Are you curious about manufacturing and how it affects our everyday lives? In this article, we will look at the basics of manufacturing, its impact on our world, and why it’s important.
The manufacturing market's value is expected to reach $2 trillion in 2024, with an annual growth rate of 1.15% from 2024 to 2029.
Whether you're a small business owner, a large corporation, or a government agency, understanding the basics of manufacturing can help you make informed decisions about your products and services. With the right knowledge and resources, manufacturing can positively impact your organization and the economy as a whole.
Manufacturing is taking raw materials and turning them into products you can use in your everyday life. Manufacturing plays a part in everything from the clothes you wear to the car you drive to the food you eat.
It's an exciting field that involves taking raw materials, combining them together with other materials, and then transforming them into finished products. It's the backbone of many industries, and it's something that has been around for centuries.
Deskera can significantly enhance manufacturing operations through its integrated business management software. By streamlining inventory management, production planning, and order management, Deskera ensures optimal stock levels, efficient resource allocation, and high-quality standards.
Its comprehensive Bill of Materials (BOM) management, financial insights, and compliance features empower manufacturers to improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and support data-driven decisions.
Manufacturing is an essential part of the economy. It involves the transformation of raw materials into finished goods, which are then sold or used as components in the production of other products. It has a long history and is constantly evolving. Manufacturing is a complex and varied process, but at its core, it involves transforming raw materials into useful products.
Let’s dive in and explore the exciting world of manufacturing!
What is Manufacturing?
Manufacturing is the process of turning raw materials into finished products. It involves a lot of steps, like designing, production, assembly, testing, and packaging. It's a big part of the global economy and is responsible for producing the things we use every day.
Manufacturing is a fantastic process that can turn a raw material like steel or plastic into something useful, like a car or a computer. It's amazing that all of these products started out as simple materials and have been transformed into something so complex.
Overview of the Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process is the way in which goods are made from raw materials. It usually involves a number of steps, from sourcing the raw materials to the final assembly of the finished product.
Generally, the process involves transforming the raw materials into components, assembling the components into the finished product, and then packaging the product for shipping. Each step of the process typically requires specific machinery or equipment and may involve manual labor or automation. The process can be complex, but the end result is high-quality products that customers can enjoy.
Steps in the Manufacturing Process
- Planning: The first step in any manufacturing process is planning. This involves determining what products to make, deciding what materials are needed, and setting production goals. This helps ensure the process runs smoothly and efficiently.
- Design: In this stage, engineers create the plans for the product. This includes designing the product, creating a prototype, and testing it to make sure it meets the desired specifications.
- Procurement: The step of procurement involves purchasing the necessary raw materials and components from outside suppliers. Quality control checks are done to make sure the materials meet the required standards.
- Production: The materials and components are then put through a series of manufacturing processes to produce the finished product. This includes cutting, molding, assembling, and testing.
- Quality Control: Quality control is a critical step in the manufacturing process. This involves testing the product to make sure it meets the required standards.
- Packaging and Shipping: The finished product is then packaged for shipping. This includes labeling, packaging, and loading onto trucks or planes for delivery.
- Maintenance: Once the product has been shipped, the manufacturing process still needs to be finished. Maintenance is needed to keep the machinery and equipment in good working order. This helps ensure the process runs smoothly and efficiently.
Component Parts and Materials
The components and materials in the manufacturing process can vary depending on the product being made. Generally speaking, these components can include raw materials, such as metals and plastics, that are shaped into the desired product.
Components like screws and wire can also be used to assemble the product. Common materials used in the manufacturing process include metals, plastics, woods, and textiles. Some products may also involve components like electronics, rubber, and glass.
Depending on the complexity of the product, the materials and components used in the manufacturing process can vary. For example, a simple product like a wooden spoon may involve wood, while a more complex product like a computer could involve dozens of different components and materials.
Finally, there can be surface treatments like painting and finishing that are applied to the product to make it look great!
Production Planning and Scheduling
Production planning and scheduling is an important part of the manufacturing process. It helps to ensure that all of the necessary steps are taken in order to produce a quality product in a timely and efficient manner.
Production planning involves creating a schedule that outlines the tasks that need to be accomplished, how long each task should take, and what resources are needed to complete it. This includes selecting materials, designing the product, and setting up machinery and production lines.
