Have you ever wondered if your machines could tell you exactly when they need maintenance—before they break down? That’s precisely what prescriptive maintenance does.
By using AI, IoT sensors, and advanced analytics, this proactive approach not only predicts failures but also provides specific recommendations on what actions to take and when.
Unlike traditional maintenance strategies, prescriptive maintenance goes beyond just identifying potential issues—it prescribes the best course of action to prevent them.
In industries where downtime can cost millions, prescriptive maintenance is a game-changer. It enables businesses to optimize equipment performance, reduce unexpected failures, and extend asset lifespan.
By leveraging real-time data, companies can transition from reactive repairs to data-driven, intelligent decision-making. This not only saves money but also enhances operational efficiency and workplace safety.
To implement prescriptive maintenance effectively, businesses need robust ERP solutions that can integrate maintenance workflows with AI-driven insights. Deskera ERP offers a comprehensive platform that helps companies streamline asset management, automate maintenance schedules, and gain predictive insights for smarter decision-making.
With features like real-time monitoring, advanced analytics, and mobile accessibility, Deskera ERP empowers organizations to optimize maintenance processes and minimize downtime.
In this guide, we’ll dive deep into what prescriptive maintenance is, how it works, and why it’s a critical strategy for modern businesses. From its benefits and industry applications to best practices and future trends, this complete guide will help you understand how prescriptive maintenance can revolutionize your asset management approach.
What is Prescriptive Maintenance?
Prescriptive maintenance (RxM) is a data-driven approach that not only predicts potential equipment failures but also prescribes the most effective course of action to prevent them.
It builds upon traditional predictive maintenance by integrating AI, machine learning, and IoT-driven insights to provide a targeted “treatment plan” for machinery and equipment.
Unlike reactive and preventive maintenance strategies, which focus on past failures or scheduled servicing, prescriptive maintenance actively identifies root causes and recommends corrective actions to optimize performance and minimize downtime.
At its core, prescriptive maintenance relies on real-time data collection and analysis. Sensors and IoT devices continuously monitor asset health, gathering key operational metrics such as temperature, vibration, and pressure levels.
Advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms process this data to detect patterns, predict failures, and suggest the most efficient repair schedules or operational adjustments. This approach ensures that maintenance efforts are both timely and cost-effective, reducing unnecessary repairs and enhancing asset longevity.
For instance, in manufacturing, a prescriptive maintenance system can detect subtle changes in a machine’s vibration levels, diagnose the issue (e.g., insufficient lubrication), and recommend an intervention during non-peak hours. This not only prevents unexpected breakdowns but also optimizes maintenance schedules, ensuring minimal disruption to production.
Moreover, when integrated with a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) or an ERP solution like Deskera, prescriptive maintenance can automate work orders, track performance history, and streamline maintenance execution.
By leveraging AI-powered insights and automating maintenance workflows, businesses can significantly reduce downtime, control costs, and improve operational efficiency.
As industries continue to embrace digital transformation, prescriptive maintenance is becoming an essential tool for asset management, helping organizations stay ahead of potential failures and maintain peak operational performance.
How Prescriptive Maintenance Works
Prescriptive maintenance follows a structured, technology-driven process that leverages real-time data, advanced analytics, and AI-powered recommendations. It goes beyond predicting equipment failures by providing specific, data-backed action plans to mitigate risks before they escalate.
The process typically involves five key steps:
1. Data Collection Through IoT Sensors
The foundation of prescriptive maintenance lies in continuous data collection from equipment and machinery. IoT sensors are installed on critical assets to monitor essential parameters such as temperature, vibration, pressure, energy consumption, and system responsiveness.
This real-time monitoring helps detect even the most subtle anomalies that could indicate early signs of wear or failure. By capturing comprehensive operational data, businesses gain a complete view of asset performance and can move beyond reactive maintenance approaches.
2. Advanced Analytics and Machine Learning
Once data is collected, it is processed using machine learning algorithms trained on historical performance data. These algorithms analyze patterns, detect inefficiencies, and identify potential failure points before they occur.
For example, AI models can spot uneven load distribution in machinery or recognize performance declines that signal the need for maintenance.
This level of analysis helps companies understand not just when a failure might occur, but why—allowing for proactive interventions.
