Property tax is a tax assessed on real estate by local governments to fund public services and projects. It is one of the most stable sources of revenue for local governments, and an important part of their overall budget. Property tax helps to generate funds for public services and projects such as police and fire departments, schools, parks, libraries, and roads. Here is all you need to know about property tax.
This article covers the following:
- What Is Property Tax?
- How Is Property Tax Calculated?
- What Is Included in Property Tax?
- What Are Homestead Exemptions?
- How Can You Appeal Your Property Tax Bill?
- What Are the Benefits of Paying Property Tax?
- What Are the Penalties for Not Paying Property Tax?
- What Are the Local Property Tax Rates?
- How Can You Save Money on Property Tax?
- What Are the Most Common Property Tax Mistakes?
What is Property Tax?
Property tax is a tax imposed on real estate. It is based on the assessed value of a property, which is determined by local governments. The tax is generally used to fund public services such as education, public safety, infrastructure, and parks and recreation.
Property tax is usually paid annually or semi-annually and is collected by local governments. Property tax is based on the value of the property, which is determined by an assessor. The assessor evaluates the property and compares it to similar properties in the area.
He or she then applies a formula to determine the assessed value of the property. This assessed value is then used to calculate the property tax owed. Property taxes are typically based on a percentage of the assessed value.
The rate depends on the jurisdiction and can range from 0.1% to 3.5%. In addition, some local governments may levy special taxes on certain types of properties, such as vacant land or rental properties.
Property taxes are generally paid by the owner of the property. However, in some cases, tenants may be responsible for paying the property tax. This depends on the terms of the lease agreement.
Property tax is an important source of revenue for local governments and is used to fund a variety of public services. Property tax is also a way for local governments to encourage development and reinvestment in their communities.
How Is Property Tax Calculated?
Property tax is a tax levied on real estate by the government. It is usually based on the value of the property and is usually paid annually. The amount of property tax that an individual must pay can vary depending on the jurisdiction they live in, as each jurisdiction will have its own rules and regulations.
Generally, the amount of property tax calculation is based on the assessed value of the property, which is determined by the local property tax assessor. The assessed value of the property is usually based on the fair market value of the property.
This value is then multiplied by the local tax rate to determine the amount of property tax due. The local tax rate can vary depending on the jurisdiction, with some jurisdictions having a fixed rate and others having a progressive rate.
In addition to the assessed value of the property, various deductions can be applied to the property tax. These deductions can include homestead exemptions, military exemptions, and senior citizen exemptions. The amount of tax due may also be reduced if the property is owned by a nonprofit organization or is used for agricultural purposes.
Once the amount of property tax due has been calculated, it must be paid on time to avoid penalties and interest. Property tax is typically due in two or more installments throughout the year, and the due dates will vary depending on the jurisdiction.
Property tax is an important source of revenue for local governments, and it is important for homeowners to understand how their property tax is calculated in order to ensure they are paying the appropriate amount.
What All is Included in Property Tax?
Property tax is a tax imposed on real estate by the government. It is usually based on the assessed value of the property. Property tax is usually paid annually, but may also be paid on a quarterly or monthly basis.
Property tax is typically used to fund local services such as Public schools -Police and fire protection -Public transportation -Maintenance of parks and recreational facilities -Emergency medical services -Public libraries -Road and bridge maintenance.
Property taxes are typically structured in a way that the owner of the property is responsible for paying the full amount of the tax. The amount of the tax is determined by the assessed value of the property.
This includes the land, any buildings on the land, and any improvements that have been made to the land or buildings. In addition to the basic property tax rate, some jurisdictions add other taxes to the property tax, such as: -School district taxes -County taxes -City taxes -Special district taxes -Utility taxes -Transfer taxes -Assessment fees -Mortgage recording fees -Mortgage tax In some cases, property taxes can be appealed or reduced in certain situations.
For example, some states have homestead exemptions that allow homeowners to reduce the amount of their property tax by a certain percentage. Additionally, some jurisdictions offer tax abatements or incentives for certain types of properties or developments.
In conclusion, property tax is a tax imposed on real estate by the government, typically based on the assessed value of the property. It is used to fund local services and can include other taxes, such as school district taxes, county taxes, city taxes, and special district taxes. Property tax can be appealed or reduced in certain situations, such as homestead exemptions or tax abatements.
What are Homestead Exemptions?
Homestead exemptions are a form of property tax exemption that is offered to homeowners in many states. Homestead exemptions provide a reduction in the assessed value of a home, which can result in a lower amount of property taxes owed.
