As we navigate through 2024, the manufacturing industry continues to experience transformative changes driven by technological advancements, shifting market demands, and a focus on sustainability.
Data shows the global manufacturing industry’s growth to be at a rate of 18.2%, underscoring the sector's robust expansion and the dynamic innovations propelling it forward (Source: Infosys BPM).
These trends not only reflect the current state of the industry but also offer a glimpse into the future of manufacturing, where efficiency, agility, and adaptability are paramount.
One of the key players in this evolving landscape is Deskera ERP, a comprehensive enterprise resource planning solution designed to streamline manufacturing processes.
Deskera ERP offers a suite of tools that enable manufacturers to manage their operations more efficiently, from inventory control and supply chain management to production planning and quality assurance.
By integrating these functions into a single platform, Deskera ERP helps manufacturers reduce costs, enhance productivity, and maintain a competitive edge in the rapidly changing market.
In this article, we will be discussing the top manufacturing trends in 2024.
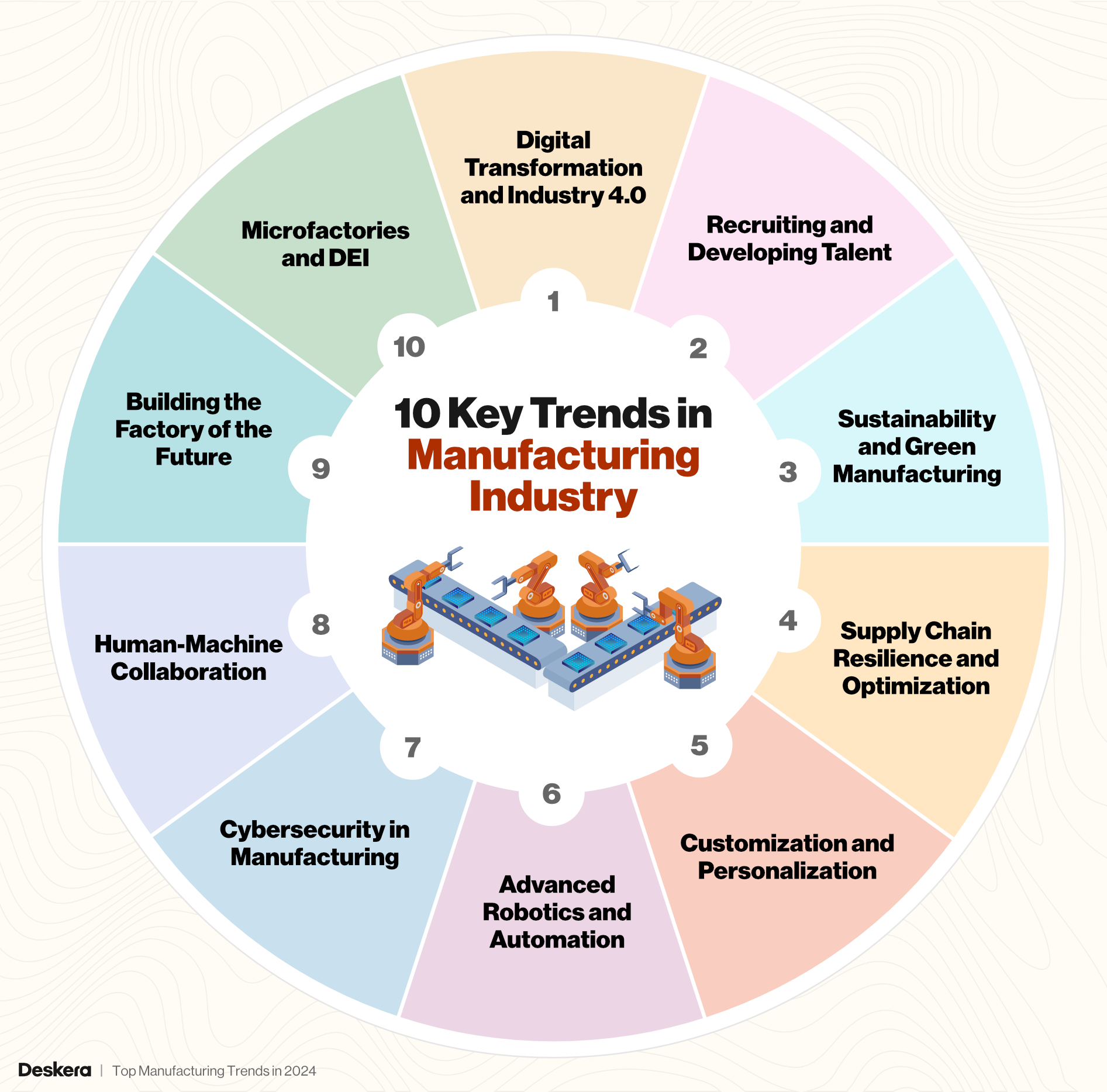
10 Key Trends in Manufacturing Industry
The manufacturing industry is at the cusp of a significant transformation, driven by rapid technological advancements and evolving market demands. As we progress through 2024, the sector is witnessing remarkable growth.
This robust growth underscores the importance of staying abreast of the latest trends that are reshaping the industry landscape.
Digital Transformation and Industry 4.0
In 2024, one of the most significant manufacturing industry trends is the digital transformation driven by Industry 4.0 technologies.
This transformative shift is marked by the integration of advanced technologies, such as IoT (Internet of Things), AI (Artificial Intelligence), machine learning, and cloud computing, into manufacturing processes.
These innovations are enabling manufacturers to achieve unparalleled levels of efficiency, agility, and productivity.
Real-Time Data and Smart Manufacturing
Digital transformation in manufacturing involves the deployment of smart manufacturing systems that collect and analyze data in real-time. This data-driven approach facilitates predictive maintenance, which helps in minimizing downtime and extending machinery lifespan.
For instance, business intelligence and data analytics software have become recent trends in manufacturing technology, with 79% of businesses expecting a positive ROI within 18 months of investing in these tools.
The Role of ERP Systems
A crucial component of this transformation is the adoption of manufacturing ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems.
These systems consolidate various functions such as inventory management, production planning, and quality control into a unified platform, offering a comprehensive view of operations.
By integrating these functions, ERP systems streamline processes, cut costs, and enhance decision-making capabilities.
AI and Machine Learning in Manufacturing
Among the top digital transformation trends in manufacturing, the use of AI and machine learning is particularly notable. These technologies automate complex tasks, improve product quality, and optimize supply chains.
Additionally, IoT devices are used to remotely monitor equipment and processes, leading to improved efficiency and reduced operational costs.
Benefits of Digital Transformation
The benefits of digital transformation in manufacturing are extensive. Companies adopting these manufacturing technology trends can expect enhanced operational efficiency, faster time-to-market, and increased customer satisfaction.
Digital tools also foster better collaboration and communication across the supply chain, resulting in more resilient and responsive operations.
Impact on the Automotive Sector
In the automotive sector, digital transformation is driving significant advancements. Automotive manufacturing trends include the rise of smart factories, where interconnected systems and automated processes enhance production capabilities.
These advancements are crucial for meeting evolving automotive market trends, such as the shift towards electric and autonomous vehicles.
The Role of IIoT and 5G
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is central to these advancements, involving networks of physical objects embedded with sensors and software that collect and exchange data over the internet.
For example, automobile manufacturers use IIoT to monitor factory robots and identify maintenance needs before they disrupt the assembly line. Industrial manufacturers also use IoT data to track assets and monitor machine conditions, such as temperature and humidity, to predict failures and perform timely maintenance.
5G technology plays a pivotal role in IIoT by providing the necessary speed and low latency for extensive sensor networks. Companies like John Deere and Ford are already utilizing 5G to connect thousands of sensors, enhancing their operational efficiency. Adoption of IIoT among manufacturers is projected to grow from about 10% in 2020 to nearly 50% by 2025.
Closing the Competitive Gap
The gap between manufacturers investing in digital transformation and those lagging behind is widening. A survey by IndustryWeek and Oracle indicates that improving efficiency, developing innovative products, responding to market demands, and strengthening customer relationships are top priorities for manufacturers.
Additionally, the trend towards microfactories—small, modular, highly automated facilities near customer bases—exemplifies the next wave of digital transformation. These microfactories reduce shipping costs, enable customization, and rely heavily on IoT and robotics.
Staying Competitive and Secure
As the manufacturing industry continues to evolve, staying informed about recent trends in manufacturing technology is essential. Investing in IT trends in manufacturing, such as cloud-based solutions and cybersecurity measures, ensures that manufacturers remain competitive and secure in the digital age.