3. AI-Driven Prescriptive Recommendations
Unlike traditional maintenance strategies that rely on human intervention to diagnose issues, prescriptive maintenance automates the decision-making process.
AI-generated recommendations suggest precise actions—such as recalibrating equipment, scheduling targeted repairs, or replacing specific components—based on real-time conditions.
This ensures that maintenance efforts are focused on the right actions at the right time, minimizing unnecessary repairs and downtime.
4. Task Prioritization and Execution
Prescriptive maintenance seamlessly integrates with Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS), Field Service Management (FSM) platforms, and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems like Deskera ERP to streamline execution.
These platforms prioritize maintenance tasks based on urgency and impact, ensuring that critical equipment receives immediate attention. Work orders are automatically generated, assigned to the right teams, and tracked through centralized dashboards, improving efficiency and coordination.
5. Continuous Monitoring, Learning, and Adaptation
Prescriptive maintenance is not a one-time process—it continuously monitors performance and adapts based on real-world results. Once maintenance actions are executed, IoT sensors track key performance metrics to validate the effectiveness of interventions.
AI-driven feedback loops analyze post-maintenance data and refine future recommendations. If discrepancies arise, the system adjusts its algorithms to improve accuracy, ensuring that maintenance strategies evolve over time to deliver increasingly precise insights and better operational outcomes.
By implementing prescriptive maintenance, businesses can reduce unplanned downtime, lower maintenance costs, and extend asset lifespan. With Deskera ERP, organizations can further enhance their maintenance strategies by integrating real-time monitoring, AI-driven analytics, and automated workflows, enabling a smarter, more efficient approach to asset management.
Use Cases of Prescriptive Maintenance
Prescriptive maintenance has widespread applications across multiple industries, helping businesses minimize downtime, optimize resource allocation, and reduce maintenance costs.
By leveraging real-time data, AI-driven insights, and predictive analytics, industries can enhance equipment efficiency and ensure operational continuity.
Below are key use cases of prescriptive maintenance across various sectors.
1. Manufacturing: Enhancing Machinery Performance
Manufacturing plants rely on highly automated production lines, where unplanned machine failures can lead to costly production halts. Prescriptive maintenance helps by:
- Monitoring equipment health in real time using IoT sensors.
- Detecting early warning signs such as abnormal vibrations or overheating.
- Providing targeted intervention plans (e.g., scheduling lubrication or replacing worn-out parts).
For example, an automotive assembly plant can predict gearbox failures in robotic arms and schedule maintenance during non-peak hours, ensuring seamless production with minimal disruption.
2. Transportation and Fleet Management: Reducing Vehicle Downtime
For logistics and transportation companies, unexpected vehicle breakdowns can lead to delayed deliveries, increased costs, and customer dissatisfaction. Prescriptive maintenance helps fleet managers:
- Monitor vehicle components like brakes, engine performance, and tire conditions.
- Predict potential failures before they result in breakdowns.
- Optimize maintenance schedules based on real-world driving conditions.
For instance, a delivery fleet using AI-powered maintenance insights can replace brake pads only when sensor data indicates wear—rather than following a fixed maintenance schedule—saving costs and extending component life.
3. Energy and Utilities: Ensuring Power Reliability
Energy companies rely on complex infrastructure, including power grids, turbines, and substations, where failures can lead to widespread outages and regulatory penalties. Prescriptive maintenance plays a vital role by:
- Tracking real-time equipment health in power plants and wind farms.
- Predicting faults in generators, transformers, or pipelines before they escalate.
- Providing AI-driven recommendations for maintenance teams.
For example, a solar power plant can detect panel degradation due to dust accumulation and schedule automated cleaning cycles, maximizing energy output and system efficiency.
4. Healthcare: Maintaining Medical Equipment Efficiency
Hospitals and healthcare facilities depend on critical medical devices like MRI scanners, ventilators, and infusion pumps. Prescriptive maintenance helps:
- Monitor usage patterns and sensor data to predict failures.
- Schedule repairs or replacements proactively to avoid service interruptions.
- Ensure compliance with medical safety standards through timely interventions.
For instance, a hospital using IoT-enabled prescriptive maintenance can prevent sudden failures of ventilators by automatically scheduling filter replacements when air pressure deviations are detected.
