The landscape of manufacturing is undergoing a profound transformation, catalyzed by the convergence of advanced technologies and changing consumer preferences. At the heart of this evolution lies the pivotal role of order management—an intricate process that can make or break a manufacturer's success.
The traditional approach to order management, once characterized by manual processes and fragmented channels, is giving way to a new paradigm: Automated Multi-Channel Order Management. This innovative approach not only streamlines operations but also enhances customer experiences, propelling manufacturing into a new era of efficiency and competitiveness.
Statistics underscore the urgency of this shift. According to a recent industry report, 75% of manufacturing companies acknowledge that order management directly impacts customer loyalty. However, only 23% have fully integrated automated systems. This discrepancy highlights the immense untapped potential for enhancing order management processes.
Moreover, the proliferation of online marketplaces and diverse sales channels has led to an exponential increase in order volumes. Research indicates that manufacturers adopting automated multi-channel order management experience a 25% reduction in order processing times and a 20% decrease in fulfillment errors.
As we delve into the multifaceted realm of revolutionizing manufacturing through automated multi-channel order management, we uncover the technologies, strategies, and success stories driving this transformation.
- Overview of the Manufacturing Industry's Evolution
- Understanding Automated Multi-Channel Order Management
- Technological Foundations
- Implementation Process
- Potential Challenges and Solutions
- Future Trends
- Conclusion
- How can Deskera Help You?
- Key Takeaways
- Related Articles
Overview of the Manufacturing Industry's Evolution
The manufacturing industry has undergone a remarkable evolution over the decades, shaped by technological advancements, changing market dynamics, and evolving consumer expectations. From the early days of manual craftsmanship to the modern era of automation and digitalization, this evolution has left an indelible mark on how products are conceptualized, produced, and distributed.
Historically rooted in labor-intensive processes, manufacturing witnessed a significant turning point during the Industrial Revolution. The introduction of mechanization and steam-powered machinery led to mass production, enabling manufacturers to produce goods on a larger scale. This era marked the beginning of standardized processes and increased efficiency, fundamentally altering the industrial landscape.
The subsequent wave of automation brought forth by the adoption of electricity and assembly lines further accelerated manufacturing capabilities. The mid-20th century saw the emergence of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), paving the way for precision engineering and enhanced product quality. This period also witnessed the rise of lean manufacturing principles, focusing on waste reduction and operational optimization.
In recent years, the advent of Industry 4.0 has ushered in a new era of manufacturing. Characterized by the integration of cyber-physical systems, the Internet of Things (IoT), and data analytics, Industry 4.0 has given rise to "smart factories." These factories leverage real-time data to optimize processes, predict maintenance needs, and respond dynamically to changing market demands.
Within this evolving landscape, the role of order management has gained prominence. As supply chains become more complex and global, efficient order management becomes a linchpin for success. The traditional approach of handling orders manually is increasingly inadequate in meeting the demands of a fast-paced, interconnected world.
Hence, the industry is embracing the concept of Automated Multi-Channel Order Management, leveraging technologies like AI, machine learning, and cloud computing to streamline operations, reduce errors, and enhance customer satisfaction.
In this dynamic environment, manufacturers are challenged not only to produce high-quality goods but also to do so with agility and responsiveness. The journey from the Industrial Revolution to Industry 4.0 reflects the industry's resilience and adaptability, with each phase marked by innovations that continue to reshape the way we conceptualize, produce, and distribute products.
As we delve deeper into the realm of revolutionizing manufacturing through automated multi-channel order management, we uncover how this crucial process is being redefined to meet the demands of a rapidly changing world.
A. Importance of order management in manufacturing
Order management stands as a cornerstone in the manufacturing process, playing a pivotal role in ensuring operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and overall business success. Its significance stems from its direct influence on various facets of the manufacturing ecosystem.
Operational Efficiency: Effective order management streamlines the entire production cycle, from raw materials procurement to final product delivery. By efficiently coordinating orders, manufacturers can optimize production schedules, allocate resources effectively, and minimize production downtime. This results in cost savings, increased productivity, and reduced waste.
Inventory Management: Accurate order management helps maintain optimal inventory levels. It prevents overstocking, which ties up capital and leads to storage costs, as well as understocking, which could lead to stockouts and lost sales opportunities. Real-time data integration enables better demand forecasting, allowing manufacturers to adjust their inventory levels based on market trends.
Customer Satisfaction: Timely and accurate order fulfillment is directly linked to customer satisfaction. A well-executed order management system ensures that customers receive their products on time and as expected. This positive experience enhances brand reputation, fosters customer loyalty, and encourages repeat business.
Data-Driven Decision Making: Modern order management systems generate valuable data insights. By analyzing this data, manufacturers can identify trends, customer preferences, and areas for improvement. This data-driven approach informs strategic decisions related to production planning, marketing strategies, and resource allocation.
Multi-Channel Integration: In today's interconnected world, manufacturers often engage with customers through various channels, such as online marketplaces, direct sales, and retail partners. Effective order management coordinates these channels seamlessly, providing a consistent experience regardless of how customers interact with the brand.
Reduced Errors: Manual order processing is prone to human errors, leading to issues like incorrect orders, delayed shipments, and dissatisfied customers. Automated order management systems minimize these errors by standardizing processes, reducing manual intervention, and enabling real-time tracking.
Scalability: As businesses grow, managing increasing order volumes becomes challenging. Automated order management systems offer scalability, adapting to changing demands without compromising accuracy or efficiency. This adaptability is crucial for manufacturers aiming to expand their market presence.
Supply Chain Visibility: Effective order management provides insight into the entire supply chain. Manufacturers can monitor the movement of raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods. This visibility allows for quick response to disruptions and proactive management of potential bottlenecks.
In the evolving manufacturing landscape, where competition is fierce and customer expectations are soaring, efficient order management is no longer a luxury but a necessity. Manufacturers that embrace automated multi-channel order management solutions position themselves to thrive in a fast-paced market environment.
This underscores the critical role that order management plays in optimizing processes, driving customer satisfaction, and ultimately propelling the manufacturing industry forward.
B. Transition to automated multi-channel order management
The transition to automated multi-channel order management represents a significant paradigm shift in the manufacturing industry, propelled by the need to adapt to changing consumer behaviors, technological advancements, and the imperative for operational excellence. This transition involves a carefully orchestrated process that encompasses technology adoption, process reengineering, and organizational alignment.
Technology Integration: The foundation of automated multi-channel order management lies in the integration of advanced technologies. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems serve as the backbone, providing a centralized platform to manage orders, inventory, production, and distribution. Integration with Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems enhances customer insights, enabling personalized interactions and tailored order experiences.
Multi-Channel Connectivity: Modern consumers engage with brands through a myriad of channels, from online marketplaces to social media platforms. An automated system connects these diverse channels seamlessly, allowing orders to flow through a unified system regardless of their origin. This integration ensures consistent order processing, accurate inventory updates, and real-time order status tracking.