All of these steps need to be carefully planned out in order to ensure that the end product meets the desired specifications. By taking the time to plan out the production process, manufacturers can save time and money by avoiding costly delays and mistakes.
There are various types of production planning. Let’s take a quick look here:
Production Line
A production line is an efficient system used in the manufacturing process to produce high volumes of the same product. It is a set of sequential processes that involve the use of specialized equipment and machinery to assemble parts into a finished product.
Production lines are designed to maximize productivity and efficiency, allowing companies to produce more items in less time. In short, a production line is a great way to streamline the manufacturing process. It helps you save time and money while producing a high-quality product.
Quality Control
You can only possibly imagine a successful manufacturing business with solid quality control in place. Quality control is essential for a successful manufacturing process. Here are some quality control steps that manufacturers can consider:
- Develop quality standards: Before production even begins, it’s important to establish quality standards that will guide the manufacturing process.
- Inspect incoming materials: All materials should be inspected for defects before they are used in production.
- Monitor production processes: During production, the process should be closely monitored to ensure that the product is made in accordance with the quality standards.
- Test the finished product: Once the product is finished, it should be tested to ensure that it meets the quality standards.
- Identify and correct problems: If any issues are discovered during testing, they should be identified and corrected as soon as possible.
By following these quality control steps, you can ensure that your products are of the highest quality.
Types of Manufacturing
There are several different types of manufacturing processes. Each process has different steps and techniques that are used to create a final product. Depending on the product, different combinations of processes may be used.
Let’s look at each of them in detail.
Batch Manufacturing
Batch manufacturing is a production process that involves making multiple items in a single production run. This is done by combining the same materials and following the same process to make each item. Batch manufacturing is a great way to increase production efficiency and reduce costs. It's also a great way to keep track of quality and consistency in production.
Overall, batch manufacturing is a great option for businesses looking for an efficient and cost-effective way to produce multiple items. It's also a great way to ensure that each item is made to the highest standard.
Mass Production
Mass production is a manufacturing process in which large numbers of identical products are made quickly and with a minimum setup time. It's an efficient way to produce a large number of goods in a short amount of time.
The process usually involves assembly lines and specialized machinery to assemble many products with minimal effort quickly. Mass production helps businesses keep overhead costs low and increase profit margins.
Continuous Manufacturing
Continuous manufacturing is a process production method that creates products in a continuous, uninterrupted flow. This method offers many advantages, such as improved efficiency and cost savings, increased safety, and shorter production cycles. It also helps to reduce waste and maximize quality control.
All in all, it's a great way to streamline the manufacturing process and produce the best possible products!
Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing is all about maximizing value for customers while minimizing waste. It's based on the idea that we should only use resources to create value, not to create extra stuff that no one needs. This means streamlining processes and finding ways to do things faster, better, and cheaper without sacrificing quality.
Lean manufacturing is a great way to make sure your business is running as efficiently as possible. In practice, this means focusing on continuous improvement and eliminating anything that doesn't add value.

This could be anything from reducing the number of steps in a process to rethinking how you store materials. It also means involving everyone in the process and making sure everyone is on the same page, from the top down.
The bottom line is, lean manufacturing is about working smarter, not harder. It's about taking the time to think through problems and find the most efficient solutions. That way, you can make sure your business is running at its best.
Repetitive Manufacturing
Repetitive manufacturing is a type of production system that involves the production of multiple identical items. This type of manufacturing typically involves the use of automated processes and machines to produce identical products in large quantities.
Repetitive manufacturing is used in industries such as automotive, electronics, and food production.
Job Shop Manufacturing
Job shop manufacturing is a type of production process that is characterized by the manufacture of a variety of different, usually complex custom-made products. In this type of production, each product is made in a series of unique steps and requires a variety of specialized skills, tools, and equipment.
Unlike mass production, which produces many copies of the same item, job shop manufacturing produces one-of-a-kind products.
Discrete Manufacturing
Discrete Manufacturing is a type of manufacturing process that produces individual items or components one at a time. It is typically used for low-volume production of highly-customized products, such as custom medical implants, aerospace components, and prototypes.
Discreet Manufacturing systems are designed to produce a single item at a time, in contrast to batch production systems, which produce multiple items in one operation.