Generally, the homeowner must live in the home to be eligible for the exemption. The amount of the exemption can vary widely from state to state, and some states may offer additional exemptions based on the age of the homeowner or the size of the home.
Homestead exemptions are often applied automatically when the homeowner applies for a property tax bill, so it is important for homeowners to check with their local tax assessor’s office to ensure they are taking advantage of all available exemptions.
How Can You Appeal Your Property Tax Bill?
Property taxes are an important source of revenue for local governments and can have a significant impact on a homeowner’s budget. Property owners have the right to appeal their property tax bill if they believe it is too high. Here is a guide to the appeals process.
Research Your Property Tax Assessment
The first step in appealing your property tax bill is to research your assessment. You can find this information on your property tax bill. The assessment is based on the value of the property and is used to calculate the amount of tax due.
Gather Evidence and Documentation
After you have reviewed your assessment, gather any evidence and documentation that supports your case. This could include comparable property values, recent appraisals, and any repairs or improvements made to the property.
Contact Your Local Tax Assessor
Once you have all the necessary information, contact your local tax assessor to discuss your appeal. Make sure to provide any supporting documentation to back up your case.
File an Appeal
The next step is to file an appeal with your local government. You may need to fill out a form and provide any additional documentation. Depending on your local laws and regulations, you may need to appeal to a higher level of assessment.
Attend a Hearing
After you have filed your appeal, you may need to attend a hearing to present your case. Make sure to come prepared with all the necessary documents and evidence.
Wait for a Decision
After the hearing, the assessor will review your appeal and make a decision. Depending on the circumstances, your property tax bill may be reduced, or you may be granted a refund.
Appealing your property tax bill can be complicated and time-consuming, but it is worth the effort if you believe your assessment is too high. Make sure to research your assessment, gather evidence and documentation, contact your local tax assessor, and file an appeal with your local government. Good luck!
What Are the Benefits of Paying Property Tax?
Property taxes are a significant source of revenue for many local governments and are used to fund a variety of services and infrastructure. The advantages of paying property taxes include the following:
Improved Infrastructure
Property taxes fund roads, bridges, public transportation, parks, and other public works projects. Without these taxes, local governments would be unable to keep up with the necessary repairs and improvements to keep communities safe and functioning well.
Quality Public services
Property taxes fund police, fire, and other public safety departments. They also help fund public schools, libraries, and other essential services.
Community Stability
Property taxes help ensure that the local government has adequate funds to provide services and infrastructure. This helps to promote economic stability within the community.
Increased property values
Property taxes help to maintain and improve the quality of life in a community. This can result in an increase in property values and make the community a desirable place to live.
Tax relief
Property taxes can help to reduce the burden of other types of taxes, such as income taxes. This can be beneficial for those with lower incomes, as well as those on fixed incomes.
Investment incentives
Property taxes can provide incentives for businesses to invest in the local community. This can create jobs and help to attract more businesses to the area, which can ultimately benefit the community.
Overall, paying property taxes can help to promote a healthy and prosperous community. It can help to improve infrastructure and public services, as well as create incentives for businesses to invest in the local community. Property taxes can also provide tax relief for those with lower incomes and help to maintain stable property values.
What are the Penalties for not Paying Property Tax?
Property tax is a tax imposed on real estate by the government. It is typically based on the estimated value of the property and is used to fund public services such as schools, police and fire departments, and infrastructure maintenance.
Failure to pay property taxes can result in a variety of penalties, depending on the jurisdiction in which the property is located. These penalties can include increased interest, late fees, fines, and even foreclosure.
In some cases, the property owner may be subject to a lien or other legal action to collect unpaid taxes. In most cases, the local government will send a notice of delinquency to the property owner and give them a certain amount of time to pay the taxes.
If the taxes are not paid within the specified deadline, the local government may begin to assess additional penalties. Interest is typically imposed on the amount owed, and this interest rate is set by the jurisdiction.
In some cases, the interest rate can be as high as 18% or more. Additionally, most jurisdictions impose late fees when taxes are paid past the due date. These fees can range from a few dollars to hundreds of dollars, depending on the amount owed.
In more severe cases, the local government may take legal action to collect unpaid taxes. This might include the filing of a lien against the property or even foreclosure proceedings. In the case of a foreclosure, the property may be sold by the local government in order to collect the unpaid taxes.
The best way to avoid these penalties is to pay property taxes on time. If you are unable to pay your taxes in full, be sure to contact your local government as soon as possible in order to avoid any additional penalties.
What is the Local Property Tax Rates?
The local property tax rate is determined by the taxing authority in each jurisdiction. It is based on the assessed value of the property, which is determined by the local assessor’s office. The tax rate is typically expressed as a percentage of the assessed value and may vary from jurisdiction to jurisdiction.