5. Aerospace: Increasing Aircraft Safety and Uptime
Aircraft maintenance is highly regulated, and failures can have catastrophic consequences. Airlines use prescriptive maintenance to:
- Monitor aircraft engines and critical components for performance anomalies.
- Predict mechanical failures before they compromise flight safety.
- Optimize maintenance schedules to ensure timely servicing without disrupting operations.
For example, an airline leveraging AI-driven prescriptive maintenance can predict fuel pump degradation based on real-time pressure readings and schedule repairs before in-flight failure risks arise.
Benefits of Prescriptive Maintenance
Prescriptive maintenance goes beyond predicting equipment failures—it provides actionable insights that enable businesses to cut costs, enhance efficiency, and improve overall operational resilience.
By leveraging real-time data, AI-driven analytics, and automated decision-making, prescriptive maintenance helps businesses optimize their maintenance strategies and resource allocation.
Here are the key benefits:
1. Increased Equipment Uptime and Reliability
Unplanned downtime can be disruptive and costly. Prescriptive maintenance predicts specific failures and provides precise corrective actions before they occur. This results in:
- Fewer breakdowns, ensuring continuous operations.
- Improved asset reliability, reducing costly disruptions.
- Minimized production delays, boosting productivity.
For example, in automotive manufacturing, prescriptive maintenance can detect early wear in robotic assembly arms, allowing proactive servicing before a major failure occurs.
2. Extended Equipment Lifespan
Replacing equipment is expensive, but early intervention can prevent excessive wear and tear. Prescriptive maintenance:
- Reduces stress on components by detecting minor inefficiencies before they escalate.
- Minimizes unnecessary replacements, ensuring businesses maximize asset value.
- Optimizes maintenance schedules, preventing both under- and over-maintenance.
For instance, wind turbine operators use prescriptive maintenance to adjust blade alignment based on real-time wind conditions, reducing mechanical strain and extending turbine life.
3. Enhanced Employee Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Malfunctioning equipment can pose serious safety hazards. Prescriptive maintenance helps:
- Identify risks early, preventing workplace accidents.
- Ensure compliance with safety regulations by maintaining optimal equipment conditions.
- Reduce liability and financial penalties associated with non-compliance.
For example, in the oil and gas industry, prescriptive maintenance predicts pipeline corrosion risks, ensuring timely repairs to prevent hazardous leaks.
4. Improved Maintenance Scheduling and Resource Allocation
Reactive maintenance leads to wasted resources and inefficient scheduling. Prescriptive maintenance:
- Ranks tasks by urgency, ensuring critical issues are addressed first.
- Aligns maintenance with operational needs, minimizing workflow disruptions.
- Prevents over-maintenance, reducing labor and material costs.
A hospital using IoT-powered prescriptive maintenance can schedule ventilator servicing only when necessary, optimizing technician workloads and equipment availability.
5. Lower Maintenance and Overhead Costs
Emergency repairs and unplanned downtime are expensive. Prescriptive maintenance reduces costs by:
- Preventing failures that require expensive emergency interventions.
- Optimizing spare parts inventory, reducing unnecessary stockpiling.
- Lowering labor costs by scheduling maintenance efficiently.
For example, in aviation, prescriptive maintenance predicts engine component wear and ensures replacement only when necessary, saving airlines millions in repair and operational costs.
6. More Efficient Operations and Workflow Continuity
Unexpected breakdowns lead to production slowdowns. Prescriptive maintenance ensures:
- Maintenance tasks are seamlessly integrated into daily workflows.
- Production schedules remain on track, avoiding costly delays.
- Real-time AI recommendations support strategic decision-making.
For instance, food processing plants use prescriptive maintenance to identify hygiene-related risks in production lines, ensuring compliance and efficiency.
7. Better Customer Satisfaction and Brand Reputation
Equipment failures can delay orders, disrupt services, and impact customer trust. With prescriptive maintenance, businesses can:
- Meet delivery timelines, improving service reliability.
- Avoid disruptions in critical services, enhancing customer experience.
- Boost brand reputation by ensuring operational excellence.
For example, retail distribution centers use prescriptive maintenance to prevent conveyor belt failures, ensuring smooth order fulfillment and customer satisfaction.
Prescriptive Maintenance vs. Other Maintenance Strategies
Prescriptive maintenance is an advanced maintenance strategy that predicts failures and recommends specific corrective actions based on real-time data. To understand its value, let’s compare it with other common maintenance approaches:
Why Choose Prescriptive Maintenance?
Compared to predictive maintenance, which only forecasts when a failure might happen, prescriptive maintenance analyzes root causes and suggests the best course of action. It enables:
- Faster, data-driven decision-making with AI-powered insights.
- Automated issue resolution to prevent failures proactively.
- More efficient resource allocation, reducing unnecessary interventions.
Challenges in Implementing Prescriptive Maintenance
Implementing prescriptive maintenance can offer significant long-term benefits, but it also presents a set of challenges that organizations need to address.
Here are the key challenges structured in a similar format to the benefits of prescriptive maintenance:
1. High Initial Costs
- Hardware & Software Investment: Retrofitting equipment with IoT sensors and integrating AI-driven analytics requires substantial investment.
- Learning and Transition Costs: Shifting from traditional maintenance techniques involves training and adapting to new systems, which adds to initial expenses.
2. Regulatory Constraints
- Fixed Maintenance Requirements: In some industries, regulations mandate time-based maintenance tasks, limiting the flexibility of prescriptive approaches.
- Compliance Challenges: Even when data shows that an asset can function reliably beyond prescribed intervals, regulatory bodies may still require scheduled interventions.
3. Organizational Culture and Trust
- Resistance to Change: Established practices and long-held beliefs about maintenance can create hurdles in adopting a data-driven approach.
- Skepticism Towards AI: Maintenance managers and teams may be reluctant to rely on AI-driven recommendations, especially for safety-critical equipment.
4. System Maturity and Learning Curve
- Dependence on Historical Data: Prescriptive systems require time to gather sufficient historical data to refine their predictions and recommendations.
- Initial Reliability Concerns: Early in the implementation phase, the system’s recommendations might not immediately match the performance of traditional methods, leading to hesitancy among decision-makers.
Addressing these challenges requires a strategic approach that includes pilot programs, continuous monitoring, and a concerted effort to align technological advancements with regulatory and cultural expectations.
Is Prescriptive Maintenance the Right Choice for You?
Deciding whether to adopt prescriptive maintenance involves evaluating your organization's current asset management strategy, technology readiness, and long-term operational goals.
Here are key indicators to help determine if prescriptive maintenance is a good fit:
1. Asset Criticality and Complexity
- High-Value Assets: If your operations rely on expensive or critical equipment where unplanned downtime is highly disruptive, prescriptive maintenance can help prevent costly failures.
- Complex Systems: Organizations with machinery that requires nuanced, data-driven insights for maintenance decisions may benefit from the precision of AI-powered prescriptions.
2. Data Availability and Technological Infrastructure
- Existing Sensor Network: If your assets already have IoT sensors or if there’s a plan to install them, you can leverage real-time data to drive prescriptive maintenance strategies.
- Data Integration Capabilities: An infrastructure that supports centralized data collection and analysis is crucial. If you’re investing in modern ERP or CMMS solutions (e.g., Deskera ERP), you’re likely positioned for prescriptive maintenance.
3. Maintenance Challenges and Operational Goals
- Frequent Downtime: If reactive maintenance and unpredictable failures are common issues, a prescriptive approach can reduce interruptions and enhance operational continuity.
- Cost Control Objectives: For companies aiming to lower maintenance expenses and extend asset lifespans, prescriptive maintenance offers a way to optimize resource allocation and prevent unnecessary repairs.
4. Organizational Readiness and Culture
- Embracing Digital Transformation: Organizations committed to leveraging advanced analytics, AI, and automation are more likely to see success with prescriptive maintenance.
- Willingness to Adapt: A culture open to change and innovation is essential. If your teams are ready to move beyond traditional maintenance approaches and trust data-driven insights, prescriptive maintenance could be the right choice.
By assessing these factors, you can better determine whether prescriptive maintenance aligns with your operational needs and strategic objectives. This proactive, technology-driven approach can transform your maintenance strategy, improve asset reliability, and ultimately drive cost savings and efficiency across your organization.
Best Practices for Implementing Prescriptive Maintenance
Implementing a prescriptive maintenance program requires careful planning, strategic investment, and ongoing refinement. Below are the key best practices to ensure a smooth and successful implementation:
1. Assess Assets and Infrastructure
- Identify Critical Components: Start by evaluating your assets to pinpoint components and systems that are crucial to operations and most susceptible to failure.
- Evaluate Potential Failure Points: Understand which areas could lead to significant downtime or safety risks, forming the basis for targeted monitoring.
2. Install Sensors and Monitoring Systems
- Deploy IoT Sensors: Equip critical equipment with IoT sensors that capture vital data such as temperature, vibration, pressure, and operating conditions.
- Establish Real-Time Monitoring: Set up a robust monitoring system to continuously track asset performance and quickly identify anomalies.
3. Collect and Integrate Data
- Centralize Data Sources: Integrate data from various channels—including sensor outputs, maintenance logs, and operational records—into a centralized database or platform.
- Ensure Data Quality: Implement processes to clean and standardize data, ensuring that your analytical models are built on reliable information.
4. Develop and Refine Machine Learning Models
- Train Predictive Models: Use the collected historical and real-time data to develop machine learning models that can predict equipment performance and flag potential issues.
- Incorporate Feedback Loops: Continuously refine these models by incorporating feedback from maintenance activities and operational outcomes, improving the accuracy of prescriptions over time.
5. Automate Maintenance Workflows
- Streamline Work Order Generation: Integrate your prescriptive maintenance system with Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) or ERP solutions like Deskera ERP to automatically generate work orders.
- Optimize Scheduling: Automate the scheduling of maintenance tasks based on real-time data and AI-driven recommendations to ensure interventions occur at the most opportune times.
6. Foster a Culture of Continuous Improvement
- Engage Cross-Functional Teams: Involve maintenance, operations, and IT teams in the implementation process to ensure broad acceptance and collaboration.
- Monitor and Adapt: Regularly assess performance metrics, gather feedback, and adjust your processes to stay ahead of evolving operational challenges and technological advances.
By following these best practices, organizations can effectively transition from traditional maintenance methods to a proactive, data-driven approach that minimizes downtime, enhances asset longevity, and drives overall operational efficiency.
Future of Prescriptive Maintenance
As digital transformation accelerates, the future of prescriptive maintenance is poised to deliver even greater value to organizations by leveraging cutting-edge technologies and integrated systems.
Here are the key future trends structured in a similar format to the benefits of prescriptive maintenance:
1. Enhanced Data Collection and Analysis
- Broader Sensor Integration: Future systems will deploy a wider range of IoT sensors to capture more detailed operational data, allowing for deeper insights into asset performance.
- Improved Analytics: Advancements in machine learning and AI will enable more accurate predictions and refined prescriptions, making maintenance strategies even more precise.
2. Integration with Digital Twins and Simulation Tools
- Virtual Asset Replicas: Digital twins—virtual models of physical assets—will allow organizations to simulate maintenance scenarios and validate interventions before actual implementation.
- Risk Reduction: This integration will help in identifying potential issues in a risk-free environment, significantly reducing the likelihood of unexpected downtime.
3. Augmented Reality (AR) and Enhanced Technician Support
- Real-Time Guidance: AR tools will provide maintenance teams with overlaid digital information directly onto physical equipment, enhancing repair accuracy and efficiency.
- Improved Training: These technologies will also serve as advanced training tools, enabling technicians to learn and apply best practices more effectively.
4. Seamless Integration with Enterprise Systems
- ERP and CMMS Synergy: Future ERP systems, such as Deskera ERP, will further integrate prescriptive maintenance functionalities with broader business operations, ensuring maintenance strategies align with overall organizational goals.
- Streamlined Workflows: Automated work order generation and scheduling will become more sophisticated, reducing manual intervention and optimizing resource allocation.
5. Adaptive, Continuous Learning Systems
- Feedback-Driven Refinement: Prescriptive maintenance systems will continually learn from both historical and real-time data, adapting their recommendations to evolving operational conditions.
- Proactive Adjustments: This adaptive capability will enable organizations to not only predict failures but also dynamically adjust maintenance strategies to mitigate emerging risks.
6. Widespread Adoption and Industry Transformation
- Cost Reduction and Efficiency Gains: As technologies mature, the cost-benefit ratio of prescriptive maintenance will further improve, driving broader adoption across industries.
- New Industry Standards: Enhanced reliability, extended asset lifespan, and improved safety will set new benchmarks for maintenance management, transforming how businesses approach asset management in the digital era.
By harnessing these advancements, organizations can expect prescriptive maintenance to evolve into an even more robust, integrated, and adaptive system—delivering unprecedented levels of operational efficiency, cost savings, and asset reliability.
Enhancing Prescriptive Maintenance with Deskera ERP
Deskera ERP integrates prescriptive maintenance into your overall asset management strategy by combining real-time data, advanced analytics, and automated workflows into a unified platform.
Here are key ways Deskera ERP can help you elevate your maintenance approach:
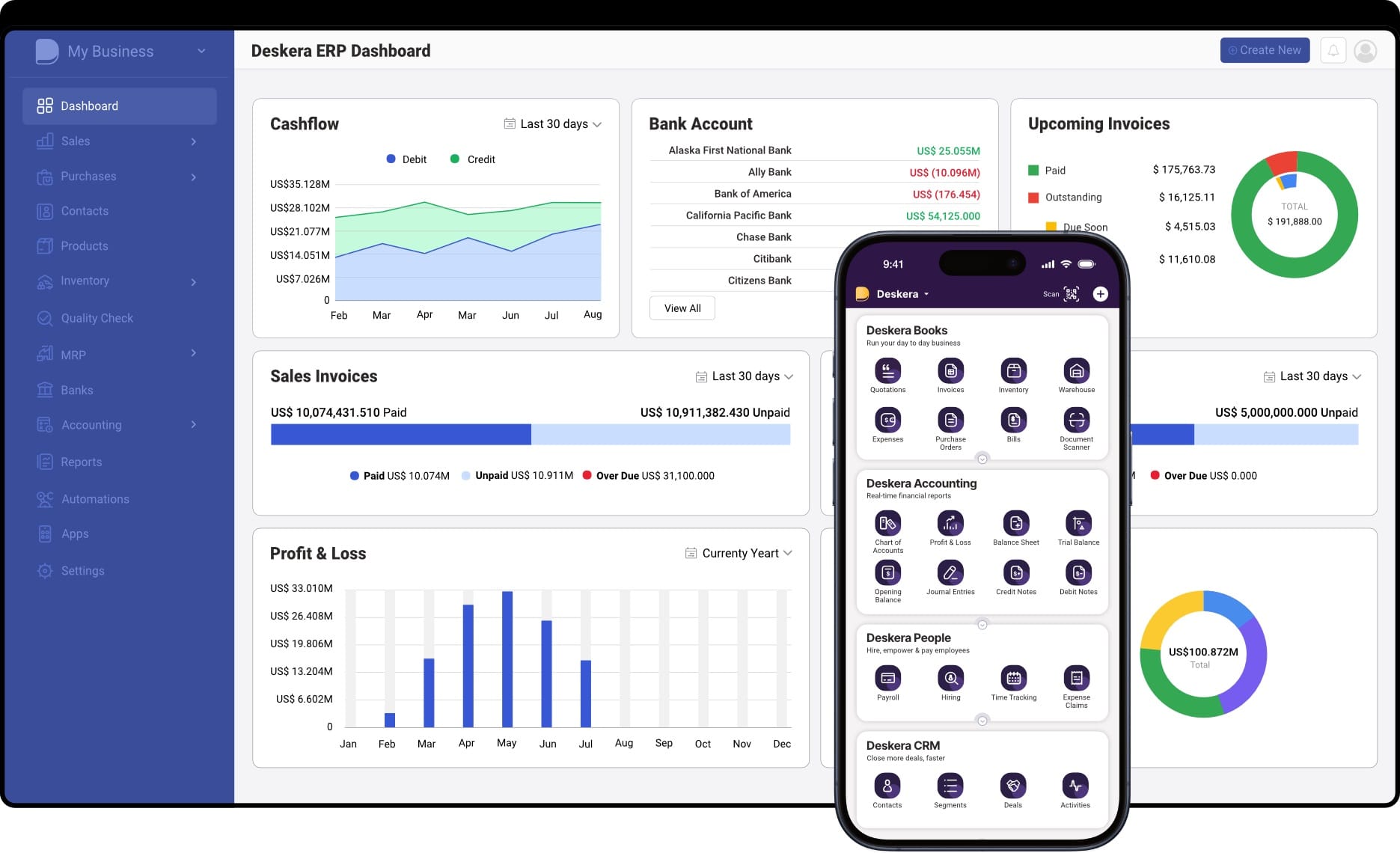
1. Centralized Data Integration
- Unified Data Hub: Deskera ERP consolidates data from IoT sensors, maintenance logs, and operational systems, providing a single source of truth for asset performance.
