According to the American Chemistry Council, plastic manufacturing in the United States in 2019 was valued at $424.5 billion, a 5.5% increase from 2018. The Council also reported that the plastic industry employed 1.4 million people in the United States in 2019, an increase of 2.1% from 2018.
These insights suggest that the plastic manufacturing sector has been a ceaseless and busy industry. Plastic Manufacturing is a sector that mostly generates intermediate products. This sector is a major provider of items to the service industry, such as packaging materials. Furthermore, these goods are also utilized in various other industries such as construction, agriculture, durable consumer goods, automotive, and electronics.

In terms of output, the Plastic Products Manufacturing Industry is becoming increasingly important in the manufacturing industry and the national economy as a whole. There is a continuous development and production work going on in their manufacturing units. All these manufacturing processes cannot go about without an efficient Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Material Requirements Planning (MRP) system in place.
This post takes us to the depths of the plastic manufacturing sector as we try to understand the industry. From the challenges it faces to the benefits it can get from an MRP, we shall be going through the following topics:
- Overview of Plastic Manufacturing
- How to Choose the Right Plastic Manufacturing Process
- Challenges in the Plastic Manufacturing Sector
- 6 Benefits of MRP for Plastic Manufacturing
- How can MRP help Plastic Manufacturing Industry?
- 3 Best Practices for Implementing MRP for Plastic Manufacturing
- Plastic Manufacturing Industry: A Promising Future
- Improve Your Plastic Manufacturing Business with MRP Software
- Conclusion
- How can Deskera Help You?
- Key Takeaways
- Related Articles
Overview of Plastic Manufacturing
Plastic manufacturing is a process of shaping, molding, and joining materials to create a wide range of products. The plastic industry is composed of many different processes, each with its own unique set of challenges. Plastic manufacturing involves the use of a variety of materials, including polymers, polyurethane foam, thermoplastics, elastomers, and additives.
The materials are combined and formed into a variety of shapes and sizes. The manufacturing process often involves the use of specialized machinery and the application of heat and pressure to shape the final product.
Types of Plastic
Plastics are available in thousands of distinct formulations with various basic chemistries, derivatives, and additives that are designed to provide a wide variety of functional and aesthetic qualities.
To make it easier to find the optimum material for a specific part or product, let's start with the two primary forms of plastic:
- Thermoplastics
- Thermosets.
Thermoplastics
The most common type of plastic is thermoplastic. The capacity to go through several melt and solidification cycles without substantial degradation distinguishes them from thermosets. Thermoplastics are often delivered in the form of small pellets or sheets that are heated and molded into the desired shape using a variety of production procedures. The procedure is fully reversible.
The following are examples of thermoplastic materials:
- Acrylic (PMMA)
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
- Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Polyamide (PA)
- Polyethylene (PE)
- Polylactic acid (PLA)
- Polyether ether ketone (PEEK)
- Polycarbonate (PC)
Thermosetting Plastics
The crosslinking of polymers in thermosetting materials occurs during the curing process generated by heat, light, or appropriate radiation. In the process of curing, a chemical bond is formed that cannot be reversed. A thermosetting plastic will break down rather than melt when heated and won't reform when cooled. Recycling thermosets or restoring them to their base components is not possible.
The following are examples of thermoplastic materials:
- Cyanate ester
- Vulcanized rubber
- Epoxy
- Polyurethane
- Polyester
- Silicone
Types of Manufacturing Processes used in Plastic Manufacturing
Plastic manufacturing companies can deploy a variety of processes. Some of the prominent ones are mentioned here:
- 3D Printing: The process of 3D printing utilizes printers that generate three-dimensional objects directly from CAD models by layering material until a full physical part is generated. While traditional plastic manufacturing procedures necessitate costly industrial machinery, specialized facilities, and expert operators, 3D printing enables businesses to easily make plastic parts and prototypes in-house.
- Injection Molding: This process is used to make large plastic products such as car bumpers, crates, and buckets. The process involves melting plastic pellets and injecting them into a pre-made mold.
- Blow Molding: This process is used to create plastic containers such as bottles and containers. A hollow tube, called a parison, is placed in a mold and hot air is blown into the parison, causing it to expand and take the shape of the mold.
- Extrusion: This process is used to produce items such as pipes, tubes, and sheets. Plastic pellets are melted and pushed through a die, which gives them their desired shape.
- Compression Molding: This process is used to make plastic items such as cups, plates, and bowls. Plastic pellets are placed between two heated molds and pressure is applied, causing the plastic to take the shape of the mold.
- Rotational Molding: This process is used to make large hollow plastic items such as tanks and kayaks. Plastic powder is placed into a heated mold which is then slowly rotated, causing the powder to melt and take the shape of the mold.
- CNC Machining: Mills, lathes, and other computer-controlled subtractive operations are examples of CNC machining. These procedures begin with solid metal or plastic blocks, bars, or rods that are sculpted by removing material through cutting, boring, drilling, and grinding. It is a subtractive process in which material is removed using either a spinning tool and a fixed part or a spinning part with a fixed tool.
- Polymer Casting: A reactive liquid resin or rubber fills a mold in polymer casting, which chemically reacts and solidifies. Polyurethane, epoxy, silicone, and acrylic are common casting polymers.
- Vacuum forming: Vacuum forming is a manufacturing technique in which a plastic is heated and shaped, often with the help of a mold. The size and complexity of vacuum forming machines range from low-cost desktop units to automated industrial gear.
How to Choose the Right Plastic Manufacturing Process
There are various kinds of plastic products, and therefore, each business becomes unique. When deciding on a manufacturing process for your product, keep the following aspects in mind:
Form: Do your products have complicated interior features or stringent tolerances? Depending on the geometry of a design, manufacturing possibilities may be limited, or extensive design for manufacturing (DFM) optimization may be required to make it cost effective to create.
Materials: companies must evaluate the stress and strain their product will have to withstand. A variety of factors influence the best material for a certain application. The cost of the project must be evaluated against the practical and aesthetic objectives. Consider the optimum properties for your individual application and compare them to the options available in a given manufacturing process.
Volume and cost: This will decide the total or annual volume of parts that you intend to manufacture. Some manufacturing processes involve substantial upfront costs for tooling and setup but yield low-cost per-part parts. Cheap volume manufacturing techniques, on the other hand, have low beginning costs, but because of shorter cycle times, less automation, and human labor, cost per part remains constant.
Lead time: Manufacturing lead time is the amount of time it takes for a manufacturing process to complete a product from start to finish. This includes the time it takes for raw materials to arrive, for the product to be completed, for it to be inspected and tested, and for it to be shipped out. Some procedures produce first items in 24 hours, whilst certain high-volume production techniques require months of equipment and setup.
Challenges in Plastic Manufacturing
The plastic manufacturing industry has had to suffer the effects of COVID-19, just like all other sectors. The industry has been making efforts to achieve progressive outcomes in the coming times.
Yet, there are some challenges that the sector is still going through.
Aside from the disruption caused by the pandemic, several manufacturing challenges have converged. These have potentially affected every aspect of the plastics industry. Some of the prime challenges include the following:
- supply chain management
- shop floor operations
- plastic parts and products
- specific threats to the production of high-quality plastic injection molding and rotational molding
Let’s cover the plastic industry’s pain points in detail here:
1. Quality Control: Quality control in manufacturing is one of the biggest challenges in plastic manufacturing due to the complex nature of the materials. Quality control requires constant monitoring and evaluation of each step of the manufacturing process to ensure that the end product meets the required standards.
2. Contamination: Contamination is a major issue in the plastic manufacturing process. This is due to the high temperatures, chemicals, and other components used in the production process. Contamination can occur in the form of dirt, dust, and particles that can affect the quality of the end product.
3. Safety: Ensuring the safety of workers in the factory is also a major challenge in plastic manufacturing due to the hazardous materials and processes involved. Proper safety equipment and protocols must be implemented in order to protect workers from any potential hazards.
4. Cost: Cost is another challenge for plastic manufacturers, as the production process is often expensive due to the materials and tools needed. Manufacturers must find ways to reduce costs in order to remain competitive in the market.
5. Waste Management: The manufacturing process often produces a large amount of waste, which must be properly managed in order to ensure a safe and healthy environment. Manufacturers must ensure that their waste management practices are compliant with local and federal regulations.
6. Shortage of Skilled Workers: Labor shortages are common in all industries, including plastics processing. It is more challenging than ever to find, train, and retain good personnel. And losing them is both simple and costly.
In the context of increasing labor demand and rising earnings in many service jobs, it is apparent that some people are reevaluating their options and are not afraid to move on.
Many manufacturers of various types are investing in new equipment to assist in maintaining output in the face of difficulty in retaining an appropriate staff.
You may have to ask your surviving workers to do more in the face of increasing turnover and the loss of senior equipment operators.
6 Benefits of MRP for Plastic Manufacturing
Plastic manufacturing can undergo a series of struggles. Here are some benefits of MRP that can help the sector overcome those challenges. Let’s take a look.
Improved Production Planning
MRP systems help plastic manufacturers plan production more efficiently by providing accurate and up-to-date information on material availability, production capacity and lead times. This allows manufacturers to better manage production schedules and ensure that materials are available when needed.
Improved Inventory Management
MRP systems help manufacturers better track and manage inventory levels, ensuring that the right materials are in stock when needed. This helps to reduce waste, eliminate overstocking and ensure that the right materials are available for production.
Reduced Cycle Times
MRP systems can help reduce the time it takes to produce plastic products by providing accurate and timely information on material and labor availability. This allows manufacturers to better plan and schedule production, resulting in a shorter lead time for products.
Cost Savings
By improving production planning and inventory management, MRP systems help manufacturers reduce costs associated with waste, overstocking and labor. This helps to improve the overall efficiency and cost-effectiveness of production.
Improved Quality
MRP systems help manufacturers improve product quality by providing accurate and timely information on material and labor availability. This helps to reduce errors and improve product quality overall.
Improved Supply Chain Management
MRP can improve the SCM for plastic manufacturing sector by helping to streamline the entire production process. MRP can help to plan the production activity, while ensuring that all of the necessary resources are available to meet customer demand.
It can also help to maintain accurate inventory levels, track orders, and manage supplier relationships. Additionally, MRP can help to reduce costs associated with production and supply chain management, while providing data insights to improve decision-making.
How can MRP Help Plastic Manufacturing Industry?
Let’s look at the detailed process of how MRP can provide a boost to the plastic manufacturing sector.
Here are the steps:
Establish a Master Production Schedule
The first step in implementing a successful MRP system is to create a master production schedule that outlines the timeline for producing each product. This schedule should include all necessary components and materials, as well as the required production steps and associated lead times.
Identify Component and Material Requirements
Once you have established a master production schedule, you need to identify all of the components and materials necessary to produce each product. This includes both raw materials inventory management and any purchased parts that may be needed.
Set up a Bill of Materials
Once you have identified all of the components and materials necessary for production, you need to create a bill of materials (BOM) for each product. This will include the quantity of each component and material required for each product, as well as any necessary information about the components, such as lead time, cost, and supplier.
Set up a Capacity Requirements Plan
In addition to the BOM, you will also need to create a capacity requirements plan (CRP) that identifies the resources required to produce each product. This plan should take into account the number of machines, personnel, and other resources necessary to meet production demands.
Establish a Production Cycle
Once the BOM and CRP are in place, you need to create a production cycle that outlines the steps required to produce each product. This should include any necessary maintenance or setup tasks, as well as the lead times required for each step.
Set up a Material Requirements Plan
Once the production cycle is in place, you need to create a material requirements plan (MRP) that will help you determine the number of components and materials necessary to meet production demands. This plan should take into account the lead times for each component and material, as well as any inventory levels that may be needed.
Track Inventory Levels
Finally, you need to track inventory levels in order to ensure that all components and materials are available when needed. This can be done manually or through an automated system, such as a software for inventory management.
3 Best Practices for an Effective Implementation
Best practices before implementing MRP for a manufacturing unit are necessary to ensure the successful implementation and use of the system. They help to identify potential problems, provide a framework for implementation, and ensure the system is used properly and efficiently.
Manufacturers can minimize implementation costs and improve the overall effectiveness of the MRP system. With these practices, they can also ensure that the system is properly integrated with other business systems. This way they can have more accurate data and help to improve efficiency.
Here are some of the best practices before implementing an MRP for your manufacturing unit:
- Identify goals and objectives
- Review existing processes
- Develop a plan of action
Identify Goals and Objectives
The companies must identify their goals for MRP implementation because it provides a clear direction and focus for the project. Goals and objectives are used to define the scope and purpose of the MRP project and determine the necessary steps to achieve the desired outcome.
They also provide a timeline for the project and help to track progress and measure success.
Additionally, they help to identify resources needed to complete the project and provide a basis for evaluating the success or failure of the implementation. Having a clear set of goals and objectives allows the team to stay on the same page, work together efficiently, and make sure they are achieving the desired results.
Review Existing Processes
This step is important because it allows for an analysis of the current system and helps identify areas that need improvement. This process can be used to develop a better understanding of the current system and identify any weaknesses or inefficiencies that should be addressed.
It also helps to identify any potential issues that could arise during the implementation of the MRP system.
The review process can be used to ensure that the MRP system will be designed in a way that best meets the needs of the business. Additionally, the review process can help to identify any potential problems that could arise during the MRP implementation process.
This can help to reduce the risk of the MRP system not working as intended and ensure that the system is implemented in a way that best meets the needs of the business.
Develop a Plan of Action
A plan of action is a best practice for MRP implementation because it helps to ensure that all necessary steps are taken in the correct order, and that deadlines are met. It also helps to ensure that all team members have a clear understanding of their roles and responsibilities throughout the implementation process.
A plan of action also helps to identify any potential obstacles or risks that could affect the successful implementation of the MRP system.
It could comprise the following steps:
- Establish Clear Goals and Objectives: Establish clear goals and objectives for the MRP implementation and ensure that everyone involved is on the same page.
- Assess Current Processes: Assess the current processes and procedures related to MRP and determine what needs to be improved or changed.
- Analyze Data: Gather and analyze data related to the MRP implementation to identify any potential issues or gaps.
- Assign Roles and Responsibilities: Assign roles and responsibilities to each team member involved in the project.
- Set a Timeline: Establish a timeline for the MRP implementation and make sure to stick to it.
- Develop a Training Plan: Develop a training plan to ensure that everyone involved in the MRP implementation is adequately trained and prepared.
- Test and Monitor: Test and monitor the MRP implementation to make sure that it is meeting the established goals and objectives.
- Analyze Results: Periodically analyze the results of the MRP implementation to make sure that it is achieving the desired results.
- Adjust and Adapt: As needed, make adjustments and adaptations to the MRP implementation to ensure that it is meeting the desired goals and objectives.
Plastic Manufacturing: A Promising Future
The future of the plastic r manufacturing sector looks promising. The industry is expected to experience continued growth as the demand for plastic products rises due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness. As manufacturers continue to innovate, the sector will continue to develop new and improved products, processes, and applications that can better meet the needs of consumers.
Additionally, the industry is expected to benefit from the increasing demand for recycled plastic materials, as well as the development of new technologies, such as 3D printing, that can help reduce waste and increase efficiency. In the future, the sector is likely to produce more sustainable and recyclable products, such as bioplastics, to meet the demands of a changing market.
Improve Your Plastic Manufacturing Business with MRP Software
We have covered a lot of aspects of MRP in this post. Having learned about its benefits, let’s look at the steps that you can take to boost your manufacturing process:
Research the Different Types of MRP Software: Start by researching the different types of MRP (Material Resource Planning) software available. Look for options that are tailored to your industry, such as those that are specifically designed for plastic manufacturing.
Determine Your Business Needs: Identify your business needs, such as inventory tracking, production scheduling, and budgeting. This will help you narrow down your software options to the ones that will best meet your needs.
Evaluate the Features: Once you have narrowed down your options, evaluate the features of each MRP software. Look for features such as scalability, ease of use, and cost.
Implement the Software: Once you have chosen an MRP software, it’s time to implement it. Train your staff on how to use the software and make sure to follow the vendor’s instructions for installation and setup.
Monitor Performance: After the software is up and running, it’s important to monitor its performance. Look for areas where efficiency can be improved and adjust the software as needed.
Utilize Reports: Take advantage of the reports that the software provides. These can be used to analyze your production processes and identify areas of improvement.
Optimize Your Processes: Once you have identified areas of improvement, work to optimize your processes. This could include streamlining the production process, reducing waste, or improving inventory management.
By implementing an MRP software and following these steps, you can improve the performance of your plastic manufacturing business. You’ll be able to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the MRP system is a valuable asset to the plastic manufacturing Industry. It helps to streamline production, reduce costs and increase efficiency, while also allowing businesses to keep track of inventory and manage their supply chain.
This system is an invaluable tool for the industry. With the increasing demand for plastic products, the MRP system is sure to remain an important part of the industry for many years to come.
Thank you for taking the time to read this article!
How can Deskera Help You?
Deskera's cloud-based software solutions for the plastic manufacturing industry can help manufacturers to streamline processes, increase efficiency, and improve customer service. The software can provide real-time visibility into production, enabling manufacturers to make informed decisions.
It also offers powerful inventory management, which helps manufacturers to optimize their supply chain and reduce costs. Deskera can also provide insightful analytics that can help manufacturers to identify areas for improvement and potentially new opportunities.
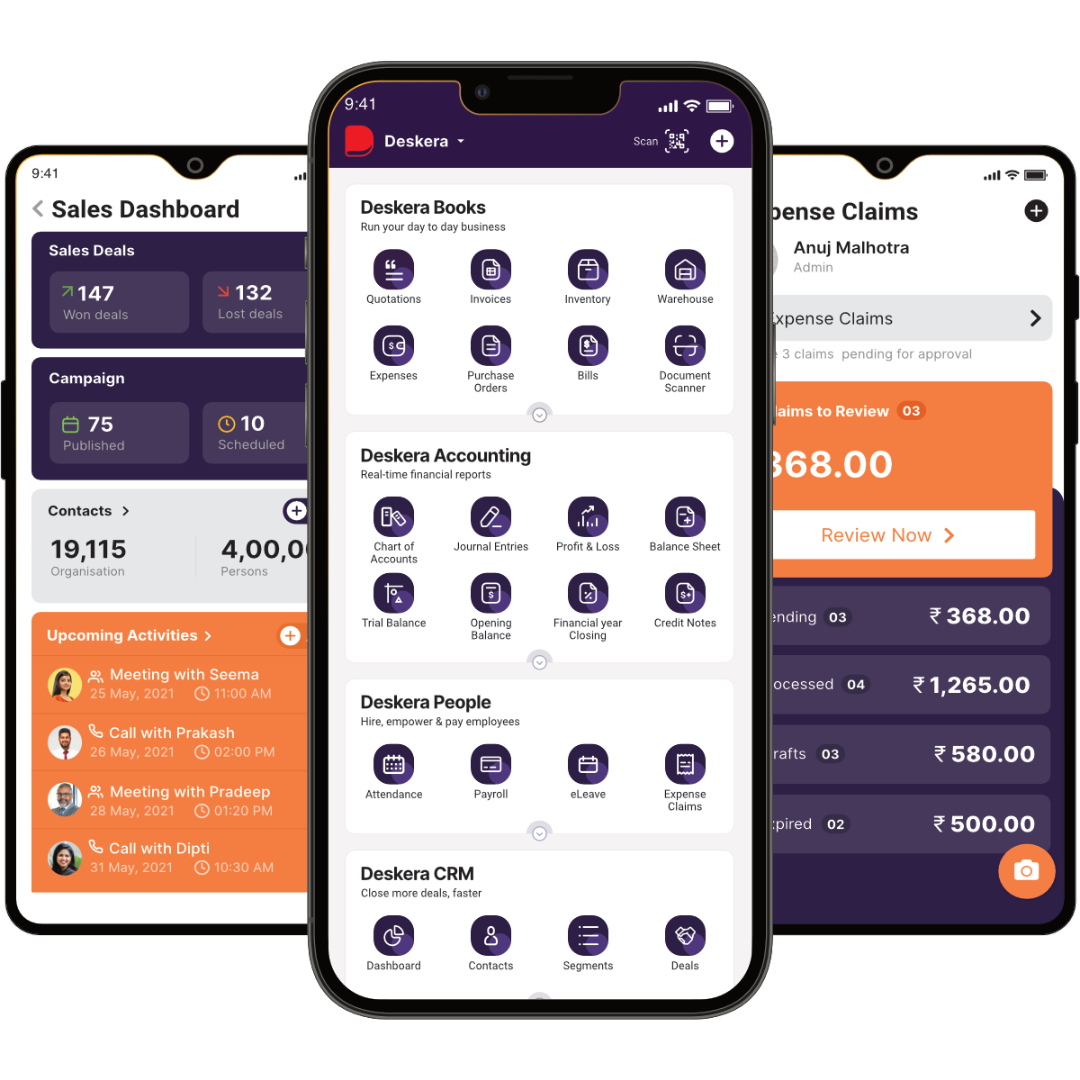
Aside from this, you can do the following:
- Track raw materials and finished goods inventory
- Manage production plans and routings
- Maintain bill of materials
- Generate detailed reports
- Create custom dashboards
Deskera Books enables you to manage your accounts and finances more effectively. Maintain sound accounting practices by automating accounting operations such as billing, invoicing, and payment processing.
Deskera CRM is a strong solution that manages your sales and assists you in closing agreements quickly. It not only allows you to do critical duties such as lead generation via email, but it also provides you with a comprehensive view of your sales funnel.
Deskera People is a simple tool for taking control of your human resource management functions. The technology speeds up payroll processing and allows you to manage all other activities such as overtime, benefits, bonuses, training programs, and much more.
Key Takeaways
- Plastic manufacturing is a process of shaping, molding, and joining materials to create a wide range of products.
- Plastic manufacturing involves the use of a variety of materials, including polymers, polyurethane foam, thermoplastics, elastomers, and additives.
- Plastics are available in thousands of distinct formulations with various basic chemistries, derivatives, and additives that are designed to provide a wide variety of functional and aesthetic qualities.
- 3D Printing, injection molding, blow molding, and extrusion are some of the methods used for plastic manufacturing.
- Choosing the right method will depend on the form, volume, and cost of the products.
- Quality control, contamination, supply chain management, and lack of skilled labor are some of the key challenges in the sector.
- While there are multiple benefits of implementing an MRP system, the key benefits include improved inventory management.
- Also, it lets you achieve a better production schedule and reduced cycle times.
- Companies can establish a master production schedule, set up BoM, and set up a capacity requirement plan, among others.
- Identify your goals, review existing processes, and develop a plan of action as some of the best practices for implementing MRP.
Related Articles