Property tax rates can also be affected by local ordinances, such as exemptions for veterans, senior citizens, and other groups. Typically, the local property tax rate is set by the governing body of the jurisdiction.
To determine the rate, the governing body considers the needs of the jurisdiction, such as the cost of providing services and the potential revenue from the taxes. The rate is then used to calculate the amount of tax due on the property. The rate can vary significantly from one jurisdiction to another.
For example, the rate in rural areas may be lower than in urban areas because of the lower cost of providing services. Additionally, some jurisdictions may have higher rates in certain areas that are subject to additional taxes, such as those for schools, libraries, or public transportation.
It is important to note that the local property tax rate is not the only factor that determines the amount of a property’s tax bill. Other factors, such as the assessed value of the property, may also affect the amount of tax due.
Additionally, some jurisdictions may offer exemptions or credits that reduce the amount of tax due. To find the local property tax rate in your area, contact the local assessor’s office or the governing body of the jurisdiction. They can provide you with information on the rate, as well as any exemptions or credits that may be available.
How Can You Save Money on Property Tax?
Property taxes can be a major expense for homeowners and a significant source of revenue for local governments. Fortunately, there are several ways to save money on property taxes.
Stay Informed
The best way to save money on property taxes is to stay informed about your current value and any potential changes to the assessment. Many municipalities provide online tools for homeowners to access their assessment information. It is important to stay up to date on these changes to ensure that your tax bill is accurate.
Appeal Your Assessment
Many municipalities allow homeowners to appeal their assessed value. If you think that your assessed value is too high, you can appeal the assessment and potentially reduce your tax bill.
Take Advantage of Exemptions
Many municipalities offer exemptions for certain categories of homeowners. These exemptions can provide significant savings on your property taxes. It is important to research your local exemptions and determine if you qualify.
Invest in Home Improvements
Investing in improvements to your home can increase its value, which can reduce your tax bill. Home improvements can include anything from installing energy-efficient appliances to upgrading your roof.
Invest in Property Tax Relief Programs
Many states and local governments offer property tax relief programs for qualifying homeowners. These programs can provide significant savings on your property taxes.
By taking advantage of these strategies, you can save money on your property taxes and maximize your savings. It is important to stay informed and take advantage of all available options to reduce your property taxes.
What Are the Most Common Property Tax Mistakes?
Not Understanding the Nature of Property Tax
Property tax is a local tax on real and personal property. It is imposed by local governments such as counties and cities. It is a tax on the value of the property, not on the income of the owner. It is important to understand that property taxes are not the same as income taxes.
Not Knowing the Tax Basis
Many people fail to understand the tax basis used to calculate their property tax. The tax basis is the value of the property used to determine the amount of property tax owed. It is important to understand the tax basis and to make sure it is accurate.
Not Knowing the Property Tax Rates
Property taxes vary from one county to the next. It is important to be aware of the property tax rates in your county and to make sure that the taxes you are paying are accurate.
Not Understanding the Homestead Exemption
Many people don't understand the homestead exemption, which is a tax break given to homeowners in some states. The homestead exemption allows a homeowner to pay a lower amount of property tax.
Not Knowing the Property Assessed Value
Many people fail to understand the property assessed value, which is the value of the property used to calculate the amount of property tax owed. It is important to understand the assessed value and to make sure it is accurate.
Not Keeping Up with Property Tax Payments
Property taxes are typically due twice a year. It is important to stay on top of property tax payments and make sure they are paid on time.
Not Taking Advantage of Property Tax Breaks
Many people don't take advantage of available property tax breaks. It is important to do research and find out what tax breaks are available in your area.
Not Understanding How Property Tax is Calculated
Many people don't understand how property tax is calculated. It is important to understand the factors that go into calculating property tax, such as the property assessed value, the local tax rate, and any available tax breaks.
How Can Deskera Assist You?
Whether you are a sales manager or running your own business, there are tons of duties and responsibilities that you have to fulfill. Using the Deskera CRM system, you can manage your contacts, leads, and sales deals.
