Is your production process struggling with inefficiencies, bottlenecks, or missed deadlines? If so, the issue likely stems from inadequate production planning and scheduling.
In today's fast-paced manufacturing environment, staying ahead of demand and efficiently managing resources is crucial for maintaining competitiveness. Production planning and scheduling ensure that your operations run smoothly, costs are minimized, and products are delivered on time.
But what is production planning exactly, and why is it so critical? Production planning is the process of determining what needs to be produced, when, and how. It involves aligning resources such as materials, labor, and machinery with the forecasted demand.
This creates a roadmap that helps businesses meet their production goals efficiently. When combined with effective scheduling, which optimizes the timing of each task, production management can drastically improve performance.
The right production planning and scheduling software can further streamline this process by automating task assignments, tracking inventory levels, and managing workflows.
Tools like Deskera MRP, for example, not only simplify the production planning process but also enhance visibility into every aspect of production. Deskera’s features, such as demand forecasting, real-time data tracking, and automated scheduling, empower businesses to respond faster to market changes while reducing waste and lead times.
By mastering production planning and control, businesses can not only meet their current production goals but also position themselves for long-term growth and efficiency. This guide will walk you through every step of the process, from foundational concepts to real-world examples and best practices.
What is Production Planning?
Production planning is the process of organizing and optimizing the production flow within a manufacturing or business environment. Its main goal is to ensure that goods are produced efficiently, with minimal waste, and meet customer demand on time. This involves determining what products to make, the quantities required, and the resources needed, including materials, labor, and equipment.
At its core, production planning aligns production activities with demand forecasts to create a clear roadmap for manufacturers. By planning the allocation of resources and production tasks, businesses can avoid delays, prevent overproduction or shortages, and make the most of their operational capacity.
In the modern business world, leveraging production planning software can significantly improve this process. Such software helps businesses automate tasks, monitor resources in real-time, and adjust schedules as demand changes. Whether you're a small business or a large enterprise, having a well-defined production planning process is essential for maintaining efficiency, reducing costs, and ensuring customer satisfaction.
A good production planning example includes coordinating raw materials for a specific batch of products to be ready at the same time that the workforce and machinery are scheduled to produce it, minimizing downtime and ensuring a smooth workflow from start to finish.
Key Components of Production Planning
Production planning is a multi-faceted process that requires careful coordination of various elements to ensure efficient production flow.
Below are the key components of production planning:
- Demand Forecasting: A successful production plan begins with accurate demand forecasting. This involves predicting customer demand based on historical data, market trends, and sales projections. By understanding future demand, companies can plan for the right amount of materials, workforce, and time to meet production goals without overproducing or under producing.
- Resource Allocation: Once demand is forecasted, the next step in production planning is determining the resources needed to meet that demand. This includes raw materials, labor, machinery, and financial resources. Proper resource allocation ensures that materials and equipment are available when needed, preventing delays and bottlenecks in production.
- Inventory Management: Managing inventory levels is essential to avoid overstocking or running out of crucial materials. Effective inventory control ensures that the right materials are available at the right time. Modern production planning software often integrates with inventory systems, enabling businesses to track stock levels in real time and reorder materials as needed.
- Production Scheduling: After resource allocation, production scheduling defines the specific tasks, timelines, and sequencing required to produce goods efficiently. Scheduling ensures that the production process flows smoothly and that all necessary resources are used optimally. Tools like Deskera MRP assist in automating these schedules and adapting to real-time changes in demand or resource availability.
- Workforce Management: Labor is a crucial resource in any production plan. Workforce management involves ensuring that the right number of skilled employees are available for each production task. It also includes shift scheduling, workload balancing, and sometimes training staff to handle specific production tasks.
- Production Control: Monitoring and controlling the production process is essential to ensure that the plan is executed as designed. This includes tracking production progress, identifying issues like delays or equipment malfunctions, and making real-time adjustments to maintain efficiency. Production control provides feedback to adjust future production planning.
- Quality Control: Maintaining high-quality standards is another vital component of production planning. By integrating quality checks at different stages of production, businesses can ensure that finished products meet customer expectations. This helps in reducing waste and avoiding costly rework.
Each of these components works together to create an efficient production planning process. By utilizing tools like ERP systems, companies can better manage their resources and improve productivity.
What is Production Scheduling?
Production scheduling is the process of organizing and assigning specific tasks, timelines, and resources to ensure that a production plan is executed efficiently. It focuses on the “when” and “how” of production, detailing which tasks should be completed, in what order, and by which resources, such as labor or machinery. In essence, production scheduling transforms a broad production plan into actionable steps that meet deadlines and optimize resource usage.
Effective production scheduling not only minimizes idle time and reduces bottlenecks but also helps companies manage capacity, balance workloads, and streamline the entire production process. It ensures that each phase of production is aligned with delivery deadlines and resource availability, helping businesses meet customer demands on time without overworking staff or equipment.
To simplify the scheduling process, many companies rely on production planning and scheduling software. This software automates the allocation of tasks, adjusts schedules in real-time as disruptions occur, and tracks resource availability. An ERP system with integrated production scheduling features, such as Deskera MRP, can help manufacturers stay agile by dynamically adjusting schedules based on demand fluctuations or unexpected delays.
When done well, production scheduling enhances productivity, reduces operational costs, and allows for more accurate planning and control of production activities. By keeping a clear, organized schedule, businesses can ensure that they meet production targets while maintaining high efficiency.
Types of Production Schedules
Production scheduling plays a critical role in ensuring that resources are used efficiently, and deadlines are met. There are several types of production schedules that companies use, each designed to manage different production environments.
Below are the main types:
1. Master Production Schedule (MPS)
The Master Production Schedule is a comprehensive plan that outlines what needs to be produced, in what quantity, and when. It serves as the foundation of the entire production process, aligning resources, inventory, and demand forecasts. The MPS is often created based on customer orders or sales projections, ensuring that production aligns with market demand.
The MPS provides an overall view of the production process, typically for the medium to long term, and is used to guide more detailed scheduling activities. Many businesses use production planning software or ERP systems like Deskera MRP to automate the creation and monitoring of the MPS.
2. Job Shop Scheduling
Job shop scheduling is used in environments where production involves custom or small-batch products, with each job having unique requirements. This type of scheduling is flexible and tailored to individual orders. It ensures that each job moves through various workstations or processes in the correct sequence and with the right timing.
For example, in manufacturing sectors like aerospace or custom fabrication, job shop scheduling helps manage the complex routing of jobs through different departments.
3. Batch Production Scheduling
In batch production, products are made in specific quantities or "batches" rather than in a continuous flow. Batch scheduling organizes the production of a certain quantity of items before switching to another batch of a different product. This is commonly used in industries like food processing, pharmaceuticals, and textiles, where different products may require similar resources but are produced in separate batches.
Batch production scheduling is essential for reducing downtime between shifts in production and optimizing the use of equipment and resources.
4. Flow Shop Scheduling
Flow shop scheduling is used in environments where production processes follow a fixed sequence of operations. In this system, products move through different workstations in the same order, making it highly suitable for high-volume, standardized production, such as automotive or electronics manufacturing.
Flow shop scheduling aims to minimize delays and bottlenecks by ensuring that each operation flows smoothly from one stage to the next, keeping production as continuous as possible.
5. Just-In-Time (JIT) Scheduling
Just-In-Time scheduling focuses on producing goods only when they are needed, minimizing waste and reducing inventory costs. This system aligns production schedules with customer demand and supply chain efficiency, ensuring that products are made to order, reducing storage costs and material waste. JIT is commonly used in industries like automotive manufacturing, where lean production is critical.
6. Project-Based Scheduling
Project-based scheduling is used for one-time or large-scale production processes, such as construction, shipbuilding, or large equipment manufacturing. This type of scheduling is highly detailed and involves managing tasks and timelines for a specific project. It accounts for unique project requirements, such as specialized resources or longer production times, and ensures that each stage is completed on time.
Production Planning vs. Production Scheduling
While production planning and production scheduling are closely related processes, they serve distinct roles in manufacturing and production management. Understanding the differences between the two can help businesses optimize their operations and meet production goals efficiently.
Here's a breakdown of each:
Production Planning
Production planning is the broader, strategic process that outlines what needs to be produced, when, and how. It involves determining the production goals based on demand forecasts, resource availability, and company objectives.
The aim of production planning is to create a detailed roadmap for resource allocation, production timelines, and workflow to ensure that products are manufactured efficiently and meet customer demand.
Key elements of production planning include:
- Forecasting demand to align production with market needs.
- Allocating resources, such as raw materials, labor, and machinery.
- Managing inventory to ensure materials are available without overstocking.
- Establishing production timelines and goals.
In essence, production planning answers the "what," "how much," and "when" questions for production. It sets the stage for a smooth production process, helping businesses avoid bottlenecks, reduce waste, and control costs.
Production Scheduling
Production scheduling, on the other hand, is more tactical and focuses on when and how the planned production will take place. It breaks down the production plan into specific tasks, assigning resources (machinery, labor) and timeframes for each task or process. Scheduling ensures that every step of the production process is optimized for time and efficiency, minimizing idle time and delays.
Key elements of production scheduling include:
- Defining the order and timing of tasks to be completed.
- Assigning tasks to specific resources, such as machines or employees.
- Monitoring real-time progress and adjusting schedules as needed.
- Ensuring that production deadlines are met without overloading resources.
In short, production scheduling answers the "when" and "who" questions, focusing on executing the production plan in the most efficient way possible.
Key Differences Between Production Planning and Production Scheduling
Example
A production planning example would be a manufacturer forecasting demand for 10,000 units of a product over the next quarter, determining the required materials, labor, and machinery, and setting timelines for production.
In contrast, production scheduling would involve assigning specific tasks to workers, scheduling machine time, and ensuring that each phase of production happens at the right time to meet the deadline.
Together, production planning and scheduling work hand in hand to ensure that manufacturing processes are efficient, cost-effective, and aligned with business goals.
Importance of Production Planning and Scheduling
Production planning and scheduling are fundamental components of manufacturing operations that directly influence efficiency, cost management, and product quality.
Here are several key reasons highlighting their importance:
1. Optimizes Resource Utilization
Effective production planning and scheduling ensure that all resources—labor, equipment, and materials—are utilized to their fullest potential. By aligning production schedules with resource availability, businesses can minimize downtime and reduce waste, ultimately maximizing efficiency.
2. Improves Customer Satisfaction
By accurately forecasting demand and scheduling production accordingly, companies can meet customer orders on time and reduce lead times. This reliability enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty, as clients are more likely to return to businesses that consistently deliver on their promises.
3. Reduces Costs
A well-structured production plan helps minimize operational costs by reducing excess inventory and lowering labor costs associated with inefficiencies. By implementing lean production practices through effective scheduling, companies can significantly decrease waste and enhance profitability.
4. Enhances Flexibility and Responsiveness
In today’s fast-paced market, the ability to adapt quickly to changing demand is crucial. Effective production planning and scheduling allow manufacturers to respond swiftly to fluctuations in customer orders, ensuring they can pivot their operations without significant disruptions.
5. Streamlines Operations
Clear production plans and schedules provide a roadmap for operations, ensuring that everyone involved understands their roles and responsibilities. This clarity helps streamline workflows, reduces errors, and improves overall production efficiency.
6. Facilitates Better Communication
A solid production schedule fosters better communication among different departments—such as production, sales, and supply chain—by providing a common reference point. This alignment ensures that all teams work collaboratively toward common goals, improving coordination and reducing misunderstandings.
7. Supports Quality Control
Production planning incorporates quality control measures, allowing manufacturers to establish standards and checkpoints throughout the production process. By scheduling regular inspections and quality assessments, companies can catch defects early and maintain high product quality.
8. Enables Strategic Decision-Making
Having a clear view of production capabilities and schedules allows management to make informed strategic decisions regarding capacity planning, inventory management, and resource allocation. This data-driven approach enables organizations to identify opportunities for improvement and growth.
9. Enhances Risk Management
Effective production planning and scheduling enable manufacturers to anticipate potential risks—such as supply chain disruptions or equipment failures—and develop contingency plans. By preparing for unforeseen circumstances, companies can mitigate risks and maintain production continuity.
10. Boosts Employee Morale
When production plans and schedules are clear and well-communicated, employees are more likely to feel engaged and empowered in their roles. This clarity reduces confusion and frustration, leading to higher morale and productivity among the workforce.
In summary, production planning and scheduling are vital for achieving operational excellence in manufacturing. By prioritizing these processes, companies can enhance efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and position themselves for long-term success in a competitive marketplace.
How Production Planning and Scheduling Work Together
Production planning and scheduling are complementary processes that work hand-in-hand to optimize manufacturing operations and ensure efficient use of resources. While production planning sets the strategic foundation for what needs to be produced, production scheduling turns that plan into actionable tasks.
Here’s how the two processes collaborate for smooth and efficient production:
Strategic Foundation with Production Planning
The process begins with production planning, which creates a high-level strategy. This includes forecasting demand, determining the resources required (materials, labor, machinery), and setting production goals.
Production planning ensures that businesses have a clear roadmap, aligning production capacity with customer demand. By allocating resources in advance, production planning prevents shortages and overstocking.
Detailed Execution with Production Scheduling
Once the production plan is in place, scheduling takes over by creating a detailed execution plan. This involves breaking down the larger production goals into specific tasks and assigning those tasks to machines and workers.
Scheduling ensures that the right resources are used at the right time, optimizing the flow of work to minimize bottlenecks, delays, and idle time.
Real-Time Coordination and Adjustments
Production planning sets the goals, but scheduling ensures that those goals are met efficiently.
If unforeseen circumstances arise—such as equipment breakdowns or labor shortages—production scheduling can adjust the timeline or resource allocation accordingly.
Real-time adjustments help keep production on track, ensuring that deadlines are met and costs are controlled.
Enhanced Efficiency and Flexibility
Together, production planning and scheduling maximize the use of resources and streamline workflows. While planning focuses on long-term strategy and resource allocation, scheduling brings in flexibility by adapting to daily or weekly production needs. This coordination allows businesses to respond more effectively to changing demand, minimizing downtime and improving overall production efficiency.
By working together, production planning and scheduling ensure that manufacturing processes are well-organized, responsive to demand, and able to deliver products on time, all while optimizing resources.
Key Steps in Production Planning and Scheduling
Effective production planning and scheduling involve a series of coordinated steps that ensure resources are allocated efficiently, production goals are met, and processes run smoothly.
