Manufacturing operations management may appear complex. But with integrated manufacturing solutions, you can gain control of your production and maximize productivity. A manufacturing execution system (MES) can assist in this situation.
If you are a manufacturer who seeks streamlined procedures, MES could be the solution. Production success necessitates the ability to regulate and track your entire manufacturing operation. It is also dependent on many other corporate obligations.
In this post, we will look at what MES manufacturing is. We shall also learn how it works, apart from other related aspects. Here is what we shall cover:
- What is MES System?
- History of MES Evolution
- Key Features of a Manufacturing Execution System in Production
- Manufacturing Execution System Architecture
- Advantages of Manufacturing Execution Systems
- MES Vs. ERP: Difference Between MES and ERP
- Can Manufacturing Execution System work with your MRP or ERP?
- Top 5 Ways ERP and MES Integration Makes Manufacturing Agile
- Should You opt for Manufacturing Execution System
- Future Trends of MES
- Conclusion
- How can Deskera Help You?
- Key Takeaways
- Related Articles
What is MES System?
A Manufacturing Execution System or an MES assists firms in ensuring that their manufacturing activities are up to the mark. The system also takes care of the efficiency of their output. It is a software system that connects the manufacturing floor's machines, work centers, and data flows. It assists in tracking and managing these data flows.
The MES accomplishes this by tracking and collecting real-time data on every piece of equipment engaged in the manufacturing process.
Throughout the production cycle, an MES provides firms with data on product tracking and genealogy. It provides insights into the performance, traceability, and management of the plant. The reliable information about the work in progress (WIP) and other plant activities from MES enables the managers in effective decision-making. This valuable insight further aids business owners in optimizing their operations.
History of MES Evolution
In the 1950s and 1960s, the advent of host mainframe computing paved the way for the incorporation of information technology into production technologies. It enabled manufacturers to gather, alter, and share information. Also, they could now venture into automated calculation and analysis. Gradually, this facilitated the creation of increasingly sophisticated goods.
Simultaneously, inventory control became very important in the framework of production management. This led to the increased creation of software in the 1960s. During this time, inventory control was often handled by BOM processors or a bill of materials. The BOMs were used to depict process plans.
This was the phase when the complexity of manufacturing operations developed tremendously. Thus, in the 1970s, the emphasis turned to Material Requirement Planning (MRP).
What is a BOM?
A bill of materials (BOM) is a detailed description of the raw materials, components, and instructions needed to build, produce, or repair a product or service. A bill of materials is typically presented in a hierarchical structure, with the finished product at the top and various components and materials at the bottom.
Read Our Detailed Guide on the Bill of Materials HERE
This managerial tool allowed finance managers to gain a better understanding of business operations. Moreover, managing things has become easier now. New functionalities came into being so as to meet the increased demand. There was an expansion of the instruments for automating business operations.
What is Material Requirements Planning (MRP)?
MRP, or Material Requirements Planning, is software that estimates the raw materials and components needed to make a product. This is accomplished by combining inventory and supply chain management for enterprises.
Read Our Detailed Guide on MRP HERE
This was when Manufacturing Resources Planning became widespread. Precisely, it was MRP II that the companies implemented in the 1980s. An MRP II proposed an extension of MRP functions to combine all aspects of personnel, material, and machine planning and control.
It was in the early 1990s that another advancement in technology found a strong foothold. This was termed ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), which the companies widely installed and used for enhancing business performance.
An ERP system is a unified information processing system that supports various corporate functions such as finance, distribution, human resources, and manufacturing. The Gartner Group has made much of the latest edition of ERP II.
Fundamentally, ERP II represents a transition in typical ERP programs. It accomplishes this by focusing on internal data gathering and process management. It could also establish external communication. So, now communicating with partners, providers, and customers over the web has become easy.
The following image depicts the broad perspective on the evolution of ERP systems.