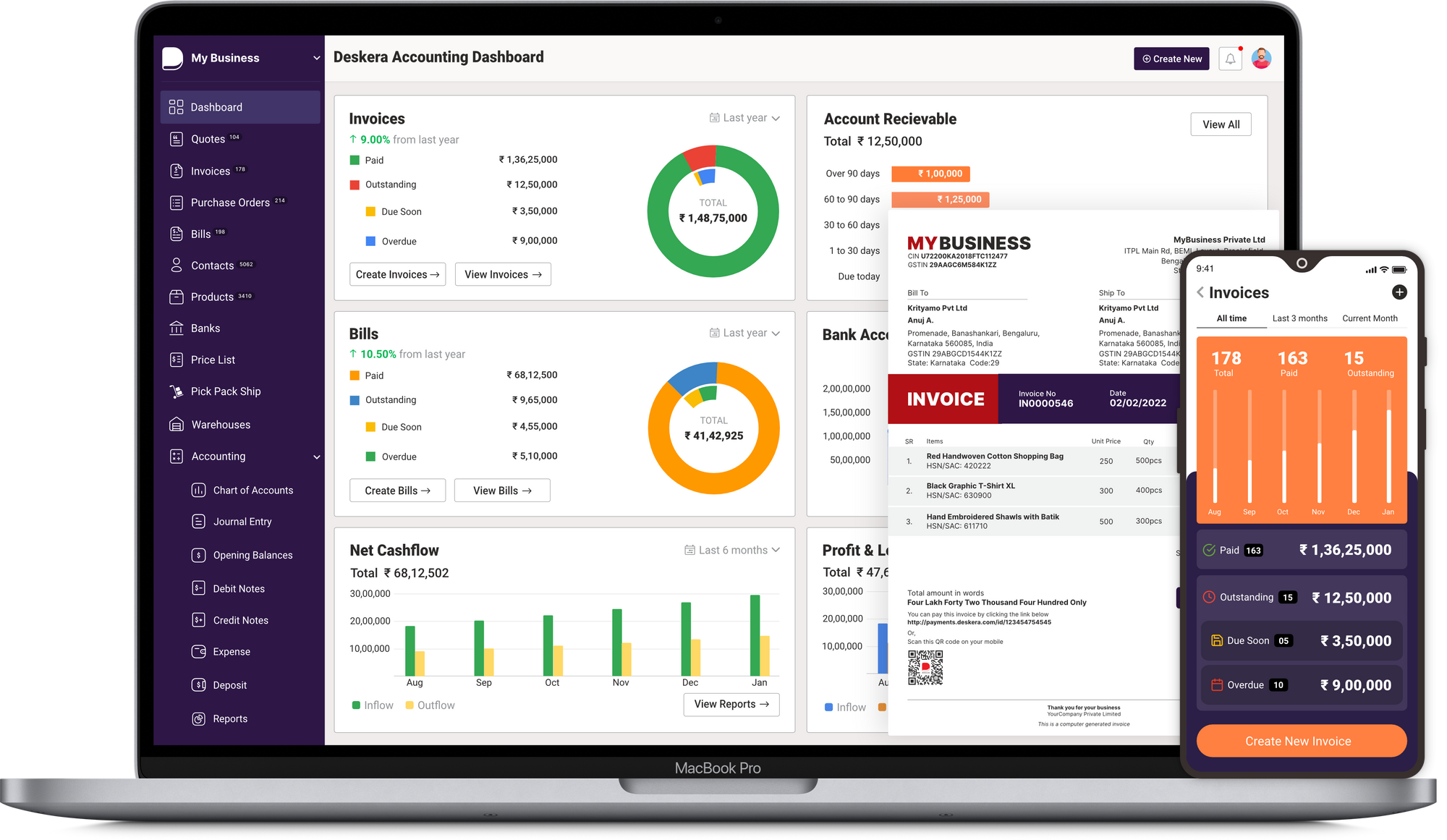
You can use the CRM system to manage all customer data and manage your leads, sales negotiations, and deals. Doing so will help you to save the time taken in transferring customer data between the different systems. Having a good CRM system will help you manage your financial and sales reports and be prepared to kick off your meetings.
Deskera can also assist you with real-time updates about your business, like cash flow status, customer satisfaction, inventory management, sales, purchases, purchase orders, customer tickets, customer satisfaction, managing leads, revenues, profit and loss statements, and balance sheets.
Moreover, it would also help in integrating sales methodology across different platforms into one system so that you have a consolidated list for email campaigns, leads management, and sales pipeline, to mention a few.
Key Takeaways:
- Property tax is a tax imposed on real estate. It is based on the assessed value of a property, which is determined by local governments.
- Generally, the amount of property tax calculation is based on the assessed value of the property, which is determined by the local property tax assessor.
- Property tax is typically used to fund local services.
- Homestead exemptions are a form of property tax exemption that is offered to homeowners in many states.
- Property taxes are a significant source of revenue for many local governments and are used to fund a variety of services and infrastructure.
Related Articles:










