How do you think the future of order management will look? Will it be more automated and analytical, or will it feature more evolutionary changes?
The future of order management is an interesting topic to discuss, as it is evolving rapidly right now. Many industries are moving towards more automation and analytics in their order management systems, which helps speed up and streamline the process. This is particularly important in industries where speed is key, such as manufacturing.
As order management systems become more automated and analytical, businesses will be able to improve their product delivery and customer service levels. This is because they will be able to better monitor and predict customer needs. Additionally, the trend of evaluating ORDER rules across hierarchies will lead to even greater efficiencies. Ultimately, the future of order management looks very promising for businesses of all sizes.
Let's take a look at the table of content below:
- Meaning of Order Management
- Importance of Effective Order Management in Business Operations
- Overview of Traditional Order Management Systems
- Automation in Order Management
- Analytics and Order Management
- Evolution of Order Management Systems
- How will Automation Impact Order Management in the Future?
- How will Analytics Contribute to Order Management in the Future?
- Will Order Management Automation Replace Human Involvement?
- How will the Future of Order Management Benefit Customers?
- Challenges and Considerations in Implementing Future Order Management Systems
- Frequently Asked Questions on Order Management: Automation, Analytics, and Evolution
- Wrapping Up
- How Deskera Can Assist You?
Let's get started!
Meaning of Order Management
Order management refers to the end-to-end process of receiving, processing, and fulfilling customer orders. It encompasses a range of activities, systems, and resources involved in efficiently managing and delivering products or services to customers.
The order management process typically starts when a customer places an order, either through a sales channel (such as a website, mobile app, or physical store) or through other means like phone or email. From that point, the order management system kicks in to handle various tasks and ensure a smooth and accurate fulfillment process.
Here is a detailed breakdown of the order management process:
Order Entry: This stage involves capturing all relevant order information, including customer details, product or service specifications, quantity, pricing, and any special requirements. The order entry can be done manually by customer service representatives or automatically through electronic channels.
Order Validation: Once the order is entered, it undergoes validation to ensure its accuracy and feasibility. This may involve checking product availability, verifying pricing and discounts, validating customer information, and confirming that the order meets specific business rules and requirements.
Inventory Management: In order to fulfill the order, the system needs to determine the availability of the requested products or services. This involves checking inventory levels in real-time, across different locations or warehouses, and ensuring that there is sufficient stock to meet the order requirements.
Order Processing: Once the order is validated and inventory availability is confirmed, the system processes the order for fulfillment. This may involve generating order documents, assigning unique identifiers or tracking numbers, and updating the order status in the system.
Order Fulfillment: This stage encompasses the physical or digital delivery of the products or services to the customer. It involves coordinating various activities such as picking and packing items, initiating shipping or delivery processes, generating shipping labels or invoices, and ensuring that the order is dispatched to the customer in a timely manner.
Shipment Tracking: In many cases, customers expect to track their orders during the shipping process. Order management systems often integrate with logistics providers or carriers to provide real-time tracking updates, allowing customers to monitor their shipments' progress and estimated delivery dates.
Order Updates and Communication: Throughout the order fulfillment process, it is essential to keep customers informed about the progress of their orders. This includes sending order confirmations, shipping notifications, and any relevant updates or changes. Effective communication helps manage customer expectations and ensures a positive experience.
Order Returns and Customer Service: In cases where customers need to return products or have inquiries or issues related to their orders, an order management system facilitates the handling of these requests. This involves managing return authorizations, processing refunds or exchanges, and providing customer support to address any concerns or questions.
Order Analytics and Reporting: Order management systems often generate data and insights that can be used for analysis and reporting. This information can help businesses assess order patterns, inventory performance, customer preferences, and other metrics. Analyzing this data allows for continuous improvement of order management processes and decision-making.
Effective order management is crucial for businesses to ensure timely and accurate order fulfillment, optimize inventory levels, minimize errors and returns, and deliver exceptional customer experiences. By leveraging technology, automation, and analytics, organizations can streamline their order management processes, enhance efficiency, and drive customer satisfaction.
Importance of Effective Order Management in Business Operations
Order management plays a crucial role in the success of any business, regardless of its size or industry. It encompasses the processes and systems that handle the entire lifecycle of an order, from initiation to fulfillment.
Effective order management ensures that customer demands are met promptly, accurately, and cost-effectively, leading to improved customer satisfaction, increased sales, and enhanced operational efficiency. This section will delve into the importance of effective order management in detail.
A. Customer Satisfaction
Efficient order management directly impacts customer satisfaction. Customers expect their orders to be processed quickly and accurately, with timely updates on the status of their purchases.
A well-executed order management system ensures that customers receive the right products or services on time, leading to positive experiences and customer loyalty. Conversely, mishandled orders, delays, or incorrect deliveries can result in dissatisfied customers, negative reviews, and potential loss of business.
B. Inventory Optimization
Order management plays a critical role in inventory optimization. By accurately tracking orders and monitoring demand patterns, businesses can forecast and plan their inventory levels more effectively.
This helps prevent stockouts, reduces excess inventory, minimizes carrying costs, and maximizes cash flow. With a well-optimized inventory, businesses can meet customer demands promptly and avoid the risk of lost sales or overstocking.
C. Cost Efficiency
Effective order management contributes to cost efficiency throughout the supply chain. By automating order processing and fulfillment, businesses can streamline operations, reduce manual errors, and minimize labor costs.
Additionally, optimized inventory levels prevent tying up capital in excess stock. Efficient order management also enables businesses to negotiate better pricing and terms with suppliers, leading to cost savings and increased profitability.
D. Operational Efficiency
An efficient order management system enhances overall operational efficiency. By automating order routing, businesses can ensure that orders are directed to the most suitable fulfillment centers or suppliers.
This further eliminates bottlenecks and reduces order processing times. Integration with other enterprise systems, such as ERP and CRM, streamlines data flow, enhances visibility and facilitates seamless order tracking and customer communication. These improvements result in streamlined processes, reduced lead times, and increased productivity.
E. Data-driven Insights
Order management generates a wealth of data that can provide valuable insights for business decision-making. By analyzing order trends, customer preferences, and buying patterns, businesses can identify opportunities for cross-selling, upselling, and targeted marketing campaigns.
Data-driven insights also help optimize pricing strategies, identify market trends, and fine-tune supply chain operations. By harnessing the power of analytics, businesses can make informed decisions that drive growth and competitive advantage.
F. Scalability and Adaptability
Effective order management systems are scalable and adaptable to accommodate business growth and changing market dynamics. As businesses expand into new markets or introduce new products, their order management processes need to handle increased order volumes and diverse requirements seamlessly.
Flexibility in order management systems allows businesses to adapt to evolving customer expectations, industry regulations, and technological advancements, ensuring sustained success in a dynamic business environment.
Overview of Traditional Order Management Systems
Traditional order management systems have been the backbone of businesses for many years, serving as the foundation for processing and fulfilling customer orders. These systems have evolved over time, starting from manual processes and progressing to computerized systems. Here is an overview of traditional order management systems:
Manual Processes:
In the early days, order management relied heavily on manual processes, including handwritten orders, filing systems, and physical order tracking. These processes were time-consuming, prone to errors, and lacked real-time visibility into order status. Communication with customers and suppliers often involved phone calls or written correspondence, leading to slower response times.
Paper-based Systems:
With the advent of technology, paper-based systems became common. Businesses started using order forms, invoices, and purchase orders to capture and track order information. These documents were manually processed and stored, which improved accuracy to some extent. However, they still required manual data entry and were susceptible to loss or damage.
Spreadsheet-based Systems:
As computers became more prevalent, businesses started using spreadsheets to manage orders. Spreadsheet software like Microsoft Excel allowed for better organization and calculations.
