Are you getting the most out of your investments, or could your returns be higher? Measuring Return on Investment (ROI) is essential for any business or individual looking to assess the value of their investments. This critical metric helps you gauge the profitability of various investments, offering insights into what's working and what could be improved.
At its core, ROI is a straightforward formula: it compares the gain or loss from an investment relative to its cost. Yet, its impact extends far beyond mere calculations. Understanding and optimizing ROI can drive smarter financial decisions, inform strategy, and increase accountability across projects and departments. For business leaders, a strong ROI means resources are being effectively allocated, leading to sustainable growth and higher profitability.
For businesses of any size, monitoring ROI is not just about finances—it’s a way to ensure every resource, whether time, money, or effort, is used efficiently. In today’s competitive landscape, optimizing ROI is essential to maintain a competitive edge. With precise ROI insights, companies can make well-informed decisions, shifting focus to high-impact areas and avoiding wasted resources on underperforming projects.
Deskera ERP can play a crucial role in tracking and enhancing ROI. As an all-in-one platform, Deskera ERP offers tools for financial management, inventory control, production planning, and sales analytics, empowering companies to gain comprehensive visibility into their operations. By streamlining processes and offering detailed reports, Deskera ERP helps businesses make data-driven decisions that maximize ROI.
What is Return on Investment (ROI)?
Return on Investment (ROI) is a widely used financial metric that helps investors and businesses measure the profitability or efficiency of an investment.
ROI represents the ratio of the net profit earned from an investment to its initial cost, allowing for quick comparison across different investments.
The simplicity of ROI makes it a go-to metric for both small and large businesses, as well as for individual investors.
ROI Formula
The formula for calculating ROI is straightforward:
ROI = (Net Profit / Cost of Investment) x 100
Where:
- Net Profit = Total returns from the investment - Cost of the investment
- Cost of Investment = The initial amount spent on the investment
This calculation provides the ROI as a percentage, making it easy to compare with other investment opportunities or industry benchmarks.
Example of Calculating ROI
Let’s say a company invests $20,000 in a marketing campaign, and as a result, it generates an additional $30,000 in revenue. The ROI would be calculated as follows:
ROI = (30,000 - 20,000 / 20,000) x 100 = 50%
In this example, the ROI is 50%, indicating that the campaign generated a 50% return on the initial investment.
Different Approaches to ROI Calculation
While the basic ROI formula offers a quick snapshot of an investment’s return, various approaches to ROI calculation can provide more nuanced insights depending on the context.
Different methods can factor in aspects like time, investment type, or specific departmental objectives, helping businesses and investors gain a more comprehensive understanding of their returns.