Process Optimization: Transitioning to automated order management often necessitates reevaluating and optimizing existing processes. Manual, siloed processes are replaced with standardized workflows that minimize manual intervention and reduce the risk of errors. Automation streamlines order processing, approvals, and communications, leading to faster fulfillment and improved accuracy.
Data Visibility and Analytics: Automation generates a wealth of data that can be harnessed for insights. Advanced analytics provide a deep understanding of customer preferences, demand patterns, and operational efficiency. These insights inform decision-making, enabling manufacturers to fine-tune their strategies and adapt to changing market conditions.
Change Management: Transitioning to automated order management requires buy-in and collaboration from all levels of the organization. Employees must be trained to use the new systems effectively and understand the benefits of automation. Clear communication about the transition's objectives and outcomes is crucial to alleviate resistance and foster a culture of innovation.
Supplier and Partner Collaboration: Automated multi-channel order management extends beyond the organization to include suppliers, distributors, and partners. Integration with their systems allows for smoother communication, timely updates on inventory levels, and improved coordination in fulfilling orders.
Scalability and Flexibility: An automated system should be designed to accommodate growth. Cloud-based solutions provide the scalability required to handle increasing order volumes without compromising performance. Cloud technology also offers the flexibility to adapt to changing business needs and to integrate new channels as they emerge.
Continuous Improvement: The transition is not a one-time event but an ongoing journey. Regular assessments of the automated system's performance, feedback from stakeholders, and industry trends should guide continuous refinements to ensure optimal results.
Embracing this transformation empowers manufacturers to navigate the complexities of modern commerce, improve operational efficiency, and deliver exceptional customer experiences, positioning themselves at the forefront of the evolving manufacturing ecosystem.
Understanding Automated Multi-Channel Order Management
In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, the convergence of technology and customer expectations has given rise to a new imperative: understanding and implementing Automated Multi-Channel Order Management. As the manufacturing industry pivots towards greater automation, the intricate dance of order processing, inventory management, and customer interactions has taken center stage.
In this section, we delve into the core principles of this transformative approach, exploring its components, benefits, and the profound impact it holds for manufacturers in a fast-paced, interconnected world.
From real-time data analytics to the integration of advanced AI and IoT technologies, this section unveils the intricate mechanisms that underpin the seamless orchestration of orders across a myriad of channels.
A. Definition and components of automated multi-channel order management
Automated Multi-Channel Order Management is a dynamic framework that unifies and automates the entire order lifecycle across multiple sales channels, from order placement to delivery and beyond. This sophisticated system integrates technology, processes, and data to seamlessly handle orders originating from diverse sources such as e-commerce platforms, retail partners, direct sales, and more.
At its core, it encompasses a range of interconnected components that work in harmony to streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and optimize supply chain efficiency.
Centralized Order Processing: At the heart of this system is a centralized platform that consolidates orders from various channels into a single repository. This eliminates the need for manual data entry and reduces the risk of errors, ensuring consistent order information and a real-time view of the order pipeline.
Inventory Management Integration: Integration with inventory management systems provides real-time visibility into stock levels. This prevents overselling, allows for efficient allocation of available stock, and enables accurate promise dates to customers based on actual inventory.
Automated Workflows: Automated workflows replace manual processes, guiding orders through predefined steps. From order validation and payment processing to fulfillment and shipping, these workflows ensure standardized processes, reducing bottlenecks and delays.
Real-Time Updates: Automated multi-channel order management systems provide real-time updates on order status. Customers can track their orders from the moment they're placed to the time they're delivered, enhancing transparency and customer satisfaction.
Customer Data Integration: Integration with Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems enables a holistic view of customer interactions and preferences. This data informs personalized order experiences, fostering customer loyalty and repeat business.
AI and Machine Learning Enhancements: Artificial Intelligence and machine learning algorithms analyze order data to predict demand patterns, optimize inventory levels, and suggest cross-selling or upselling opportunities. These technologies enhance decision-making and help manufacturers stay proactive.
Communication Channels: Automated systems often include communication channels such as email notifications, SMS updates, and customer portals. These channels keep customers informed about order progress, delivery times, and any potential delays.
Data Analytics and Reporting: The wealth of data generated by automated systems can be harnessed for strategic insights. Advanced analytics provide valuable information on order trends, customer behaviors, and operational efficiency, enabling manufacturers to make data-driven decisions.
Automated Multi-Channel Order Management not only streamlines processes but also empowers manufacturers to adapt to changing market dynamics. It serves as a bridge between technology and customer-centricity, offering a comprehensive solution to the challenges posed by an increasingly complex and interconnected business landscape.
B. Benefits for manufacturing companies
The adoption of Automated Multi-Channel Order Management brings forth a multitude of benefits that directly impact manufacturing companies, transforming the way they operate, interact with customers, and compete in today's dynamic business environment.
- Streamlined Order Processing: Automated workflows eliminate manual processing bottlenecks, ensuring orders are accurately validated, processed, and fulfilled. This leads to faster order cycle times, reduced errors, and improved efficiency.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Automation enables consistent and timely order updates, improving communication with customers. Real-time tracking, accurate delivery estimates, and personalized interactions enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Improved Inventory Management: Real-time inventory visibility prevents stockouts and overstock situations. Manufacturers can optimize inventory levels based on actual demand, reducing holding costs and increasing turnover rates.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: With a clear view of order volumes and processing times, manufacturers can allocate resources more efficiently. This leads to optimized production schedules, reduced idle time, and increased resource utilization.
- Data-Driven Insights: Automated systems generate comprehensive data that can be analyzed to uncover trends and opportunities. This data-driven approach informs strategic decision-making, enabling manufacturers to respond proactively to market shifts.
- Reduced Fulfillment Errors: Automation minimizes manual intervention, reducing the risk of human errors. Accurate order processing and fulfillment lead to fewer returns, fewer customer complaints, and improved brand reputation.
- Multi-Channel Consistency: Regardless of the sales channel, customers experience consistent order handling and service quality. This consistency builds trust and encourages repeat business.
- Adaptability to Market Changes: Automated systems can quickly adjust to changes in demand, market trends, and supply chain disruptions. Manufacturers can adapt their strategies and operations in real-time, maintaining competitiveness.
- Cost Savings: Increased efficiency, reduced errors, and optimized resource utilization contribute to cost savings. Over time, the return on investment from automation becomes evident through improved margins.
- Scalability and Growth: Automated multi-channel order management systems are designed to scale as the business grows. Manufacturers can seamlessly integrate new sales channels, products, and partners without compromising operational efficiency.
- Strategic Customer Insights: Data collected through automated systems offers valuable insights into customer behaviors, preferences, and buying patterns. Manufacturers can tailor their marketing strategies and product offerings accordingly.