However, these systems were limited in their capabilities and often lacked integration with other business systems. They required manual data entry and were prone to errors, making it challenging to maintain accuracy and efficiency as order volumes increased.
On-Premises Order Management Systems:
As technology advanced, businesses adopted on-premises order management systems. These systems were installed and maintained locally on the company's servers.
Furthermore, they provided more robust features for order processing, inventory management, and reporting. However, they often required significant upfront investments in hardware, software licenses, and IT infrastructure. Upgrades and maintenance were also time-consuming and costly.
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI):
EDI emerged as a standard for electronic order processing and communication between businesses. It allowed for the exchange of structured order information in a standardized format, eliminating the need for manual data entry and reducing errors. However, implementing EDI required businesses to establish and maintain connections with trading partners, which could be complex and costly.
Integrated Order Management Systems:
Integrated order management systems brought together various functionalities, such as order processing, inventory management, and customer relationship management (CRM). These systems allowed businesses to streamline processes, automate tasks, and improve visibility into order status.
Integration with other enterprise systems, like accounting or shipping, facilitated end-to-end order management. However, these systems were often complex, expensive, and required dedicated IT resources for maintenance and customization.
Overall, traditional order management systems have served businesses well, improving efficiency and accuracy compared to manual processes. However, they often had limitations in terms of scalability, integration, and real-time visibility. Businesses constantly sought more advanced solutions to address these challenges, leading to the emergence of automation, analytics, and cloud-based order management systems in the pursuit of a more efficient and future-ready approach.
Automation in Order Management
Following, we've discussed automation in order management. Let's learn:
A. Definition and benefits of automation in order management:
Automation in order management refers to the use of technology and software systems to automate various tasks and processes involved in order processing, fulfillment, and management. It aims to reduce manual efforts, increase efficiency, and improve accuracy in order-related operations. The benefits of automation in order management include:
Increased Efficiency: Automation eliminates time-consuming manual tasks, such as data entry, order routing, and invoice generation. It enables faster order processing, reduces bottlenecks, and improves overall operational efficiency.
Enhanced Accuracy: Manual data entry is prone to errors, which can lead to order discrepancies and delays. Automation minimizes human errors by ensuring consistent and accurate data entry, reducing the likelihood of order fulfillment mistakes.
Improved Speed: Automated systems can process orders in real-time, enabling faster order cycles and reducing the time between order placement and delivery. This leads to improved customer satisfaction and a competitive advantage in fast-paced markets.
Cost Savings: By reducing manual labor and improving operational efficiency, automation in order management can result in significant cost savings for businesses. It minimizes the need for additional staffing and lowers the risk of costly errors or delays.
B. Integration of robotic process automation (RPA) and artificial intelligence (AI):
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies play a vital role in automating order management processes.
RPA involves the use of software robots or bots that can mimic human actions to automate repetitive tasks. In order management, RPA can be applied to tasks like order entry, order routing, and generating invoices. By implementing RPA, businesses can significantly reduce manual effort, speed up processes, and improve accuracy.
AI technologies, such as natural language processing and machine learning, can be employed to automate more complex order management tasks. AI can assist in order classification, fraud detection, and predictive analytics for demand forecasting. By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI algorithms can identify patterns, make predictions, and optimize decision-making in order management.
The integration of RPA and AI in order management systems can deliver powerful automation capabilities, combining the efficiency of RPA with the intelligence of AI to streamline and optimize various order management processes.
C. Streamlining order processing and fulfillment through automation:
Automation streamlines order processing and fulfillment by eliminating manual interventions and optimizing workflow. Here are some key areas where automation can be applied:
Order Entry: Automation allows for seamless integration between sales channels, order capture systems, and order management systems. This eliminates the need for manual data entry and reduces the risk of errors. Orders can be automatically captured, validated, and transferred to the appropriate fulfillment channels.
Inventory Management: Automation enables real-time inventory tracking and synchronization across multiple sales channels. When an order is received, the inventory levels can be automatically updated, ensuring accurate stock availability information and preventing overselling or stockouts.
Order Routing: Automated systems can intelligently route orders based on predefined rules, such as geographic proximity, available inventory, or service level agreements. This ensures efficient order allocation to the most suitable fulfillment centers or suppliers.
Order Tracking and Communication: Automation enables real-time order tracking and proactive communication with customers. Automated notifications and updates can be sent to customers at various stages of the order fulfillment process, providing transparency and improving customer satisfaction.
D. Case studies and real-world examples of successful automation implementations:
Amazon: Amazon's order management system is a prime example of automation in action. From seamless online ordering to advanced warehouse robotics and automated sorting systems, Amazon has heavily invested in automation to optimize its order processing and fulfillment. This has enabled the company to achieve rapid order cycles and deliver a vast range of products to customers efficiently.
Zappos: Zappos, an online shoe and clothing retailer, implemented automation in its order management processes. By integrating its e-commerce platform with automated order routing and inventory management systems, Zappos achieved faster order processing and reduced lead times. This allowed them to deliver exceptional customer service and maintain a loyal customer base.
Shopify: As a leading e-commerce platform, Shopify offers automation capabilities to its merchants. Through integration with order management systems, inventory management tools, and shipping providers, Shopify enables businesses to automate order processing, inventory updates, and shipping label generation. This automation saves time, reduces errors, and improves overall efficiency for businesses using the platform.
These case studies demonstrate the successful implementation of automation in order management, resulting in improved operational efficiency, reduced errors, and enhanced customer satisfaction. They highlight the significant benefits that businesses can achieve by embracing automation in their order management processes.
Analytics and Order Management
Following, we've discussed analytics and order management. Let's learn:
A. Utilizing data analytics for order forecasting and demand planning:
Data analytics plays a crucial role in order management by providing insights into order forecasting and demand planning. By analyzing historical sales data, market trends, and customer behavior, businesses can make accurate predictions about future demand.
Furthermore, this helps in aligning inventory levels, production schedules, and supply chain operations to meet customer demands effectively. Data analytics also enables businesses to identify seasonal trends, new product opportunities, and customer preferences, enabling them to make informed decisions and optimize their order management strategies.
B. Leveraging predictive analytics to optimize inventory management:
Predictive analytics is instrumental in optimizing inventory management. By analyzing historical data, market trends, and other variables, businesses can forecast future demand patterns more accurately. This allows them to optimize inventory levels, prevent stockouts, and minimize excess inventory.
Predictive analytics helps in identifying the optimal reorder points, safety stock levels, and replenishment strategies. By aligning inventory levels with anticipated demand, businesses can reduce carrying costs, improve cash flow, and ensure a seamless order fulfillment process.
C. Applying machine learning algorithms for fraud detection and prevention:
Machine learning algorithms can be applied to order management systems for fraud detection and prevention. By analyzing historical transaction data, customer behavior patterns, and various risk factors, machine learning models can identify suspicious activities or anomalies indicative of potential fraud.
These algorithms can automatically flag and investigate potentially fraudulent orders, reducing the risk of financial losses and protecting businesses and customers from fraudulent activities. Machine learning-based fraud detection systems continuously learn and adapt, improving their accuracy over time.
D. Enhancing customer experience through personalized recommendations and cross-selling:
Data analytics enables businesses to enhance the customer experience in order management by providing personalized recommendations and cross-selling opportunities. By analyzing customer purchase history, browsing behavior, and demographic information, businesses can offer targeted product recommendations, upsell relevant items, and facilitate cross-selling.
This level of personalization improves customer engagement, increases sales, and fosters customer loyalty. By leveraging analytics-driven insights, businesses can tailor their order management processes to meet individual customer preferences, resulting in a more satisfying and personalized shopping experience.
E. Case studies highlighting the impact of analytics in order management:
Walmart: Walmart, a multinational retail corporation, leverages analytics to optimize its order management processes. By analyzing historical sales data, weather patterns, and customer behavior, Walmart accurately forecasts demand and adjusts inventory levels accordingly. This allows them to minimize stockouts, improve replenishment strategies, and optimize their supply chain operations, resulting in enhanced customer satisfaction and increased sales.
Netflix: Netflix utilizes data analytics to provide personalized recommendations to its subscribers. By analyzing user viewing history, ratings, and preferences, Netflix's recommendation engine suggests relevant movies and TV shows to each user, improving their streaming experience and increasing user engagement. This demonstrates the power of analytics in understanding customer preferences and delivering personalized recommendations.
These case studies illustrate the significant impact of analytics in order management. By leveraging data analytics, businesses can make informed decisions, optimize inventory levels, prevent fraud, enhance customer experience, and ultimately drive growth and profitability. Analytics-driven order management strategies enable businesses to stay competitive in the dynamic and customer-centric marketplace.
Evolution of Order Management Systems
Following, we've discussed evolution of order management. Let's learn:
A. Transition from on-premises systems to cloud-based solutions:
The evolution of order management systems has seen a transition from traditional on-premises systems to cloud-based solutions. On-premises systems required businesses to install and maintain software and hardware locally, resulting in high upfront costs and limited scalability.
Cloud-based order management systems, on the other hand, are hosted and managed by service providers, offering scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. Businesses can access these systems through web browsers, enabling real-time data access, seamless updates, and integration with other cloud-based services. Cloud-based solutions also provide enhanced security, data backup, and disaster recovery capabilities, making them an attractive option for businesses of all sizes.
B. Adoption of omnichannel order management for seamless customer experiences:
The rise of omnichannel retailing has necessitated the adoption of omnichannel order management systems. Customers now expect a seamless shopping experience across various channels, including online marketplaces, social media platforms, mobile apps, and brick-and-mortar stores.
An omnichannel order management system integrates all these channels, allowing customers to place orders, track shipments, and make returns or exchanges seamlessly. This integration enables businesses to provide consistent product information, pricing, and inventory availability across channels, resulting in improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
C. Integration of order management with other enterprise systems (ERP, CRM):
Order management systems have evolved to integrate with other enterprise systems, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM). This integration allows for seamless data exchange and collaboration across different departments within an organization.
For example, integrating order management with ERP systems enables businesses to streamline inventory management, financials, and production planning. Integration with CRM systems provides a holistic view of customer interactions, enabling personalized order processing and effective customer support. By breaking down silos and enabling cross-functional collaboration, integrated order management systems improve efficiency, accuracy, and customer experiences.
D. Incorporating blockchain technology for secure and transparent order tracking:
The incorporation of blockchain technology is an emerging trend in order management. Blockchain provides a decentralized and immutable ledger that can securely track and record order transactions. By leveraging blockchain, businesses can ensure transparent and tamper-proof order tracking, enhancing trust and accountability throughout the supply chain.
Blockchain technology also enables the secure sharing of order-related information with stakeholders, such as suppliers and customers, reducing disputes and improving efficiency. By providing a single source of truth for order data, blockchain enhances traceability, reduces fraud, and improves overall order management processes.
E. Exploring emerging technologies and their impact on order management:
Emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and 5G connectivity, have a significant impact on order management.
The IoT enables the connection of devices, sensors, and equipment, facilitating real-time data exchange and monitoring. In order management, IoT devices can track inventory levels, monitor shipment conditions, and provide real-time visibility into order status. This data can be integrated with order management systems, enabling proactive decision-making and automated processes.
Additionally, 5G connectivity offers faster and more reliable data transmission, enabling real-time communication between systems, devices, and stakeholders. The combination of IoT and 5G technologies enhances order management by enabling seamless data exchange, faster order cycles, and improved operational efficiency.
In summary, the evolution of order management systems involves transitioning to cloud-based solutions, adopting omnichannel capabilities, integrating with other enterprise systems, incorporating blockchain technology, and exploring emerging technologies like IoT and 5G. These advancements empower businesses to optimize order processing, enhance customer experiences, improve transparency, and adapt to the changing dynamics of the digital marketplace.
How will Automation Impact Order Management in the Future?
Automation will have a profound impact on order management in the future, revolutionizing the way businesses process, fulfill, and manage customer orders. Here are some key ways automation will impact order management:
Streamlined Order Processing: Automation can significantly streamline the order processing phase. By leveraging technologies like robotic process automation (RPA) and artificial intelligence (AI), businesses can automate repetitive tasks such as order entry, data validation, and document generation. This reduces manual errors, improves speed and accuracy, and frees up human resources for more value-added activities.
Efficient Inventory Management: Automation plays a crucial role in optimizing inventory management. Advanced algorithms and predictive analytics can analyze historical data, customer demand patterns, and market trends to forecast future demand accurately. This enables businesses to maintain optimal inventory levels, minimize stockouts and overstock situations, and ensure timely order fulfillment.
Intelligent Order Routing: Automation can intelligently route orders based on various factors such as product availability, proximity to customers, and shipping costs. By integrating order management systems with intelligent routing algorithms, businesses can determine the most efficient and cost-effective ways to fulfill orders, considering factors like inventory distribution, shipping carriers, and delivery timelines.
Real-Time Order Tracking and Notifications: Automation enables businesses to provide customers with real-time updates on their order status, shipment tracking, and estimated delivery dates. This improves transparency and customer satisfaction by keeping them informed throughout the order fulfillment process. Automated notifications can be sent via email, SMS, or through online customer portals.
Seamless Integration with Supply Chain Partners: Automation facilitates seamless integration with supply chain partners such as suppliers, manufacturers, and logistics providers. This enables real-time data exchange, synchronization of inventory levels, and collaborative order management. By automating the communication and data-sharing processes, businesses can enhance supply chain visibility, coordination, and overall efficiency.
Personalized Customer Experiences: Automation, combined with data analytics, allows businesses to provide personalized customer experiences. By analyzing customer data, purchase history, and preferences, businesses can offer personalized product recommendations, tailored promotions, and customized pricing. Automation enables the delivery of personalized offers and experiences at scale, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Enhanced Customer Service: Automation can enhance customer service in order management. Chatbots and virtual assistants powered by AI can handle customer inquiries, provide order updates, and assist with common order-related issues. This reduces response times, increases availability, and improves the overall customer experience.
Data Analytics and Insights: Automation generates vast amounts of data that can be analyzed to gain valuable insights. By leveraging analytics tools, businesses can analyze order patterns, customer behavior, and operational performance. These insights can inform decision-making, optimize processes, identify bottlenecks, and drive continuous improvement in order management.
While automation offers significant benefits, it is important to note that human involvement remains essential. Human intervention will be needed to handle complex customer inquiries, manage exceptions, make strategic decisions, and build customer relationships. Automation complements human capabilities, allowing employees to focus on higher-value tasks that require creativity, critical thinking, and customer interaction.
Overall, automation in order management will lead to improved efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction. It will enable businesses to process orders faster, optimize inventory levels, deliver personalized experiences, and enhance supply chain collaboration, ultimately driving business growth and success.
How will Analytics Contribute to Order Management in the Future?
Analytics will play a crucial role in order management in the future, providing valuable insights and driving data-driven decision-making. Here are some ways analytics will contribute to order management:
Demand Forecasting and Inventory Optimization: By analyzing historical order data, customer behavior, market trends, and external factors, analytics can help businesses forecast demand more accurately. This enables optimized inventory management, ensuring the right products are available at the right time and reducing stockouts or overstock situations. Advanced analytics techniques, such as machine learning algorithms, can continuously refine demand forecasts based on real-time data.
Order Prioritization and Allocation: Analytics can help prioritize and allocate resources for order fulfillment based on various factors. By considering factors like customer value, order value, and service level agreements, analytics can assist in determining the order in which orders should be processed, which customers should be given priority, and how resources should be allocated for optimal efficiency.