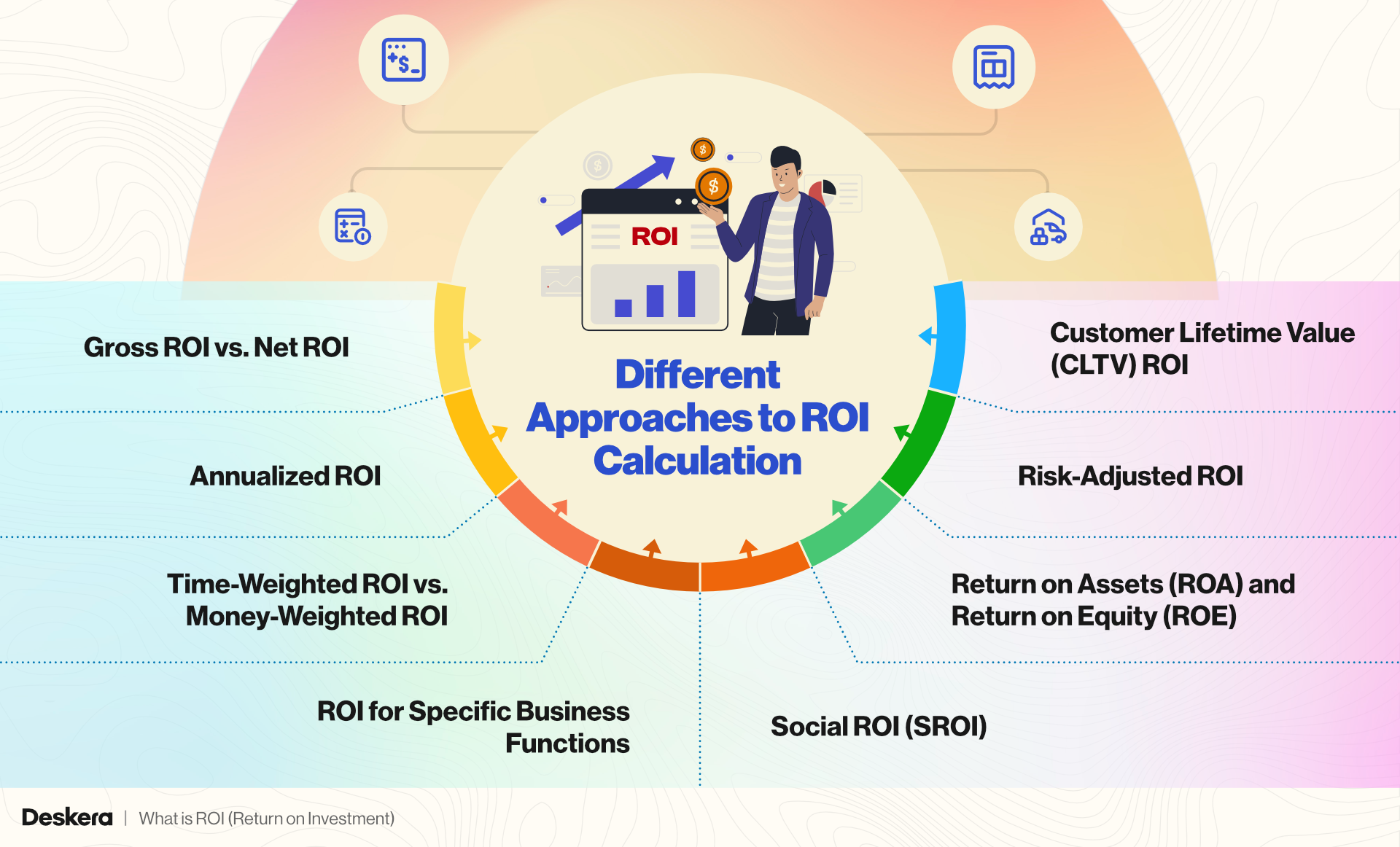
1. Gross ROI vs. Net ROI
- Gross ROI: Measures the overall return without accounting for additional costs or taxes. Gross ROI can be useful for a quick overview but may not accurately reflect profitability.
- Net ROI: Considers all costs, including taxes, fees, and additional expenses related to the investment. Net ROI provides a more precise measure of actual profitability, especially important for investments with significant operational costs.
2. Annualized ROI
- Annualized ROI: Factors in the time period of the investment, showing the return on an annual basis. This approach is especially useful for comparing investments held over different time frames.
- Formula:
Annualized ROI = [(1 + ROI) 1/ Number of Years -1 ] x 100
- Example: If an investment has a 50% ROI over five years, the annualized ROI would reflect the average yearly return, making it easier to compare with shorter-term investments.
3. Time-Weighted ROI vs. Money-Weighted ROI
- Time-Weighted ROI: Calculates ROI by ignoring cash flows or additional contributions throughout the investment period. It’s ideal for comparing the performance of different investment managers or strategies, as it isolates the rate of return from external cash flows.
- Money-Weighted ROI: Takes into account the size and timing of cash flows, giving more weight to periods with larger investments. This approach is commonly used for personal investments where contributions or withdrawals vary over time.
4. ROI for Specific Business Functions
- Marketing ROI: Focuses on returns from marketing initiatives, calculating the effectiveness of campaigns, ads, and promotions.
- Formula:
Marketing ROI = (Incremental Revenue - Marketing Spend / Marketing Spend) x 100
- Sales ROI: Measures the return generated by sales activities, evaluating the productivity and efficiency of sales teams.
- Human Resources ROI: Assesses the impact of training programs, employee engagement initiatives, or hiring processes. For instance, HR ROI can be measured by improvements in productivity, retention, or cost savings from reduced turnover.
- Technology ROI: Evaluates returns from technology investments such as ERP software or automation tools. Technology ROI often factors in cost savings, productivity boosts, and enhanced scalability.
5. Social ROI (SROI)
- Social ROI expands the ROI concept by measuring not only financial returns but also social and environmental benefits. This approach is often used by companies focused on corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives or non-profits. SROI aims to quantify the broader value of an investment, including intangible benefits to society or the environment.
6. Return on Assets (ROA) and Return on Equity (ROE)
- Return on Assets (ROA): Measures how efficiently a company uses its assets to generate profit, useful for assessing operational efficiency.
Formula:
ROA = (Net Income/Total Assets) x 100
- Return on Equity (ROE): Examines how effectively a company generates profit from shareholders’ equity, a common measure of financial health for investors.