- Competitive Edge: Manufacturers embracing automation gain a competitive edge by delivering superior customer experiences and more efficient operations. This positioning helps secure market share and drives business growth.
By embracing Automated Multi-Channel Order Management, manufacturing companies not only address the challenges of a rapidly evolving landscape but also unlock new levels of efficiency, agility, and customer-centricity. The benefits span from the shop floor to the customer's doorstep, laying the groundwork for sustained success in an interconnected and competitive market.
Technological Foundations
In a world where seamless integration, real-time insights, and adaptable systems are paramount, this section delves into the core technologies that empower manufacturers to navigate the complexities of modern commerce. From the integration of ERP systems to harnessing the power of AI, IoT, and cloud solutions, this exploration illuminates how technology is shaping the future of order management.
As we venture into the depths of these technological foundations, a landscape of possibilities emerges, showcasing how innovation is poised to amplify manufacturing efficiency, customer experiences, and competitive advantage in ways previously unimagined.
A. Integration of ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems
An ERP system functions as a comprehensive digital nervous system, interconnecting various departments and processes within an organization. This integration becomes particularly instrumental in the context of Automated Multi-Channel Order Management, where the seamless flow of information across the entire order lifecycle is paramount.
- Centralized Data Hub: An ERP system serves as a centralized repository for critical business data, encompassing everything from inventory levels and production schedules to customer information and financial records. This centralized data repository becomes the foundation upon which accurate order management rests.
- Unified Process Visibility: ERP integration provides a unified view of various operational processes. From order initiation to fulfillment, manufacturers gain real-time visibility into each stage of the order lifecycle. This transparency enables timely decision-making and enhances customer service.
- Enhanced Data Accuracy: Automating data entry reduces manual errors that can arise from data rekeying. Accurate and consistent data entry throughout the order management process minimizes discrepancies, leading to higher order accuracy and customer satisfaction.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: By seamlessly integrating with production and inventory modules, ERP systems optimize resource allocation. Manufacturers can allocate materials, labor, and equipment more effectively, resulting in streamlined production and timely order fulfillment.
- Real-Time Insights: ERP systems generate real-time insights into various aspects of the manufacturing process, such as production capacity, material availability, and labor utilization. These insights inform decision-making, allowing manufacturers to adjust operations to meet changing demand.
- Responsive Supply Chain: Integration with supplier and vendor data allows manufacturers to monitor supply chain performance in real time. Any disruptions or delays can be identified promptly, enabling timely interventions to maintain order fulfillment.
- Accurate Financial Tracking: ERP integration facilitates accurate financial tracking by automatically updating financial data as orders are processed. This integration provides accurate cost tracking, revenue recognition, and helps in managing financial planning and performance.
- Scalability and Flexibility: ERP systems designed with scalability in mind can accommodate business growth. As order volumes increase and new channels are integrated, the ERP system adapts to support the expanding operations seamlessly.
- Customization and Tailoring: ERP systems can be customized to align with specific manufacturing workflows and processes. This tailoring ensures that the order management process is aligned with the unique requirements of the business.
The integration of ERP systems into Automated Multi-Channel Order Management empowers manufacturers to orchestrate their operations with precision, agility, and informed decision-making. As a fundamental enabler of cross-functional collaboration and real-time data exchange, ERP integration sets the stage for the interconnected, automated manufacturing ecosystem of the future.
B. Role of AI (Artificial Intelligence) and machine learning
In the age of automation and data-driven decision-making, the convergence of AI and machine learning stands as a transformative force within Automated Multi-Channel Order Management. These technologies empower manufacturing companies to unlock insights, predict trends, and optimize operations in ways previously unimaginable.
The role of AI and machine learning extends beyond mere efficiency to infuse intelligence and adaptability into the very fabric of order management.
Demand Forecasting and Inventory Optimization: AI and machine learning algorithms analyze historical data to predict demand patterns with remarkable accuracy. Manufacturers can optimize inventory levels based on these predictions, reducing excess inventory costs and minimizing stockouts.
Personalized Customer Interactions: By analyzing customer data, AI-driven systems offer insights into individual preferences and behaviors. This information fuels personalized product recommendations and targeted marketing strategies, enhancing the customer experience.
Fraud Detection and Prevention: AI algorithms can identify patterns indicative of fraudulent activities in real time. By analyzing transaction data and customer behavior, manufacturers can mitigate the risk of fraudulent orders and protect their customers.
Optimized Pricing Strategies: Machine learning models can dynamically adjust pricing based on factors like demand, competition, and market trends. This enables manufacturers to maximize revenue while remaining competitive.
Automated Customer Support: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can handle customer queries and issues, offering 24/7 support and freeing up human agents for more complex tasks. This ensures timely and consistent customer service.
Process Automation and Efficiency: Machine learning algorithms can identify process bottlenecks and inefficiencies within order management workflows. By analyzing these patterns, manufacturers can streamline processes for greater efficiency.
Quality Control and Defect Detection: AI-driven image recognition and machine vision systems can inspect products for defects or inconsistencies. This technology ensures that only high-quality products are shipped to customers.
Dynamic Order Routing: AI can optimize order routing decisions based on factors like location, shipping costs, and delivery times. This ensures efficient order fulfillment while minimizing operational costs.
Continuous Learning and Improvement: Machine learning models adapt over time as they process more data, resulting in increasingly accurate predictions and insights. This adaptability drives continuous improvement in decision-making.
Resource Allocation Optimization: AI algorithms can analyze production and resource data to optimize allocation, ensuring that resources are allocated in the most efficient and cost-effective manner.
The infusion of AI and machine learning transforms Automated Multi-Channel Order Management into an intelligent, proactive, and adaptive system. By leveraging the power of data-driven insights, manufacturers not only enhance their operational efficiency but also elevate the quality of customer experiences and strategic decision-making.
The role of AI and machine learning in order management underscores their potential to reshape the manufacturing landscape and create a more agile, customer-centric, and competitive industry.
C. IoT (Internet of Things) in manufacturing and order management
The Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a game-changing paradigm within manufacturing, redefining how products are made, monitored, and managed. Its integration within Automated Multi-Channel Order Management introduces a new dimension of connectivity, intelligence, and efficiency.
IoT technologies empower manufacturers to gather real-time data from devices, machinery, and sensors, creating a holistic ecosystem that transcends traditional boundaries.
- Real-Time Visibility and Tracking: IoT-enabled sensors and RFID technology provide real-time visibility into the location and status of products, materials, and equipment. Manufacturers can track orders, shipments, and inventory levels across the entire supply chain.
- Predictive Maintenance: IoT devices collect data on equipment performance, enabling predictive maintenance. By analyzing this data, manufacturers can identify maintenance needs before equipment failure occurs, minimizing downtime and disruptions.
- Quality Control and Assurance: IoT sensors can monitor production processes to detect anomalies and variations. This ensures that products adhere to quality standards and reduces the likelihood of defects reaching customers.