Here’s a breakdown of the key steps involved in each phase:
1. Demand Forecasting
- Objective: Estimate future customer demand based on historical data, market trends, and sales forecasts.
- Action: Analyze sales patterns, seasonal trends, and economic indicators to create accurate demand forecasts. This forms the basis for planning production levels.
2. Resource Assessment
- Objective: Evaluate the resources available for production, including raw materials, labor, and machinery.
- Action: Conduct an inventory check to ensure the necessary materials are available and assess the capacity and availability of labor and equipment.
3. Production Planning
- Objective: Develop a comprehensive production plan that aligns with the demand forecast and resource availability.
- Action: Set production targets, allocate resources, and establish timelines. This includes determining how much of each product will be produced and scheduling the necessary operations.
4. Production Scheduling
- Objective: Translate the production plan into a detailed schedule that outlines specific tasks and timelines.
- Action: Create a schedule that assigns tasks to specific machines and workers, outlines the order of operations, and sets start and end times for each task. This includes defining production batches and setting up workstations.
5. Implementation
- Objective: Execute the production schedule as planned.
- Action: Begin the production process, ensuring that all resources are in place and that workers understand their tasks and timelines. Maintain clear communication among teams to facilitate smooth operations.
6. Monitoring and Adjusting
- Objective: Track progress in real-time and ensure the production schedule is being followed.
- Action: Use production management software to monitor performance against the schedule. If issues arise, such as delays or resource shortages, make adjustments to the schedule to stay on track.
7. Quality Control
- Objective: Ensure that the products being produced meet quality standards.
- Action: Implement quality checks throughout the production process to identify and address any defects or issues immediately, reducing waste and rework.
8. Performance Evaluation
- Objective: Assess the effectiveness of the production planning and scheduling process.
- Action: After production is complete, evaluate performance metrics, such as adherence to schedules, resource utilization, and product quality. Analyze this data to identify areas for improvement.
9. Continuous Improvement
- Objective: Refine the production planning and scheduling process over time.
- Action: Incorporate feedback from performance evaluations to make adjustments to future production plans and schedules. Utilize insights from data analysis to enhance forecasting accuracy and optimize resource allocation.
By following these key steps, businesses can create an efficient production planning and scheduling process that enhances productivity, reduces costs, and improves overall operational performance.
Methods and Tools for Effective Production Planning and Scheduling
Efficient production planning and scheduling are crucial for optimizing manufacturing operations, meeting customer demand, and maintaining cost-effectiveness. Various methods and tools can be employed to achieve these objectives.
Here’s a look at some of the most effective approaches and tools available for production planning and scheduling:
1. Methods of Production Planning and Scheduling
A. Just-In-Time (JIT) Production
- Description: JIT focuses on minimizing inventory levels by scheduling production to meet customer demand precisely when needed.
- Benefits: Reduces waste, lowers inventory holding costs, and increases efficiency by aligning production with actual sales.
B. Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
- Description: MRP is a method that calculates material requirements and scheduling based on production plans and inventory levels.
- Benefits: Helps manage inventory levels, ensures timely procurement of materials, and aligns production schedules with demand.
C. Lean Manufacturing
- Description: Lean focuses on maximizing value by eliminating waste throughout the production process.
- Benefits: Enhances efficiency, reduces costs, and improves product quality by streamlining operations and workflows.
D. Theory of Constraints (TOC)
- Description: TOC is a management philosophy that identifies and addresses the bottlenecks or constraints that hinder production flow.
- Benefits: Enhances throughput, optimizes resource allocation, and improves overall system performance by focusing on constraints.
E. Agile Manufacturing
- Description: Agile manufacturing emphasizes flexibility and responsiveness to changing market demands and customer needs.
- Benefits: Increases adaptability, allowing businesses to quickly pivot in response to demand fluctuations.
2. Tools for Production Planning and Scheduling
A. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
- Description: ERP systems integrate various business processes, including production planning, inventory management, and finance, into a single platform.
- Example: Deskera ERP offers features for demand forecasting, resource allocation, and real-time scheduling, helping streamline production planning and control.
B. Production Planning Software
- Description: Dedicated software solutions designed specifically for production planning and scheduling tasks.
- Features: These tools often include features for Gantt charts, capacity planning, scheduling algorithms, and real-time tracking.
C. Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) Systems
- Description: APS systems use complex algorithms to optimize production schedules based on various constraints, such as resource availability and demand fluctuations.
- Benefits: They allow for more dynamic scheduling, helping manufacturers adapt to changing conditions and resource limitations.
D. Kanban Boards
- Description: A visual scheduling tool that helps manage workflow and tasks by using cards or sticky notes to represent tasks on a board.
- Benefits: Provides a clear overview of the production process, facilitates communication among team members, and enhances workflow visibility.
E. Gantt Charts
- Description: Gantt charts are visual timelines that represent tasks, their durations, and dependencies in a production schedule.
- Benefits: They help track progress, identify overlaps, and manage resource allocation effectively.
F. Capacity Planning Tools
- Description: Tools that analyze production capacity and help identify potential bottlenecks in the workflow.
- Benefits: These tools enable manufacturers to optimize resource allocation and ensure that production schedules align with available capacity.
3. Best Practices for Implementation
- Integrate Systems: Use integrated tools and software to ensure that production planning and scheduling are connected to inventory management, sales, and procurement.
- Train Employees: Provide training for staff on new tools and methods to ensure effective implementation and maximize the benefits of production planning and scheduling systems.
- Continuously Monitor and Adjust: Regularly review and analyze production performance data to identify areas for improvement and adjust processes as needed.
- Encourage Collaboration: Foster communication and collaboration among different departments to align production planning and scheduling with sales and customer service teams.
By employing these methods and tools, businesses can enhance their production planning and scheduling processes, resulting in improved efficiency, reduced costs, and better alignment with customer demand.
Challenges in Production Planning and Scheduling and How to Overcome Them
Production planning and scheduling are critical to successful manufacturing operations, but they come with several challenges that can disrupt workflows, increase costs, and affect product quality.
Here’s a look at common challenges faced in production planning and scheduling, along with effective strategies to overcome them.
1. Demand Variability
Challenge: Fluctuations in customer demand can lead to overproduction or underproduction, resulting in excess inventory or stockouts.
Solution: Implement demand forecasting tools and techniques, such as statistical analysis or machine learning algorithms, to predict changes in demand more accurately. Regularly review forecasts and adjust production schedules accordingly to maintain balance.
2. Resource Constraints
Challenge: Limited availability of resources, such as labor, machinery, and raw materials, can disrupt production schedules and delay orders.
Solution: Conduct regular assessments of resource availability and use capacity planning tools to identify potential bottlenecks. Develop contingency plans for resource shortages and explore partnerships with suppliers to ensure timely delivery of materials.
3. Production Delays
Challenge: Equipment failures, maintenance issues, or labor shortages can lead to unexpected delays in production.
Solution: Adopt a proactive maintenance strategy for machinery to minimize breakdowns and schedule regular maintenance during non-peak hours. Cross-train employees to fill in for absent workers, ensuring that production continues smoothly even with staff shortages.
4. Complexity of Production Processes
Challenge: Complex production processes with numerous tasks and dependencies can make scheduling difficult and lead to confusion among workers.
Solution: Utilize production planning and scheduling software that offers visualization tools, such as Gantt charts and Kanban boards, to simplify the scheduling process. Clear documentation of workflows and employee responsibilities can also help mitigate confusion.
5. Lack of Real-Time Data
Challenge: Inadequate access to real-time data can hinder decision-making and lead to misalignment between production and demand.
Solution: Invest in integrated systems, such as ERP and MRP software, that provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, production status, and resource availability. Use this data to make informed adjustments to production plans and schedules promptly.
6. Ineffective Communication
Challenge: Poor communication between departments can lead to misalignment of production schedules and expectations, causing delays and inefficiencies.
Solution: Foster a culture of open communication by implementing regular meetings and updates between teams involved in production, sales, and supply chain management. Utilize collaboration tools and platforms to ensure all stakeholders are informed and aligned on production plans.
7. Resistance to Change
Challenge: Employees may resist new methods, technologies, or processes, hindering the implementation of efficient production planning and scheduling practices.
Solution: Provide training and support to employees when introducing new tools or processes, highlighting the benefits of these changes. Involve team members in the decision-making process to foster buy-in and reduce resistance.
By identifying and addressing these challenges in production planning and scheduling, manufacturers can create a more efficient, responsive, and effective production environment. Implementing the right strategies and tools will lead to improved resource utilization, enhanced product quality, and ultimately, greater customer satisfaction.
The Role of Technology in Production Planning and Scheduling
Technology plays a pivotal role in modern production planning and scheduling, transforming traditional manufacturing practices into efficient, data-driven processes. By leveraging advanced tools and systems, manufacturers can optimize their operations, enhance productivity, and respond to market demands more effectively.
Here’s an overview of how technology influences production planning and scheduling:
1. Automation of Processes
Role: Automation technologies, such as robotics and AI, streamline repetitive tasks in production planning and scheduling, reducing manual intervention.
Benefits: This automation leads to increased efficiency, fewer errors, and faster processing times, allowing employees to focus on more strategic tasks.
2. Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) Systems
Role: APS systems utilize sophisticated algorithms and data analytics to optimize production schedules based on various constraints, such as resource availability and demand fluctuations.
Benefits: These systems enable real-time adjustments to schedules, ensuring that production aligns with customer needs while minimizing delays and bottlenecks.
3. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Software
Role: ERP systems integrate various business processes, including production planning, inventory management, and finance, into a unified platform.
Benefits: By providing a holistic view of operations, ERP software facilitates better decision-making and enhances communication among different departments, leading to more efficient production planning and scheduling.
4. Internet of Things (IoT)
Role: IoT devices collect real-time data from machinery and equipment, providing insights into production performance and resource utilization.
Benefits: This data enables manufacturers to monitor operations closely, identify potential issues before they escalate, and make informed adjustments to production plans and schedules.
5. Data Analytics and Forecasting Tools
Role: Data analytics tools analyze historical data and market trends to improve demand forecasting and inform production planning.
Benefits: Enhanced forecasting accuracy allows manufacturers to align production schedules more closely with customer demand, reducing the risk of overproduction or stockouts.
6. Cloud-Based Solutions
Role: Cloud-based software solutions offer flexibility and scalability for production planning and scheduling, allowing manufacturers to access and manage data from anywhere.
Benefits: This accessibility promotes collaboration among teams, improves responsiveness to changes in demand, and supports remote work environments.
7. Visualization Tools
Role: Tools like Gantt charts and Kanban boards provide visual representations of production schedules and workflows, making it easier to understand and manage complex processes.
Benefits: These tools enhance transparency, improve communication among team members, and facilitate quicker adjustments to production plans.
8. Integration with Supply Chain Management
Role: Technology enables seamless integration between production planning and supply chain management, allowing for real-time updates on inventory levels and supplier statuses.
Benefits: This integration enhances coordination between production and procurement, ensuring that materials are available when needed and reducing lead times.
9. Simulation and Modeling Software
Role: Simulation tools allow manufacturers to model different production scenarios, enabling them to test various planning and scheduling approaches without disrupting actual operations.
Benefits: This capability helps identify optimal production strategies, assess the impact of changes, and make informed decisions based on data-driven insights.
10. Continuous Improvement through Technology
Role: Technology fosters a culture of continuous improvement by providing the tools and data necessary to analyze performance and identify areas for enhancement.
Benefits: By leveraging insights from technology, manufacturers can refine their production planning and scheduling processes over time, leading to ongoing efficiency gains and cost reductions.
In conclusion, technology is a critical enabler of effective production planning and scheduling in modern manufacturing. By embracing advanced tools and systems, organizations can optimize their operations, enhance flexibility, and better meet customer demands, ultimately driving competitiveness and profitability in the marketplace.
Best Practices for Streamlining Production Planning and Scheduling
Streamlining production planning and scheduling is essential for enhancing operational efficiency, reducing costs, and improving overall productivity. By adopting best practices, manufacturers can create a more agile and responsive production environment.
Here are some effective strategies to consider:
1. Define Clear Objectives and KPIs
Establishing clear objectives for production planning and scheduling is vital. Identify key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with business goals, such as on-time delivery rates, production efficiency, and inventory turnover. Regularly monitor these metrics to assess performance and make informed adjustments.
2. Implement Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) Systems
Utilizing APS systems can significantly enhance scheduling accuracy and efficiency. These systems leverage algorithms to optimize production schedules based on various constraints, such as resource availability and demand fluctuations. Investing in robust APS technology can streamline workflows and reduce lead times.
3. Foster Cross-Department Collaboration
Effective communication and collaboration between departments—such as production, sales, and supply chain—are crucial for successful planning and scheduling. Regular meetings and updates can ensure alignment on production priorities and customer demands, leading to more coordinated efforts.
4. Utilize Demand Forecasting
Accurate demand forecasting is essential for effective production planning. Employ statistical analysis and data analytics tools to predict customer demand accurately. Regularly update forecasts based on market trends and historical data to ensure that production schedules align with actual demand.
5. Embrace Lean Manufacturing Principles
Adopting lean manufacturing principles can help eliminate waste and optimize processes. Focus on value-added activities and continuously assess production workflows for inefficiencies. Implementing practices such as Just-In-Time (JIT) production can reduce excess inventory and streamline scheduling.
6. Leverage Technology and Automation
Investing in technology and automation tools can enhance efficiency in production planning and scheduling. Automated systems can handle repetitive tasks, improve data accuracy, and provide real-time insights into production performance. Consider integrating ERP systems for a holistic view of operations.
7. Develop Flexible Production Schedules
Creating flexible production schedules allows manufacturers to adapt quickly to changes in demand or unforeseen disruptions. Use techniques like rolling scheduling, where schedules are continuously updated based on real-time data, to maintain responsiveness and agility in production operations.
8. Optimize Resource Allocation
Efficient resource allocation is critical for successful production scheduling. Regularly assess resource availability, including labor, equipment, and materials. Implement capacity planning tools to identify potential bottlenecks and optimize resource utilization to minimize downtime.
9. Monitor and Adjust in Real-Time
Real-time monitoring of production processes is essential for effective scheduling. Utilize IoT devices and data analytics to track production progress, identify issues, and make immediate adjustments to schedules. This proactive approach helps maintain efficiency and reduces the impact of disruptions.