Just-in-Time (JIT) Manufacturing
Just-in-Time (JIT) manufacturing is a production strategy aimed at increasing efficiency and reducing waste by receiving goods only as they are needed in the production process.
This approach minimizes inventory costs and enhances the responsiveness to market demands. JIT involves meticulous planning of the entire supply chain, from raw materials to delivery of finished products.
Key elements include reducing setup times, streamlining operations, and fostering strong relationships with suppliers. By producing items in response to current demand rather than forecasted demand, JIT reduces overproduction and holding costs.
Originating from the Toyota Production System, JIT has been widely adopted across various industries, emphasizing lean production and continuous improvement.
Contract Manufacturing
Contract manufacturing involves a company outsourcing the production of its products to a third-party manufacturer. This approach allows businesses to focus on core activities such as design, marketing, and sales while leveraging the specialized production capabilities of the contract manufacturer.
Benefits include cost savings, access to advanced manufacturing technologies, and flexibility in scaling production up or down based on demand. Contract manufacturers often provide services ranging from component manufacturing to full product assembly and testing.
This model is prevalent in industries like electronics, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods, where high capital investment in production facilities can be prohibitive.
By partnering with experienced manufacturers, companies can improve product quality, reduce time-to-market, and enhance their competitive edge.
Technologies Used in Manufacturing
Technology used in manufacturing is all about making production faster, more efficient, and more cost-effective. It includes everything from automation systems to 3D printing and robotics. Automation helps keep production operations running smoothly and efficiently, while 3D printing allows for rapid prototyping and the creation of complex components.
Robotics helps to reduce the need for manual labor, making it easier to produce products quickly and accurately.
Finally, data analytics and cloud computing allow manufacturers to better track and analyze production data and make more informed decisions. All of these technologies are helping to revolutionize the manufacturing industry and make it more efficient than ever before.
Overall, technology is playing an essential role in the manufacturing industry, and it's only going to become more important in the future.
Let’s walk through each of these in the upcoming sub-sections.
Computer-aided Design (CAD)
Computer-aided Design (CAD) is a type of software that makes it easier for designers, engineers, and architects to create detailed technical drawings or plans. It allows users to create accurate, detailed models and diagrams with the help of a computer. CAD can also be used to create 3D models, allowing designers to visualize the end product better. CAD is a great tool for anyone who needs to create detailed designs quickly and accurately.
CAD is an invaluable tool in the manufacturing industry. It allows engineers to create detailed designs quickly and accurately, reducing time spent on the design process and making it easier to incorporate changes. CAD also helps to reduce the cost of production by allowing designers to fabricate components at a faster rate and with higher precision. It also eliminates the need for physical prototypes, saving time and money. All of these advantages make CAD an incredibly valuable tool in the manufacturing process.
Computer-aided Manufacturing (CAM)
Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) is an essential part of modern manufacturing. It can help enhance production efficiency and accuracy, reduce production costs, and produce higher quality products.
CAM software can be used to control and optimize the manufacturing process, from creating the product design to controlling the machines used in production. It can also help to streamline scheduling, tracking, and inventory management.
In short, CAM technology is invaluable for any modern manufacturer looking to stay competitive.
3D Printing
3D printing is revolutionizing manufacturing by providing a cost-effective and efficient way to create custom parts and products. By using 3D printing technology, manufacturers can produce parts in less time, with less waste, and with more precise results.
3D printing also allows manufacturers to produce large-scale parts and products with complex geometries that would otherwise be impossible to create. Best of all, 3D printing can be used to create parts and products with a high degree of customization, allowing manufacturers to create products that are tailored to meet the specific needs of their customers.
For these reasons, 3D printing is quickly becoming an essential part of the manufacturing process.
Robotics
Robotics in manufacturing is an incredibly important part of the production process. Robots are fast, accurate, and efficient, and they are able to do tasks that are too complex or too dangerous for humans. They can also be programmed to handle highly repetitive tasks, giving manufacturers the capability to produce higher-quality products faster and with less waste.

As a result, robotics can help manufacturers optimize their production and reduce costs, making them more competitive in the market.
Automation
Automation is a key part of modern manufacturing, and it can make a huge difference for both small and large-scale businesses. Automation helps to reduce costs, improve safety, increase production, and enhance product quality. Automation also helps reduce the need for manual labor, which can help reduce workplace injuries and illnesses.
