According to the US Census Bureau, in 2019, the total revenue for the Foundry industry was estimated to be $24.4 billion, representing a 5.4% increase from the previous year. The number of establishments in the Foundry industry was estimated to be 2,867, with a total of 5,167 establishments in the related industry sectors.
With those insights, we shall move to look at some of the pressing issues and challenges in a foundry business. We shall also be gathering insights into how implementing Materials Requirements Planning (MRP) software can help subside these issues.
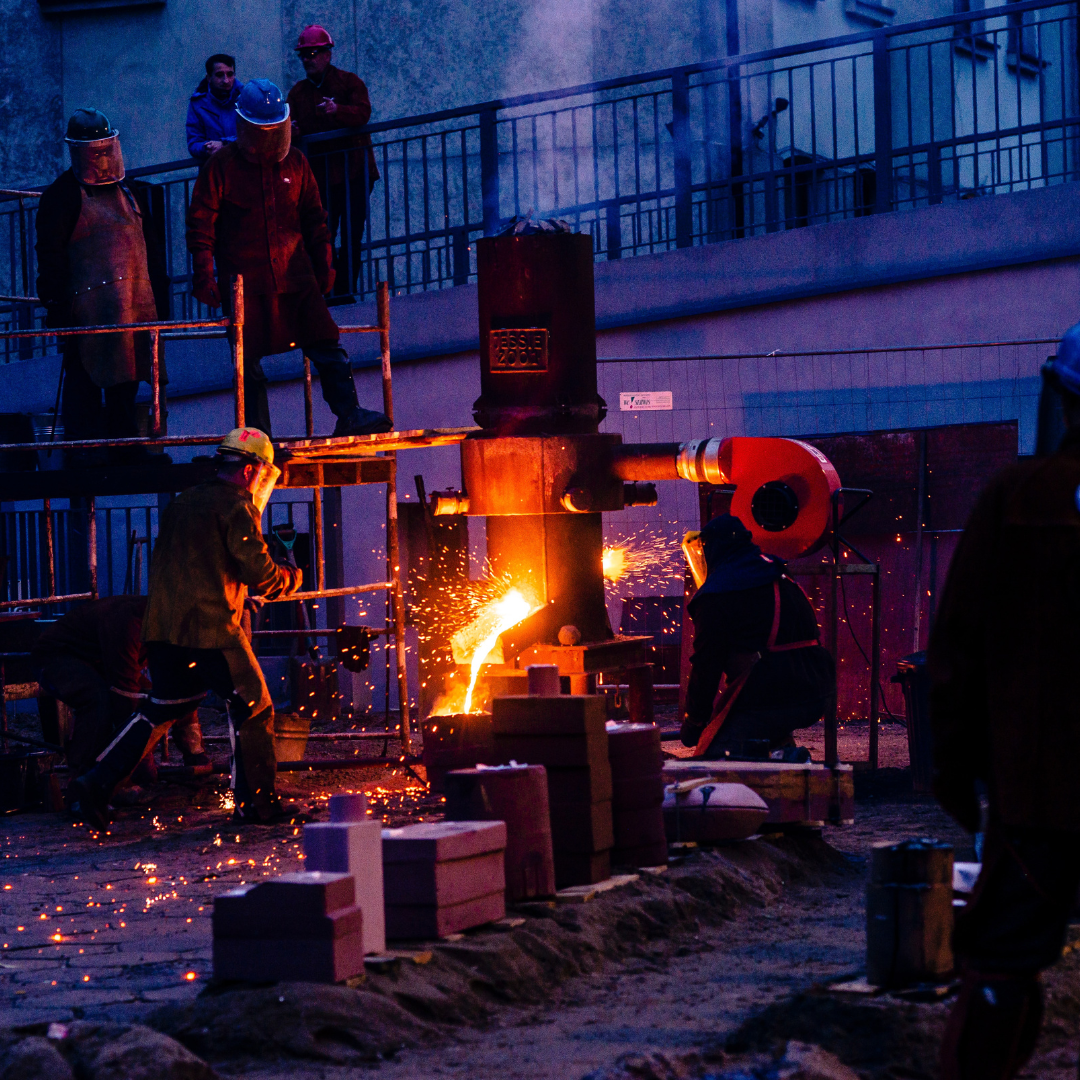
The use of MRP for foundries is a powerful tool for enabling the optimization of production scheduling, inventory control, and cost management. MRP provides insight into the current and future needs of the foundry. Organizations can efficiently acquire raw materials and components needed for production.
By leveraging the power of MRP, foundries can reduce costs, improve customer satisfaction, and increase operational efficiency. This article will provide an overview of the core principles and components of an MRP system, as well as best practices for implementation and utilization.
We will explore how MRP can be used to manage the supply chain of foundries and how it can be used to improve customer satisfaction, reduce costs, and increase efficiency.
- What is a Foundry?
- How do Foundries Work?
- Why do Foundries need MRP?
- Challenges faced by Foundries Today
- Benefits of MRP Implementation for Foundries
- How to Implement MRP in Foundries?
- Conclusion
- How can Deskera Help You?
- Key Takeaways
- Related Articles
What is a Foundry?
A foundry is a factory that melts and shapes metal into various forms and products. Foundries are used in the production of many different materials and objects, including car parts, machine parts, kitchen appliances, and even sculptures.
Foundries use a range of different metals, including aluminum, iron, steel, brass, and bronze. The process of melting and shaping metal requires exceptionally high temperatures, achieved using furnaces or crucibles.
The metal is first melted in the furnace or crucible. This liquid metal is then poured into molds, which are usually made from sand or metal. The molds are designed to the specifications of the desired object. The metal cools and solidifies in the molds, and then the molds are broken open to reveal the finished product. This process can be used to create intricate and complex shapes as well as simple ones.
Foundries are a critical part of the manufacturing industry, as they are necessary for the production of many different products. They are used in automotive, aerospace, and many other industries.
Foundries are also used in the production of coins and other currency and in the creation of artwork and sculptures. Foundries are a vital part of society, as they enable us to create a wide range of products with precision and accuracy.
How do Foundries Work?
Foundries produce metal castings. They melt down scrap metal or pig iron, pour it into molds, and then cool and solidify it into the desired shape. Foundries typically produce a wide range of metal products, such as car and truck components, cookware, railroad parts, valves, and other industrial components.
Some foundries may specialize in specific types of metal castings, such as aluminum, bronze, iron, or steel. Foundries may also provide machining, heat treating, and other finishing services to complete the production process.
Foundries use a variety of processes to heat and shape metal into the desired form. The process typically begins with melting the metal down, usually in a furnace. Once the metal is liquid, it is poured into a mold, which is usually made of sand. The metal then cools and solidifies in the mold and is then removed. Additional processes such as machining, grinding, and polishing may be used to shape the metal further.
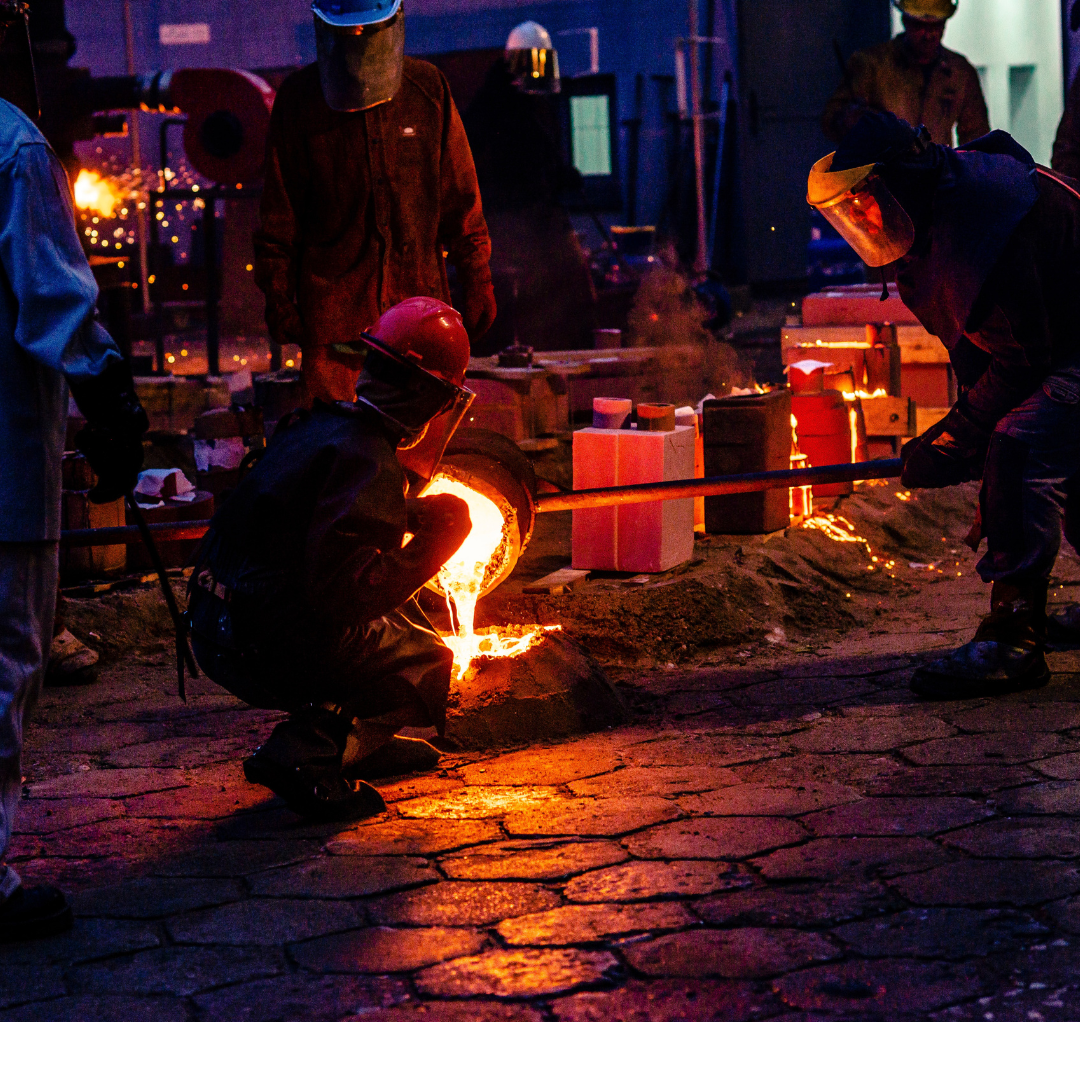

Iron, steel, aluminum, and copper are the most common metals used in foundries. Foundries may also utilize alloys and non-metallic materials. Foundries typically specialize in one particular type of metal so that they can become experts in shaping that particular material.
Workflow in a Foundry
A foundry is an industrial facility where metal is melted and poured into molds to create the desired shape and size. The process includes several steps.
- Melting: The metal is first placed in a furnace and heated to a high temperature until it melts. The melting temperature of the metal depends on the type of metal being used.
- Pouring: Once the metal is melted, it is poured into the mold. The mold is usually made out of the sand and is designed to create the desired shape and size of the finished product.
- Cooling: After the metal is poured, it is allowed to cool and solidify. This is done by running cold water over the mold or by allowing the metal to cool naturally.
- Finishing: After the metal has cooled, it is removed from the mold, and any excess metal is trimmed away. The metal can then be polished, painted, or coated with a protective coating.
- Inspection: The finished product is then inspected for any defects or flaws. If any are found, the product is discarded or reworked.
These are the basic steps in the foundry process. The exact process and workflow may vary depending on the type of metal being used and the desired end product.
Why do Foundries need MRP?
Foundries need MRP to manage the production of their products efficiently. MRP helps them plan material, production, and inventory needs and track costs and resources.
Material Planning
Material planning for foundries involves determining the type and amount of raw materials needed to produce the required finished products. This involves analyzing the production schedule, forecasting customer demand, and evaluating inventory levels.
The material planner must also ensure that the right materials are available when needed and in the right quantities to avoid delays in production.
The process also includes:
- Selecting suppliers
- Determining the right quantities
- Ensuring that the right materials are in stock
- Organizing logistics
MRP tools can help with this process by automating the planning and tracking of materials, components, and associated costs. MRP can be instrumental in driving efficient raw material inventory management for the foundries.
Production Planning
Production planning for foundries involves determining the quantity, quality, timing, and cost of all the necessary activities to produce a particular product. This includes material sourcing and procurement, production scheduling, labor allocation, quality assurance, and inventory control.
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is a system used to manage and optimize the production planning process. It can help coordinate production and purchase orders, generate reports on materials and labor availability, and track inventory. It can also provide cost estimates and identify material shortages or excesses to ensure that the necessary materials are available.
MRP also helps to minimize inventory costs and optimize the production process by taking into account the cost of materials and labor, as well as the availability of the necessary parts and components. By using MRP, foundries can reduce lead times and improve customer satisfaction.
Forecasting Customer Demand
Forecasting demand is a process that involves the analysis of historical customer demand data and the use of predictive analytics to anticipate future customer demand. This forecasting process requires foundries to analyze customer demand patterns, identify trends, and develop appropriate forecasts to meet and understand customer needs.
Foundries must also consider factors such as economic conditions, changes in customer preferences, and other external forces that may affect demand. MRP can help to manage inventory and production planning. It takes into account customer demand, inventory levels, production schedules, and other factors in determining what materials and components need to be ordered when those materials and components need to be ordered, and how much of each item needs to be ordered.
MRP can be used to forecast customer demand for foundries by allowing foundries to create accurate forecasts based on customer demand data and production schedules. This, in turn, helps foundries to better manage their inventory, maximize production efficiency, and ensure that customer orders are fulfilled promptly.
Inventory Management
Inventory management for foundries is a process of controlling the raw materials, components, and finished goods that are used in the production of castings and other products. It involves tracking, storing, and ordering materials, and tracking production and inventory levels. It also includes assessing the quality of materials used.
Material requirements planning helps foundries to manage their inventory and production more efficiently. It is designed to identify the best way to meet production requirements by managing the availability of materials in the most efficient way.
MRP helps foundries determine what materials are needed, when, and in what quantities.
Preparing a BoM or Bill of Materials is another attribute of the MRP system. A BoM can be helpful to foundries by giving them a comprehensive list of the materials and components needed to produce a particular product. This list can be used to help them efficiently manage the supply chain, plan production, and ensure that the necessary materials are available on time and in the correct quantities.
Additionally, a BoM can provide a clear breakdown of the cost of each component, enabling foundries to accurately estimate their costs and set competitive prices for their products.
It also helps to track the progress of orders and shipments and to assess the effectiveness of inventory control activities. MRP can also be used to monitor inventory levels and forecast future materials demand. This can help foundries to avoid shortages or overstocking of materials, resulting in improved cost efficiency and productivity.
Supply Chain Management
The supply chain can be a challenge for foundries. Foundries must manage the supply of raw materials, ensure timely delivery of components, and manage the production process for the finished product.
Raw material acquisition: Foundries face the challenge of acquiring raw materials for production. They must source materials from reliable suppliers, ensure the material meets their quality standards and ensure it is delivered on time.
Ensure cost-efficiency of raw material: Additionally, they must make sure that the material is cost-effective and of the right quantity. Finally, they must also ensure that the material is environmentally friendly. All of these factors can be difficult to manage and require detailed planning.
Managing distribution: They must also manage the distribution of their products to customers. In addition, they must be able to respond quickly to changes in customer needs and the market. All this requires a well-coordinated supply chain that is able to respond quickly and efficiently to changes in customer demand and market conditions.
Cost of supply chain operations: In addition, foundries must manage the cost of their supply chain operations and ensure that they are able to remain competitive in terms of the quality and price of their products. This requires careful planning and monitoring of their supply chain operations. Moreover, it requires a strong understanding of the cost of their products.
MRP can help foundries to better manage their supply chain in several ways.
- Get historical and current data: MRP systems use historical data and current inventory levels to determine which materials will be needed for upcoming orders. This helps the foundry to plan for upcoming production cycles more accurately and minimize the chances of running out of materials.
- Track stock in real time: MRP systems can track inventory levels throughout the supply chain, alerting the foundry when stock is running low or when materials need to be reordered. This helps ensure that the foundry always has the right materials to meet production demands.
- Updates on supplier schedules: Finally, MRP systems can provide the foundry with real-time data about supplier delivery schedules and lead times. This helps the foundry to plan more effectively for upcoming orders. Furthermore, the foundry has the materials when it needs them.
Challenges Faced by Foundries Today
Foundries today face many challenges, including an increasingly competitive global market, rising raw material costs, and a shortage of skilled labor. Additionally, they must adhere to strict environmental regulations, improve their energy efficiency, and keep up with advances in technology. All of these factors require foundries to remain agile and up-to-date in their operations in order to stay competitive.
Let’s walk through the challenges the foundries face today.
Rising Raw Material Costs
Foundries are facing higher costs for raw materials like sand, fuel, and energy, which affects their profits. Rising raw material costs are a challenge for foundries because they are responsible for buying and sourcing the raw materials needed to produce their products. As the price of raw materials rises, foundries must either increase the prices of their products or find ways to reduce their costs.
This can be especially difficult for small foundries, which may need more resources to purchase materials in bulk or negotiate better deals with suppliers. Additionally, the rising cost of raw materials can cause foundries to focus on more profitable products and shift away from less profitable ones. This can have a negative impact on their business.
Increasing Competition
Foundries are facing increased competition from other foundries and from foreign manufacturers who can produce goods at lower costs. Increasing competition is a challenge for the foundries because it reduces profit margins as competitors try to undercut each other's prices.
Additionally, as competition increases, companies have to focus more on marketing and product differentiation, which can be costly. Finally, because of the competitive environment, companies must constantly innovate and seek out new technologies and processes to remain competitive.
All of these challenges make it difficult for foundries to remain profitable and competitive in a crowded market.
Environmental Regulations
Foundries must comply with a lot of environmental regulations and laws, which can be costly to implement. Environmental regulations can present a challenge for foundries due to the potential for large fines and other penalties for non-compliance.
- Environmental hazards: Foundries are especially vulnerable to environmental regulations because they can produce large amounts of hazardous air pollutants, including particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides.
- Water and waste regulations: Foundries are also vulnerable to water and waste regulations since they use large amounts of water and generate large amounts of waste.
- Disposal of byproducts: Additionally, they may be subject to regulations regarding the disposal of byproducts and the storage and handling of hazardous materials. Complying with all of these regulations can be costly and time-consuming, requiring foundries to invest in new technologies and procedures to ensure compliance.
Failure to comply with environmental regulations can result in significant fines, penalties, and reputational damage. Additionally, it can have a negative impact on the local environment, which could lead to further remediation.
Shortage of Skilled Labor
Foundries are facing a shortage of skilled labor, which makes it difficult to find qualified employees and increases labor costs. The shortage of skilled labor is a major challenge for the foundries, as it makes it difficult to find specialized personnel with the required skill sets to meet the demands of the business.
Longer production times: There could be higher labor costs and longer production times, as foundries have to rely on less experienced staff and pay more to retain them.
Lack of innovation: In addition, the need for more skilled labor can lead to a lack of innovation and disruption in the foundry industry due to the lack of experienced personnel. This can put foundries at a competitive disadvantage compared to other foundries that have access to more skilled labor.
Safety issues: Finally, the shortage of skilled labor can lead to an increased risk of accidents and safety hazards in the foundry environment. Without the right personnel to monitor and oversee operations, the chances of long-term damage or injury resulting from improper handling of equipment or materials are significantly increased.
Technology Adoption
Foundries must adopt new technologies in order to remain competitive and improve efficiency, but this can be costly and time-consuming.
Technology can be expensive to adopt: Technology adoption is a major challenge for the foundries due to its complexity and cost. Foundries need to invest in the latest technologies to stay competitive, but this requires significant capital expenditure and resources.
Often complicated procedure: Additionally, the complexity of the technology and the need to modify existing processes to accommodate the new technology can be a barrier to adoption. Inertia to adopting new technologies: Finally, the foundry's customers may need more time to be ready to purchase products made with the new technology, which can slow or stop the adoption.
Aging Infrastructure
Infrastructure is a tangible asset. Many foundries need more infrastructure and equipment, which can lead to inefficiencies and higher maintenance costs. This could be indicative of problematic asset management.
Aging infrastructure is a challenge for the foundries business because it can lead to increased maintenance costs and operational inefficiencies. As foundries age, the equipment and materials used to produce castings may need to be updated. Also, the technology used to monitor and manage production processes may become obsolete.
Aging infrastructure can also cause operational downtime due to equipment breakdowns, resulting in lost production time and potentially lost orders. Finally, as infrastructure ages, ongoing maintenance and repair costs increase due to the need for more frequent and expensive replacement parts.
Quality Control
Foundries must maintain high quality standards in order to remain competitive, but this can take time and effort to achieve. Quality control is a challenge for the foundries business because the manufacturing process involves many steps, each of which must be carefully monitored and controlled.
Foundry workers must ensure that the finished products meet all specifications and standards for quality. Quality control also requires strict adherence to safety protocols and procedures to protect workers, the environment, and the products the foundry is creating.
- Monitor consistency of the used materials: Additionally, foundries must monitor and control the consistency of the materials used in their products to ensure that they meet the desired specifications.
- Ensure quality on diverse parameters: Finally, foundries must also ensure that their products are within the acceptable parameters for cost, quality, and delivery.
The challenge of quality control is compounded by the fact that many foundries are highly specialized, with processes and materials that are unique to their industry. This requires a thorough understanding of the foundry's processes and materials and their corresponding quality control requirements.
Cost of Compliance
Foundries must comply with a lot of regulations, including safety, environmental, and labor laws, which can be expensive and time-consuming. The cost of compliance is a major challenge for the foundries business due to the ever-evolving regulatory landscape.
Foundries must comply with a variety of environmental, health and safety regulations, including those related to air and water pollution, hazardous materials, and workplace safety.
The cost of compliance can be significant, including the cost of implementing and monitoring new processes and equipment and the cost of fines and penalties associated with non-compliance. Additionally, compliance costs are often ongoing due to the need to regularly update processes and equipment to comply with new regulations.
Benefits of MRP Implementation for Foundries
We have seen the numerous challenges foundries face. From controlling inventory to customer service, foundries may have to deal with a host of issues. MRP systems can help foundries to improve inventory accuracy, reduce lead times, improve customer service, and reduce operating costs.
Improved Inventory Management
MRP systems can help foundries better manage their inventory levels by providing up-to-date information on the availability of materials and parts. This reduces the chances of stockouts and allows for more accurate forecasting of future inventory needs.
MRP for foundries can improve inventory management in the following ways:
- Allowing foundries to track their inventory levels in real time
- Optimize inventory levels to meet demand
- Minimize the cost of excess inventory
- Automate the ordering of new materials when stock levels dip below a predetermined threshold
Increased Efficiency
MRP systems can help foundries by streamlining their production processes, allowing them to work faster and more efficiently. This can lead to improved customer service and shorter lead times.
- MRP enables foundries to plan and schedule materials and resources more accurately, resulting in improved efficiency.
- It allows foundries to track and monitor inventory levels in real time, reducing the risk of overstocking or understocking.
- MRP systems help automate production processes and eliminate manual data entry errors, resulting in greater accuracy and fewer delays.
- MRP provides a unified view of data across the entire foundry, enabling better decision-making and improved efficiency.
Improved Quality
MRP systems can help foundries improve their product quality by providing more accurate information regarding the availability of materials and parts. This can lead to fewer mistakes and less waste.
- MRP helps reduce errors in production, resulting in improved quality.
- MRP enables foundries to better tracking of materials, ensuring higher quality products.
- MRP simplifies production planning and scheduling, leading to better quality control.
- MRP helps to identify and eliminate bottlenecks, resulting in improved quality.
Reduced Costs
MRP systems can help foundries reduce their costs by providing more accurate information about the availability of materials. This can lead to lower overhead costs, fewer stockouts, and fewer mistakes.
- MRP reduces costs for foundries by eliminating the need to store inventory and reducing the amount of labor required to manage production.
- MRP optimizes material requirements. Thus, fewer materials are being purchased and used, as well as more efficient utilization of existing materials.
- MRP helps to reduce setup times and improve scheduling. Thereby resulting in faster production cycles and fewer delays.
- MRP also helps foundries to identify areas of waste and inefficiency that can be addressed to reduce overall costs.
Improved Visibility
MRP systems can provide foundries with more visibility into their operations, allowing them to track and monitor their production processes better. This can lead to improved decision-making and better customer service.
- MRP increases visibility by providing detailed information about inventory levels, production schedules, and supplier performance.
- MRP helps foundries to make informed decisions about materials, capacity, and cost.
- MRP provides increased traceability of material and parts throughout the production process.
- MRP makes it easier to track and manage production costs. Thus, enabling better cost control and improved profitability.
Increased Flexibility
MRP systems can provide foundries with the flexibility to quickly adapt to changing customer demands and production schedules. This can lead to improved customer service and shorter lead times.
How to Implement MRP in Foundries?
There could be several steps that the companies may need to consider before implementing. Let’s look at them in detail in this section:
- Determine what components need to be produced: Before implementing an MRP system, it is important to determine what components need to be produced in the foundry. This should include the type of components, the quantity of each component, and the timeline for production.
- Set up a database: Once the components to be produced have been identified, a database must be established. This database should contain information on the components, such as part numbers, descriptions, and any other pertinent data. The database should also include the inventory levels of each component, as well as the lead times for each component.
- Create a bill of materials: Once the database is established, a bill of materials (BOM) can be created. The BOM should contain information on the components and the quantity of each component required for the production of each item. It should also include information on any sub-components that may be required.
- Establish production requirements: Once the BOM is created, the production requirements can be established. This includes the number of components needed for each item, the lead time required for production, and any other factors that may affect the production process.
- Calculate material requirements: Once the production requirements are established, the material requirements can be calculated. This includes the amount of each component needed, the timeline for production, and any other factors that may affect the production process.
- Generate production schedules: Once the material requirements are calculated, production schedules can be generated. This includes the production timeline, production order, and other factors that may affect the production process.
- Monitor and adjust schedules: Once the production schedules are generated, they should be monitored and adjusted as needed. This includes ensuring that the production process is running smoothly, that the timeline is being met, and that any issues are being addressed promptly.
- Monitor inventory levels: Finally, it is important to monitor inventory levels to ensure that the necessary components are available when needed. This includes ensuring that the inventory levels are sufficient to meet the production needs and that any issues are addressed promptly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, MRP for foundries is an important tool for streamlining production processes and improving efficiency. It helps to minimize waste and maximize output, resulting in increased profits. MRP for foundries also helps to reduce inventory costs and improve customer service.
Additionally, it enables foundries to react quickly and efficiently to changes in demand and customer requirements. MRP for foundries is an effective planning tool that enables foundries to plan and manage their resources efficiently and effectively. This can lead to improved productivity, cost savings, and customer satisfaction.
Overall, MRP for foundries is beneficial for both the foundries and the customers. It helps to optimize production processes and resource use, resulting in increased profits. It also helps to improve customer service and reduce inventory costs.
How can Deskera Help You?
Deskera can help foundries streamline their processes, reduce labor costs, and increase efficiency by providing accurate real-time data. It can help streamline supply chain management, automate customer invoicing and payment, and track inventory levels. It can also help with automating inventory processes and forecasting.
Deskera MRP is the one tool that lets you do all of the above. With Deskera, you can:
- Track raw materials and finished goods inventory
- Manage production plans and routings
- Maintain bill of materials
- Generate detailed reports
- Create custom dashboards
Deskera Books is an accounting software designed to help small businesses manage their accounts and finances. It is a cloud-based solution that is easy to use and can be accessed from anywhere, anytime. It helps businesses to track their expenses and income, generate invoices and reconcile accounts. It also offers features such as budgeting, forecasting and reporting.
Deskera People is a cloud-based HR and payroll software solution designed to help businesses streamline their HR processes. The software offers a range of features and tools to help businesses manage their HR operations more efficiently, including employee onboarding, leave and shift management, time and attendance tracking, payroll processing, benefits administration, and more.
Deskera CRM is a comprehensive customer relationship management (CRM) solution designed to help businesses of any size better manage their customer relationships. It provides a range of features to help businesses improve customer satisfaction and maximize revenue. The platform includes tools for managing contacts, automating marketing activities, tracking sales and customer service activities, and integrating with other enterprise systems.
Key Takeaways
- A foundry is a factory that melts and shapes metal into various forms and products. Foundries are used in the production of many different materials and objects, including car parts, machine parts, kitchen appliances, and even sculptures.
- Iron, steel, aluminum, and copper are the most common metals used in foundries.
- Foundries need MRP to manage the production of their products efficiently. MRP helps them plan material, production, and inventory needs and track costs and resources.
- Material planning, production planning, demand forecasting, inventory management, and supply chain management are the areas where the foundries need MRP systems.
- Foundries face challenges like increasing raw material costs, increasing competition, environmental regulations, and technology adoption, among others.
- MRP can be beneficial to foundries' business by improving inventory management, efficiency, quality, visibility, and flexibility.
- There are various steps in implementing MRP for foundries. These include setting up a database, creating BoMs, and establishing production requirements.
Related Articles