- Supply Chain Optimization: IoT devices offer insights into supply chain processes, such as transportation conditions, storage conditions, and delivery times. This optimization ensures efficient and timely order fulfillment.
- Customer Engagement: IoT-enabled products provide manufacturers with insights into how customers use their products. This data informs product improvements, design iterations, and personalized customer interactions.
- Smart Inventory Management: IoT sensors in warehouses and storage areas monitor inventory levels in real time. Automated reordering systems can trigger orders when the stock reaches predefined thresholds, ensuring optimal inventory levels.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: IoT-enabled devices can communicate directly with customers, providing updates on order status, delivery times, and personalized offers. This real-time engagement enhances the overall customer experience.
- Demand-Driven Production: IoT data on customer preferences and usage patterns can guide production decisions. Manufacturers can align production with actual demand, reducing overproduction and waste.
- Energy Efficiency: IoT technology can monitor energy consumption within the manufacturing process. By optimizing energy usage, manufacturers can reduce costs and minimize environmental impact.
- Data-Driven Insights: The massive amount of data collected by IoT devices can be analyzed to uncover patterns, trends, and correlations. These insights inform strategic decision-making and process improvements.
The integration of IoT within Automated Multi-Channel Order Management ushers in a new era of data-driven decision-making, precision, and agility. By creating a seamlessly connected network of devices and systems, manufacturers can harness the power of real-time data to optimize operations, enhance customer experiences, and drive innovation.
D. Cloud-based solutions for scalability and flexibility
Cloud-based solutions have emerged as a cornerstone in the transformation of manufacturing and order management. With their inherent scalability, flexibility, and accessibility, these solutions enable manufacturers to embrace the demands of the modern business landscape, particularly in the context of Automated Multi-Channel Order Management.
Scalability: Cloud solutions offer virtually limitless scalability, accommodating the fluctuating demands of order processing without the need for extensive infrastructure investments. As order volumes grow, the cloud can seamlessly expand to meet the increased workload.
Flexibility and Accessibility: Cloud-based platforms provide remote access to order management systems. Manufacturers can access critical data, track orders, and manage operations from anywhere, enhancing flexibility and enabling remote work scenarios.
Reduced IT Infrastructure Costs: Cloud solutions eliminate the need for substantial upfront hardware investments. Manufacturers can avoid the costs associated with maintaining and upgrading physical servers, translating into cost savings.
Rapid Deployment and Updates: Cloud-based solutions can be deployed rapidly, reducing the time to implement new order management systems. Updates and enhancements are also easier to implement, ensuring manufacturers have access to the latest features.
Data Security and Compliance: Reputable cloud providers offer robust security measures, including encryption and authentication protocols. They also ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations, enhancing data security.
Data Integration: Cloud-based platforms facilitate seamless integration with other systems, such as CRM, ERP, and analytics tools. This integration ensures consistent data flow and a holistic view of business operations.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: Cloud solutions offer built-in disaster recovery mechanisms, ensuring data is backed up and can be restored in case of system failures or data loss. This enhances business continuity.
Pay-as-You-Go Model: Cloud services often follow a pay-as-you-go pricing model, allowing manufacturers to pay only for the resources they consume. This scalability contributes to cost efficiency.
Innovation and Experimentation: Cloud platforms provide a fertile ground for innovation. Manufacturers can experiment with new technologies, test new features, and pilot new order management strategies without committing to long-term investments.
Global Accessibility: Cloud-based solutions enable manufacturers to serve global markets without geographic limitations. Orders can be processed and fulfilled across different regions, ensuring a consistent customer experience.
The adoption of cloud-based solutions within Automated Multi-Channel Order Management aligns with the dynamic and interconnected nature of modern manufacturing. By providing the foundation for scalability, accessibility, and innovation, these solutions empower manufacturers to optimize operations, enhance customer experiences, and remain adaptable in a rapidly changing business landscape.
Implementation Process
From migrating data to integrating new technologies, from upskilling the workforce to orchestrating organizational change, this section sheds light on the step-by-step process that manufacturers undertake to bring the vision of automated, multi-channel order management to fruition. As we go through the implementation process, we uncover the challenges, successes, and best practices that shape the transition.
A. Data migration and system integration challenges
The implementation of Automated Multi-Channel Order Management necessitates the seamless transfer of data from existing systems and the integration of new technologies. While this transformation promises substantial benefits, it also presents a range of challenges that manufacturers must address to ensure a smooth transition.
- Data Complexity and Volume: Migrating extensive historical and real-time data from legacy systems can be complex and time-consuming. Manufacturers must ensure data accuracy and integrity throughout the migration process.
- Data Mapping and Transformation: Aligning data structures and formats between old and new systems requires meticulous mapping and transformation. Ensuring that data remains coherent and meaningful during this process is a significant challenge.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating new technologies, such as ERP, CRM, and IoT systems, with the existing order management infrastructure requires careful planning and technical expertise. Ensuring compatibility and smooth data exchange is critical.
- Diverse Data Sources: In a multi-channel environment, data may originate from various sources, including e-commerce platforms, retail partners, and direct sales. Integrating data from these disparate sources while maintaining accuracy poses a challenge.
- Data Security and Privacy: Ensuring data security and compliance during migration and integration is crucial. Manufacturers must safeguard sensitive customer information and adhere to data protection regulations.
- Process Reengineering: Integrating new technologies often necessitates reengineering existing processes to align with the capabilities of the new systems. Managing this transition without disrupting operations requires careful planning.
- Customization and Adaptation: Configuring new systems to meet the unique needs of the manufacturing business may require customization. Balancing customization with maintaining system compatibility can be challenging.
- Training and User Adoption: Transitioning to new systems requires training the workforce to effectively use the technology. Overcoming resistance to change and ensuring smooth user adoption can be a significant hurdle.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: Rigorous testing is essential to identify and rectify any issues before full implementation. Ensuring that all integrated components work seamlessly together is critical for a successful rollout.
- Resource Allocation: The implementation process demands resources in terms of time, budget, and personnel. Proper resource allocation and management are essential to prevent disruptions in day-to-day operations.
Successfully overcoming these challenges requires a comprehensive strategy that encompasses thorough planning, clear communication, collaboration among different teams, and close coordination with technology partners.
B. Selecting the right software and technology partners
Choosing the appropriate software solutions and technology partners is a pivotal step in the successful implementation of Automated Multi-Channel Order Management. The selection process directly impacts the efficiency, effectiveness, and long-term viability of the automation initiative.
However, this decision-making journey is fraught with considerations and complexities.
- Business Needs Assessment: The first step is to conduct a comprehensive assessment of the business's specific needs, goals, and pain points. Understanding the unique requirements of the manufacturing operations is essential for identifying software that aligns with these objectives.
- Scalability and Flexibility: The selected software must be scalable to accommodate growth and flexible enough to adapt to changing business conditions. It should support the addition of new channels, products, and features without disrupting operations.