- Seamless Analytics: By integrating various data streams, it ensures that your prescriptive maintenance models are built on comprehensive, reliable data.
2. AI-Driven Predictive Insights
- Advanced Analytics: With built-in AI and machine learning capabilities, Deskera ERP processes real-time data to predict potential failures and prescribe targeted maintenance actions.
- Actionable Recommendations: The system not only forecasts issues but also provides clear, actionable steps, helping maintenance teams make informed decisions quickly.
3. Automated Maintenance Workflows
- Work Order Automation: Deskera ERP automatically generates work orders based on predictive insights, streamlining task assignment and scheduling.
- Optimized Resource Allocation: By prioritizing maintenance tasks according to urgency and impact, it ensures that resources are efficiently deployed where they are needed most.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Feedback
- Real-Time Dashboards: With dynamic dashboards, you can monitor asset health, track maintenance progress, and adjust strategies based on real-time performance data.
- Feedback Loops: Post-maintenance analytics help refine AI models, ensuring that the system learns and adapts to deliver increasingly precise recommendations over time.
5. Enhanced Collaboration and Compliance
- Cross-Functional Integration: Deskera ERP bridges gaps between maintenance, operations, and management teams, ensuring everyone is aligned with the prescriptive maintenance strategy.
- Regulatory Compliance: The platform helps maintain detailed records and audit trails, supporting compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements.
By leveraging these features, Deskera ERP transforms prescriptive maintenance from a reactive process into a proactive, efficient, and continuously improving strategy—helping your organization minimize downtime, control maintenance costs, and extend asset lifespans.
Key Takeaways
- Prescriptive maintenance offers a proactive, data-driven approach that transforms how organizations anticipate and resolve equipment issues, setting the stage for reduced downtime and enhanced operational efficiency.
- It goes beyond traditional maintenance by not only predicting potential failures but also prescribing precise, actionable solutions to keep systems running optimally.
- By integrating IoT sensor data, advanced analytics, and AI-driven algorithms, prescriptive maintenance continuously monitors asset conditions and delivers tailored recommendations for timely interventions.
- Across various industries—from manufacturing to healthcare—this approach optimizes performance by targeting maintenance efforts where they matter most, ensuring uninterrupted operations and cost savings.
- It improves equipment reliability, extends asset lifespan, enhances safety, and streamlines operations by performing maintenance precisely when needed, ultimately reducing both downtime and maintenance costs.
- Unlike reactive, preventive, and predictive maintenance, prescriptive maintenance not only forecasts issues but also provides clear, actionable plans, making it a more effective strategy for long-term asset management.
- High initial costs, regulatory constraints, integration hurdles, and cultural resistance are common challenges that organizations must overcome to successfully adopt prescriptive maintenance.
- A successful implementation requires thorough asset assessment, robust sensor installation, seamless data integration, continuous model refinement, and automation of maintenance workflows.
- Emerging technologies—such as digital twins, augmented reality, AI advancements, and cloud-based solutions—will further enhance the precision, scalability, and adaptability of prescriptive maintenance strategies.
- Assessing your asset criticality, data infrastructure, and organizational readiness can help determine if prescriptive maintenance is the ideal solution to meet your operational needs.
- Deskera ERP centralizes data, automates maintenance workflows, and leverages AI-driven insights to provide a seamless and effective prescriptive maintenance solution, ensuring optimized asset performance and reduced operational costs.
Related Articles