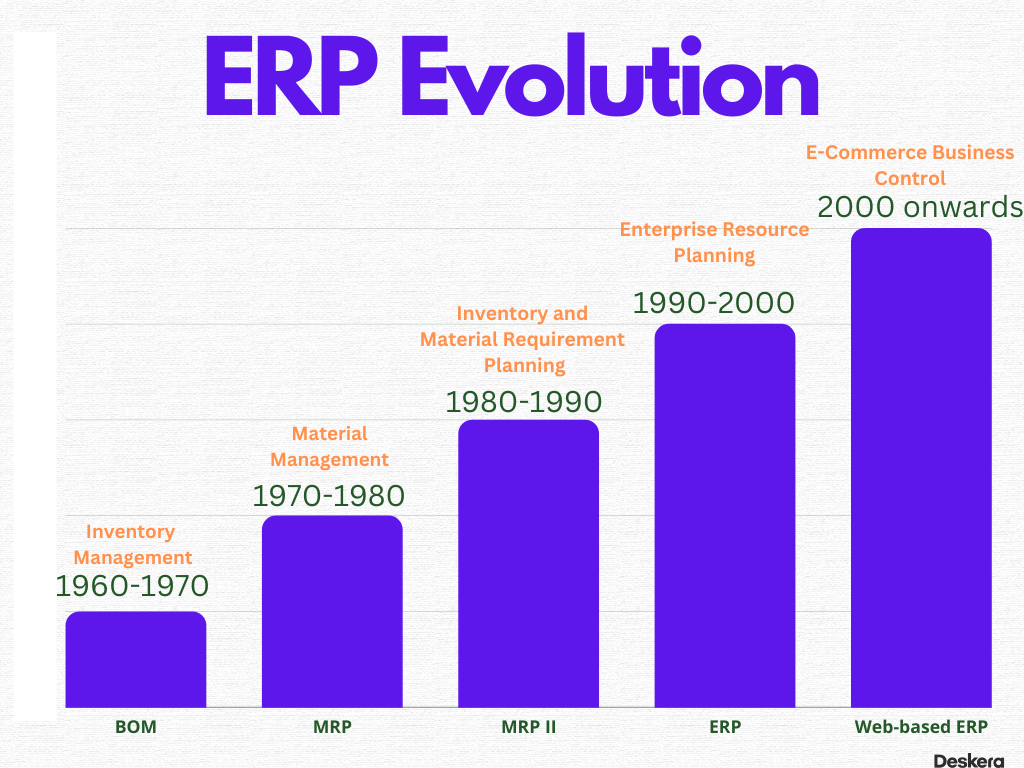
This model was initially popular among manufacturers. However, as the scope of controlled systems expanded, the ERP system was no longer adequate. The scenarios necessitated the use of systems needed for supervising activity on the shop floor.
During the 1990s, a new manufacturing management tool known as Manufacturing Execution Systems was developed and used for this purpose. There are different interpretations of MES depending on the manufacturing conditions. However, the common feature is that an MES intends to act as an interface between an ERP system and shop floor controllers. It does so by enabling diverse functionalities. These include activities such as planning, order release, quality management, and data capture.
Key Features of a Manufacturing Execution System in Production
Engineering professionals strive to build and implement standard and customized MES systems. They developed these systems to deploy customized MES solutions for in-house processes as well as to serve their customers. Catering to a wide range of customers is a daunting task. This was made feasible through the use of a global network of renowned software partners.
Industrial execution requirements vary a lot. While there is no single solution that meets all criteria, a successful solution includes the automation of a lot of key features. These key features can be termed the primary characteristics of MES.
The following image depicts some of those:
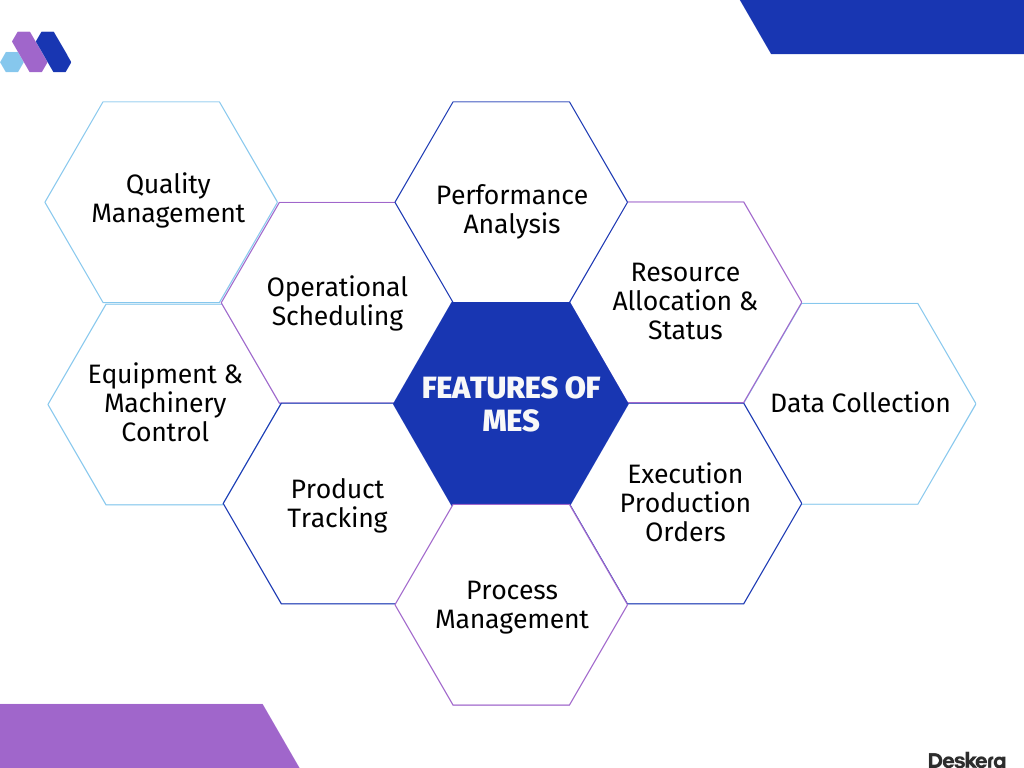
Process Management
One of the most important elements of manufacturing, process management, is extremely crucial to successful production cycles. Manufacturing largely thrives on automation. It would be almost impossible to achieve optimal automation without process control.
The reason why process management is so important is that it offers manufacturing processes insights that include the following:
Safety
Manufacturing processes that involve hazardous activities need to fall back on data that informs them about the potential hazards. Some industries like petrochemical, oil & gas, and chemicals deal with this on a regular basis.
Minor fluctuations and tiny variations in the readings can snowball into huge safety concerns. Process control intercepts any deviations from the usual and guarantees workers’ safety.
Automation
To make goods, modern manufacturing plants employ incredibly complicated machinery. Automation has reduced the number of people required to operate this machinery. Yet, automated machinery needs process control to collect data and verify that the plant's output is optimal. Eventually, it boils down to the effectiveness of the final performance.
Data from industrial processes is collected using automated sensors in process control. This information is then used to make decisions.
Energy Efficiency
Many industrial operations use a lot of energy, which raises production prices. Because manufacturers are constantly seeking ways to cut costs, making a plant more energy efficient is critical.
Factory managers can closely monitor the energy efficiency levels of manufacturing processes thanks to process control. Fewer defective items will be generated if the equipment is run at peak efficiency without expending energy.
Production Order Execution
Production orders allow you to plan the manufacturing process from the start to the end of its execution. They contain all of the information required for production. This comprises determining input products and input products. They also help determine which resources are required and when the activities should be processed.
Following the creation of the production order, the system estimates the planned quantities, durations, and dates. This also includes the scheduled dates. Scheduling helps estimate the time of commencement of production. These schedules are based on the timelines so as to meet the projected demand.
There are the following statuses assigned to the products based on their completion:
- In preparation: indicates the stage where the production orders are being prepared but are not released yet.
- Released: Indicates the release of the production order to production execution.
- Started: Indicates the commencement of the process of production tasks
- Finished: Indicates a finished production order (often signals the completion of all the related production tasks and production lot)
- Closed: The production order is closed and is not relevant to the logistics any longer.
- Canceled: Indicates the cancellation of a production order (this can happen only when none of the related tasks have been started.)
All these stages indicate the existing state of the production orders. If production execution generates less or more than projected, planners must be informed. Thereafter, the team can plan for how to deal with unfulfilled or overfilled demands.
Resource Allocation and Status
Scheduling available resources in the most efficient and cost-effective manner feasible is known as resource allocation. Manufacturing projects will always require resources. However, they may face scarcity at times. As a result, it is the project manager's responsibility to decide the right scheduling and allocation of those resources within the project timetable.
In other words, it is the management and delegation of resources during a project to ensure its seamless and effective completion.
Data Collection/Acquisition
Controlling costs and ensuring seamless operations are one of the primary goals of the manufacturing process. However, data collection could be a challenge for many companies. Implementing data collection techniques at the right point is crucial. Without this, the data collected may not be relevant or may be of no use to the company.
Therefore, in recent times, companies are finding it useful to implement a touchscreen data collection system. This system can be deployed on the shop floor to enable the manufacturers to derive maximum value from it.
The touchscreen eliminates the need for a keyboard, making it a more user-friendly choice for employees. A single portable touchscreen data collection system is quick and simple to set up. It requires minimal employee training, saving time and money. It also reduces disturbances to your routine operating procedures.
Product Tracking and Traceability
Product traceability enables manufacturers to follow inventory movements from beginning to end. This way, they can track things to locations where they were transported or visit their operational processes.
Traceability is quickly becoming a key aspect of the manufacturing process for businesses across all industries. While this is great in the case of recalled products, it finds relevance and applicability across many other sectors. It would be a recommended procedure for all manufacturers.
By welcoming product tracking, companies can avail of multi-level benefits. From economic productivity to resource capabilities, they would see an improvement in all related areas. Organizations can gain more granular control over their manufacturing processes by deploying systems that enable high-level tracking and tracing capabilities. After all, building safer and quality products can offer continual improvements.
Here is how the traceability of products can help manufacturers:
- Tracing the origin of elements
- Tracking production lifecycle
- Maintaining inspection notes
- Learn about time spent at each workstation
- Knowing the right product destinations
Performance Analysis
When we speak of performance analysis, we are essentially trying to examine if the implemented processes have yielded the expected results. In short, it is the assessment of the system’s capacities to meet the demand for deliveries.
Performance analysis in manufacturing helps evaluate the efficiency of the equipment. The analysis works on information to present an interpretation of different business processes. The manufacturers can then review and analyze it.
Consequently, it aids in providing a competitive advantage by increasing margins, cutting costs, and competing at a higher level. Real-time visibility assists in identifying the weakest links in your lines. You can manage them to obtain an optimal operational capacity.
The analysis allows you to differentiate between unplanned downtime and product changeover or idle time. Moreover, there could be other planned occurrences that can be prepared for beforehand. The performance analysis helps in making modifications based on real-time indications of schedule adherence.
By capturing production data, integration with the plant control system aids in performance management.
Operational Scheduling
Maintaining a timely and effective production schedule is one of the most significant issues in industrial operations. When faced with issues relating to timely deliveries, businesses adopt the process known as Operations Scheduling.
This process includes allocating jobs or activities to the appropriate machinery and labor personnel. We know that planning determines which resources and supplies will be assigned to each job. On the other hand, scheduling adds the timing component to the production schedule.
It is concerned with optimizing the sequence of activities on the given resources in order to establish and execute the most efficient production plan.
The objectives fulfilled by operational scheduling are as follows:
Maximize resource utilization: This helps in lowering business expenses due to poor utilization of resources.
Manufacturing time reduction: with a well-crafted scheduling process, manufacturing time can be lowered. The end-to-end process time can be reduced for the diverse operations in the company.
Optimizing labor efficiency: A well-thought production schedule will minimize the setup time on machines. Also, it boosts the efficiency of the labor force.
Inventory minimization: When you have a shorter manufacturing time, there will be fewer products in the WIP state. So, this will require you to hold on to lesser inventory.
Service level improvement: Having an effective production schedule benefits, not just the shop floor workers but also the customer service employees. They can determine when products will be finished by looking at the schedule. They will also be able to alert customers ahead of time if a slowdown arises. Overall, this helps improve services.
Maximizing Revenue and Output: Having an effective timetable will improve the number of products that can be produced overall. As a result, production costs will be reduced because all resources will be utilized optimally. The end outcome will be improved profits and on-time delivery.
Quality Management
As a manufacturer, you certainly understand the importance of the quality of products. Having a consistent and high standard of quality underlines the business's success. Moreover, if you largely rely on your suppliers for your manufacturing, then quality management becomes quite crucial.
A strong quality control program is integral to a successful manufacturing off-shoring strategy. It must include all aspects, from the standard of the raw materials to production techniques and part inspections. A professional contract manufacturing supplier will have quality control systems in place to ensure a regular and standardized supply of quality products.
With the automation feature of the MES, the manufacturers can guarantee the consistency of the quality of the products. Thus automating quality management can provide excellent solutions while trying to achieve good quality. Furthermore, the system can help further this process at affordable costs.
The key benefits of quality management with MES are as follows:
- Maintain good and consistent quality of products
- Improve customer satisfaction
- Remain compliant with the latest rules and guidelines
MES, with internal quality capabilities, enables quality management to delve deeper into issue areas for nonconformance detection and real-time corrective action. Some sectors that could benefit immensely from this feature include medical supplies, nuclear, aerospace, and defense.
This list of MES features is not exhaustive. There is a wise array of functions and values that the MES system can bring along. The manufacturing companies can zero in on the features that they find the most suitable for their business size and type.
Manufacturing Execution System Architecture
We must know that the ANSI/ISA-95 is an international standard for business and control system integration. To develop a functional hierarchy for MES, the ANSI/ISA-95 integrated the MESA-11 model with the Purdue Reference Model.
The following image lets us know the position of MES based on the ISA-95 functional hierarchy.
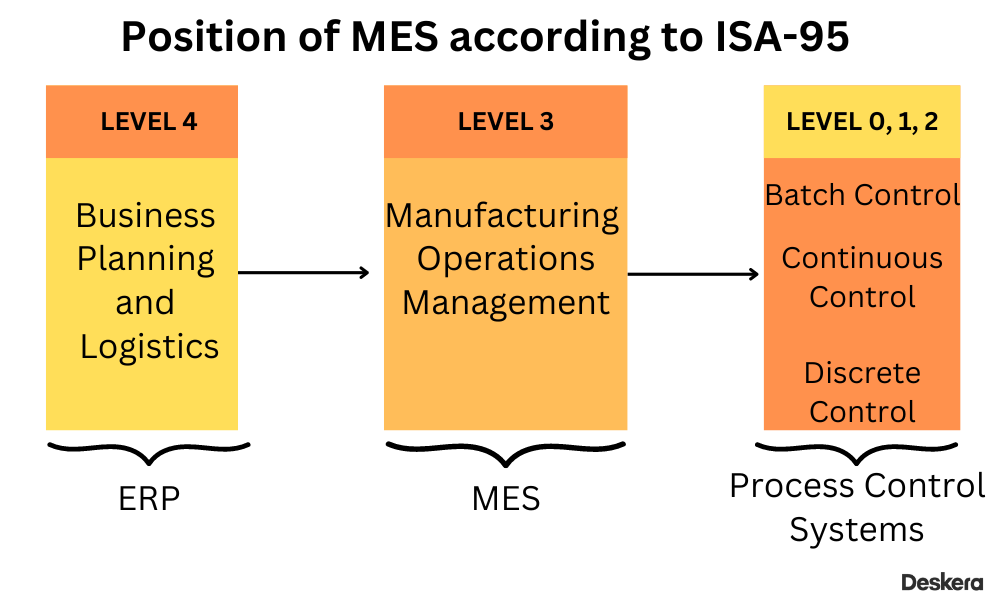
A Manufacturing Execution System sits between a business planning and logistics system and a manufacturing process control system. With this technology, manufacturing floor decision-makers can improve productivity and quality by utilizing its real-time workflow visibility, flexibility, and analytics.
While it benefits all, MES offers various benefits for certain industries. Businesses that must adhere to stringent requirements benefit greatly from MES technology due to its ability to track materials.
A wide range of industries is covered, including food and beverage, automobiles, medical devices, aeronautics, and aerospace. MES records processes, events, and activities, as well as their verification. These are important elements when manufacturing regulated products.
Advantages of Manufacturing Execution Systems
If you think your business requires MES, it would be a good idea to learn about the various benefits the system offers. This section takes us through those.
ERP Integration
MESA illustrates how an MES can integrate with other systems. Thus, by using a single system, stand-alone systems and unnecessary data re-entry are eliminated. Additionally, companies can achieve more accurate delivery date projections and improved decision-making.
Paperless Manufacturing
MES records and presents real-time information from the plant floor. This information could pertain to labor, maintenance, downtime, and so on. As this data is auto-recorded, you can eradicate the use of spreadsheets and other manual methods of data recording. With an MES, labor, downtime, and maintenance are all recorded in real time from the plant floor.
This allows you to keep a record of all the various costs without using paper notes and spreadsheets. The system also makes it possible to evaluate unprofitable business models and predict future prices based on the collected data. By utilizing MES in your plant, you can increase production and efficiency.
Decreases Downtime
An MES generates accurate production schedules. It also keeps track of raw materials and inventory. This saves time spent rearranging schedules while components are in transit. This can also be applied to employees. In other words, it is rewarding to have an MES for efficient scheduling of the available workforce.
Reduces Waste and Improves Efficacy
An MES gives you real-time data on all of your processes. You may streamline operations and enhance efficiency by using real-time data to make decisions on the product, time, and manpower required to accomplish a project.
This technique finally allows you to save money on orders while also freeing up people from operating manufacturing lines and monitoring inventory.
Reduce Inventory
As previously discussed, MES facilitates inventory recording regularly. So, when you have updated records of new products and goods, you have easy access to many components. Your purchasing, shipping, and scheduling departments can easily access what is available and what needs to be ordered.
Businesses spend a considerable amount on transporting, storing, and monitoring products. The MES ensures that you always have the proper amount of inventory on hand while minimizing overstock.
Reduce Costs
An MES gives you real-time data on all of your processes. You may optimize operations and enhance efficiency by using real-time data. It helps with making decisions on the product, time, and manpower required to accomplish a project.
This technique finally allows you to save money on orders while also freeing up people from operating manufacturing lines and monitoring inventory.
All of these efforts help to create a more efficient workforce. MES has been instrumental in providing improved quality and profitability. There are also other types of MES available, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks. Therefore, businesses must analyze their requirements to choose the apt MES with the right integrations.
MES Vs. ERP: Difference Between MES and ERP
With a fair idea of MES now, you may wonder what distinguishes MES from ERP. This section highlights a few basic fundamentals of ERP. This is followed by the main differences between the two software categories.
Let’s begin.
What is ERP?
Enterprise Resource Planning is a software system that allows companies to access and store all of the integrated data belonging to various departments in real-time.
These modules are constantly delivering critical information to the firm. Bills, invoices, stock-in and stock-out information, staff information, and customer data are all included. All of these components necessitate careful monitoring and analysis. These are all required for the preparation of reliable financial accounts. Real-time reports on these aspects allow the organization to examine its growth factors.
An ERP system can be thought of as a framework that binds together real-time information entered into it. It can coherently store and manage this data from multiple departments inside the firm. Furthermore, this data can be monitored and used for evaluations by the company's owners, managers, and employees.
Features of ERP
Let’s take a quick look at the primary features an ERP offers:
Benefits of ERP
ERP offers multiple benefits. Let’s look at them one by one here.
ERP has been driving important advancements in manufacturing of late. This makes one wonder why they would need MES. This question could be phrased and vice versa.
Also, if a company wants to choose a system to improve its operations, then which one should they opt for: MES or ERP? Well, the questions are too many. We hope to seek the answers in the next section here.
Top 5 Differences between MES and ERP
Now that we have looked through the details of both ERP and MES, we can better understand the differences. Let’s visit each aspect to compare the two.
Integration: This could be said to be the most noticeable difference. MES and ERP are integrated differently. MES integrates directly with the machines whereas ERP integrates with other business systems. These could be any including CRM, HR, SCM, or sales.
Data Visualization: The MES system generates real-time reports, allowing users to see the latest information on production progress and performance. ERP generates reports on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis. This requires the users to be patient and wait for the report. Once generated, the reports present the relevant data to the users.
MES is necessary to track transient or short-term trends. At the same time, ERP is more appropriate for long-term planning. As a result, many businesses employ both systems to obtain a complete picture of their data.
Operations: MES software supervises and manages the factory floor production process. On the other hand, ERP software provides a broader picture of the business, including accounting, sales, and supply chain management. While both are critical to the production process, MES and ERP perform distinct functions.
Complexity: Integrating one system with the other gives rise to complexity in its use. The same goes for ERP. ERP gets integrated with the business's other systems, such as CRM or Sales. When this is done, it induces complexity. Thus, making ERP a bit complex in functionality.
On the other hand, MES is not integrated with any other system. In fact, it is focused on the management of manufacturing processes. This way, it avoids complexity.
Cost of Implementation: MES systems are designed to handle just a single aspect of the manufacturing process. This makes them less expensive than ERP systems. ERP systems, on the other hand, are more extensive and might be more expensive to implement.
The following table lists the distinguishment between the two:
Can Manufacturing Execution System work with your MRP or ERP?
So, if you currently have an ERP or MRP system in place, you may wonder, can your MES integrate with your other systems? If your system is not currently executing the functions that all three systems require, as some cloud-based manufacturing software does, here is how MES systems can help.
MES ERP
Your ERP tools can help you plan business operations. It can assist in scheduling deliveries, among many other benefits. With an MES ERP system, you can monitor task progress from the floor level.
MES MRP
To begin with, MRP is software that manages your inventory, planning, and scheduling details.
Your MRP will assist you in preparing your inventory for production, and your MES will assist you in tracking your raw material usage on the shop floor. This aspect can be termed as a similarity between MES ERP and MES MRP systems.
Top 5 Ways ERP and MES Integration makes Manufacturing Agile
Let’s go through the top 5 ways in which the integration of the two systems: MES and ERP can boost manufacturing processes:
JIT Delivery for Better Management of Inventories
Just-in-time (JIT) delivery enables producers to receive inventory just when it is required. In a way, this helps them to avoid preoccupation of space in the warehouse. Furthermore, it reduces the carrying cost of stock that may not be used in the near future. You can cut overhead and lower the cost of doing business by having vendors supply as needed.
With integrated ERP and MES systems, you may manage inventory more efficiently. You can better coordinate sales and service with production to understand supply demands. As a result, this decreases business expenses. These savings can then be passed on to customers, increasing your competitive advantage and market share.
Also, when you closely monitor inventory requirements, modifying supply orders becomes easy. You can indicate the change to your supplies based on the demand.
JIT delivery also helps you address staff allocation problems. It can also assist you in determining whether extra staff are required on the manufacturing floor. Thus, allowing you to free up warehouse space for expanding manufacturing activities. JIT delivery delivers value to the client by allowing a more flexible workforce to focus on quality. Furthermore, this lowers the overhead, making space for more economic goods and products.
Avoid Rush Orders and Production Delays
Companies often experience rush orders which could be a significant risk. Yet, the supply chain managers are compelled to accept them at times. In such situations, material delivery, client order formation, and delivery all take place on the same day.
This situation is difficult since there are so many potential pitfalls. Supplies may not arrive on time or may not be available. Or a machine may malfunction, creating a delivery delay. Even worse, personnel may make mistakes owing to the short turnaround.
MES and ERP connectivity could rescue you from rush orders. The system integration allows you to understand when to repurchase from suppliers. You can take a corrective step before inventory falls below a certain level. Having more control over supply demands reduces production delays and errors while eliminating urgent delivery expenses.
Improve Demand Forecasting Accuracy
Inadequate inventory causes delivery delays. This results in lower client satisfaction. Additionally, the company suffers due to the reduced bottom line and hampered reputation.
Similarly, excess inventory also consumes cash flow. The amount that could be used for the organization’s progress sits with the inventory. You could use this amount to make significant investments in purchasing new assets.
ERP and MES software integration builds the bridge between shop floor operations and customer service. Other units like the logistics and delivery also start looking better. This helps the companies to better estimate demand and keep inventory at the proper levels.
Knowing how much stock is required also ensures that there is no employee or machine downtime due to an inability to produce orders. Companies can also get clear visibility into various aspects. With visibility into customer trends, they can stay on top of inventory needs.
Gain Real-time Insight into Quality Issues
MES and ERP integration enable you to observe what is occurring in the manufacturing process. With such real-time updates, you are better positioned to address issues. You can track the supplies and recognize faulty or defective products rapidly.
Thus, you can expedite the return of vendor supplies after inspection. ERP with MES software also helps to reduce product liability and monitors machines. Real-time visibility provided by ERP and MES software enables you to generate higher-quality products and gain a competitive advantage.
Better Connectivity leads to Increased Productivity
With smart devices on the shop floor, manufacturing can be efficient and leaner. With their implementation, arranging the correct quantity of goods for production becomes easy. This access puts executives in the back office and front office on the same page. Such transparency eliminates any space for error or misinterpretation. This connection between systems can boost productivity and assure optimal uptime. In other words, it promotes growth for the company.
Should You Opt for Manufacturing Execution System?
Often, business owners face scenarios where they are confused about choosing one of the systems. There is no clear vision available to them. We shall clearly segregate what each system offers in comparison to their requirements. This will help in making the right choice for your business.
In essence, here is what the MES and ERP systems can do for your business:
What can ERP do for your business?
ERP system can:
- Tell you which materials you need to complete an order
- Tell you the quantity of the materials required to complete the order
- Tell you how soon the order must leave your plant
- Help you gather production data
What can MES do for your business?
With the MES system:
- In order to automate production orchestration, AI-based process control can be used
- Your maintenance processes can be optimized by using intelligent asset monitoring and predictive maintenance technologies.
- Orders are downloaded and executed automatically on the production floor, connecting the supply chain and the production floor.
Future Trends of MES
In the current scenario, we observe that MES is in its early stages. Yet, given the rate at which technology is growing, the manufacturing business is poised to expand dramatically.
- There are anticipations that MES integration with ERP will be more cloud-based. There is also a likelihood of them being connected to a wide range of devices via the Internet of Things or IoT.
- Wireless sensor and actuator networks are two other elements that are set to rise for in-progress production changes. They are promoted by Industry 4.0. There are multiple other features being added that improve shop floor efficiency.
- RFID tags are commonly used on the shop floor. These are hugely helpful in tracking work-in-process commodities. They are also instrumental in controlling asset use and availability.
It can be summarized that MES technology can incredibly boost the manufacturing sector. This innovative technology can be used by a modern ERP and MES system to keep track of all industrial activities.
Conclusion
In manufacturing, there is a bulk of enterprise information and control systems at all levels. This information is generated and analyzed using incompatible technologies. The disparate and assorted architectures only make things more difficult for the manufacturers.
Furthermore, these systems are usually at different stages of their own lifecycles. Adding to the problems, they have varying levels of receptivity. Due to the lack of common interfaces, supplemental integration of disparate information systems becomes fairly complex.
When you do not have enterprise information and control systems, you will need a plant-wide system tailored to the needs of each facility. This leads to manufacturers facing an imbalanced scale of MES functionalities. As previously said, it is dependent on a number of circumstances.
For a better understanding, we can consider an existing ERP system that has manufacturing floor control functionality. Also, we assume that the MES feature model is just supplemental. So, here we may combine the MES and ERP systems to overcome the aforementioned topical difficulties.
This integration is likely to lessen the implementation issues of information system integration. While integration could be a solution, the chances of eliminating MES completely are negligible.
How can Deskera Help You?
Manufacturing processes can be a lot easier with clear visibility. Let Deskera MRP takeover the hassles while you focus on the core tasks related to manufacturing.
Here are some ways Deskera ERP and MRP systems can assist you:
- Control production schedules
- Keep a Bill of Materials
- Produce thorough reports
- Make your own dashboard and much more!
Deskera offers a fully integrated, compliant, and easy-to-implement ERP software system. It is a web-based business management tool that delivers an accurate, real-time picture of your business operations.
Deskera Books, an accounting expert included with Deskera ERP, enables you to automate all of your accounting activities, including invoicing, billing, costs, payments, taxes, reporting, approval flows, multiple currency payments, payment getaways, and much more.
Deskera CRM makes it easy to expand your customer base through email marketing, CTAs, landing pages, help desk options, and other methods. Furthermore, it is now straightforward to automate sales and closing transactions, move them through the sales pipeline at the appropriate stages, and collect real-time data.
Deskera People is a straightforward tool for centralizing human resource management duties. Technology speeds up payroll processing and helps you with other tasks like overtime, employee benefits, training programs, and much more.
Key Takeaways
- A Manufacturing Execution System or an MES assists firms in ensuring that their manufacturing activities are up to the mark.
- It is a software system that connects the manufacturing floor's machines, work centers, and data flows. It assists in tracking and managing these data flows.
- Throughout the production cycle, an MES provides firms with data on product tracking and genealogy.
- Key Features of MES include product tracking, process management, equipment control, production order execution, data collection, and so on.
- Advantages of MES include ERP integration, paperless manufacturing, decrease downtime, reduced waste, and reduced costs.
- When compared to ERP, MES is less expensive and easy to install and use.
- ERP and MES integration can help manufacturers in multiple ways.
- The integration enables the manufacturing teams to avoid last-minute orders and production delays.
- It can also improve demand forecasting and aid in obtaining real time insights into quality issues.
- While both ERP and MES offer value to manufacturers, MES is designed specifically to boost manufacturing processes.
- MES can help automate production processes with AI-based controls.
- With intelligent asset monitoring and smart maintenance solutions, companies can easily follow and optimize maintenance protocols.
- If your company seeks connection of supply chain with the factory floor, MES implementation can help you achieve this through automatic order download and execution.
Related Articles