- Integration Capabilities: Compatibility with existing systems, such as ERP, CRM, and inventory management, is crucial. The software should offer robust integration capabilities to ensure seamless data exchange and process continuity.
- Functionality and Features: Evaluating the software's functionality and features in the context of order management is essential. It should offer capabilities for order processing, inventory management, customer communications, and real-time tracking.
- User-Friendly Interface: The software's user interface should be intuitive and user-friendly. A complex or convoluted interface could lead to a steep learning curve and hinder user adoption.
- Vendor Reputation and Experience: Research the reputation and experience of potential technology partners. A track record of successful implementations and positive customer reviews can provide valuable insights into a vendor's reliability.
- Customization and Support: Consider whether the software can be customized to meet specific business needs. Additionally, assess the level of customer support and training that the vendor offers post-implementation.
- Security and Compliance: The software must adhere to robust security standards to safeguard sensitive customer data and ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
- Cost and ROI Analysis: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including licensing fees, implementation costs, and potential ongoing expenses. Conduct a thorough ROI analysis to ensure the chosen solution justifies the investment.
- Long-Term Viability: Assess the software vendor's roadmap and commitment to continuous development and updates. Choose a solution that will remain relevant and adaptable as technology evolves.
- Proof of Concept: A proof of concept (PoC) or pilot phase can provide hands-on experience with the software's capabilities before committing to a full implementation. This minimizes risks and allows for adjustments based on real-world testing.
The process of selecting the right software and technology partners requires a balanced approach that considers both short-term requirements and long-term strategic goals. Collaborating closely with vendors, conducting thorough evaluations, and aligning software choices with business objectives are essential steps in ensuring a successful partnership that drives the seamless transition to Automated Multi-Channel Order Management.
C. Training and upskilling the workforce
The successful implementation of Automated Multi-Channel Order Management is not solely reliant on technology; it hinges equally on the preparedness and proficiency of the workforce. Training and upskilling employees to navigate the new systems and processes are critical to maximizing the benefits of automation and ensuring a smooth transition.
Comprehensive Training Programs: Develop comprehensive training programs that cover all aspects of the new systems, from order processing and inventory management to using the integrated technologies. Training should cater to employees across various roles and departments.
Role-Specific Training: Tailor training sessions to specific job roles. Different teams may interact with the new systems differently, and customized training ensures that employees acquire the skills relevant to their responsibilities.
Hands-On Learning: Provide hands-on training that allows employees to actively engage with the new software and technologies. Practical experience fosters better understanding and confidence in using the systems effectively.
User-Friendly Training Materials: Develop user-friendly training materials, including guides, tutorials, and videos. These resources should be easily accessible and serve as references for employees as they navigate the new systems.
Continuous Learning Opportunities: Recognize that the implementation process is just the beginning. Offer ongoing training opportunities that keep employees updated on new features, best practices, and any system enhancements.
Change Management Guidance: Address resistance to change by providing guidance on adapting to the new systems. Highlight the benefits of automation and how it contributes to improved processes and job performance.
Feedback and Support Channels: Establish channels for employees to provide feedback and seek support. Creating an environment where employees can voice their concerns or questions fosters a smoother transition.
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Encourage collaboration between different departments during training. This facilitates knowledge sharing and encourages a unified approach to using the new systems.
Champion Network: Identify enthusiastic employees who can serve as champions for the new systems. These individuals can provide peer-to-peer support, share best practices, and motivate their colleagues.
Assessment and Certification: Implement assessments or certification programs to evaluate employee proficiency. This not only validates their skills but also encourages a sense of achievement and accountability.
Executive Support and Communication: Secure support from top management for training initiatives. Clear communication about the importance of upskilling and its alignment with the organization's goals is vital.
By investing in training and upskilling, manufacturers empower their workforce to fully leverage the potential of Automated Multi-Channel Order Management. A well-trained workforce is not only equipped to navigate the complexities of new technologies but also plays a crucial role in driving the efficiency, accuracy, and customer-centricity that automation promises.
D. Change management strategies for a smooth transition
The successful implementation of Automated Multi-Channel Order Management is not solely reliant on technology; it hinges equally on the preparedness and proficiency of the workforce. Training and upskilling employees to navigate the new systems and processes are critical to maximizing the benefits of automation and ensuring a smooth transition.
- Comprehensive Training Programs: Develop comprehensive training programs that cover all aspects of the new systems, from order processing and inventory management to using the integrated technologies. Training should cater to employees across various roles and departments.
- Role-Specific Training: Tailor training sessions to specific job roles. Different teams may interact with the new systems differently, and customized training ensures that employees acquire the skills relevant to their responsibilities.
- Hands-On Learning: Provide hands-on training that allows employees to actively engage with the new software and technologies. Practical experience fosters better understanding and confidence in using the systems effectively.
- User-Friendly Training Materials: Develop user-friendly training materials, including guides, tutorials, and videos. These resources should be easily accessible and serve as references for employees as they navigate the new systems.
- Continuous Learning Opportunities: Recognize that the implementation process is just the beginning. Offer ongoing training opportunities that keep employees updated on new features, best practices, and any system enhancements.
- Change Management Guidance: Address resistance to change by providing guidance on adapting to the new systems. Highlight the benefits of automation and how it contributes to improved processes and job performance.
- Feedback and Support Channels: Establish channels for employees to provide feedback and seek support. Creating an environment where employees can voice their concerns or questions fosters a smoother transition.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Encourage collaboration between different departments during training. This facilitates knowledge sharing and encourages a unified approach to using the new systems.
- Champion Network: Identify enthusiastic employees who can serve as champions for the new systems. These individuals can provide peer-to-peer support, share best practices, and motivate their colleagues.
- Assessment and Certification: Implement assessments or certification programs to evaluate employee proficiency. This not only validates their skills but also encourages a sense of achievement and accountability.
- Executive Support and Communication: Secure support from top management for training initiatives. Clear communication about the importance of upskilling and its alignment with the organization's goals is vital.
By investing in training and upskilling, manufacturers empower their workforce to fully leverage the potential of Automated Multi-Channel Order Management. A well-trained workforce is not only equipped to navigate the complexities of new technologies but also plays a crucial role in driving the efficiency, accuracy, and customer-centricity that automation promises.
Potential Challenges and Solutions
From overcoming resistance to change to addressing technical complexities, this section explores these challenges in-depth, offering insightful solutions that empower manufacturers to navigate these hurdles with confidence and clarity.
By acknowledging and proactively addressing these challenges, manufacturers can position themselves for a successful transition and unlock the full potential of automation in modern order management.
A. Data security and privacy concerns
As manufacturing companies embrace Automated Multi-Channel Order Management, concerns around data security and privacy come to the forefront. The digitalization of order processes and the integration of various systems bring with them the responsibility to safeguard sensitive information and comply with stringent data protection regulations.
