Is managing your company’s finances becoming more complex and time-consuming as your business grows? If so, you're not alone. Many organizations struggle with manual processes, scattered data, and inconsistent reporting.
Fortunately, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems offer a powerful solution by streamlining financial management and integrating all key financial processes into a single, centralized platform. With ERP, businesses can reduce errors, improve decision-making, and enhance overall efficiency.
At its core, ERP software helps automate and standardize financial operations such as invoicing, budgeting, payroll, and reporting. By consolidating financial data from various departments into a unified system, ERP enables real-time visibility into an organization’s financial health.
This level of transparency not only simplifies day-to-day operations but also helps in maintaining compliance with regulations and generating accurate financial reports quickly. The result is more informed decision-making, improved cash flow management, and a better handle on expenses.
One of the key players in this space is Deskera ERP, a robust solution designed specifically for small to medium-sized businesses. Deskera ERP offers comprehensive financial management features, including automated accounting, real-time reporting, and seamless integration with other business functions like inventory and payroll. Its AI-driven insights and intuitive interface make it easier for businesses to manage their finances efficiently and scale as they grow.
By integrating financial processes into a single ERP system, companies can eliminate redundancy, reduce the risk of human error, and accelerate their financial workflows. This not only saves time and resources but also improves financial forecasting and budgeting, helping businesses stay ahead in a competitive market.
What is Financial Management?
Financial management refers to the strategic planning, organizing, directing, and controlling of financial activities within an organization. It encompasses a wide range of functions that are essential for maintaining the financial health of a business, ensuring that it can effectively meet its financial goals and obligations.
Here are the key components and objectives of financial management:
Key Components of Financial Management
- Financial Planning: This involves estimating future financial needs and creating a budget to allocate resources effectively. Financial planning helps organizations prepare for anticipated expenses and investment opportunities.
- Capital Structure Management: Financial management involves determining the optimal mix of debt and equity financing to fund the organization’s operations and growth. This includes analyzing the cost of capital and assessing risk.
- Investment Management: Financial managers evaluate potential investment opportunities to ensure they align with the organization’s goals and provide satisfactory returns. This includes conducting feasibility studies and risk assessments.
- Cash Flow Management: Ensuring adequate cash flow is crucial for day-to-day operations. Financial management involves monitoring cash inflows and outflows, managing working capital, and ensuring liquidity to meet short-term obligations.
- Financial Reporting and Analysis: This includes preparing and analyzing financial statements such as balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements. Accurate reporting provides insights into financial performance and guides decision-making.
- Risk Management: Financial management involves identifying and mitigating financial risks, such as market fluctuations, credit risks, and operational risks. Effective risk management protects the organization’s assets and ensures stability.
Objectives of Financial Management
- Maximizing Shareholder Value: One of the primary goals of financial management is to maximize the wealth of shareholders by ensuring that the organization is profitable and its stock price appreciates.
- Ensuring Financial Stability: Financial management aims to maintain the organization’s financial health by managing risks and ensuring sufficient liquidity to meet obligations.
- Facilitating Strategic Decision-Making: By providing relevant financial information and analysis, financial management supports strategic planning and decision-making, allowing the organization to respond effectively to market changes.
- Optimizing Resource Allocation: Financial management seeks to allocate resources efficiently to ensure that funds are directed toward the most profitable opportunities.
In summary, financial management is a critical function that encompasses a range of activities aimed at ensuring the financial stability and success of an organization. By effectively managing finances, organizations can achieve their goals, optimize performance, and create value for stakeholders.
The Interplay of Financial Management with Organizational Success
Financial management is a critical component of any organization's overall strategy and success. It influences how resources are allocated, how risks are managed, and how strategic decisions are made.
The interplay between effective financial management and organizational success is multifaceted and significant. By aligning financial goals with broader business objectives, organizations can enhance their growth, improve operational efficiency, and strengthen their competitive position in the market.
Effective Resource Allocation
One of the primary ways financial management contributes to organizational success is through effective resource allocation. By analyzing financial data, organizations can identify areas of strength and weakness, enabling them to allocate resources more efficiently.