Performance Monitoring and KPI Tracking: Analytics provides the ability to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) related to order management. Metrics such as order cycle time, order accuracy, fulfillment rate, and customer satisfaction can be tracked and analyzed in real-time. This allows businesses to identify bottlenecks, track performance trends, and take corrective actions to improve operational efficiency and customer service.
Root Cause Analysis and Issue Resolution: Analytics can help identify the root causes of order-related issues or exceptions. By analyzing data, businesses can uncover patterns, trends, and anomalies that contribute to errors, delays, or customer dissatisfaction. This enables proactive problem-solving and process improvement, leading to better order management outcomes.
Customer Segmentation and Personalization: Analytics allows businesses to segment their customer base and gain insights into customer behavior, preferences, and purchase patterns. By analyzing this data, businesses can personalize their order management processes, provide targeted offers, and deliver customized experiences. This enhances customer satisfaction, drives repeat purchases, and increases customer loyalty.
Pricing and Promotion Optimization: Analytics can assist in optimizing pricing strategies and promotional activities. By analyzing historical sales data, market trends, and competitor pricing, businesses can determine optimal price points, discounts, and promotions. This helps maximize revenue, improve profit margins, and drive customer acquisition and retention.
Continuous Improvement and Predictive Analytics: By leveraging predictive analytics, businesses can anticipate future order management challenges and take proactive measures. Predictive models can forecast potential supply chain disruptions, identify areas of process improvement, and suggest corrective actions. This allows businesses to stay ahead of potential issues, minimize risks, and continually enhance their order management practices.
Data Visualization and Reporting: Analytics tools enable the visualization of order management data through dashboards and reports. Visual representations of data make it easier to understand trends, patterns, and performance metrics. This empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions, monitor progress, and communicate insights effectively across the organization.
In summary, analytics in order management provides valuable insights, enables data-driven decision-making, and drives continuous improvement. By leveraging analytics, businesses can optimize inventory, improve operational efficiency, enhance customer experiences, and ultimately achieve better business outcomes in the increasingly competitive marketplace.
Will Order Management Automation Replace Human Involvement?
Order management automation has the potential to significantly reduce the need for manual intervention and repetitive tasks in the process. However, it is unlikely to completely replace human involvement in order management. Here's a detailed explanation of why human involvement will remain essential:
Complex Decision-Making: While automation can handle routine tasks and streamline processes, complex decision-making often requires human judgment and expertise. For example, resolving exceptional issues, handling customer escalations, managing unique order requirements, and making strategic decisions may involve considerations beyond the capabilities of automation systems.
Exception Handling: In order management, there are situations that fall outside the scope of predefined rules or standard processes. These exceptions require human intervention to assess the situation, evaluate alternatives, and make appropriate decisions. Examples include addressing product defects, managing urgent requests, and handling complex order cancellations or returns.
Customer Interactions: Building and maintaining strong customer relationships often necessitate human interaction. While automation can handle basic customer inquiries and provide updates, complex or sensitive situations may require personalized communication and empathy. Human representatives can provide a level of understanding, empathy, and problem-solving that automation systems cannot replicate fully.
Adaptability and Creativity: Automation systems excel at performing repetitive tasks with speed and accuracy. However, they may struggle when faced with rapidly changing situations or non-standard scenarios. Human involvement brings adaptability, creativity, and the ability to think critically, which are essential for managing unexpected challenges, adapting to customer needs, and finding innovative solutions.
Continuous Improvement: Human involvement is crucial for analyzing and improving order management processes. While automation can provide data and insights, humans play a vital role in interpreting the data, identifying improvement opportunities, and implementing changes. Humans can also leverage their experience and knowledge to suggest process enhancements, refine automation algorithms, and adapt to evolving customer demands.
Complex Customer Relationships: Some order management processes involve managing complex relationships with customers, suppliers, and partners. Human involvement is vital for building trust, negotiating contracts, resolving disputes, and fostering collaborative relationships. These relationship management skills and emotional intelligence are difficult to replicate through automation.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Order management involves compliance with various legal and regulatory requirements. Human involvement is essential to ensure adherence to applicable laws, regulations, and industry standards. Humans can exercise judgment, apply ethical considerations, and navigate nuanced compliance issues that may arise in order management.
While automation can handle a significant portion of order management tasks, human involvement remains crucial for complex decision-making, exception handling, customer interactions, adaptability, creativity, continuous improvement, relationship management, and compliance. The optimal approach is to leverage automation to streamline routine tasks and free up human resources for more value-added activities, thereby creating a balance between automation and human involvement to achieve operational efficiency and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
How will the Future of Order Management Benefit Customers?
The future of order management holds numerous benefits for customers, enhancing their overall shopping experience and satisfaction. Here's a detailed explanation of how customers will benefit:
Faster and Efficient Order Processing: Automation and advanced technologies will expedite order processing, reducing delays and ensuring faster order fulfillment. Customers will experience shorter order cycle times, from placing an order to receiving it, resulting in increased convenience and satisfaction.
Improved Order Accuracy: Automation minimizes manual errors, such as data entry mistakes or incorrect order details. Advanced order management systems can validate customer information, verify product selections, and ensure accurate order processing. Customers will receive the correct items, quantities, and specifications, reducing the need for returns or exchanges.
Real-time Order Tracking and Notifications: Future order management systems will provide customers with real-time updates on their order status, shipment tracking, and estimated delivery dates. Customers can stay informed and track their orders at any stage, enhancing transparency, trust, and peace of mind.
Personalized Experiences: Advanced analytics and customer profiling will enable businesses to deliver personalized experiences in order management. By analyzing customer data, purchase history, and preferences, businesses can offer tailored recommendations, promotions, and pricing. Customers will receive personalized offers and experiences, making their shopping journey more engaging and satisfying.
Multiple Channel Options: The future of order management will support a variety of channels for customers to place orders. Customers can choose to order through websites, mobile apps, social media platforms, voice assistants, or even in-store kiosks. This flexibility allows customers to use their preferred channel and shop at their convenience, enhancing their overall shopping experience.
Enhanced Customer Service: Automation and AI-powered technologies enable improved customer service in order management. Chatbots and virtual assistants can handle routine inquiries, provide order updates, and offer basic support, ensuring 24/7 availability. This reduces response times, increases accessibility, and enhances overall customer service experience.
Simplified Returns and Refunds: Future order management systems will streamline the returns and refunds process. Automation can simplify return authorization, generate return labels, and facilitate faster processing of refunds. This hassle-free return experience improves customer satisfaction, builds trust, and encourages repeat purchases.
Enhanced Product Information: Order management systems can provide customers with comprehensive product information, including detailed descriptions, specifications, and customer reviews. Customers can make informed decisions, compare products, and choose the most suitable options. This access to accurate and rich product information improves customer confidence and satisfaction.
Efficient Customer Support: Future order management systems can integrate customer support features, allowing customers to contact support directly from order management platforms. This integration eliminates the need for customers to navigate multiple channels for assistance, leading to quicker issue resolution and improved customer support experience.
Seamless Cross-channel Experiences: With the integration of omnichannel capabilities, customers can experience a seamless shopping journey across different channels. They can start an order on one channel and complete it on another without losing information or progress. This provides convenience and flexibility, accommodating customers' preferences and enabling a consistent experience.
Overall, the future of order management will benefit customers by offering faster processing, improved accuracy, real-time tracking, personalized experiences, multiple channel options, enhanced customer service, simplified returns, comprehensive product information, efficient support, and seamless cross-channel experiences. These advancements will enhance customer satisfaction, loyalty, and overall shopping experiences.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing Future Order Management Systems
Following, we’ve discussed challenges and crucial considerations in implementing future order management systems. Let’s learn:
A. Data security and privacy concerns:
Implementing future order management systems brings about concerns regarding data security and privacy. As businesses collect and process large volumes of customer and transactional data, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of that data becomes paramount. Organizations must implement robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular vulnerability assessments, to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access or breaches. Compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA, should also be considered to avoid legal and reputational risks.
B. Integration complexities and legacy system limitations:
Integrating future order management systems with existing enterprise systems and legacy applications can be complex. Legacy systems may have limited compatibility, lack standardized interfaces, or require custom integration efforts. Businesses need to assess the compatibility and scalability of their current systems and evaluate the feasibility of integrating new order management solutions. Integration challenges may require the development of custom middleware or the adoption of integration platforms to facilitate seamless data flow between systems.
C. Training and upskilling employees for new technologies:
Implementing future order management systems often involves the adoption of new technologies and software solutions. Employees need to be trained and upskilled to effectively use these systems and leverage their capabilities. Training programs should be designed to familiarize employees with the new tools, processes, and workflows. It is crucial to provide ongoing support and resources to ensure a smooth transition and optimize the utilization of the new order management systems.
D. Regulatory compliance and legal considerations:
When implementing future order management systems, organizations must consider regulatory compliance and legal requirements specific to their industry and geographic location. Compliance with regulations related to data privacy, consumer protection, financial transactions, and export/import regulations is essential.
Legal considerations may include contract negotiations with vendors, intellectual property protection, and ensuring adherence to industry-specific standards. Engaging legal counsel and compliance professionals can help organizations navigate these complexities and ensure adherence to applicable laws and regulations.
E. Cost implications and return on investment (ROI) analysis:
Implementing future order management systems involves financial considerations. Organizations need to assess the cost implications, including software licensing, infrastructure upgrades, implementation costs, and ongoing maintenance expenses.
Conducting a thorough ROI analysis helps evaluate the potential benefits and cost savings associated with the new system. Factors such as increased operational efficiency, improved customer satisfaction, reduced errors, and streamlined processes should be considered when assessing the ROI.
Additionally, organizations should identify key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success and effectiveness of the new order management systems.
By addressing these challenges and considerations, businesses can mitigate risks, ensure compliance, and maximize the value derived from implementing future order management systems. Proper planning, stakeholder involvement, and a comprehensive approach are essential for a successful implementation that enhances operational efficiency, optimizes customer experiences, and drives business growth.
Frequently Asked Questions on Order Management: Automation, Analytics, and Evolution
Following, we’ve discussed important frequently asked questions (FAQs) associated with order management: automation, analytics, and evolution. Let’s learn:
Que 1: Order Management in Simple Words?
Ans: Order management refers to the process of handling and fulfilling customer orders from the point of receipt to delivery. It involves activities such as order processing, inventory management, order tracking, and customer communication.
Automation in order management can bring several benefits, including faster order processing, reduced errors, improved inventory management, enhanced customer experiences, increased operational efficiency, and streamlined fulfillment processes.
Que 2: What is the role of analytics in order management?
Ans: Analytics in order management involves using data analysis techniques to gain insights into customer behavior, demand patterns, inventory management, fraud detection, and personalized recommendations. It helps businesses make informed decisions, optimize operations, improve forecasting accuracy, and enhance the overall order management process.
Que 3: How does integrating order management with other enterprise systems help?
Ans: Integrating order management with other enterprise systems, such as ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and CRM (Customer Relationship Management), enables seamless data exchange, improved collaboration, and a unified view of business processes. It streamlines operations, enhances data accuracy, and enables better decision-making across departments.
Que 4: What is the significance of adopting omnichannel order management?
Ans: Omnichannel order management allows businesses to provide a consistent and seamless customer experience across multiple channels, such as online platforms, mobile apps, and physical stores. It ensures that customers can place orders, track shipments, and make returns or exchanges effortlessly, irrespective of the channel they choose.
Que 5: How can blockchain technology impact order management?
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize order management by introducing transparency, security, and efficiency into the process. Here's a detailed explanation of how blockchain can impact order management:
Enhanced Transparency: Blockchain provides a decentralized and immutable ledger that records all transactions and order-related information. This transparency allows all stakeholders, including customers, suppliers, manufacturers, and logistics providers, to have real-time visibility into the order status, inventory levels, shipment tracking, and payment details. The transparency reduces information asymmetry, disputes, and delays, enabling better collaboration and trust among supply chain partners.
Improved Security: Blockchain technology ensures high levels of data security and integrity. The decentralized nature of blockchain, coupled with cryptographic algorithms, makes it difficult for unauthorized parties to tamper with or manipulate order data. This enhances the security and authenticity of transactions, mitigates the risk of fraud or counterfeiting, and protects sensitive customer information. Additionally, smart contracts on the blockchain can automate and enforce contract terms, reducing the need for intermediaries and minimizing the potential for human error.
Streamlined Payments and Smart Contracts: Blockchain-based order management can streamline payment processes by enabling secure and instant peer-to-peer transactions. Smart contracts, self-executing agreements coded on the blockchain, can automatically trigger payments once predefined conditions are met. This eliminates the need for intermediaries, reduces payment processing time, minimizes transaction fees, and enhances financial efficiency in the order management process.
Supply Chain Traceability: Blockchain technology enables end-to-end traceability and provenance tracking of products throughout the supply chain. Each step of the order fulfillment process, including sourcing, manufacturing, packaging, and shipping, can be recorded on the blockchain. This transparency allows businesses and consumers to verify the origin, authenticity, and quality of products. It also facilitates compliance with regulations, ethical sourcing, and sustainability initiatives.
Efficient Dispute Resolution: Blockchain's transparent and immutable nature simplifies dispute resolution in order management. In the event of discrepancies or disputes, all relevant transaction details are readily available on the blockchain, making it easier to identify and resolve issues. The tamper-proof nature of blockchain records helps to establish trust and eliminate the need for lengthy investigations or third-party interventions.
Streamlined Supply Chain Financing: Blockchain-based order management can facilitate supply chain financing by providing a secure and auditable record of transactions. The transparency and accuracy of order-related data on the blockchain enable financial institutions to assess the creditworthiness of businesses more effectively. This can expedite the approval and disbursement of financing, improving cash flow and working capital management for supply chain participants.
Data Analytics and Insights: Blockchain technology can generate valuable data for analytics and insights. By analyzing the order-related data stored on the blockchain, businesses can gain valuable insights into customer preferences, demand patterns, supply chain inefficiencies, and market trends. These insights can drive data-driven decision-making, enable proactive demand planning, and optimize inventory management strategies.
Collaboration and Trust among Partners: Blockchain technology fosters collaboration and trust among supply chain partners. The decentralized and consensus-based nature of blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and friction in the order management process. Smart contracts on the blockchain can automate and enforce agreed-upon rules and conditions, ensuring that all parties adhere to their commitments. This increased collaboration and trust enable faster, more efficient order fulfillment and better overall supply chain performance.
In summary, blockchain technology can have a transformative impact on order management by providing enhanced transparency, improved security, streamlined payments, supply chain traceability, efficient dispute resolution, supply chain financing, data analytics, and fostering collaboration and trust among supply chain partners. By leveraging blockchain, businesses can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, improve customer experiences, and drive innovation in the order management process.
Blockchain technology can enhance order management by providing secure and transparent order tracking, reducing fraud risks, and improving traceability. It enables businesses to establish trust, streamline supply chain processes, and ensure the integrity of order-related data.
Que 6: What are some challenges in implementing future order management systems?
Ans: Challenges in implementing future order management systems include data security and privacy concerns, integration complexities with legacy systems, training employees for new technologies, regulatory compliance, legal considerations, and assessing the cost implications and ROI of implementation.
Que 7: How can businesses ensure data security and privacy in order management systems?
Businesses can ensure data security and privacy in order management systems by implementing robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular vulnerability assessments. Compliance with data protection regulations and industry best practices is also essential.
Que 8: What factors should be considered when assessing the ROI of implementing order management systems?
Ans: Factors to consider when assessing the ROI of implementing order management systems include increased operational efficiency, improved customer satisfaction, reduced errors, streamlined processes, and potential cost savings from optimized inventory management and order fulfillment.
Que 9: How can businesses prepare their employees for the implementation of new order management systems?
Ans: Businesses can prepare their employees for the implementation of new order management systems by providing training programs that familiarize them with the new tools, processes, and workflows. Ongoing support and resources should be provided to facilitate a smooth transition and maximize the utilization of the new systems.
Que 10: Will automation in order management eliminate the need for customer support representatives?
Automation in order management has the potential to handle routine customer inquiries and provide basic support, but it is unlikely to completely eliminate the need for customer support representatives. While automation can efficiently handle common inquiries and standard processes, there are several reasons why human customer support representatives will remain essential:
Complex and Unique Situations: There are instances where customer inquiries or issues fall outside the scope of predefined rules or standard processes. These complex or unique situations require human intervention. Customer support representatives possess the critical thinking skills and expertise to assess the situation, evaluate alternatives, and make appropriate decisions. They can handle escalated or non-standard cases that require empathy, creativity, and problem-solving abilities.
Empathy and Emotional Intelligence: Dealing with customer emotions and providing empathetic support is an area where human representatives excel. They can understand customer frustrations, concerns, and expectations, and respond in a compassionate and understanding manner. Empathy and emotional intelligence are essential in building rapport, diffusing difficult situations, and ensuring customer satisfaction.
Contextual Understanding: Human customer support representatives can interpret the context of a customer's query or concern effectively. They can ask follow-up questions, clarify ambiguities, and dig deeper to understand the underlying issue. This contextual understanding enables them to provide accurate and relevant responses, ensuring that customer needs are fully addressed.
Flexibility and Adaptability: Automation systems typically operate based on predefined rules and algorithms. In complex or changing scenarios, they may struggle to adapt. Human representatives, on the other hand, possess the flexibility and adaptability to handle evolving situations. They can quickly adjust their approach, find creative solutions, and tailor their responses based on the specific needs of each customer.
Building Trust and Relationships: Customer support representatives play a vital role in building trust and nurturing customer relationships. They provide a human connection, actively listen to customer concerns, and invest time in understanding their needs. Through personalized interactions, representatives can build rapport, establish trust, and create a positive customer experience that fosters loyalty.
Feedback and Improvement: Customer support representatives are a valuable source of feedback for businesses. They interact directly with customers, gather insights, and provide feedback on recurring issues or improvement opportunities. This feedback loop helps organizations identify pain points, refine processes, and enhance the overall order management experience.
Handling Multichannel Support: Automation systems can handle basic inquiries and support on specific channels, but when it comes to managing multichannel support seamlessly, human representatives play a crucial role. They can engage with customers across various channels, such as phone calls, live chats, social media, or email, ensuring a consistent and unified customer experience.
While automation in order management can significantly streamline processes and handle routine inquiries, human customer support representatives bring a unique set of skills, including complex decision-making, empathy, adaptability, contextual understanding, relationship building, and feedback provision. The optimal approach is to strike a balance between automation and human involvement, leveraging automation for efficiency while utilizing human representatives for personalized and exceptional customer support.
Que 11: How will order management automation impact order customization and personalization?
Order management automation can have a positive impact on order customization and personalization, enhancing the overall customer experience. Here's a detailed explanation of how automation can influence these aspects:
Streamlined Customization Processes: Automation can simplify and streamline the order customization process. Through automation systems, customers can easily select and customize products according to their preferences, such as choosing specific features, colors, sizes, or configurations. Automated workflows ensure that the selected customization options are accurately captured and incorporated into the order, minimizing errors and manual intervention.
Real-time Pricing and Promotions: Order management automation can integrate with pricing engines and promotional systems to provide real-time pricing information and personalized offers to customers. By analyzing customer data and purchase history, automation systems can dynamically adjust prices and offer tailored promotions based on individual preferences, loyalty status, or previous interactions. This enables customers to receive personalized pricing and promotions that align with their needs and purchasing patterns.
Efficient Order Routing: Automation systems can intelligently route orders based on customer preferences and requirements. For example, if a customer has specified a preferred shipping method, automation can automatically assign the order to the appropriate shipping carrier or service. Similarly, if a customer has chosen to pick up the order from a specific store location, automation can route the order accordingly. This ensures that orders are processed and fulfilled according to the customer's preferences, enhancing customization and convenience.
Dynamic Order Tracking: Order management automation can provide customers with real-time tracking information and updates on their customized orders. Customers can access information about the status, location, and estimated delivery time of their orders through self-service portals, mobile apps, or email notifications. This level of transparency and visibility allows customers to stay informed and track the progress of their customized orders, enhancing their overall satisfaction.
Personalized Recommendations: Automation systems can leverage customer data and purchase history to generate personalized product recommendations. By analyzing past orders, browsing behavior, and preferences, automation can suggest complementary or relevant products that align with a customer's customization choices. This enables customers to discover additional options or accessories that enhance their customized order, providing a personalized and tailored shopping experience.
Order History and Reordering Convenience: Automation systems can maintain comprehensive order history for customers. This allows customers to easily review their past customized orders, including specific customization details, quantities, and preferences. The ability to access and reorder previous customizations with minimal effort simplifies the purchasing process and provides a seamless experience for customers.
Data-driven Insights for Personalization: Order management automation generates valuable data and insights on customer preferences, customization trends, and buying patterns. Businesses can leverage this data to gain a deeper understanding of their customers, enabling them to refine their customization options, develop targeted marketing strategies, and offer more relevant and personalized experiences in the future. Data-driven insights help businesses continuously improve their order customization and personalization efforts.
By leveraging automation in order management, businesses can enhance order customization and personalization processes. Automation simplifies customization options, offers real-time pricing and promotions, enables efficient order routing, provides dynamic order tracking, delivers personalized recommendations, facilitates convenient order history access, and generates valuable data-driven insights. These benefits contribute to a more engaging and personalized shopping experience for customers, fostering loyalty and satisfaction.
Que 12: What are the potential risks or challenges associated with increased automation in order management?
While automation brings significant benefits, there are potential risks and challenges to consider. These include technical issues, such as system failures or data breaches, which could disrupt order management processes. Additionally, over-reliance on automation without proper oversight may lead to errors or issues going unnoticed. It is crucial for businesses to maintain appropriate controls, monitoring mechanisms, and human oversight to mitigate these risks.
Que 13: Will the future of order management affect small businesses differently than larger enterprises?
Yes, the future of order management may have different impacts on small businesses compared to larger enterprises. Here's a detailed explanation of how these differences may manifest:
Implementation Costs: Implementing advanced order management systems and technologies can involve significant upfront costs. Larger enterprises with larger budgets may find it relatively easier to invest in and adopt new order management solutions. On the other hand, small businesses with limited financial resources may face challenges in funding the implementation and integration of advanced automation technologies. They may need to explore more cost-effective solutions or opt for phased implementation to manage expenses.
Scalability and Flexibility: Order management systems designed for larger enterprises often offer extensive scalability and customization options to accommodate complex operations. Small businesses, with their comparatively simpler order management requirements, may find that their needs can be met with more streamlined and affordable solutions. They may also have the advantage of being more agile and able to adapt quickly to changing market demands, enabling them to leverage emerging technologies more rapidly.
Resource Constraints: Small businesses typically have limited resources, including personnel, infrastructure, and IT capabilities. The adoption of advanced order management automation may require additional training or hiring of skilled personnel, which can pose a challenge for smaller enterprises with fewer resources. Larger enterprises, on the other hand, may have dedicated IT teams and resources to manage the implementation and maintenance of advanced order management systems more effectively.
Competitive Advantage: While both small businesses and larger enterprises can benefit from order management automation, the impact on their competitive advantage may differ. For small businesses, implementing automation can level the playing field by enhancing operational efficiency, improving customer experiences, and enabling them to compete with larger competitors. On the other hand, larger enterprises may have the resources and scale to leverage automation for greater market dominance and efficiency gains.
Customer Relationships: Small businesses often have closer and more personal relationships with their customers compared to larger enterprises. The future of order management, with its focus on customization, personalization, and customer experience, can enable small businesses to further strengthen these relationships. They can leverage automation to provide personalized services, offer tailored recommendations, and deliver exceptional customer support, fostering loyalty and differentiation in the market.
Adaptability and Decision-making: Small businesses are often more nimble and agile in decision-making compared to larger enterprises. This flexibility can allow them to adopt new order management technologies and practices more quickly, responding to changing customer demands and market trends. Their smaller size and simplified organizational structure may enable faster decision-making and implementation of new strategies.
Collaboration Opportunities: While both small businesses and larger enterprises can benefit from collaboration in the supply chain, small businesses may have more flexibility in partnering with suppliers, manufacturers, and logistics providers. They can forge strategic partnerships with niche or specialized service providers to enhance their order management capabilities. This agility in collaboration can enable small businesses to access advanced technologies and expertise that might otherwise be financially challenging to develop in-house.
In summary, the future of order management may impact small businesses and larger enterprises differently due to variations in implementation costs, scalability, resource constraints, competitive advantage, customer relationships, adaptability, decision-making speed, and collaboration opportunities. Small businesses can leverage their agility, customer relationships, and collaboration potential to adopt automation solutions that align with their unique needs and unlock competitive advantages.
Que 14: How will order management automation impact supply chain visibility and collaboration?
Order management automation can significantly improve supply chain visibility and collaboration. By integrating with suppliers, logistics providers, and other partners, automation systems can provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, order status, and shipment tracking. This enables better coordination, proactive issue resolution, and streamlined collaboration among stakeholders, resulting in improved efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Que 15: What role will data analytics play in the future of order management?
Data analytics will play a crucial role in the future of order management. By analyzing order data, customer behavior, market trends, and operational metrics, businesses can gain valuable insights for demand forecasting, inventory optimization, performance monitoring, customer segmentation, and process improvement. Data analytics will empower businesses to make data-driven decisions, enhance operational efficiency, and deliver personalized experiences to customers.
Que 16: How will the future of order management impact inventory management?
The future of order management will have a significant impact on inventory management, revolutionizing the way businesses handle and optimize their inventory. Here's a detailed explanation of how the future of order management will impact inventory management:
Real-time Inventory Visibility: Advanced order management systems will provide real-time visibility into inventory levels. Businesses will have accurate and up-to-date information on available stock across multiple locations, such as warehouses, distribution centers, and stores. Real-time inventory visibility enables businesses to make informed decisions regarding order fulfillment, preventing stockouts or overstock situations.
Demand Forecasting and Inventory Planning: Future order management systems will leverage advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to forecast demand more accurately. By analyzing historical data, market trends, seasonality, and other relevant factors, businesses can predict future demand patterns. This enables proactive inventory planning and optimization, ensuring that the right products are available at the right time and in the right quantities.
Just-in-Time Inventory Management: Automation in order management will facilitate just-in-time inventory management. With real-time order data and demand forecasting, businesses can align their inventory levels closely with anticipated demand. By reducing excess inventory and optimizing replenishment cycles, businesses can minimize carrying costs, reduce the risk of obsolescence, and improve cash flow.
Centralized Inventory Management: Future order management systems will enable centralized inventory management across various sales channels, including online stores, brick-and-mortar stores, and marketplaces. Centralized inventory management provides a holistic view of inventory, allowing businesses to allocate stock efficiently and avoid overselling or underselling. This enhances operational efficiency and prevents customer dissatisfaction caused by stock discrepancies.
Inventory Turnover and Stock Rotation: The future of order management will empower businesses to optimize inventory turnover and implement effective stock rotation strategies. By analyzing sales data, shelf life, expiration dates, and other factors, businesses can prioritize the sale of products with shorter shelf life or nearing expiration. This reduces waste, ensures product freshness, and improves profitability.
Supplier Integration and Automated Reordering: Automation in order management can integrate with suppliers and facilitate automated reordering processes. When inventory levels reach predetermined thresholds, automated systems can generate purchase orders and communicate with suppliers for replenishment. This streamlines the reordering process, reduces manual intervention, and ensures timely stock replenishment to meet customer demand.
Returns and Reverse Logistics Management: The future of order management will enhance returns and reverse logistics management. Advanced systems can automate return authorization, streamline the returns process, and facilitate efficient inventory handling for returned items. By automating these processes, businesses can minimize the impact of returns on inventory, optimize restocking efforts, and improve customer satisfaction.
Data Analytics for Inventory Optimization: Data analytics will play a crucial role in inventory management. By analyzing sales data, customer behavior, market trends, and operational metrics, businesses can gain insights into demand patterns, identify slow-moving or obsolete inventory, and make data-driven decisions to optimize their inventory levels. Data analytics enable businesses to improve inventory accuracy, reduce carrying costs, and maximize profitability.
Integration with Supply Chain Partners: Future order management systems will integrate seamlessly with supply chain partners, such as suppliers, manufacturers, and logistics providers. This integration enables better collaboration, information sharing, and synchronization of inventory-related activities. Businesses can optimize order fulfillment, streamline supply chain operations, and improve overall efficiency.
Enhanced Forecasting Accuracy and Inventory Optimization: By leveraging artificial intelligence, machine learning, and predictive analytics, the future of order management will significantly improve forecasting accuracy and inventory optimization. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and generate accurate demand forecasts. This enables businesses to optimize inventory levels, reduce carrying costs, and meet customer demand effectively.
Overall, the future of order management will have a profound impact on inventory management. It will provide real-time inventory visibility, enable demand forecasting and planning, facilitate just-in-time inventory management, centralize inventory management across channels, automate reordering processes, streamline returns and reverse logistics, leverage data analytics for optimization, integrate with supply chain partners, and enhance forecasting accuracy. These advancements will help businesses improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, minimize stockouts and overstock situations, and deliver better customer experiences.
Que 17: Will the future of order management lead to job loss in the industry?
The future of order management, with its increasing automation and advanced technologies, may lead to changes in job roles and responsibilities within the industry. While there may be some impact on certain job functions, it is unlikely to result in widespread job loss. Here's a detailed explanation:
Shift in Job Roles: As order management becomes more automated, some traditional job roles may evolve or undergo changes. For example, tasks that are repetitive and rule-based, such as data entry or order processing, can be automated, reducing the need for manual intervention. However, this shift in job roles does not necessarily mean job loss. Instead, it opens up opportunities for employees to transition to more strategic and value-added roles within order management.
Focus on Customer Support and Relationship Management: As automation takes over routine tasks, the role of human employees may shift towards customer support and relationship management. Customer support representatives will continue to play a crucial role in handling complex inquiries, providing personalized assistance, and building rapport with customers. The focus will be on delivering exceptional customer experiences that go beyond what automation can provide.
Maintenance and Management of Automation Systems: With increased automation, there will be a growing need for professionals skilled in managing and maintaining the automated order management systems. These individuals will be responsible for configuring, monitoring, and troubleshooting the automation systems to ensure their smooth operation. They will also be involved in analyzing system performance, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing enhancements.
Data Analysis and Insights: The future of order management will generate a vast amount of data related to customer behavior, order patterns, inventory levels, and more. Data analysts and specialists will be required to extract meaningful insights from this data. They will analyze trends, identify patterns, and provide valuable information to drive decision-making in areas such as demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and customer segmentation. These roles will be critical for business growth and strategy development.
Process Optimization and Continuous Improvement: Automation in order management opens up opportunities for professionals specializing in process optimization and continuous improvement. These individuals will be responsible for evaluating existing order management processes, identifying bottlenecks, and implementing improvements to enhance efficiency, reduce errors, and streamline operations. Their expertise will be valuable in ensuring that automation systems are optimized and aligned with business objectives.
Strategic Planning and Innovation: The future of order management will require professionals who can strategically plan for the integration of new technologies, assess market trends, and drive innovation. These individuals will be responsible for identifying emerging technologies, evaluating their potential impact, and making strategic decisions regarding their adoption and implementation. They will play a vital role in keeping businesses competitive and adapting to evolving customer expectations.
It's important to note that while automation may lead to some job role changes, it also has the potential to create new job opportunities within the industry. The implementation and maintenance of automation systems, data analysis, process optimization, and strategic planning will require skilled professionals with expertise in these areas. Additionally, as businesses embrace automation, they may experience growth and expansion, leading to overall job creation.
In summary, while the future of order management may result in changes to certain job roles, it is unlikely to lead to significant job loss. Instead, it will require a shift in skill sets and the creation of new job roles that leverage automation, data analysis, customer support, process optimization, and strategic thinking to drive business success.
These FAQs provide a brief overview of key concepts and considerations related to the future of order management. For more detailed information, please refer to the full article.
Wrapping Up
In conclusion, the future of order management is driven by automation, analytics, and continuous evolution. Businesses are increasingly leveraging technology to optimize their order management processes, enhance operational efficiency, and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
The implementation of automation in order management brings benefits such as faster order processing, reduced errors, and streamlined fulfillment processes. Analytics plays a crucial role in forecasting demand, optimizing inventory management, and detecting fraud. Integration with other enterprise systems, such as ERP and CRM, ensures seamless data exchange and collaboration across departments. The adoption of emerging technologies, such as blockchain, IoT, and 5G, further enhances order management capabilities.
However, implementing future order management systems is not without its challenges. Data security and privacy concerns, integration complexities with legacy systems, and the need to upskill employees for new technologies require careful consideration. Regulatory compliance and legal considerations must also be addressed to avoid legal and reputational risks. Additionally, assessing the cost implications and conducting a thorough ROI analysis is essential to determine the value and benefits of implementing new systems.
By addressing these challenges and embracing the opportunities presented by automation, analytics, and evolving technologies, businesses can transform their order management processes. The future of order management lies in harnessing the power of data, leveraging automation and analytics, integrating systems, and embracing emerging technologies. This transformation enables businesses to achieve operational excellence, deliver seamless customer experiences, and stay competitive in an ever-evolving marketplace.
As businesses navigate the future of order management, it is crucial to approach the implementation process with strategic planning, stakeholder involvement, and a focus on aligning technology with business objectives. By embracing the potential of automation, leveraging the insights provided by analytics, and adapting to emerging technologies, businesses can unlock new opportunities, enhance efficiency, and drive growth in their order management operations.
Overall, the future of order management is an exciting and dynamic landscape, offering businesses the potential to optimize processes, improve customer satisfaction, and achieve sustainable success in the rapidly evolving business environment. By embracing the power of automation, analytics, and continuous evolution, businesses can position themselves at the forefront of efficient and customer-centric order management.
How Deskera Can Assist You?
Deskera ERP and MRP systems help you to keep your business units organized. The system's key features of demand forecasting with Deskera include as follows:
- Establish Demand Forecasting Process
- Automate Data Collection
- Monitor Market Trends
- Analyze Historical Data
- Estimate Future Demand
- Adjust Production Levels
- Manage Supply Chain...and much more!
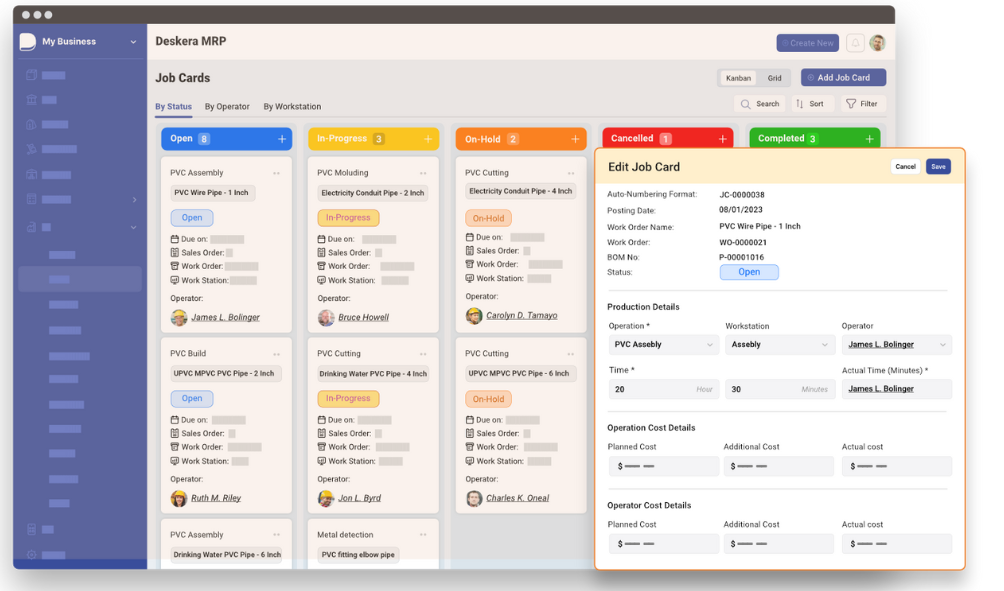
- Deskera's integrated financial planning tools enable investors to better plan and track their investments. It can assist investors in making faster and more accurate decisions.
- Deskera CRM is a powerful solution that manages your sales and helps you close deals quickly. It not only enables you to perform critical tasks like lead generation via email, but it also gives you a comprehensive view of your sales funnel.
- Deskera Books allows you to better manage your accounts and finances. Maintain good accounting practices by automating tasks like billing, invoicing, and payment processing.
- Deskera People is a straightforward tool for centralizing your human resource management functions.
Final Takeaways
We've arrived at the last section of this guide. Let's have a look at some of the most important points to remember:
- Order management refers to the end-to-end process of receiving, processing, and fulfilling customer orders. It encompasses a range of activities, systems, and resources involved in efficiently managing and delivering products or services to customers.
- Automation can significantly streamline the order processing phase. By leveraging technologies like robotic process automation (RPA) and artificial intelligence (AI), businesses can automate repetitive tasks such as order entry, data validation, and document generation.
- Efficient order management directly impacts customer satisfaction. Customers expect their orders to be processed quickly and accurately, with timely updates on the status of their purchases. A well-executed order management system ensures that customers receive the right products or services on time, leading to positive experiences and customer loyalty.
- By analyzing historical order data, customer behavior, market trends, and external factors, analytics can help businesses forecast demand more accurately. This enables optimized inventory management, ensuring the right products are available at the right time and reducing stockouts or overstock situations.
- In order management, there are situations that fall outside the scope of predefined rules or standard processes. These exceptions require human intervention to assess the situation, evaluate alternatives, and make appropriate decisions. Examples include addressing product defects, managing urgent requests, and handling complex order cancellations or returns.
- Automation minimizes manual errors, such as data entry mistakes or incorrect order details. Advanced order management systems can validate customer information, verify product selections, and ensure accurate order processing. Customers will receive the correct items, quantities, and specifications, reducing the need for returns or exchanges.
- With the integration of omnichannel capabilities, customers can experience a seamless shopping journey across different channels. They can start an order on one channel and complete it on another without losing information or progress. This provides convenience and flexibility, accommodating customers' preferences and enabling a consistent experience.
Related Articles