Challenges:
- Data Breaches and Hacking Threats: With increased digital presence, the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks rises. Sensitive customer information, order details, and financial data become potential targets for malicious actors.
- Compliance with Regulations: Data protection regulations such as GDPR and CCPA mandate strict standards for handling and storing personal data. Ensuring compliance across multiple sales channels and systems can be complex.
- Third-Party Vulnerabilities: Integrating third-party systems and vendors introduces potential vulnerabilities. Data shared between partners could be exposed to risks beyond a manufacturer's direct control.
Solutions:
- Robust Encryption and Authentication: Implement strong encryption mechanisms to protect data in transit and at rest. Multi-factor authentication adds an additional layer of security to prevent unauthorized access.
- Regular Security Audits and Assessments: Conduct routine security audits to identify vulnerabilities and assess risks. Regular assessments help in promptly addressing any weaknesses in the system.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Educate employees about data security best practices and the importance of safeguarding sensitive information. Human errors are often a weak point in security.
- Secure Third-Party Integration: Vet and select technology partners with a strong focus on data security. Ensure that third-party systems adhere to robust security measures and compliance standards.
- Data Minimization: Collect and store only the data necessary for order processing and customer interaction. Minimizing the data footprint reduces the risk associated with holding unnecessary information.
- Granular Access Controls: Implement role-based access controls to restrict data access based on an individual's role and responsibilities. This prevents unauthorized personnel from accessing sensitive information.
- Regular Updates and Patch Management: Keep all systems and software up to date with the latest security patches. This helps in addressing known vulnerabilities and staying ahead of potential threats.
- Transparent Privacy Policies: Clearly communicate privacy policies to customers. Explain how their data will be used and reassure them about the measures taken to protect their information.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop a robust incident response plan that outlines steps to take in case of a data breach. This ensures a swift and coordinated response to mitigate damage.
By proactively addressing data security and privacy concerns, manufacturing companies can instill trust among customers, protect sensitive information, and ensure compliance with data protection regulations. A well-rounded approach that combines technology, policies, and awareness ensures that data remains secure while benefiting from the advantages of Automated Multi-Channel Order Management.
B. Customization and adaptability for varying manufacturing workflows
One of the challenges in implementing Automated Multi-Channel Order Management lies in tailoring the system to accommodate diverse manufacturing workflows. Each manufacturing operation is unique, and finding the balance between automation and customization to align with specific processes can be complex.
Challenges:
- Diverse Workflow Requirements: Different manufacturing departments may have varying processes and requirements. Ensuring the system adapts to these diverse needs while maintaining efficiency is a challenge.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating the new order management system with existing ERP, CRM, and inventory management systems requires seamless data exchange and process alignment.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may be accustomed to existing workflows and resistant to adopting new systems. Convincing them of the benefits of change can be challenging.
Solutions:
- Customization Options: Choose an order management system that offers customization options. This allows manufacturers to configure the system to match their specific workflow needs.
- Workflow Mapping and Analysis: Conduct a thorough analysis of existing workflows. Identify areas where automation can enhance efficiency and align the new system accordingly.
- Modular Implementation: Implement the new system in modules. This approach allows for step-by-step integration, giving employees time to adjust and reducing disruption.
- User Feedback and Input: Involve employees in the customization process. Their input can offer valuable insights into workflow nuances and streamline system adaptation.
- Change Management and Training: Offer comprehensive training and change management programs. Address concerns and educate employees about the benefits of the new system.
- Flexibility in System Architecture: Opt for a system architecture that allows for scalability and adaptability. Cloud-based solutions, for example, can easily accommodate customization.
- User Interface Customization: Choose a system that allows users to customize their interface based on their roles and preferences. This enhances usability and acceptance.
- Workflow Integration Consultants: Consider involving consultants who specialize in workflow integration. Their expertise can help in aligning the new system with existing processes.
- Pilot Testing and Iterative Approach: Pilot test the new system with a smaller group of users. Gather feedback and iterate on customization before rolling it out to a larger audience.
- Continuous Improvement Culture: Foster a culture of continuous improvement. Encourage employees to suggest workflow enhancements that can be incorporated into the system.
Balancing customization with standardization is a delicate endeavor, but it ensures that Automated Multi-Channel Order Management harmonizes with the unique demands of different manufacturing workflows. By finding the optimal equilibrium between automation and customization, manufacturers can streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and ensure that the new system aligns seamlessly with the intricacies of their processes.
C. Overcoming resistance to automation from employees
The introduction of Automated Multi-Channel Order Management often encounters resistance from employees who may be apprehensive about the changes automation brings. Addressing this resistance and fostering a culture of acceptance and collaboration is crucial for a successful transition.
Challenges:
- Fear of Job Loss: Employees may worry that automation will render their roles redundant. This fear can lead to resistance and reluctance to embrace the new systems.
- Lack of Familiarity: Employees who are accustomed to manual processes may be unfamiliar with new technologies. This lack of familiarity can breed resistance to change.
- Perceived Complexity: Employees might perceive the new systems as overly complex or difficult to learn. This perception can hinder their willingness to adopt automation.
Solutions:
- Communication and Transparency: Clearly communicate the purpose of automation and the benefits it brings. Address concerns about job security and explain how automation can enhance roles.
- Involvement and Empowerment: Involve employees in the decision-making process. Empower them to contribute to the implementation plans and share their insights.
- Education and Training: Provide comprehensive training programs that cater to employees' varying levels of familiarity with technology. Training builds confidence and reduces resistance.
- Showcase Success Stories: Highlight successful automation implementations in other organizations or within the company. Real-life examples can inspire confidence and dispel fears.
- Change Champions: Identify and enlist employees who are receptive to change as change champions. They can serve as advocates and mentors for their colleagues.
- Address Concerns Proactively: Create platforms for employees to voice their concerns and questions. Addressing these concerns proactively demonstrates empathy and understanding.
- Incentives and Recognition: Offer incentives and recognition for employees who actively embrace and excel in using the new systems. Positive reinforcement encourages adoption.
- Gradual Transition: Implement automation gradually, allowing employees time to adjust. Gradual changes are less disruptive and provide employees with the opportunity to learn and adapt.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Choose systems with intuitive and user-friendly interfaces. Simplifying the user experience reduces the perceived complexity of automation.
- Open Door Policy: Maintain an open door policy for employees to voice their concerns. Provide reassurance that their input is valued and taken into consideration.
- Celebrate Milestones: Celebrate achievements and milestones during the transition. Recognizing progress boosts morale and demonstrates that the change is positive.
By addressing resistance with empathy, effective communication, and comprehensive support, manufacturing companies can turn skeptics into champions of automation. Creating an environment where employees feel valued, empowered, and informed fosters a smoother transition and paves the way for the successful adoption of Automated Multi-Channel Order Management.
D. Continuous monitoring and system updates
The implementation of Automated Multi-Channel Order Management marks the beginning of a dynamic journey rather than a static destination. Continuous monitoring and timely system updates are crucial to ensure that the automation remains aligned with evolving business needs and technological advancements.
Challenges:
- Technological Evolution: Technology is ever-evolving. Failure to keep up with advancements can result in the system becoming outdated and less effective over time.
- Changing Business Requirements: Business needs and processes may change due to market shifts or organizational growth. The system needs to adapt to these changes for optimal performance.
- Security and Compliance Updates: Data security standards and compliance regulations are subject to change. Neglecting updates can lead to vulnerabilities and legal risks.
Solutions:
- Regular Performance Reviews: Conduct periodic reviews of system performance and alignment with business objectives. Identify areas that need improvement or updates.
- Stay Abreast of Technology Trends: Stay informed about emerging technologies and trends relevant to order management. Leverage innovations that can enhance system capabilities.
- Vendor Relationship: Maintain a strong relationship with technology partners or vendors. Regular communication ensures that updates and enhancements are promptly implemented.
- User Feedback Loop: Encourage users to provide feedback on the system's functionality and usability. Incorporate user suggestions into updates to enhance user experience.
- Scheduled Maintenance: Plan and execute scheduled maintenance and updates to avoid disruptions during critical business periods. Notify users in advance about any system downtime.
- Security Patches and Upgrades: Regularly apply security patches and upgrades to safeguard against vulnerabilities and maintain compliance with data protection regulations.
- Scalability and Future-Proofing: Design the system architecture with scalability in mind. Ensure it can accommodate future growth and changes without requiring a major overhaul.
- Automated Monitoring Tools: Utilize automated monitoring tools that track system performance, uptime, and potential issues. This allows for proactive intervention before problems escalate.
- User Training on Updates: Provide training to users whenever updates are implemented. Familiarize them with new features and changes to ensure smooth adoption.
- Testing Before Implementation: Test updates thoroughly in a controlled environment before rolling them out to the entire system. This minimizes the risk of unexpected disruptions.
- Long-Term Roadmap: Develop a long-term roadmap for system updates and enhancements. This ensures a strategic approach to maintaining and improving the system over time.
By embracing a culture of continuous improvement and proactively addressing system updates, manufacturing companies can ensure that Automated Multi-Channel Order Management remains a valuable asset that adapts to changing requirements and technological landscapes. Continuous monitoring and updates are the keys to deriving sustained benefits from automation and staying competitive in a rapidly evolving business environment.
Future Trends
From the integration of artificial intelligence to the rise of omnichannel experiences, this section provides a glimpse into the trends that will shape the future of order management, offering insights into the strategies manufacturers can adopt to stay ahead and deliver exceptional customer experiences in the increasingly interconnected world of commerce.
A. AI-driven predictive analytics for demand forecasting
As the manufacturing landscape becomes more complex and consumer expectations continue to evolve, the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in Automated Multi-Channel Order Management is poised to take a significant leap forward. AI-driven predictive analytics are set to revolutionize demand forecasting, enabling manufacturers to anticipate customer needs with unparalleled accuracy.
Trends:
- Data-Driven Insights: AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of historical and real-time data, extracting patterns, trends, and correlations that human analysis might miss. This data-driven approach enhances the accuracy of demand forecasting.
- Dynamic Demand Prediction: AI can adjust forecasts in real-time based on factors such as market trends, seasonality, promotions, and even external events. This adaptability ensures that demand predictions remain relevant and precise.
- Personalization and Customer Behavior: AI can analyze customer behavior and preferences to tailor demand forecasts at the individual level. This personalized approach enhances customer experiences and minimizes supply-demand mismatches.
- Inventory Optimization: AI-driven demand forecasting enables manufacturers to optimize inventory levels. This reduces overstocking or understocking scenarios, leading to cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
- Risk Mitigation: By factoring in external factors like economic conditions, geopolitical events, and supply chain disruptions, AI-driven demand forecasting helps manufacturers proactively mitigate risks and make informed decisions.
Strategies:
- Data Collection and Integration: Gather and integrate data from various sources, including sales history, customer interactions, market trends, and social media. A robust data foundation is crucial for accurate predictions.
- Machine Learning Algorithms: Implement advanced machine learning algorithms that can process and analyze large datasets. These algorithms learn from historical data to make accurate future predictions.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Implement real-time monitoring of various data streams to capture sudden changes in demand patterns and adapt forecasts accordingly.
- Collaboration Across Departments: Foster collaboration between departments like sales, marketing, and supply chain. Sharing insights and data helps improve the accuracy of predictions.
- Feedback Loop and Iteration: Continuously refine the AI models based on actual outcomes. A feedback loop ensures that the models learn from their predictions and improve over time.
- Ethical and Responsible AI Use: Ensure that AI-driven decisions are transparent, unbiased, and in line with ethical considerations. Customer trust remains paramount in the adoption of AI technologies.
B. Expansion of 5G technology for real-time communication
The proliferation of 5G technology is set to reshape the capabilities of Automated Multi-Channel Order Management by enabling real-time communication and interaction across various channels. This emerging trend promises to unlock new dimensions of speed, efficiency, and connectivity in manufacturing operations.
Trends:
- Ultra-Fast Data Transfer: 5G's unparalleled data transfer speeds allow for instantaneous communication between devices and systems. This speed facilitates real-time updates, order tracking, and instant response to customer queries.
- Low Latency: The minimal latency offered by 5G ensures almost instant communication between devices. This is crucial for applications like real-time inventory management, demand forecasting, and order processing.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: 5G's capacity to connect a massive number of devices simultaneously supports the seamless integration of IoT devices. This enables continuous monitoring, data collection, and process optimization.
- Enhanced Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): 5G's bandwidth and low latency are ideal for AR and VR applications. Manufacturers can use these technologies to provide remote assistance, training, and immersive customer experiences.
- Multi-Channel Synchronization: 5G's capabilities enable synchronization across multiple channels, ensuring that data is updated in real-time across all touchpoints. This leads to consistent and up-to-date customer interactions.
Strategies:
- 5G Infrastructure Investment: Invest in upgrading infrastructure to accommodate 5G technology. This includes not only communication networks but also IoT devices and systems.
- Real-Time Analytics: Leverage the real-time data flow enabled by 5G to conduct instant analytics. This allows for timely decision-making and responsiveness to changing market conditions.
- Connected Ecosystems: Develop interconnected ecosystems that utilize 5G for communication. This can include integrating production lines, supply chain partners, and customer-facing systems.
- Enhanced Customer Experiences: Capitalize on 5G's capabilities to offer immersive customer experiences through AR and VR technologies. This can include virtual showrooms, product demonstrations, and guided tours.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Use 5G to remotely monitor and control manufacturing processes, equipment, and inventory levels. This enhances efficiency and reduces operational downtime.