Formula:
ROE = (Net Income / Shareholders’ Equity) x 100
7. Risk-Adjusted ROI
- Risk-Adjusted ROI: Adjusts the ROI based on the risk involved in the investment, often used in finance to compare returns on investments with different risk profiles. This approach is crucial for investors seeking to maximize returns without exposing themselves to undue risk.
8. Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV) ROI
- Customer Lifetime Value ROI focuses on the long-term profitability of acquiring a customer by analyzing the cost to acquire and retain customers versus their projected lifetime value. This is particularly useful in subscription-based or service-oriented businesses.
- Formula:
CLTV ROI = ( Customer Lifetime Value - Customer Acquisition Cost / Customer Acquisition Cost ) x 100
Example: If the lifetime value of a customer is $500, and the cost to acquire them is $100, the CLTV ROI would be 400%.
Each approach to ROI calculation offers a tailored perspective, helping businesses and investors choose the best method to meet their specific goals. By applying the right ROI calculation, companies and investors can make smarter decisions, accurately assess profitability, and better understand the impact of their investments over time.
Importance of ROI in Business
Return on Investment (ROI) is a critical metric that helps businesses assess the profitability of various activities, investments, and projects. By calculating ROI, companies can determine the effectiveness of their expenditures and make informed decisions about where to allocate resources.
This essential metric influences strategies across multiple business functions, from marketing to operations, ultimately supporting sustainable growth and financial health.
1. Informed Decision-Making
- ROI serves as a key decision-making tool, allowing businesses to evaluate the potential returns of proposed projects or investments. By comparing ROI across options, companies can prioritize high-return initiatives and minimize spending on low-performing areas. Whether it’s expanding into a new market or investing in new technology, ROI analysis guides leaders toward financially sound choices.
2. Resource Optimization
- In today’s competitive business environment, maximizing resource efficiency is essential. ROI helps businesses identify areas where resources are best utilized, ensuring investments generate maximum benefit.
- For example, a company might calculate the ROI of different marketing channels to identify which one yields the highest return and concentrate efforts there. This approach helps businesses avoid waste and increase productivity.
3. Setting Measurable Goals
- ROI provides a clear, quantifiable benchmark for success, enabling companies to set and track performance goals. By measuring ROI at regular intervals, businesses can monitor progress, assess project effectiveness, and make adjustments as needed. This metric also helps teams align their activities with the company’s broader financial objectives, fostering a results-driven culture.
4. Risk Management
- Understanding ROI allows companies to evaluate the risk associated with different investments. By assessing expected returns alongside potential risks, decision-makers can make balanced choices that align with their risk tolerance. This is especially valuable for high-stakes investments, such as new product development or mergers and acquisitions, where a well-calculated ROI can help mitigate financial loss.
5. Enhancing Stakeholder Confidence
- Investors, shareholders, and stakeholders rely on ROI to gauge the financial health and potential of a business. High ROI demonstrates that a company uses its resources wisely and generates strong returns, which can increase investor confidence and attract new funding. Regularly reporting ROI for key projects or initiatives can help businesses build credibility and reinforce stakeholder trust.
6. Evaluating Long-Term Viability
- ROI doesn’t just measure short-term gains; it can also be used to assess the long-term impact of strategic investments. For example, when investing in employee training or sustainable practices, companies may experience gradual returns that build value over time. ROI enables leaders to weigh these long-term benefits against immediate costs, supporting decisions that drive future growth.
ROI’s importance in business cannot be overstated, as it empowers companies to pursue strategies that enhance profitability, optimize resources, and maintain a competitive edge.
By regularly calculating and analyzing ROI, businesses not only improve financial outcomes but also cultivate a data-driven approach that fosters continuous improvement across operations.
Benefits of ROI
ROI is an essential metric for businesses, as it provides clear insights into the financial performance of investments. The benefits of using ROI as a key performance indicator (KPI) include:
Helps in Decision-Making
ROI allows businesses to evaluate the effectiveness of their investments, helping decision-makers decide where to allocate resources for the best returns. Whether for marketing campaigns, technology purchases, or employee training programs, understanding ROI ensures that investments are well-directed.
Identifies Profitable Areas
By calculating ROI across different areas (e.g., marketing, operations, or technology), businesses can identify which projects or departments yield the highest returns. This helps prioritize initiatives with the greatest potential for growth and profitability, maximizing overall business performance.
Tracks Financial Performance Over Time
ROI enables companies to track their financial performance over time. By comparing the ROI of different investments or business initiatives, companies can assess whether they are improving or need to reevaluate their strategies. It serves as a vital tool for long-term financial planning and sustainability.
Measures Efficiency
ROI measures the efficiency of an investment by comparing the returns to the costs incurred. This helps businesses ensure that they are maximizing their resources and achieving the best possible outcomes with minimal waste. A high ROI signifies operational efficiency and well-utilized capital.
Encourages Accountability
ROI provides a clear and measurable way to evaluate the success of specific projects or initiatives. It encourages accountability among teams, departments, and stakeholders, as everyone involved is aware of the financial objectives and expected returns. This fosters a results-driven culture within the organization.
Facilitates Benchmarking
Businesses can use ROI to compare their performance against industry standards or competitors. Benchmarking ROI against peers helps companies understand where they stand in the market and whether their investment strategies are competitive. This can inform future strategies and investments.
Justifies Investments to Stakeholders
ROI provides a compelling financial justification for investments, making it easier to gain approval from stakeholders, such as executives, board members, or investors. It allows businesses to demonstrate the potential returns of an initiative, making it more likely to receive funding and support.
Improves Strategic Planning
ROI is a powerful tool for strategic planning, as it provides data-driven insights into what works and what doesn’t. By analyzing the ROI of past projects, businesses can refine their strategies, improve resource allocation, and develop a more focused approach to achieving growth and profitability.
Supports Risk Management
By calculating ROI, businesses can better assess the risks associated with a particular investment. ROI helps businesses determine whether the potential returns outweigh the risks and costs involved, allowing them to make more informed and less risky investment choices.
Encourages Long-Term Investment Thinking
A focus on ROI helps businesses evaluate the long-term value of investments rather than just short-term gains. This encourages strategic decision-making that considers the future sustainability of investments, which is essential for long-term growth and profitability.
Overall, ROI is a versatile and powerful tool that provides businesses with clarity, helps drive performance, and fosters a culture of continuous improvement and accountability. By using ROI effectively, businesses can maximize returns, minimize risk, and make more informed decisions that align with their strategic objectives.
Types of ROI Calculations
ROI is a versatile metric that can be tailored to assess various investments across different business functions. Each type of ROI calculation focuses on specific metrics relevant to a given area, providing insights that help decision-makers evaluate effectiveness, justify budgets, and optimize strategies.
Below are some key types of ROI calculations in common business domains.
1. ROI on Marketing
- Marketing ROI measures the returns generated from marketing initiatives. Calculating ROI in marketing is essential for understanding which campaigns, channels, or strategies drive revenue and which may need improvement.
Subtopics:
- Digital Marketing ROI: Evaluates the performance of digital marketing efforts, such as online ads, email campaigns, and content marketing. It helps businesses measure the effectiveness of these digital initiatives in generating leads, conversions, and revenue.
- SEO ROI: Assesses the return on investments made in search engine optimization. This metric considers organic traffic growth, keyword rankings, and conversion rates, helping businesses understand the long-term value of SEO efforts.
- Social Media Campaign ROI: Measures the impact of social media campaigns on brand awareness, engagement, and sales. This calculation often includes metrics like engagement rates, reach, conversions, and revenue generated from social media channels.
2. ROI on Human Resources (HR)
- HR ROI focuses on the return from investments in people and talent-related initiatives. Calculating HR ROI helps organizations understand the impact of recruitment, training, retention, and engagement efforts on overall productivity and profitability.
Subtopics:
- ROI in Employee Engagement: Evaluates the effectiveness of engagement programs, such as team-building activities, flexible working policies, or recognition programs, in boosting employee satisfaction and productivity. Engaged employees tend to stay longer and perform better, which adds long-term value to the organization.
- ROI of Employee Benefits: Measures the return on investments in employee benefits, such as health insurance, wellness programs, or retirement plans. This ROI calculation can help assess if these perks contribute to attracting and retaining top talent, reducing turnover, and enhancing job satisfaction.
3. ROI on Technology Investments
- Technology ROI calculations help businesses determine the financial impact of investments in software, hardware, or digital tools. Given the high costs associated with tech investments, understanding their ROI is critical for justifying expenses and aligning them with strategic goals.
Subtopics:
- ROI of ERP Systems: Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems streamline operations by integrating various business functions. Calculating ERP ROI involves analyzing cost savings from improved efficiency, reduced errors, and enhanced productivity, helping justify the substantial investment.
- ROI of CRM Systems: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software helps in managing customer data and interactions. CRM ROI can be measured by examining improvements in customer retention, sales, and service efficiency.
- ROI of Automation Tools: Automation tools reduce manual tasks and enhance productivity across departments. By calculating the ROI of automation tools, businesses can assess gains in efficiency and cost savings, along with reductions in labor-intensive processes.
4. ROI on Product Development
- Product development ROI assesses the return on investments made in creating or improving products. Calculating ROI in this area helps determine if the resources devoted to research, development, and marketing of new products lead to profitable outcomes.
- Example: If a company invests in developing a new product and launches it successfully, the product’s ROI calculation would factor in the development costs, marketing expenses, and revenue generated. This helps determine whether the product line contributes positively to the company’s growth and profitability.
5. ROI on Real Estate and Infrastructure
- Real estate and infrastructure ROI calculations are used to evaluate returns on physical assets, such as property purchases, building upgrades, or facility expansions. This type of ROI is critical for businesses with significant investments in fixed assets, such as retail, manufacturing, or hospitality industries.
- Example: In a real estate context, ROI might be calculated by analyzing rental income, property appreciation, or savings from owning versus leasing. For infrastructure, ROI might include cost savings from energy efficiency upgrades or the value gained from building expansions that increase production capacity.
These varied ROI calculations enable businesses to make informed investment choices across all key areas, from marketing and HR to technology and real estate. By understanding which initiatives deliver high returns, companies can strategically allocate resources, streamline operations, and drive sustained growth.
Challenges in Measuring ROI
While ROI is an invaluable metric for assessing the success of investments, measuring it accurately can be complex due to various factors that can influence calculations and interpretations.
From identifying relevant metrics to accounting for external factors, here are some of the main challenges in measuring ROI:
1. Defining Clear Metrics and Goals
- One of the initial challenges in measuring ROI is defining what success looks like for a specific investment. ROI metrics vary greatly across different departments and initiatives, such as marketing, technology, or HR, each requiring its unique criteria.
- For example, marketing teams may focus on conversion rates, while HR might prioritize employee retention. Without clear, consistent metrics and goals, it becomes challenging to compare ROI across projects or gauge overall effectiveness.
2. Quantifying Intangible Benefits
- Many investments offer intangible or indirect benefits that are difficult to quantify, such as improved employee morale, brand reputation, or customer satisfaction. These qualitative outcomes don’t have immediate financial metrics attached to them, yet they contribute to long-term growth.
- In HR initiatives, for instance, engagement programs can boost productivity and morale, which contribute to better performance but may not show immediate returns. Quantifying these intangible aspects requires sophisticated metrics or long-term tracking that many companies struggle to implement effectively.
3. Time Lag in Realizing Returns
- Some investments take time to yield returns, making it difficult to measure ROI accurately in the short term. Investments in new technologies, product development, or infrastructure upgrades may take years to produce a measurable return.
- For instance, a major ERP implementation may involve a high upfront cost and extended onboarding period, while its benefits in terms of efficiency and cost savings accrue gradually. This time lag can create challenges in justifying the ROI of long-term projects to stakeholders.
4. Attribution Complexity in Multi-Channel Investments
- Modern businesses often invest across multiple channels and platforms simultaneously, such as digital marketing, CRM systems, and customer support. Isolating the impact of each channel or investment in driving ROI can be challenging, especially when these channels overlap and interact.
- For example, if a company runs a multi-channel marketing campaign, attributing a sale to a specific channel, such as email marketing or social media, can be difficult. This complexity can lead to either overestimating or underestimating the ROI for individual channels.
5. External Market and Economic Factors
- External factors like market trends, economic conditions, and changes in consumer behavior can affect the ROI of a project or initiative. These factors are often unpredictable and beyond a company’s control, yet they significantly impact returns.
- For example, an economic downturn may lead to reduced consumer spending, affecting the ROI of a marketing campaign even if the campaign itself is well-executed. Such external influences add volatility to ROI calculations and complicate long-term projections.
6. Data Quality and Accuracy
- Accurate ROI measurement relies on high-quality data; however, data collection issues can distort calculations. Missing, outdated, or inaccurate data can lead to incorrect ROI estimations, impacting decision-making and strategy.
- For example, incomplete data on sales or costs associated with a project may skew the ROI calculation. Ensuring accurate and comprehensive data across departments, while also addressing privacy and compliance concerns, is a constant challenge for many organizations.
7. Changing Business Objectives
- Business goals and priorities often evolve over time, and an investment that aligns with initial objectives may no longer support the company’s direction later on. This shift makes it difficult to measure an investment’s ROI accurately if the parameters for success change.
- For instance, a company may initially prioritize customer acquisition, but over time, it might shift focus toward customer retention. Calculating ROI based on original objectives rather than current priorities can provide a skewed perspective on an investment’s value.
Despite these challenges, businesses can improve the accuracy of their ROI measurements by setting clear objectives, choosing relevant metrics, and adopting flexible, data-driven approaches. By addressing these obstacles, companies can leverage ROI more effectively to guide investments and strategic planning.
10 Strategies to Improve ROI
Improving Return on Investment (ROI) is crucial for maximizing the value of a company's resources and driving sustainable growth. Here are some effective strategies that organizations can use to enhance their ROI across various business functions:
1. Optimize Resource Allocation
- Efficiently allocating resources to high-impact areas helps maximize returns. This involves regularly assessing which projects, campaigns, or departments generate the highest ROI and reallocating funds accordingly.
- Using data-driven analysis to identify underperforming areas also enables a business to reduce waste and focus on activities that yield better returns.
2. Enhance Employee Training and Productivity
- Investing in employee training can boost productivity and improve the overall efficiency of the workforce. When employees are well-trained, they work more efficiently, make fewer errors, and contribute more effectively to the company's goals.
- Providing relevant skill-building programs and regularly updating training materials also helps in maintaining a motivated and skilled workforce, ultimately enhancing ROI.
3. Leverage Data Analytics
- Data analytics enables businesses to make informed decisions, predict trends, and uncover areas for improvement. By using analytics tools, companies can track performance metrics, measure the effectiveness of various investments, and identify opportunities to optimize processes.
- Advanced analytics can also aid in segmenting customers, tailoring marketing efforts, and accurately forecasting demand—all of which contribute to higher ROI.
4. Focus on Customer Retention
- Acquiring a new customer often costs significantly more than retaining an existing one. Improving customer retention rates through excellent customer service, loyalty programs, and personalized engagement can lead to consistent revenue streams and a higher lifetime value per customer.
- Focusing on customer retention reduces churn and increases profitability, directly impacting ROI.
5. Automate Repetitive Processes
- Automation streamlines workflows and reduces manual errors, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic tasks. Implementing automation in areas like data entry, inventory management, or customer service can significantly cut costs and improve efficiency.
- Investing in tools that automate routine tasks results in lower labor costs and faster processing times, thereby improving overall ROI.
6. Refine Marketing Strategies
- Regularly assessing marketing strategies and optimizing campaigns based on performance data can improve ROI. Targeted, data-driven marketing strategies—such as personalized content, search engine optimization (SEO), and retargeting—lead to more effective customer acquisition and engagement.
- Using tools to measure the performance of marketing efforts, adjusting campaigns, and reallocating budgets to high-performing channels are all effective ways to enhance marketing ROI.
7. Invest in Scalable Technology Solutions
- Investing in technology that scales with the business allows companies to increase output without proportionally increasing costs. Scalable solutions, such as cloud-based ERP or CRM systems, improve operational efficiency and provide data visibility across departments.
- Scalable technology grows with the business, reducing the need for frequent replacements and upgrades, which translates into higher long-term ROI.
8. Implement Continuous Improvement Programs
- Adopting a culture of continuous improvement—such as Lean or Six Sigma methodologies—helps identify waste, improve processes, and enhance product quality. By regularly refining processes and eliminating inefficiencies, companies can achieve better output with fewer resources.
- Continuous improvement not only enhances ROI but also creates a proactive culture that emphasizes quality and efficiency across all levels of the organization.
9. Use ROI as a Benchmark for Decision-Making
- Making ROI a key consideration in decision-making can help the organization prioritize high-value projects. By regularly evaluating the potential ROI of new initiatives, businesses can select projects that are most likely to contribute to growth.
- Instituting ROI benchmarks for decision-making encourages accountability and ensures that resources are invested in the most impactful areas.
10. Enhance Cross-Departmental Collaboration
- Encouraging departments to work together improves information flow and helps avoid duplicated efforts. Cross-functional teams can pool expertise and resources to develop more efficient processes and innovative solutions, improving outcomes across departments.
- Collaboration leads to a more unified strategy, reducing inefficiencies and driving a higher return on each initiative.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can create a more efficient, data-driven environment that maximizes the value of their investments, ultimately boosting ROI and supporting long-term business success.
Practical Tips for Measuring and Enhancing ROI
For businesses seeking to maximize their investments, measuring and enhancing ROI is essential. Here are practical, actionable tips that can help refine ROI measurements and boost overall returns.
1. Set Clear Objectives and Metrics
- Before starting any project, define specific objectives and metrics to guide the ROI measurement process. Establishing clear KPIs relevant to each department or project type helps in tracking performance and making comparisons easier.
- For example, marketing departments may focus on conversion rates, while product development may look at customer satisfaction or usage rates. These tailored metrics create a structured approach to measure ROI effectively.