By embracing these manufacturing trends examples, companies can navigate the complexities of the modern industrial landscape and thrive in 2024 and beyond.
Recruiting and Developing Talent
The labor shortages in the US manufacturing industry are expected to intensify due to several factors.
With an aging workforce retiring faster than they can be replaced, many workers are leaving for other sectors that offer higher pay and more stable employment.
Additionally, there is a significant challenge in attracting younger specialists to manage the robots, sensors, and software integral to Industry 4.0 factories.
McKinsey predicts a 30% decline in demand for traditional skills involving physical labor over the next decade, while the need for technical skills will increase by 50%. Despite this shift, manufacturers still struggle to find skilled machinists, welders, metalworkers, and production supervisors.
Implementing Employee Retention Strategies
The skills shortage in the US manufacturing sector could result in 2.1 million unfilled jobs by 2030, potentially costing the industry $1 trillion in that year alone, according to a 2021 Deloitte and The Manufacturing Institute study.
Attracting and retaining workers is a top priority for 83% of US-based manufacturing leaders surveyed, with 45% reporting that they had turned down business opportunities due to a lack of workers.
To address this challenge, manufacturers are employing various strategies. According to a 2022 survey by the National Institute of Manufacturers, nearly three-quarters of respondents planned to raise wages by an average of 3% in 2022, following larger increases in 2021 during the pandemic.
As manufacturing shifts towards digitalization, companies are reskilling their workforce and ensuring employees understand how their roles contribute to the company’s success.
Developing comprehensive recognition programs has also proven effective. A 2020 survey by The Manufacturing Institute’s Center for Manufacturing Research and the American Psychological Association found that nearly all respondents who felt valued by their employer were highly motivated (97%), satisfied with their job (97%), and would recommend their company (96%).
Modernizing facilities to improve the work environment is another approach. Manufacturers are introducing robots and drones to handle dangerous tasks and are enabling hybrid and remote work options.
Decades of labor offshoring and outsourcing have tarnished the manufacturing industry’s reputation as a source of stable, well-paying jobs. To counter this perception, manufacturers are focusing on career development and continuous learning to retain the next-generation workforce.
Overcoming Workforce Shortages Through Reskilling
Investing in reskilling programs is crucial for attracting young employees. A 2020 study by The Manufacturing Institute’s Center for Manufacturing Research and the American Psychological Association found that nearly 70% of manufacturing employees under 25 remained with their employers because of skill development opportunities, and 65% stayed due to career advancement prospects.
Employers should offer diverse reskilling programs, including live courses, recorded videos, and augmented/virtual reality training.
Programs like America’s Cutting Edge, initiated by the Institute for Advanced Composites Manufacturing Innovation (IACMI), aim to train individuals for the machine tools industry.
The National Association of Manufacturers and The Manufacturing Institute’s Creators Wanted program connects people with training, job openings, and new career pathways.
Additionally, colleges and universities, such as Northeast Wisconsin Technical College and Northwestern University, offer Industry 4.0 study programs covering cybersecurity, the Industrial Internet of Things, and robotics.
Diversifying the Workforce
Manufacturers face difficulties in finding entry-level candidates and technically skilled workers for modern factory systems. To meet this challenge, they must attract more women and underrepresented ethnic groups.
Women account for less than one-third of the manufacturing workforce, while Black, Asian, and Latinx employees make up 36%, according to 2022 data from the US Bureau of Labor Statistics.
National efforts include a Department of Defense-sponsored $6.2 billion initiative to train and reskill the future workforce and a National Association of Manufacturers campaign that provides mentors to women and aims to change industry perceptions.
Current Concerns and Investment in Technology
Looking into the year ahead, manufacturing businesses are primarily concerned about finding qualified talent (35%), acquiring new customers or clients (35%), and training and upskilling employees (34%). To navigate these challenges, manufacturers are increasingly investing in technology.
For instance, 61% of industry professionals in growth-mode businesses plan to spend 10% or more on software in 2024 compared to 2023. Business intelligence and data analytics software are among the top recent trends in manufacturing technology, with 79% of businesses expecting a positive ROI within 18 months of purchase.
Sustainability and Green Manufacturing
Sustainability is becoming one of the most important manufacturing industry trends as companies strive to reduce their environmental impact and embrace green manufacturing practices.