C. Integration of blockchain for transparent supply chain management
The integration of blockchain technology into Automated Multi-Channel Order Management holds the promise of revolutionizing supply chain management through enhanced transparency, traceability, and trust. This trend is set to reshape the way manufacturers manage their supply chains and interact with stakeholders.
Trends:
- Immutable Transaction Records: Blockchain's decentralized nature ensures that every transaction is recorded in an immutable and transparent manner. This traceability enhances accountability and reduces the risk of fraud.
- End-to-End Transparency: Blockchain enables real-time visibility into every step of the supply chain. This transparency ensures that customers and stakeholders can trace the origin and journey of products.
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts, powered by blockchain, facilitate automated and self-executing agreements. They streamline processes like payment verification, order fulfillment, and compliance enforcement.
- Counterfeit Prevention: Blockchain's ability to authenticate products at every stage of the supply chain helps in combating counterfeit goods and ensuring the authenticity of products.
- Supplier Collaboration: Blockchain fosters collaboration between suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors. Data sharing becomes secure and efficient, leading to streamlined operations.
Strategies:
- Blockchain Consortiums: Collaborate with suppliers, distributors, and other stakeholders to establish blockchain consortiums. These shared networks enhance transparency and data sharing.
- Traceability Solutions: Implement blockchain-based traceability solutions that enable customers to track the entire journey of products, from raw materials to finished goods.
- Secure Data Sharing: Utilize blockchain to securely share data across the supply chain without compromising sensitive information. This ensures privacy while enhancing collaboration.
Conclusion
In the dynamic landscape of manufacturing, the adoption of Automated Multi-Channel Order Management stands as a transformative force that promises to reshape how companies operate, engage with customers, and navigate the complexities of modern commerce. Through this exploration of the revolutionizing potential of automated multi-channel order management, it becomes evident that the convergence of technology, strategy, and adaptability is essential for success.
From understanding the importance of order management in manufacturing to delving into the technological foundations that underpin automation, this journey has shed light on the intricacies of this evolving landscape. The significance of customization, training, and change management strategies have been highlighted as crucial enablers in ensuring a smooth transition and effective utilization of automation.
As the manufacturing sector marches towards the future, the implementation of Automated Multi-Channel Order Management is poised to unleash unparalleled efficiencies, elevate customer experiences, and fuel growth. With trends like AI-driven predictive analytics, 5G technology, and blockchain integration on the horizon, manufacturers are primed to embrace innovation and adapt to the demands of a digitally empowered world.
In conclusion, the road to revolutionizing manufacturing through Automated Multi-Channel Order Management is not without its challenges, but it holds immense promise.
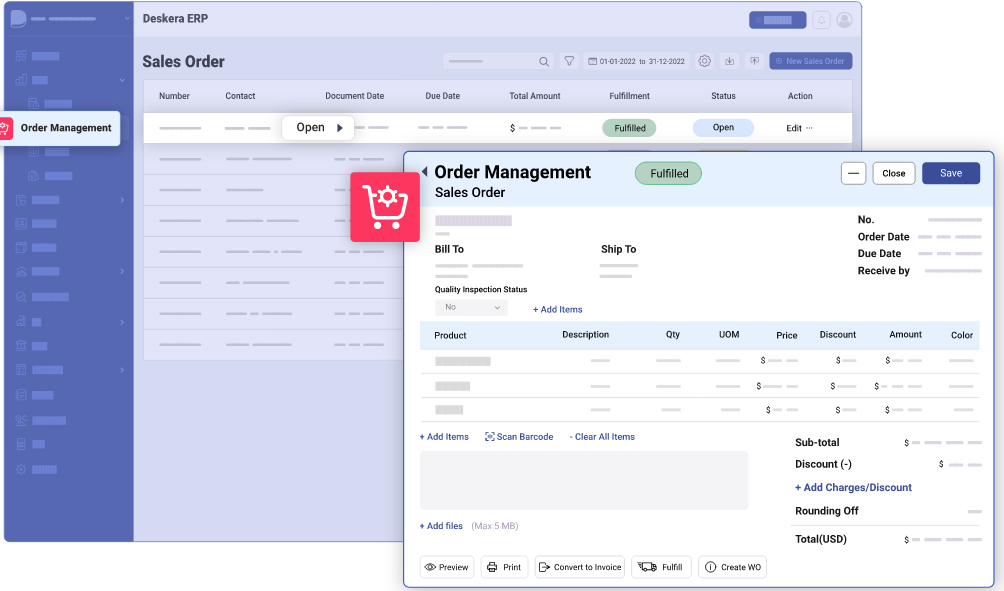
How can Deskera Help You?
Deskera ERP and MRP systems help you to keep your business units organized. The system's primary functions are as follows:
- Keep track of your raw materials and final items inventories
- Control production schedules and routings
- Keep a bill of materials
- Produce thorough reports
- Make your own dashboards
Deskera's integrated financial planning tools enable investors to better plan and track their investments. It can assist investors in making faster and more accurate decisions.
Deskera Books allows you to better manage your accounts and finances. Maintain good accounting practices by automating tasks like billing, invoicing, and payment processing.
Deskera CRM is a powerful solution that manages your sales and helps you close deals quickly. It not only enables you to perform critical tasks like lead generation via email, but it also gives you a comprehensive view of your sales funnel.
Deskera People is a straightforward tool for centralizing your human resource management functions.
Key Takeaways
As we conclude the exploration of Automated Multi-Channel Order Management's transformative impact on the manufacturing sector, here are the key takeaways that encapsulate the insights gained:
- Strategic Evolution of Manufacturing: The adoption of Automated Multi-Channel Order Management represents a strategic evolution that empowers manufacturers to enhance efficiency, customer experiences, and overall competitiveness.
- Importance of Order Management: Effective order management is the backbone of manufacturing operations, ensuring seamless processing, inventory control, and timely customer fulfillment.
- Automated Multi-Channel Integration: Automation brings together multiple sales channels, enabling cohesive order processing, real-time tracking, and consistent customer interactions across platforms.
- AI and Machine Learning's Power: Artificial Intelligence and machine learning revolutionize manufacturing by enabling predictive analytics for demand forecasting, empowering agile decision-making.
- 5G's Real-Time Revolution: The expansion of 5G technology revolutionizes communication, allowing for real-time updates, instant response, and immersive experiences in multi-channel operations.
- Blockchain's Transparency Boost: Integrating blockchain enhances supply chain transparency, traceability, and trust by securely recording transactions, combating counterfeits, and streamlining collaborations.
- Customization Balancing Act: Balancing customization with standardization ensures Automated Multi-Channel Order Management aligns with diverse manufacturing workflows while maintaining operational efficiency.
- Change Management's Vital Role: Overcoming resistance to automation relies on change management strategies that foster understanding, engagement, and collaboration among employees.
- Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation: Continuous monitoring and timely updates are crucial to keeping the system aligned with evolving business needs, technological advancements, and compliance requirements.
Related Articles