2. Conduct Regular Financial Analysis
- Periodic financial analysis, such as monthly or quarterly reviews, helps identify trends, address any variances, and assess ongoing projects. Regular analysis ensures that resources are allocated efficiently and that ROI is monitored consistently.
- Businesses can compare the actual results against projections to identify any gaps, allowing them to make adjustments to optimize ROI further.
3. Utilize Technology and Data Analytics Tools
- Leverage data analytics tools and software to gather, track, and analyze performance data across all departments. Tools like ERP systems, CRM platforms, and data visualization software provide insights into real-time data, helping pinpoint opportunities for ROI improvement.
- For instance, CRM tools offer metrics on customer engagement and lifetime value, which are essential for evaluating ROI in sales and marketing efforts.
4. Prioritize High-Impact Projects
- Focusing on high-impact projects with the highest potential ROI allows for better resource allocation. Use ROI as a guiding principle in project selection, ensuring that resources are directed toward initiatives that align with strategic goals.
- Prioritizing high-return projects not only improves financial outcomes but also enhances efficiency, as team members can concentrate on activities that add the most value.
5. Measure Intangible Benefits
- Some investments offer indirect benefits that are challenging to quantify, such as improved brand reputation or employee morale. For a more accurate ROI calculation, incorporate methods to measure these intangible benefits, such as using customer satisfaction surveys or employee feedback.
- A long-term perspective on intangible benefits allows companies to see their contribution to ROI more clearly, adding depth to financial metrics.
6. Leverage Benchmarking
- Benchmarking involves comparing your ROI performance to industry standards or competitors to gauge effectiveness. This comparison highlights areas of potential improvement and helps establish realistic goals.
- By understanding where the organization stands relative to its peers, decision-makers can identify weaknesses in processes and take steps to optimize ROI.
7. Automate Reporting and Data Collection
- Automating data collection and reporting through software or specialized tools improves accuracy and saves time, allowing teams to focus on analysis and strategy rather than manual data handling.
- Automation ensures that data is up-to-date and easily accessible, making ROI calculations more reliable and reducing the risk of errors in analysis.
8. Account for External Influences
- Consider external factors such as economic trends, market conditions, and industry changes when calculating ROI, as these can impact the results significantly. Including these variables in projections provides a more realistic understanding of ROI and prevents overestimations.
- For instance, fluctuating consumer demand due to economic changes may temporarily lower ROI in sales and marketing. Being mindful of such factors allows companies to adjust expectations and make informed decisions.
9. Conduct Post-Investment Analysis
- Once a project is completed, conduct a thorough post-investment analysis to evaluate if the initial goals and ROI expectations were met. This assessment provides insights into the factors that contributed to success or underperformance.
- Post-investment analysis enables a continuous learning process, helping companies refine their strategies for future projects and investments.
10. Continuously Improve Based on Insights
- Use insights gained from ROI analysis to refine strategies and improve future performance. By identifying trends and recurring challenges, companies can adjust processes, reallocate resources, and optimize for higher ROI in future initiatives.
- Continuously improving based on past performance strengthens ROI over time, creating a culture of growth and efficiency.
Implementing these tips not only helps in accurately measuring ROI but also fosters a proactive approach to enhancing returns. Through structured goal-setting, data-driven decision-making, and ongoing improvement, companies can maximize the value of their investments and ensure sustainable growth.
What is Considered as a ‘Good' ROI?
A "good" ROI (Return on Investment) can vary depending on the industry, type of investment, and specific business goals. However, there are general guidelines for interpreting ROI:
Industry Benchmarks
Different industries have different standards for ROI. For example, in the technology sector, a 15-20% ROI might be considered good, while in real estate investments, a return of 10-12% might be favorable. Businesses should compare their ROI against industry averages to determine if their returns are on par with competitors.
Investment Type
Low-risk investments, like bonds or savings accounts, generally offer lower ROIs (often in the 3-6% range), whereas high-risk investments, such as startups or venture capital, might yield much higher returns (often 20% or more). A "good" ROI depends on how much risk is involved in the investment.
Business Goals
For a small business, an ROI of 15-20% on marketing spend might be considered excellent. For large corporations, especially those investing in capital-intensive projects, a 5-10% ROI might be acceptable, as it indicates stability and profitability over time.
Time Frame
ROI should also be assessed over time. Short-term projects may have a higher ROI, while long-term projects may have lower but more sustainable returns. For instance, if a project takes several years to show its full potential, even a 10% ROI can be highly valuable over time.