Strategic allocation of funds ensures that investments are directed toward high-impact projects, maximizing returns and fostering innovation. A strong financial management system supports informed decision-making, allowing leaders to evaluate potential investments and assess their alignment with organizational goals.
Risk Management
Sound financial management plays a vital role in risk management. By monitoring financial performance and conducting regular audits, organizations can identify potential risks and implement measures to mitigate them.
This proactive approach to financial oversight helps organizations navigate uncertainties and maintain stability during economic volatility.
Furthermore, effective financial management fosters transparency and accountability, essential for building trust with stakeholders, including investors, employees, and customers.
Integration with Business Functions
The integration of financial management with other business functions—such as marketing, operations, and human resources—can enhance overall organizational performance.
For instance, aligning financial objectives with marketing strategies leads to more effective budget allocation for campaigns, resulting in improved customer engagement and higher sales.
Similarly, integrating financial planning with operational processes ensures that production levels and inventory management align with financial targets, optimizing efficiency and reducing costs.
Long-Term Sustainability
Ultimately, the interplay between financial management and organizational success is a dynamic relationship that drives growth and sustainability. Organizations that prioritize effective financial management are better equipped to adapt to changing market conditions, seize new opportunities, and achieve long-term success.
By recognizing the importance of financial management as a strategic function, organizations can create a solid foundation for their future, enabling them to thrive in an increasingly competitive landscape.
In conclusion, effective financial management is not merely a backend function but a strategic driver that significantly influences an organization’s success. By understanding and leveraging this interplay, organizations can navigate challenges, optimize resources, and foster a culture of accountability and transparency that supports their overall goals.
Key Financial Processes Streamlined by ERP
The key financial processes that can be streamlined by Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are:
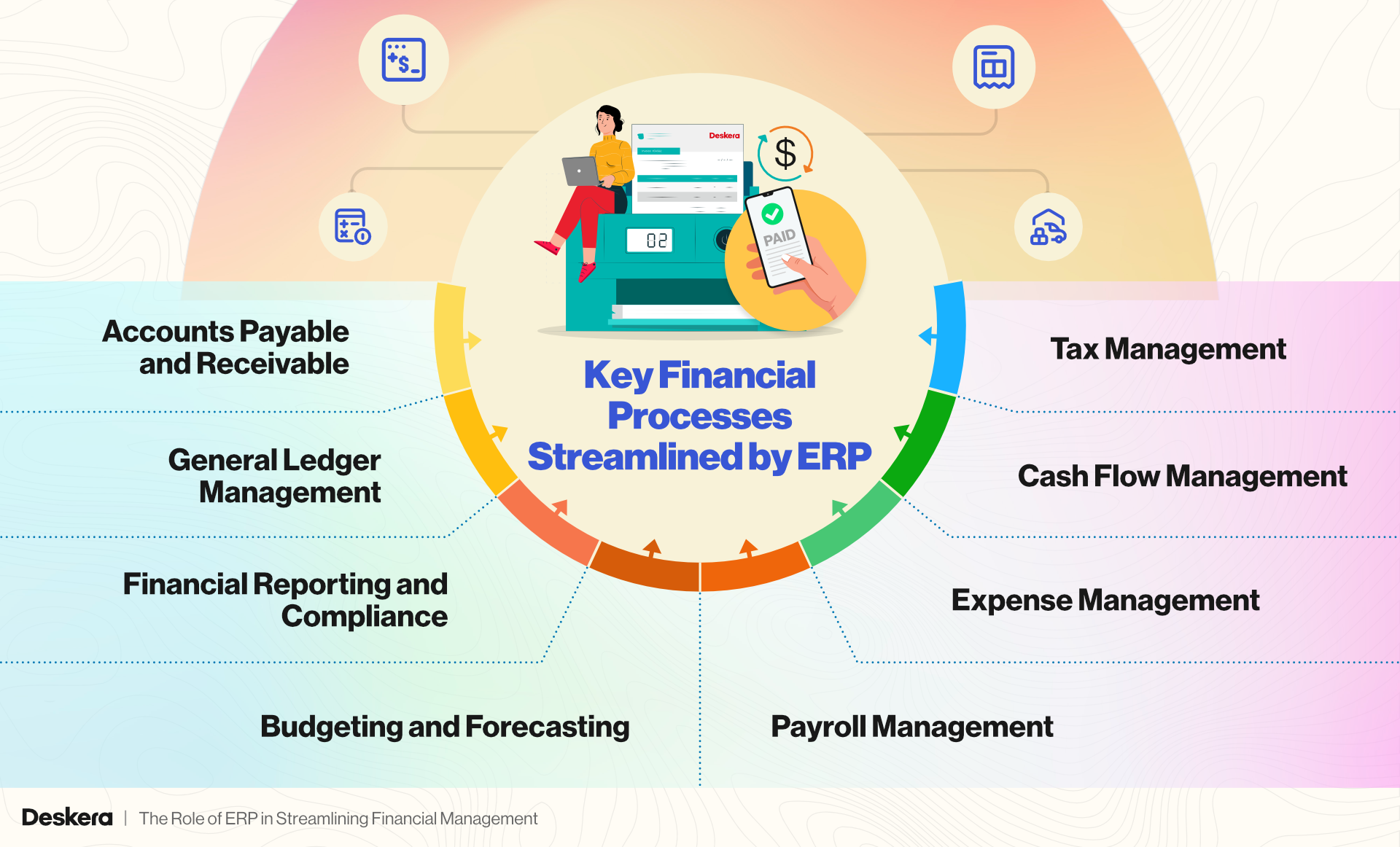
Accounts Payable and Receivable
ERP systems streamline both accounts payable (AP) and accounts receivable (AR) processes by automating tasks such as invoice generation, payment tracking, and reconciliation.
Businesses can easily manage incoming and outgoing payments, reducing manual errors and improving cash flow management. The system also enables faster invoicing, automates reminders for overdue payments, and ensures that financial records are always up-to-date, making the collection and payment process more efficient.
General Ledger Management
The general ledger (GL) is the backbone of any financial management system, and ERP solutions simplify GL management by automatically recording every financial transaction. ERP systems consolidate financial data from various departments, ensuring that it is recorded in real-time.
This centralized approach provides finance teams with a clear, up-to-date picture of the organization’s financial status, which is essential for accurate reporting and compliance with accounting standards like GAAP or IFRS.
Financial Reporting and Compliance
Financial reporting can be a time-consuming process when managed manually, but ERP systems make it easier by offering built-in reporting tools. ERP software can generate a variety of financial reports, such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow reports, in just a few clicks.
Additionally, ERP systems help businesses remain compliant with financial regulations by automating tax calculations, generating audit trails, and ensuring proper documentation for audits.
Budgeting and Forecasting
ERP systems support budgeting and forecasting by providing accurate, real-time financial data that allows businesses to make informed decisions.
Integrated financial planning modules within ERP systems enable organizations to create detailed budgets, track actual performance against budgeted amounts, and adjust forecasts accordingly.
By pulling data from across the company, ERP systems enhance long-term financial planning and enable scenario analysis, which is critical for responding to market changes or business growth.
Payroll Management
ERP systems simplify payroll management by automating the calculation of employee wages, tax deductions, and benefits. Payroll processing, which can be time-consuming and prone to human error when done manually, becomes much more efficient with ERP.
The system integrates with attendance tracking and HR systems, ensuring that all employee compensation data is accurate and up-to-date. This not only reduces the administrative burden but also ensures compliance with tax laws and labor regulations.
Expense Management
Managing employee expenses, from travel costs to reimbursement requests, can be challenging without proper tools. ERP systems provide automated expense management solutions that allow employees to submit expenses online, while finance teams can approve, track, and process these expenses within the system. By consolidating expense data, ERP systems offer better control over business spending and ensure that all expenses are accurately recorded in financial reports.
Cash Flow Management
Cash flow is the lifeblood of any organization, and ERP systems help streamline its management by offering real-time visibility into cash inflows and outflows. By tracking invoices, payments, and other financial transactions, ERP systems provide an accurate picture of the company's liquidity. This helps businesses better manage their cash reserves, identify trends, and make timely decisions to avoid cash shortages or optimize surplus cash.
Tax Management
ERP systems simplify tax management by automating tax calculation processes, including sales tax, VAT, and corporate tax. With an ERP system, tax rates can be updated in real-time across the system, ensuring that all transactions comply with current tax regulations.
The system can also generate tax reports, reducing the time spent on preparing tax filings and lowering the risk of errors. Additionally, ERP systems maintain a comprehensive record of tax-related transactions, making audits and tax compliance easier to manage.
Benefits of ERP in Financial Management
In today's fast-paced business environment, managing financial operations manually can be overwhelming and inefficient. From tracking expenses to generating reports, businesses often face challenges in maintaining accuracy, transparency, and compliance.
This is where Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems come into play, offering a comprehensive solution that transforms how financial processes are handled.
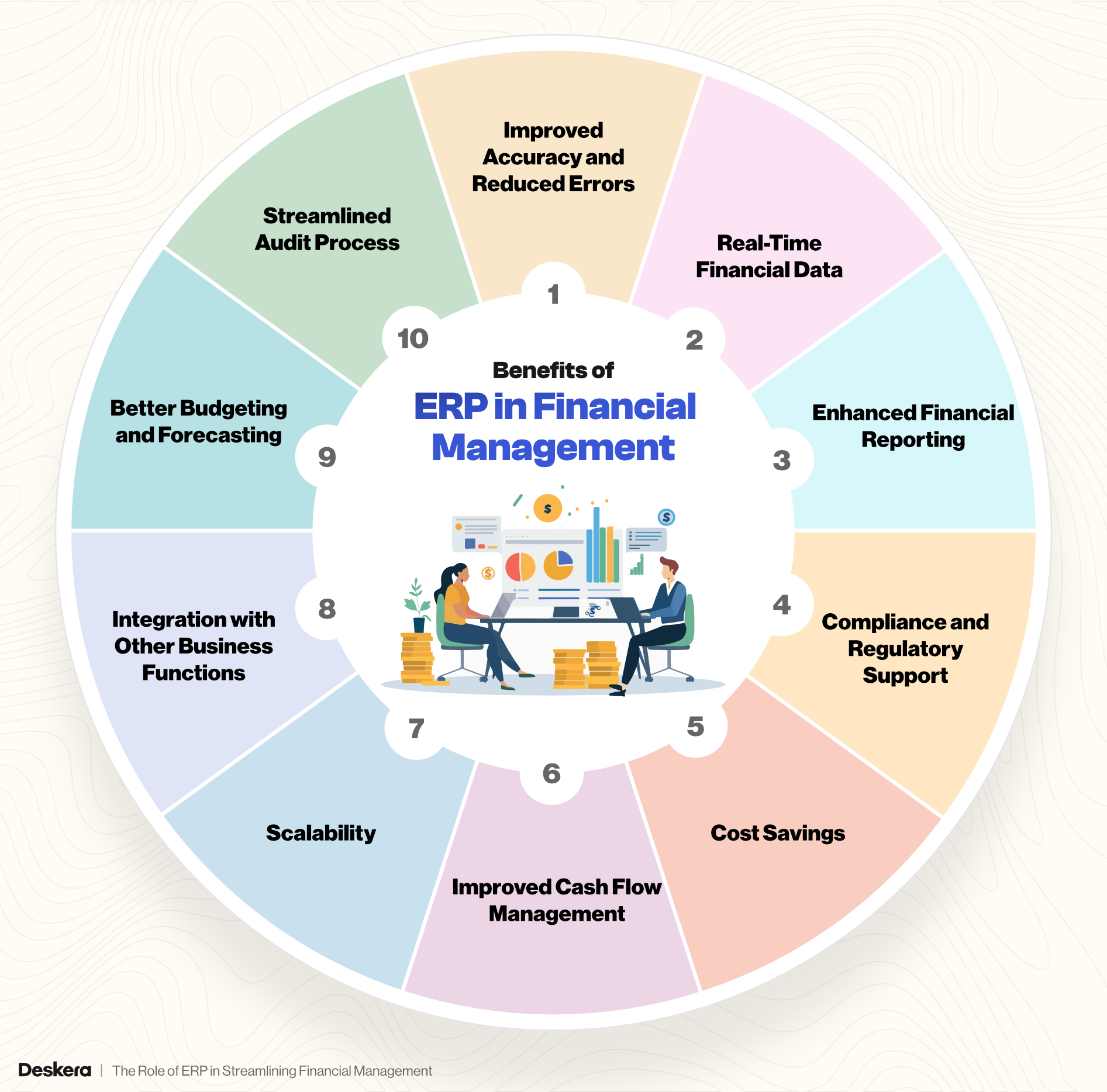
Improved Accuracy and Reduced Errors
ERP systems automate repetitive financial tasks like data entry, invoicing, and reconciliation, minimizing the risk of human error. This ensures greater accuracy in financial records, which is essential for informed decision-making and regulatory compliance.
Real-Time Financial Data
With ERP, businesses have access to real-time financial data, enabling faster decision-making. Stakeholders can monitor cash flow, expenses, and financial performance instantly, which helps in making timely adjustments to budgets or strategies.
Enhanced Financial Reporting
ERP systems come with built-in reporting tools that generate detailed financial reports such as balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements. These reports can be produced quickly and tailored to meet various stakeholder needs, ensuring transparency and improved financial analysis.
Compliance and Regulatory Support
ERP systems help businesses stay compliant with various financial regulations, such as GAAP or IFRS, by automatically generating audit trails, maintaining accurate records, and offering tools for tax compliance. This reduces the risk of regulatory fines or penalties.
Cost Savings
By automating financial processes, ERP systems reduce the need for manual labor and eliminate redundant systems, leading to significant cost savings. ERP also streamlines workflows, allowing businesses to run more efficiently with fewer resources.
Improved Cash Flow Management
ERP systems provide real-time insights into accounts payable and receivable, enabling better control over cash flow. With accurate tracking of incoming and outgoing payments, businesses can optimize their cash reserves and avoid liquidity issues.
Scalability
As businesses grow, their financial management needs become more complex. ERP systems are scalable and can be customized to accommodate expanding operations, new financial regulations, and additional business functions without the need for multiple new software solutions.
Integration with Other Business Functions
ERP systems integrate financial management with other business processes like procurement, inventory, and sales, creating a cohesive environment where data flows seamlessly between departments. This improves overall efficiency and ensures that financial information is always in sync with operational activities.
Better Budgeting and Forecasting
ERP systems enhance budgeting and forecasting capabilities by providing accurate, real-time data. Businesses can create more realistic budgets, compare them with actual financial performance, and adjust forecasts as necessary. This leads to better financial planning and resource allocation.
Streamlined Audit Process
With ERP, audit trails are automatically created for all financial transactions, making it easier for finance teams to conduct internal or external audits. The system ensures that all documentation is stored securely and can be retrieved quickly, reducing the time and effort needed for audits.
These benefits highlight how ERP systems optimize financial management by automating processes, improving data visibility, and supporting compliance, ultimately driving better business outcomes.
How ERP Enhances Financial Planning and Budgeting
Effective financial planning and budgeting are crucial for a company's success, but these processes can be complex and time-consuming without the right tools. ERP systems play a vital role in simplifying and enhancing financial planning by integrating data from all departments into one centralized platform. With ERP, businesses gain real-time access to accurate financial data, allowing for more informed decision-making and precise budgeting.
In addition to automating the budgeting process, ERP systems offer advanced features like scenario analysis and forecasting, enabling companies to anticipate and respond to market changes. By aligning financial goals with operational data, ERP systems provide a comprehensive view of business performance, resulting in more accurate budgets and improved resource allocation.
How ERP Enhances Financial Planning and Budgeting:
- Centralized Financial Data: ERP consolidates data from all departments, giving finance teams access to real-time, accurate information for better budgeting and forecasting.
- Automated Budgeting Process: ERP automates routine budgeting tasks, reducing manual effort and minimizing the risk of errors.
- Scenario Analysis and Forecasting: ERP offers tools for what-if analysis, helping businesses prepare for different financial scenarios and market fluctuations.
- Continuous Budget Monitoring: ERP enables real-time tracking of actual performance against budgeted figures, allowing for timely adjustments to forecasts.
- Linking Financial and Operational Data: ERP integrates various business functions, ensuring that financial plans reflect overall company performance for more accurate and comprehensive budgeting.
- Improved Resource Allocation: With better visibility into financial and operational data, ERP helps optimize resource allocation and align budgets with business objectives.
With these features, ERP systems allow businesses to take a more strategic and proactive approach to financial planning and budgeting.
Challenges Addressed by ERP in Financial Management
Managing finances efficiently can be a complex task for any business, especially when faced with challenges such as manual data entry, fragmented processes, and inconsistent reporting.
These issues not only slow down operations but also increase the risk of errors, missed opportunities, and non-compliance with financial regulations. For organizations seeking to overcome these obstacles, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems offer a comprehensive solution.
- Manual Data Entry and Errors: One of the biggest challenges in financial management is the reliance on manual data entry, which increases the risk of errors and inconsistencies. ERP systems address this by automating data collection and processing, ensuring that financial records are accurate and up-to-date, reducing the chances of costly mistakes.
- Lack of Real-Time Financial Data: Without access to real-time data, financial decision-making can be delayed or based on outdated information. ERP systems provide real-time visibility into financial transactions and performance, enabling companies to make timely and informed decisions.
- Fragmented Financial Processes: In many businesses, financial processes are managed using multiple disconnected systems, leading to inefficiencies and data silos. ERP integrates all financial processes—such as accounting, budgeting, and reporting—into a single platform, streamlining workflows and improving efficiency.
- Difficulty in Compliance and Audits: Meeting regulatory requirements and preparing for audits can be challenging when financial data is dispersed across multiple systems. ERP systems offer built-in compliance tools, generate audit trails, and simplify documentation, making it easier for businesses to meet financial regulations and pass audits.
- Inconsistent Financial Reporting: Producing consistent and accurate financial reports can be difficult when data is spread across different systems or departments. ERP systems centralize financial data, ensuring that reports are accurate, consistent, and generated quickly, improving financial transparency and decision-making.
- Limited Cash Flow Visibility: Poor visibility into cash inflows and outflows can lead to liquidity issues. ERP systems provide detailed insights into cash flow by tracking payments, invoices, and expenses in real-time, helping businesses manage their liquidity more effectively.
- Complexity in Budgeting and Forecasting: Budgeting and forecasting can become cumbersome without proper data integration and tools. ERP systems simplify these processes by providing accurate, real-time financial data and forecasting tools that enable businesses to create detailed budgets and make more accurate financial projections.
- Time-Consuming Financial Reconciliation: Reconciling financial data from different systems can be labor-intensive and prone to errors. ERP automates reconciliation tasks, ensuring that financial data from various sources is matched accurately, saving time and effort for the finance team.
By addressing these challenges, ERP systems transform financial management into a more streamlined, accurate, and efficient process, allowing businesses to focus on growth and profitability.
Future Trends: Innovations in ERP-Driven Financial Management
As technology continues to evolve, so does the landscape of financial management. ERP systems are at the forefront of this transformation, leveraging innovations to enhance financial operations and decision-making processes.
The future of ERP-driven financial management is shaped by several key trends that promise to revolutionize how businesses manage their finances.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: The integration of AI and machine learning into ERP systems is set to transform financial management by enabling predictive analytics, automating routine tasks, and enhancing decision-making. These technologies can analyze historical data, identify trends, and provide insights that help finance teams make more informed strategic decisions.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): RPA is becoming increasingly popular in financial management, allowing businesses to automate repetitive tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, and reconciliation. By reducing manual effort, RPA not only increases efficiency but also minimizes errors, allowing finance teams to focus on more complex tasks.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: The shift to cloud-based ERP systems continues to grow, offering businesses greater flexibility and scalability. Cloud solutions enable real-time access to financial data from anywhere, facilitate collaboration among teams, and reduce the need for on-premise infrastructure, making financial management more agile and cost-effective.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain has the potential to enhance transparency and security in financial transactions. By providing a decentralized ledger that records all transactions, blockchain can help reduce fraud, improve traceability, and streamline auditing processes, thus fostering greater trust in financial data.
- Enhanced Data Visualization and Reporting Tools: Future ERP systems will likely feature advanced data visualization tools that allow finance teams to create dynamic reports and dashboards. These tools will enable stakeholders to gain deeper insights into financial performance, track key metrics, and identify areas for improvement in real time.
- Integration with Other Emerging Technologies: As businesses adopt technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) and big data analytics, ERP systems will increasingly integrate with these innovations. This will allow for more comprehensive financial management by combining financial data with operational and market data, enabling businesses to make more informed decisions.
- Focus on Sustainability and Social Responsibility: Financial management is evolving to include sustainability metrics and reporting. Future ERP systems will integrate sustainability considerations into financial planning and analysis, helping businesses track their environmental impact and align financial goals with corporate social responsibility initiatives.
- Personalized User Experiences: User experience is becoming a priority in ERP development. Future systems will focus on creating personalized interfaces that cater to individual user preferences and roles, making it easier for finance teams to navigate complex financial data and processes.
By embracing these innovations, businesses can enhance their financial management capabilities, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge in an increasingly dynamic market. The future of ERP-driven financial management is bright, with the potential to transform how organizations approach finance, strategy, and growth.
How Deskera ERP Can Help Streamline Financial Management
Deskera ERP is a powerful tool designed to streamline financial management for businesses of all sizes. By automating core financial processes and integrating them into a single platform, Deskera ERP ensures that businesses can manage their finances with greater accuracy, efficiency, and real-time visibility.
Automated Accounting and Bookkeeping
Deskera ERP simplifies the complexities of accounting by automating tasks such as invoicing, accounts payable/receivable, and general ledger management. This reduces manual effort and minimizes the risk of errors, allowing finance teams to focus on more strategic activities.
Real-Time Financial Reporting
With Deskera ERP, businesses can generate financial reports like balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow reports instantly. This real-time access to financial data enables better decision-making, as stakeholders have up-to-date information at their fingertips.
Efficient Cash Flow Management
Managing cash flow is critical for any business, and Deskera ERP offers tools that provide visibility into inflows and outflows. By tracking payments, expenses, and other transactions, businesses can monitor their liquidity, optimize cash reserves, and avoid financial bottlenecks.
Seamless Budgeting and Forecasting
Deskera ERP enhances budgeting and forecasting processes by integrating all financial data in one place. Finance teams can create more accurate budgets, run what-if analyses, and adjust forecasts based on real-time data, helping businesses stay agile and responsive to market changes.
Compliance and Audit Readiness
Staying compliant with financial regulations is easier with Deskera ERP. The platform provides audit trails for all financial transactions and automates tax calculations, helping businesses meet regulatory requirements and simplifying the audit process.
Integration with Other Business Functions
Deskera ERP connects financial management with other business operations such as inventory, sales, and procurement. This integration ensures that financial data is always accurate and aligned with operational activities, improving overall efficiency and financial transparency.
Key Takeaways
- The Interplay of Financial Management with Organizational Success: Effective financial management through ERP aligns financial goals with overall business objectives, optimizes resource allocation, and fosters risk mitigation, ultimately driving growth and organizational stability.
- Key Financial Processes Streamlined by ERP: ERP systems automate and integrate essential financial processes such as accounting, cash flow management, budgeting, compliance, and reporting, resulting in improved accuracy and efficiency across the organization.
- Benefits of ERP in Financial Management: By streamlining financial operations, ERP systems reduce costs, enhance data accuracy, improve decision-making, increase efficiency, and provide scalable solutions that facilitate better financial planning.
- ERP's Role in Financial Planning and Budgeting: ERP systems centralize financial data, enabling streamlined budgeting processes and informed resource allocation that align with organizational goals.
- Challenges Addressed by ERP in Financial Management: ERP systems enhance risk mitigation and transparency by providing real-time monitoring and detailed transaction records, enabling proactive financial oversight.
- Deskera ERP Streamlines Financial Management: Deskera ERP helps businesses optimize their financial management processes, reduce costs, and gain deeper insights into their financial performance. This allows companies to focus on growth while maintaining financial stability and control.
Related Articles