10. Invest in Employee Training
Equipping employees with the necessary skills and knowledge is vital for successful production planning and scheduling. Provide regular training on new technologies, processes, and best practices to enhance workforce capabilities. Empowering employees to contribute to planning efforts can lead to innovative solutions and improved outcomes.
11. Evaluate and Refine Processes Continuously
Continuous improvement is key to streamlining production planning and scheduling. Regularly evaluate existing processes, gather feedback from employees, and identify areas for enhancement. Implement a culture of continuous improvement to foster innovation and adaptability in production operations.
12. Use Visualization Tools
Incorporating visualization tools, such as Gantt charts or Kanban boards, can help teams better understand production schedules and workflows. These tools provide a clear visual representation of tasks and timelines, improving communication and coordination across departments.
By implementing these best practices, manufacturers can streamline their production planning and scheduling processes, leading to improved efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced customer satisfaction. Embracing a proactive and data-driven approach will enable organizations to thrive in a competitive manufacturing landscape.
How Deskera MRP Can Help with Production Planning and Scheduling
Deskera MRP (Material Requirements Planning) offers a comprehensive suite of tools designed to streamline production planning and scheduling processes. By leveraging advanced features and functionalities, Deskera MRP enables businesses to optimize their operations, enhance efficiency, and improve decision-making.
Here are several ways Deskera MRP can assist with production planning and scheduling:
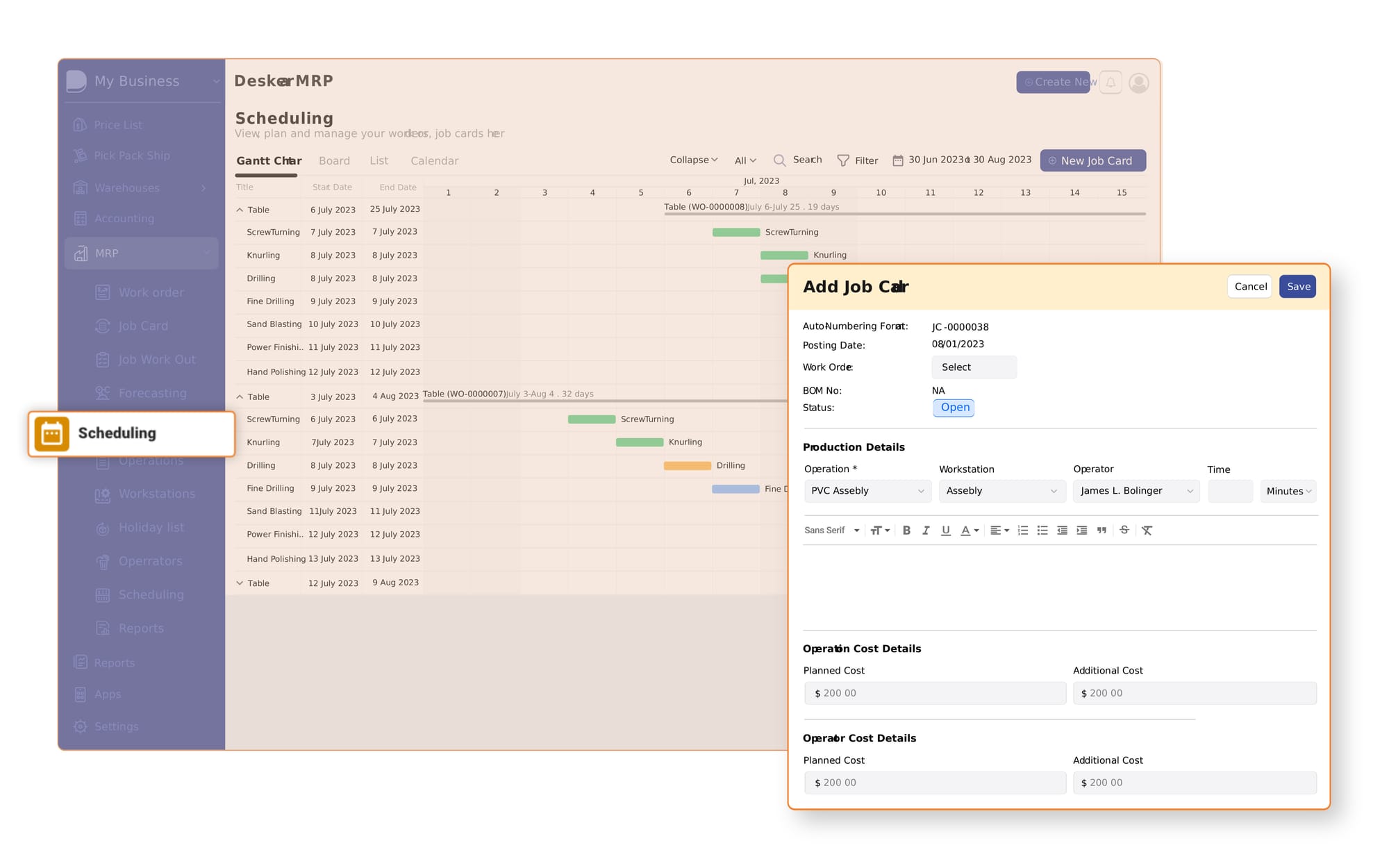
1. Real-Time Data Access
Deskera MRP provides real-time access to critical data, including inventory levels, production status, and demand forecasts. This visibility allows manufacturers to make informed decisions quickly, ensuring that production plans align with current business needs and market conditions.