Opportunity Cost
A "good" ROI also depends on alternative investment options. If your business could achieve a 10% return with relatively low risk, then an investment yielding a 5% return might not be considered a good ROI because the opportunity cost of other available investments is too high.
In general, a higher ROI indicates better returns on investments, but it's essential to consider the context in which that ROI was achieved, including the risks taken, the capital invested, and the time frame for those returns to materialize.
A “good” ROI is one that aligns with your company’s financial goals, risk tolerance, and industry expectations.
How Deskera ERP Can Help Boost Your ROI
Deskera ERP is designed to streamline operations, reduce costs, and optimize resource allocation—all of which play a crucial role in enhancing ROI.
Here are key ways Deskera ERP can drive higher returns on your investments:
Automation of Routine Tasks
Deskera ERP automates repetitive tasks across various functions, including finance, inventory management, and customer relationship management. Automation not only reduces labor costs but also speeds up workflows, allowing employees to focus on strategic tasks that add value to the business.
Data-Driven Insights for Better Decision-Making
With powerful data analytics and real-time reporting features, Deskera ERP provides detailed insights into all aspects of business operations. From sales performance to inventory levels, these insights help managers make informed decisions, optimize processes, and allocate resources effectively, all of which contribute to a stronger ROI.
Inventory and Supply Chain Optimization
Deskera ERP offers inventory management tools that help reduce overstocking and stockouts, minimizing carrying costs and improving cash flow. Enhanced supply chain visibility ensures efficient order processing and delivery, resulting in cost savings and higher customer satisfaction.
Improved Financial Management
Deskera’s financial modules streamline accounting, budgeting, and financial reporting, enabling businesses to maintain tight control over finances. By tracking expenses and revenues accurately, companies can identify cost-saving opportunities and improve profitability.
Enhanced Employee Productivity
Deskera ERP centralizes data and streamlines workflows, making it easier for employees to access the information they need to complete tasks efficiently. With everything in one system, employees can collaborate more effectively, reducing bottlenecks and enhancing overall productivity, which positively impacts ROI.
Scalability and Flexibility for Growth
Deskera ERP is designed to grow with your business, providing scalable solutions that meet your evolving needs without requiring major reinvestments. This scalability helps companies maintain high ROI as they expand, offering long-term value and adaptability in a dynamic business environment.
By leveraging Deskera ERP’s robust features, businesses can cut costs, improve efficiency, and gain better control over resources—all contributing to a higher return on investment and a stronger competitive edge.
Key Takeaways
- ROI, or Return on Investment, is a key performance metric used to assess the profitability of an investment by comparing its returns to the initial cost. Understanding ROI helps businesses evaluate the financial success of various initiatives.
- Measuring ROI is essential for identifying which activities and projects generate the most value, enabling companies to make informed investment decisions that drive profitability and growth.
- ROI provides valuable insights that help businesses make informed decisions, prioritize investments, track financial performance, and ensure efficient resource allocation. By using ROI, companies can measure the success of various initiatives, improve accountability, and justify investments to stakeholders, all while maximizing returns and minimizing risk.
- The standard ROI formula is: ROI = (Net Profit / Cost of Investment) x 100, while basic, this formula provides a quick, quantifiable way to assess returns across different investments.
- ROI can be calculated in specific areas such as marketing, human resources, technology, product development, and real estate. Each calculation focuses on measuring the returns in these targeted investments, offering deeper insights into departmental efficiency and impact.
- Measuring ROI can be complex due to factors like time delays in returns, indirect benefits, and the difficulty of quantifying intangible assets. Recognizing these challenges is key to refining ROI measurements.
- Beyond the traditional formula, other methods like payback period, net present value (NPV), and internal rate of return (IRR) can provide additional perspectives on the potential profitability of long-term investments.
- Businesses can enhance ROI by optimizing resource allocation, using data analytics, automating processes, focusing on customer retention, and prioritizing high-impact projects. These strategies help maximize the returns from each investment.
- Practical steps for measuring and improving ROI include setting clear objectives, conducting regular financial analysis, leveraging technology, and incorporating benchmarking. These tips ensure accurate ROI assessment and help uncover opportunities for improvement.
- A "good" ROI is context-dependent, varying by industry, investment type, and business goals. Generally, higher ROI signifies better returns, but the ideal ROI should be compared to industry standards, alternative investment options, and the time frame of the investment. A "good" ROI aligns with your company's financial goals and risk tolerance while delivering substantial value.
- Deskera ERP supports ROI enhancement by streamlining operations, improving data visibility, optimizing inventory, and automating tasks. This ERP solution helps businesses cut costs, increase productivity, and achieve a higher ROI.
Related Articles