Automation can also speed up production, which can help businesses to meet their deadlines and stay competitive. In short, automation is an important tool for any manufacturer who is looking to increase efficiency and maximize their profits.
Laser Cutting
It is an incredibly useful tool in the manufacturing process. It's a precise and efficient way to cut materials like metal, wood, and plastic. With laser cutting, you can create intricate designs with high accuracy, meaning that the products you create will be of the highest quality. Plus, laser cutting is fast and cost-effective, so it helps to keep production costs down. All in all, laser cutting is a great way to create top-notch products quickly and cost-effectively.
CNC Machining
CNC machining is a crucial part of modern manufacturing. It's a process that takes raw materials and uses computer-controlled machinery to shape them into the desired product. This process is highly accurate, efficient, and cost-effective, allowing for the creation of complex parts with tight specifications. It's also much faster than traditional machining, making it ideal for mass production.
CNC machining has revolutionized the manufacturing industry and is essential for creating quality products.
Injection Molding
Injection molding is one of the most important and widely used manufacturing processes in the world. It's an incredibly versatile tool that can be used to make a wide variety of products, from tiny medical devices to large automotive parts.
It also offers high accuracy and repeatability, making it ideal for mass production. Injection molding is a great choice for manufacturers looking to make high-quality parts quickly and cost-effectively.
Industrial Printing
Industrial printing is a crucial part of the manufacturing process. It allows companies to quickly and cost-effectively produce a wide range of products with custom designs and labels. By using industrial printing, companies can produce high-quality labels, product packaging, signage, and other materials that can help them stand out in the market.
Additionally, industrial printing can help manufacturers save time by streamlining the production process, reducing material costs, and ensuring that the right materials are used. Overall, industrial printing is a powerful tool that helps manufacturers create attractive and cost-effective products.
Vacuum Forming
Vacuum forming is a manufacturing process that uses thermoforming polymers to make pieces. It is an adaptable and cost-effective method of producing high-quality parts for a wide range of applications. Vacuum forming is utilized in a variety of manufacturing applications, including medical, automotive, aerospace, and consumer items. It is very handy for quickly and precisely creating complex forms.
Furthermore, vacuum forming is an excellent method for producing custom parts with high consistency and homogeneity. As a result, it's great for mass-producing parts with consistent dimensions and quality.
Let’s Talk about Small Scale Manufacturing
When we are discussing manufacturing in such detail, let us also talk about small scale manufacturing. We have seen some of the latest technologies that make the manufacturing process efficient. But what goes on in a small scale manufacturing business?
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, there were 2.34 million small-scale manufacturers in the United States in 2019. These businesses employed 11.7 million people and had sales and receipts of $1.43 trillion. The number of small-scale manufacturers increased by 1.2% from 2018, and the number of employees increased by 1%. The sales and receipts for small-scale manufacturing businesses increased by 1.6% from 2018.
Small Scale Manufacturing (SSM) refers to the production of goods in smaller batches or limited quantities. It is typically used in businesses that are too small to be part of the larger manufacturing industry, but large enough to produce their own goods.
SSM can be used to produce a wide variety of products, from clothing and furniture to electronics and pharmaceuticals.
When most people think about manufacturing, they envision enormous factories, warehouses, heavy machinery, and other structures. However, you do not have to be an industrial giant to make goods.
If you're a baker with a tiny local shop, you possibly specialize in handcrafted cakes for special events. You can dominate the market by creating individualized delicacies for your consumers, as opposed to them, simply purchasing a generic apple pie from a store made by some large-scale factory.
Yet, you may need to opt for a manufacturing process that lets you handle all the orders and demands in time. An assembly line as a manufacturing technique is only a viable choice for you if there is a demand for your pies and your existing resources can handle it.
Numerous such examples can let you make a calculated attempt to get into the manufacturer’s shoes. You may also tap your unrealized talent or hobby that makes money.
Do Small Manufacturers Make a Lot of Money?
This may not be easy to answer. It depends on the type of product being manufactured. You shall also need to consider the size of the company and the overall market for the product. Generally speaking, large manufacturers have the potential to make more money than small manufacturers due to economies of scale. However, small manufacturers can still be successful and make a good living if they have a good product and the right market.
