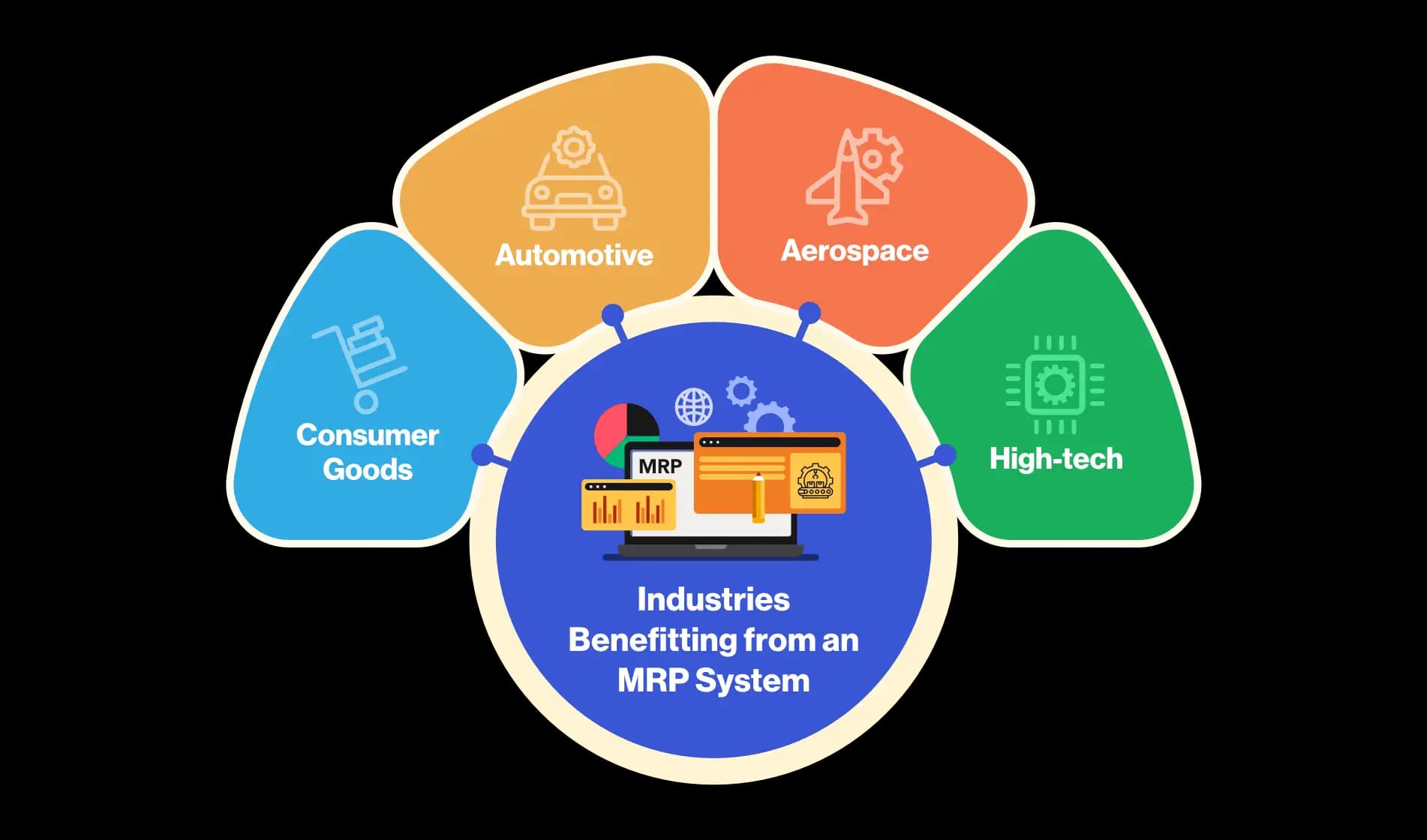
There are a variety of industries that can benefit from using an MRP system. Some of the most common include:
Automotive:
The automotive industry is a major user of MRP systems. In fact, many of the world's leading automakers, such as Ford, General Motors, and Toyota, use MRP systems to manage their production operations.
Aerospace:
The aerospace industry is another major user of MRP systems. Many of the world's leading aerospace companies, such as Boeing, Airbus, and Lockheed Martin, use MRP systems to manage their production and inventory operations.
High-tech:
The high-tech industry is another major user of MRP systems. Many of the world's leading high-tech companies, such as Apple, IBM, and Microsoft, use MRP systems to manage their production and inventory operations.
Consumer goods:
The consumer goods industry is another major user of MRP systems. Many of the world's leading consumer goods companies, such as Procter & Gamble, Nestle, and Unilever, use MRP systems to manage their production and inventory operations.
Key Components of an MRP
An MRP system is composed of three main modules:
The master production schedule (MPS) module
The MPS module is the heart of the MRP system and provides the overall production plan for the entire company. It includes information on the products to be produced, the production quantities, the due dates, and the priorities.
The inventory module
The inventory module keeps track of all the materials and components in the company's inventory. It includes information on what materials are available, what materials are needed, and when the materials are needed.
The bills of materials (BOM) module
The BOM module contains the information on the materials and components required to produce a product. It includes information on the quantity of each material or component needed, the unit of measure, and the source of the material or component.
How do you maintain MRP
The first step in maintaining an MRP system is to understand the production process. This includes understanding the bill of materials (BOM), the production schedule, and the inventory levels. The BOM is a list of all the materials that are needed to produce a product. The production schedule is a list of all the steps that are needed to produce a product. The inventory levels are the amount of each material that is on hand.
The second step in maintaining an MRP system is to understand the system itself. This includes understanding the software and the hardware. The software is the program that is used to manage the system. The hardware is the computer that is used to run the software.
The third step in maintaining an MRP system is to keep the system updated. This includes updating the software and the hardware. The software is updated by installing updates. The hardware is updated by replacing old components with new ones.
How do you do capacity planning with MRP
Making sure you have just the right amount of inventory is called capacity planning There are two types of capacity planning:
Long-term capacity planning:
This type of capacity planning is done on a strategic level and looks at capacity needs over a period of several years.
Short-term or tactical capacity planning:
This type of capacity planning is done on an operational level and looks at capacity needs over a shorter period of time, usually one year or less.
There are a lot of factors to consider in capacity planning, such as:
The amount of raw materials needed to make a product
The time it takes to make a product
The amount of finished products you need to have on hand
The amount of space you have to store inventory
The lead time for ordering new inventory
MRP systems are well suited to capacity planning because they track both the demand for a product and the available capacity to produce it. This information can be used to generate production plans that balance customer demand with the available capacity.
Examples of MRP Software
Deskera:
Deskera MRP is a cloud based, integrated platform that combines Accounting, CRM, and HR Management into a single, easy-to-use platform. Deskera MRP offers the ability to predict material requirements, track work center activities, manage labor resources, optimize routing, and so much more, powered by automation and advanced tools to save you time and reduce costs. Deskera is rated 4.7 by Capterra, the highest among its peers in the MRP industry.
Netsuite:
Netsuite MRP is a cloud-based inventory management software that offers features such as real-time inventory tracking, demand forecasting, and purchase order management.
Odoo:
Odoo is a highly technical MRP system that includes some features to help businesses streamline manufacturing processes.
Fishbowl:
Fishbowl Manufacturing is an inventory and manufacturing software.
SAP:
SAP is a German software company that offers a variety of enterprise software solutions, including an MRP solution.
Katana:
Katana provides a limited set of inventory management solutions as part of its MRP software.
History of MRP
In the early 1960s, Joseph Orlicky, a production manager at General Motors, developed a system called "material requirements planning" (MRP). This system was designed to help GM keep track of the parts and materials needed to build its cars. The MRP system was later adopted by other companies, and became the basis for the modern MRP system. In the late 1960s and early 1970s, manufacturers began to look for ways to improve their production planning and control processes. They were motivated by the need to reduce inventory levels and production costs, and to respond more quickly to customer demand. These objectives led to the development of new production planning and control systems, including materials requirements planning (MRP) systems.
In the late 1960s, a group of engineers at Ford Motor Company developed a system called Manufacturing Resources Planning (MRP II). This system was designed to manage inventory and production using a computer. MRP II was a breakthrough in manufacturing and soon became the standard for production planning.
The first MRP systems were developed in the early 1970s. The first MRP system was developed by Orlicky, who is considered the father of MRP. Orlicky’s book, Materials Requirements Planning, was published in 1974 and outlined the MRP system that he had developed.
In the early days of MRP systems, data were entered into the system manually. This was a time-consuming and error-prone process. In the early 1980s, most MRP systems were still stand-alone, mainframe-based packages that were inflexible, difficult to use, and expensive. These systems were designed to support manufacturing operations in large, complex organizations.
In the mid-1980s, client/server MRP systems began to emerge. These systems were more flexible and easier to use than their mainframe-based predecessors, and they were also much less expensive. As a result, client/server MRP systems quickly became the preferred choice for manufacturing organizations of all sizes.
MRP systems have evolved a lot over the years. The first generation of MRP systems was focused on inventory management. The second generation of MRP systems added features for production planning and scheduling. The third generation of MRP systems added features for supply chain management. Today’s MRP systems are complex, powerful systems that can help manufacturers manage all aspects of production, from materials procurement to finished goods inventory.
Future of MRP
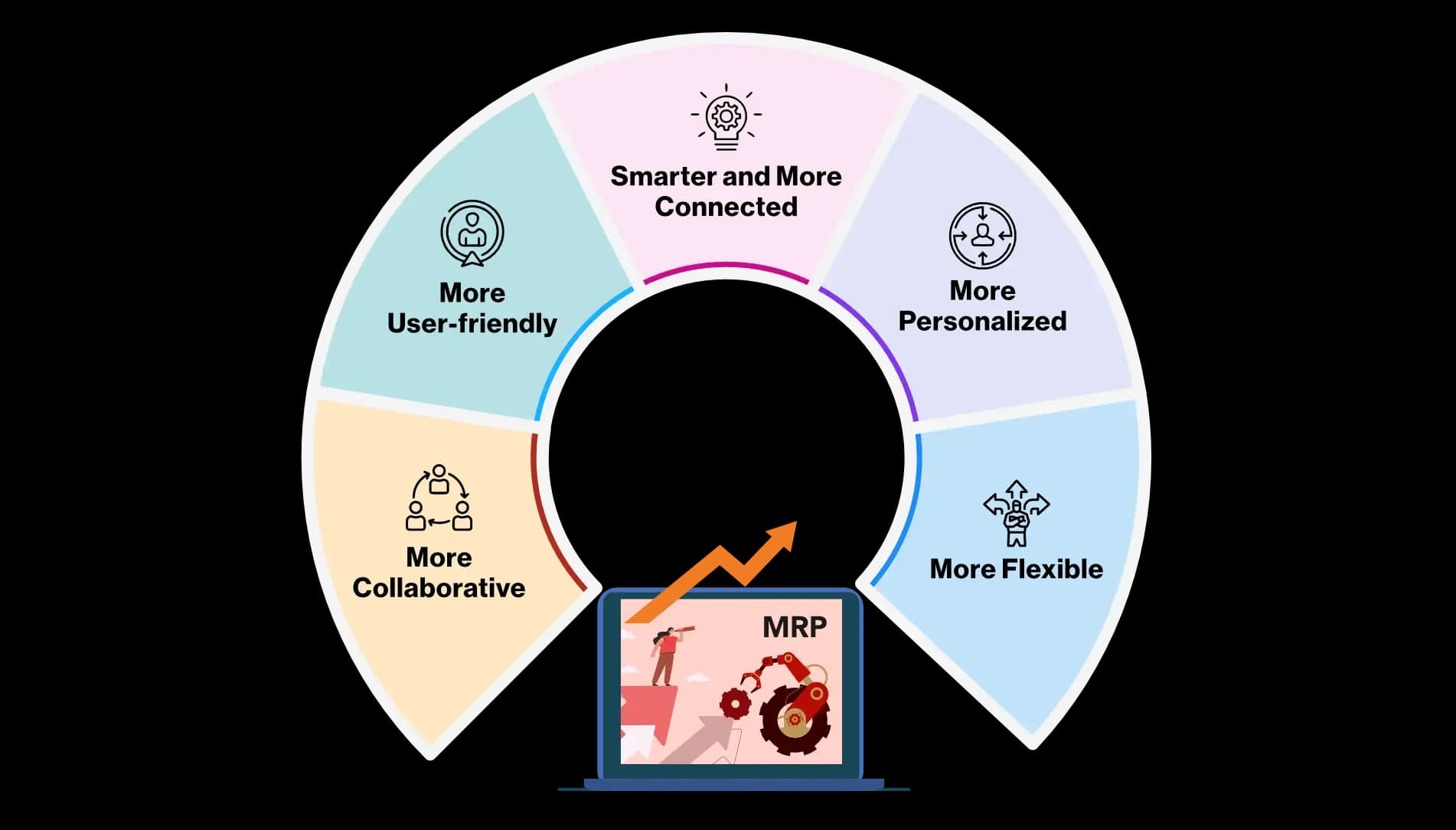
The future of Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP) systems is exciting. With the advent of Industry 4.0, the opportunities for MRP systems are endless. Here are some of the ways that MRP systems will evolve in the future:
Smarter and more connected:
MRP systems will become more intelligent and better connected. With the help of artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT), MRP systems will be able to collect and analyze data more effectively. This will enable MRP systems to make better decisions and provide more accurate predictions.
More personalized:
In the future, MRP systems will be able to provide more personalized experiences. This means that MRP systems will be able to take into account the specific needs of each user. For example, MRP systems will be able to provide recommendations for individual users based on their specific preferences.
More flexible:
In the future, MRP systems will be more flexible. This means that MRP systems will be able to adapt to changes more easily. For example, if a company decides to change its manufacturing process, the MRP system will be able to adapt to the new process quickly and easily.
More collaborative:
In the future, MRP systems will be more collaborative. This means that MRP systems will be able to work with other systems more effectively. For example, MRP systems will be able to share data with other systems such as ERP systems. This will enable MRP systems to provide a more holistic view of the manufacturing process.
More user-friendly:
In the future, MRP systems will be more user-friendly. This means that MRP systems will be easier to use and more intuitive. For example, MRP systems will be able to provide step-by-step instructions for users. This will make it easier for users to use MRP systems and will make MRP systems more accessible to a wider range of users.
Contact Us
What our Customers Say About Us
Whatever your business
size, Deskera enables you to
simplify operations across
business functions. Here's
what our customers say
about us.


At GoDo, we understand that managing our finances and customer relationships is essential for our success. Deskera has provided us with an easy to use and intuitive platform that has enabled us to access our financial data, track customer relationships, and manage our finances with ease. We have been able to streamline our processes, better manage our finances, and stay on top of our customer relationships. We highly recommend Deskera to any business that is looking to stay organized and efficient.
Wesley Wright
CEO, GoDo Life


We are extremely pleased with our decision to switch to Deskera and have seen a significant improvement in our business operations since making the switch. The sales process was smooth from start to finish and customer support at every step of the implementation was stellar. Highly recommend Deskera to those looking for a great ERP solution.
Wally Mears
CEO, The Jungle

We implemented Deskera's integrated platform to improve our procurement and inventory management processes to streamline our operations and improve efficiencies. I highly recommend their platform to any company looking to accelerate their growth.
Scott Phetsalod
Laboratory Manager
Run Your Business With Deskera

Products
Use Cases
 , India
, India  , Singapore
, Singapore  , and Canada
, and Canada  with
with 