2. Demand Forecasting
Utilizing advanced analytics, Deskera MRP enables accurate demand forecasting based on historical data and market trends. This capability helps manufacturers anticipate customer needs and adjust production schedules accordingly, reducing the risk of overproduction or stockouts.
3. Resource Management
With Deskera MRP, businesses can efficiently manage resources such as labor, materials, and equipment. The platform provides insights into resource allocation, helping manufacturers optimize utilization and reduce idle time. This efficient resource management enhances overall productivity.
4. Integration with Inventory Management
Deskera MRP integrates seamlessly with inventory management functions, ensuring that production planning is aligned with inventory levels. By maintaining optimal stock levels and ensuring timely availability of materials, manufacturers can prevent delays in production schedules.
5. Flexible Production Planning
Deskera MRP supports flexible production planning, allowing businesses to quickly adapt to changes in demand or production constraints. Users can easily adjust schedules and resources based on real-time data, promoting agility in response to market fluctuations.
6. Visualization Tools
The platform offers visualization tools, such as dashboards, to provide a clear overview of production schedules and workflows. These tools enhance communication among team members and facilitate better coordination across departments, leading to smoother operations.
7. Reporting and Analytics
Deskera MRP includes robust reporting and analytics features that help manufacturers evaluate production performance. By analyzing key metrics and trends, businesses can identify areas for improvement, make data-driven decisions, and refine their production planning and scheduling processes.
8. Collaboration Features
Deskera MRP fosters collaboration among different teams involved in production planning and scheduling. The platform enables easy sharing of information and updates, ensuring that everyone is aligned on priorities and deadlines, which enhances overall operational efficiency.
9. Continuous Improvement
By leveraging Deskera MRP’s insights and analytics, businesses can establish a culture of continuous improvement. Regularly evaluating production processes and making data-driven adjustments enables manufacturers to enhance efficiency and responsiveness over time.
Key Takeaways
- Production planning involves strategizing the entire production process to ensure that products are manufactured efficiently and meet customer demands. A well-defined production planning process lays the foundation for successful operations.
- Production scheduling focuses on assigning specific tasks to resources at particular times to optimize manufacturing processes. Effective scheduling is critical to achieving production targets while minimizing downtime and resource waste.
- Key components of production planning include demand forecasting, resource allocation, and production scheduling. Understanding and integrating these elements is essential for a cohesive production strategy.
- Various types of production schedules—such as master schedules, weekly schedules, and daily schedules—serve different purposes. Selecting the right scheduling method based on production needs is vital for operational success.
- While production planning encompasses the broader strategy of organizing production activities, production scheduling focuses on the detailed timing of these activities. Both are crucial for seamless manufacturing operations and must work together effectively.
- Production planning and scheduling are interdependent processes that ensure resources are optimally utilized while meeting production goals. Collaboration between these two functions enhances overall efficiency and responsiveness.
- The key steps in production planning and scheduling include defining objectives, gathering data, creating schedules, and monitoring progress. Following a systematic approach facilitates better decision-making and operational agility.
- Utilizing various methods and tools, such as Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) systems and ERP software, can significantly improve the efficiency of production planning and scheduling. Investing in the right technology is crucial for success.
- Challenges such as demand variability, resource constraints, and production delays can hinder effective planning and scheduling. Identifying these challenges and implementing proactive solutions can mitigate their impact.
- Production planning and scheduling are critical for optimizing resources, reducing costs, and ensuring timely delivery of products. Their effective implementation directly contributes to a company’s competitiveness and customer satisfaction.
- Technology plays a vital role in enhancing production planning and scheduling processes through automation, real-time data access, and advanced analytics. Embracing technology can lead to more efficient and agile manufacturing operations.
- Adopting best practices, such as clear objectives, effective communication, and continuous improvement, is essential for streamlining production planning and scheduling processes. These practices foster a more responsive and efficient production environment.
- Deskera MRP is a powerful tool that can significantly enhance production planning and scheduling capabilities for manufacturers. By providing real-time data, automating processes, and integrating various functions, Deskera MRP empowers businesses to optimize their production operations, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. With its user-friendly interface and comprehensive features, Deskera MRP stands out as an invaluable asset for any manufacturing organization seeking to thrive in a competitive landscape.
Related Articles