Manufacturing contributed $2.38 trillion to the U.S. economy in 2020, or 11.9% of GDP. This is down slightly from 2019 when manufacturing accounted for 12.2% of GDP.
Yet, the amount suggests that the markets are good for anyone who is competent. It's only a matter of figuring out ways to make money.
Challenges Facing the Manufacturing Industry
Like any other industry, the manufacturing industry has to deal with its own set of challenges. These may differ from business to business and the type of product.
Let’s learn about them here.
- Increasing Labor Costs: The rising cost of labor can be a challenge for manufacturers, as wages and benefits increase and the availability of qualified workers decreases.
- Changing Consumer Preferences: With increasing competition, manufacturers must stay ahead of changing consumer preferences. This means that manufacturers must have the ability to quickly adapt to changing trends and keep up with the latest technologies.
- Globalization: Globalization has increased competition in the manufacturing industry. Manufacturers must be able to compete on a global scale, producing quality products at a competitive price.
- Resource Availability: Manufacturing relies heavily on the availability of resources such as raw materials, energy, and labor. If any of these resources become scarce, manufacturers may have to find alternative sources or increase their costs.
- Technological Changes: Technological developments have enabled manufacturers to increase efficiency, but the pace of change can be difficult to keep up with. Manufacturers must stay up to date on the latest technologies and invest in the necessary equipment to remain competitive.
- Environmental Regulations: Increasing environmental regulations can be a challenge for manufacturers, as they must invest in the necessary equipment and processes to remain compliant.
- Government Regulations: Government regulations, such as trade agreements and tariffs, can significantly impact the manufacturing industry. Manufacturers must be aware of any changes in regulations that could affect their business.
- Cyber Security: As technology becomes more important in the manufacturing industry, cyber security becomes a major issue. Manufacturers must invest in security measures to protect their data and systems from malicious attacks.
Types of Manufacturing Businesses
Today’s times do not restrict any production process, and therefore, there are many manufacturing businesses. Let’s take a look at some of the most promising manufacturing businesses today:
- Electronics Manufacturing: This type of manufacturing business designs, manufactures, and sells electronic products. Electronic manufacturing involves selling computers, televisions, sound systems, and other digital devices.
- Automotive Manufacturing: This type of manufacturing business focuses on producing automobiles. Automotive manufacturing is involved in the manufacturing of cars, trucks, vans, and other motor vehicles.
- Aerospace Manufacturing: This type of manufacturing business builds and designs aircraft, spacecraft, satellites, and other related components.
- Chemical Manufacturing: Chemical manufacturing type of manufacturing business manufactures and sells chemicals such as acids, alkalis, and other chemical compounds.
- Food Manufacturing: This type of manufacturing business produces and packages food such as cereals, snacks, and frozen foods.
- Textile Manufacturing: A textile manufacturing business produces and sells fabrics, clothing, and other related items.
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: This type of manufacturing business produces and sells prescription and over-the-counter medications.
- Plastic Manufacturing: This type of manufacturing business produces products such as containers, packaging, and plastic products.
- Beverage and Tobacco Products:
- Garment Manufacturing: The companies in the garment manufacturing sector involve the process of laying, marking, cutting, stitching, checking, finishing, pressing, and packaging. It turns a fabric into a wearable outfit.
- Appliance and Component Manufacturing: This industry deals with the manufacturing of the parts and components of appliances.
- Transportation Equipment Manufacturing: Transportation equipment manufacturing industries develop equipment for carrying people and cargo.
- Furniture Manufacturing: The companies in this sector engage in the manufacturing of furniture and related products.
- Fabricated Metal Manufacturing: This industry is all about shaping metal into the desired or required parts. There are several techniques to achieve this.

What are MTS, MTO, and ATO?
MTS, MTO, and ATO are terms used in the field of supply chain management. Let’s see what each of them stands for.
MTS
MTS stands for Make-To-Stock, which is a production and inventory control system where items are made in advance and stored in inventory until they are needed.
This strategy enables companies to respond quickly to customer orders and maintain inventory levels of products that are in high demand. Companies that use this strategy typically have a wide range of products, and they are able to keep their inventory levels low by relying on their ability to produce and deliver their products quickly. The main advantage of this strategy is that it allows companies to respond quickly to customer orders and maintain their competitive edge.
MTO
MTO stands for Make-To-Order, a production and inventory control system where items are made only after a customer orders.
This strategy is used to meet customer needs with customized products and services. The customer orders are received from the sales department and then the order is planned, produced, and delivered. The production process can be flexible and can be changed based on customer needs.
The MTO strategy is used by companies with a product or service that needs to be tailored to the customer’s requirements, allowing them to provide an individualized product or service. This strategy is also used when the demand for the product or service is low or unpredictable, as it allows the company to produce only what they need when they need it.
ATO
ATO stands for Assemble-To-Order, a production and inventory control system where a product is assembled from components already stocked in inventory after a customer places an order. In all three systems, there is no pre-production of the items, only produced in response to customer demand.
With ATO, the customer specifies the product configuration and the manufacturer assembles the product from components in its inventory. The components of the product can be manufactured by the same company, or purchased from external suppliers.
The ATO process reduces the amount of inventory required, while still providing customers with custom orders. It also helps to reduce production costs by eliminating the need for large batches of the same product.
Important Aspects Manufacturers Must Know
If you are someone who aims to pursue manufacturing or you are a manufacturing engineer, then there are certain key terminologies you must be aware of. There could be several manufacturing challenges you may encounter on your journey. What would your manufacturing costs look like? What are the overheads?
These are very significant elements that a new manufacturer or manufacturing engineer must be well aware of. Let’s learn about them here.
Manufacturing Overheads
Manufacturing Overheads are the indirect costs of production associated with the manufacturing process. These costs do not include the direct costs of materials and labor used in the production process.
Examples of manufacturing overheads include utilities, plant maintenance, facility rental, insurance, and other administrative costs. These costs are necessary for the production process to occur and are part of the cost of goods sold (COGS).
Manufacturing Cost
Manufacturing cost is the total cost incurred by a business to produce goods or services. This includes the cost of materials, labor, overhead, and other expenses related to the manufacturing process.
It is important to note that the cost of goods sold is not the same as the manufacturing cost. COGS is the cost of the actual goods that were sold while manufacturing cost is the cost of the entire process that went into producing those goods.
Bill of Materials
Bill of Materials or BoM is a comprehensive list of parts, items, assemblies, and other materials required to create a product or assembly. A Bill of materials is a hierarchical structure of assemblies, components, and raw materials used to create an end product.
A BoM can be used for communication between manufacturers, suppliers, and customers and is an integral part of engineering and production processes.
There are several types of BoMs, some of which are enlisted here:
- Single-level BoM
- Multi-level BoM
- Configurable BoM
- Engineering BoM
Manufacturing Order (MO)
A manufacturing order (MO) is an order from a customer to a manufacturer to produce and deliver a specific quantity of goods. The order is usually placed when the customer needs a specific product and wants it manufactured to their exact specifications.
The MO typically includes product details, such as materials, measurements, and delivery dates. The manufacturer will use the information to create the product and then ship it to the customer.
Throughput Time
Throughput time is the total time it takes to complete a product from start to finish in a manufacturing process. This includes the time for raw materials to be processed and assembled and any time spent in inspection, packaging, and shipping.
Manufacturing Lead Time
Manufacturing lead time is the time that elapses between placing an order for a product and when it is shipped from the factory. It includes the time for raw materials to be acquired, for production to be completed, for quality assurance testing, and for the product to be packaged and shipped.
Manufacturing Floor-Level Control
Manufacturing Floor-Level Control is a type of automation system used in manufacturing and other industrial settings to control the production process. It is designed to provide real-time control and monitoring of machines and processes on the production floor.
This system helps manufacturers to reduce production costs, improve quality, and increase productivity. It also ensures compliance with safety standards and regulations. The system can be used to control various operations such as material handling, machine scheduling, process control, and product tracking.
Streamline your Manufacturing Process with an MRP Software
MRP or Material Requirements Planning software streamlines the manufacturing process by automating key tasks. These include ordering and tracking raw materials, scheduling production tasks, tracking production progress, and generating reports. It helps ensure that production runs smoothly and efficiently, reducing potential errors and delays.
Additionally, it helps to keep costs down by providing visibility into the supply chain and inventory levels, enabling manufacturers to make better purchasing decisions.
Some of the eminent features of the MRP system are as follows:
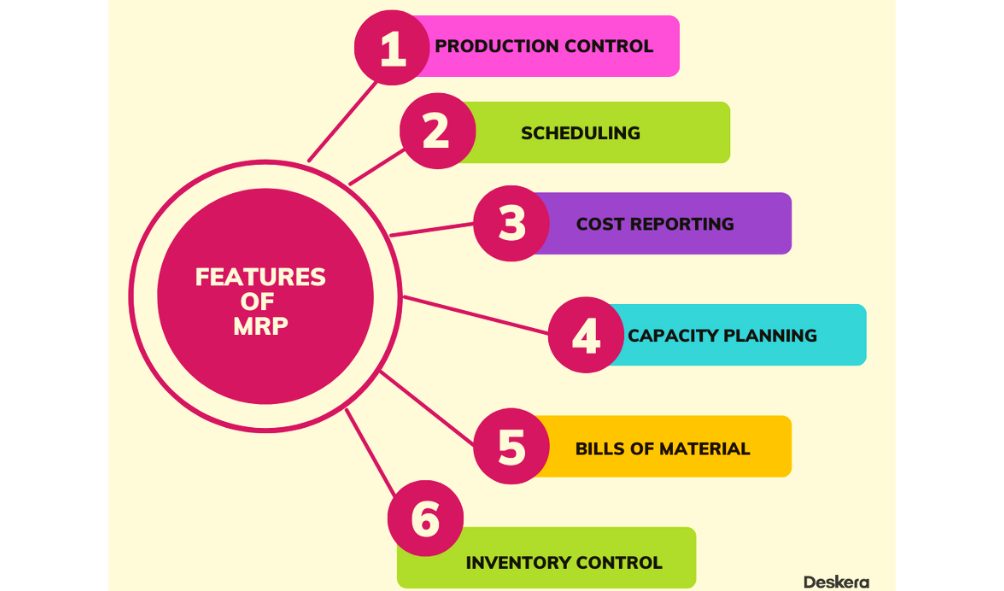
In the earlier part of the articles, we have already seen what is production planning and scheduling. Let’s understand the other features of the MRP system here in this section.
Master Production Schedule or MPS is a plan for individual components required to manufacture finished products. It includes information about the timing and quantity of production and is used to generate material requirements and production schedules. The MPS is typically used in conjunction with the Material Requirements Planning system.
Capacity planning is determining the production capacity needed by an organization to meet changing demands for its products. It is the process of adjusting the organization's production capacity and resources to meet its products' current and future demands.
It is an ongoing process that involves analyzing the organization's current capacity, forecasting demand, and determining the necessary capacity to meet the forecasted demand. Capacity planning is important for organizations because it helps them to ensure that they are producing the right number of products, at the right time, and with the right resources.
As we have seen earlier in the document, a BOM is essential in ensuring that the right parts are ordered and used in the manufacturing process. MRP helps to analyze the demand for parts, determine the most efficient way to order them, and track the inventory levels of all components. This helps reduce costs, ensure quality control, and provide a detailed record of the production process.
Supply chain management is the oversight of materials, information, and finances as they move in a process from supplier to manufacturer to wholesaler to retailer to consumer. Supply chain management involves coordinating and integrating these flows both within and among companies.
It is said that the ultimate goal of any effective supply chain management system is to reduce inventory (with the assumption that products are available when needed).
Inventory management in manufacturing is managing and tracking the stock of raw materials, finished products, and goods in progress to meet customer demand and sustain production operations. It involves periodically counting and recording the inventory levels, and establishing minimum and maximum stock levels.
Also, it involves ordering new stock to maintain the necessary levels of goods. Inventory control helps to ensure that the supply chain runs efficiently and that customers receive their orders on time.
Outlook for the Manufacturing Industry
Outlook for the manufacturing industry is looking good, with plenty of potential for growth. With the global economy continuing to improve, the demand for manufactured goods is growing, and more businesses are looking for reliable suppliers of quality products.
This is great news for manufacturers as it means more orders, jobs, and industry investment. The industry has also seen a rise in technology, with the introduction of automation, robotics, and 3D printing.
This means that manufacturers are able to move faster and become more efficient. It also allows them to take on more complex projects, which can lead to new revenue streams. Overall, the manufacturing industry is in a strong position and is expected to continue to thrive over the coming years.
With the right investments, manufacturers will be able to capitalize on the rising demand and increase their market share. This could lead to more jobs and an even brighter future for the industry.
How can Deskera Help with Manufacturing?
Deskera is an integrated business management software that offers a suite of tools specifically designed to assist manufacturing companies.
Here’s how Deskera can help with manufacturing:
- Inventory Management: Deskera ERP enables real-time tracking of inventory levels, helping manufacturers maintain optimal stock levels, reduce excess inventory, and avoid stockouts.
- Production Planning: The software facilitates efficient production scheduling and planning, ensuring that resources are allocated effectively and production timelines are met.
- Order Management: Deskera MRP streamlines the entire order-to-cash process, from order creation to delivery and invoicing, enhancing order accuracy and customer satisfaction.
- Supply Chain Management: It offers comprehensive supply chain management tools, allowing manufacturers to manage suppliers, procurement processes, and logistics more effectively.
- Quality Control: Deskera MRP helps maintain high-quality standards by enabling detailed tracking of quality checks and compliance with industry standards.
- Bill of Materials (BOM): Deskera manages comprehensive BOMs, detailing all the components, raw materials, and subassemblies required to manufacture a product. This ensures accurate planning, cost estimation, and efficient inventory management.
- Financial Management: Integrated financial tools provide real-time financial insights, budget tracking, and expense management, aiding in better financial decision-making.
- Reporting and Analytics: Deskera’s robust reporting and analytics capabilities allow manufacturers to gain insights into production performance, identify bottlenecks, and make data-driven improvements.
- Compliance and Traceability: The software assists in maintaining compliance with regulatory standards and offers traceability features, crucial for industries like pharmaceuticals and food production.
By integrating these features, Deskera helps manufacturing businesses optimize operations, reduce costs, improve quality, and enhance overall productivity.
Key Takeaways
Manufacturing is essential to the modern economy and has helped create jobs and improved the quality of life in many parts of the world. It is an important part of the global economy and will continue to be so.
- Manufacturing is the process of turning raw materials into finished products. It involves a lot of steps, like designing, production, assembly, testing, and packaging.
- It usually involves a number of steps, from sourcing the raw materials to the final assembly of the finished product.
- Planning, designing, procuring, production, quality control, and packaging are the steps in the manufacturing process.
- Production planning and scheduling are an important part of the manufacturing process. It helps to ensure that all of the necessary steps are taken in order to produce a quality product in a timely and efficient manner.
- Batch manufacturing, mass production, and lean manufacturing are some of the types of manufacturing.
- Batch manufacturing is a production process that involves making multiple items in a single production run. This is done by combining the same materials and following the same process to make each item.
- Mass production is a manufacturing process in which large numbers of identical products are made quickly and with a minimum setup time. It's an efficient way to produce a large number of goods in a short amount of time.
- Continuous manufacturing is a process production method that creates products in a continuous, uninterrupted flow.
- Lean manufacturing is all about maximizing value for customers while minimizing waste. It's based on the idea that we should only use resources to create value, not to create extra stuff that no one needs.
- Repetitive manufacturing is a type of production system that involves the production of multiple identical items.
- Job shop manufacturing is a production process characterized by the manufacture of a variety of different, usually complex custom-made products.
- Discrete manufacturing is a type of manufacturing process that produces individual items or components one at a time.
- The technology used in manufacturing is all about making production faster, more efficient, and more cost-effective. It includes everything from automation systems to 3D printing and robotics.
- Increasing labor costs, globalization, regulations, and technological changes are some of the challenges the manufacturing sector faces today.
- MRP or Material Requirements Planning software streamlines the manufacturing process by automating key tasks. These include ordering and tracking raw materials, scheduling production tasks, tracking production progress, and generating reports.
Deskera ERP and MRP is a cloud-based comprehensive business software that will enhance manufacturing by streamlining inventory management, production planning, and order management. It ensures optimal stock levels, efficient resource allocation, and high-quality standards.
With comprehensive BOM management, financial insights, and compliance features, Deskera boosts operational efficiency, reduces costs, and supports data-driven decisions.
Related Articles