According to a 2023 report by the US Environmental Protection Agency, the manufacturing and raw materials industries account for 23% of greenhouse gas emissions in the US.
Although there has been progress in reducing these emissions, there is still significant work to be done. Manufacturers must evaluate their entire supply chain to identify opportunities for waste reduction, increased supplier diversity, and the use of fuel-efficient and electric vehicles both on the factory floor and for product delivery.
Prioritizing Sustainability and Carbon Neutrality
A 2022 study by Climate Impact Partners highlighted that 42% of the companies in the Fortune Global 500 have reached significant climate milestones or committed to doing so by 2030.
Achieving carbon neutrality, where companies remove as much carbon dioxide from the atmosphere as they emit, is a critical initial step. However, climate experts emphasize that to meet zero-carbon goals, companies must address emissions across the entire supply chain.
Recent trends in manufacturing technology include investing in smart building technologies like sensor-controlled heating, cooling, and lighting systems. Manufacturers are also increasingly turning to renewable energy sources for their facilities and utilizing electric vehicles for the transportation of raw materials, benefiting from clean vehicle tax credits.
In a 2021 McKinsey survey, 22% of manufacturers reported generating value from sustainability initiatives over the past five years, and 40% expect to generate value in the next five years. These benefits include cost savings from reduced energy usage and enhanced customer engagement.
Prioritizing Corporate Social Responsibility
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is another key area of focus for manufacturers. The US Environmental Protection Agency defines CSR as a form of self-regulation where a company ensures its activities positively impact the environment, consumers, employees, and communities.
In the manufacturing industry, CSR efforts typically encompass two main areas: environmental sustainability and social progress.
Environmental sustainability includes initiatives like recycling, reducing fossil fuel consumption, and minimizing waste. Social progress involves addressing issues such as the gender wage gap, equitable hiring and promotion practices, paying a living wage, and improving workplace safety.
The benefits of these initiatives extend beyond environmental and social impacts—they also positively affect the bottom line.
A 2022 survey by Lab42 found that 84% of respondents are willing to pay more for products from companies they perceive as socially responsible.
This consumer preference underscores the importance of integrating sustainability and CSR into the core strategies of manufacturing companies.
Embracing Sustainable Manufacturing Trends
As sustainability becomes a central aspect of manufacturing trends in 2024, companies are increasingly aware of the benefits of digital transformation in manufacturing.
Implementing Manufacturing ERP systems helps integrate sustainability initiatives into everyday operations, providing insights into energy usage, waste management, and supply chain efficiency. These manufacturing trends examples illustrate how technology can drive significant improvements in sustainability.
In the automotive sector, manufacturers are responding to automotive market trends by incorporating green manufacturing practices. Electric vehicles (EVs) are a prominent example, as automakers invest in sustainable production processes and supply chains to support the growing demand for EVs.
This shift aligns with broader automotive manufacturing trends focused on reducing carbon footprints and enhancing environmental stewardship.
Overall, the manufacturing industry is at a pivotal point where embracing sustainability and green manufacturing practices is not just beneficial but essential.
By staying ahead of manufacturing technology trends and incorporating CSR into their operations, manufacturers can achieve long-term success while contributing to a healthier planet.
Supply Chain Resilience and Optimization
In today's dynamic manufacturing landscape, supply chain resilience and optimization have emerged as critical trends in the manufacturing industry.
The persistent supply chain disruptions over recent years have compelled manufacturers to reevaluate their sourcing strategies and production locations. Historically, manufacturers began sourcing materials from lower-cost countries and offshoring operations in the 1960s to capitalize on reduced labor expenses.
However, rising labor costs in these countries, escalating shipping expenses, fluctuating exchange rates, and the increasing emphasis on environmental and social sustainability goals are driving a shift back towards reshoring and supplier diversification.
Solving Supply Chain Disruptions
A 2021 survey by the industrial sourcing marketplace Thomas found that 83% of North American-based manufacturers were likely or extremely likely to reshore at least part of their operations, a significant increase from 54% the previous year. This trend reflects a broader movement towards diversifying the supplier base by onboarding suppliers from different regions.
According to a 2021 survey by advisory firm BDO, more than half of manufacturers were seeking alternative or backup suppliers. However, manufacturers must carefully balance the benefits of supplier diversification with the added complexity and cost of managing a larger supplier network.
The recent trends in manufacturing technology, such as advanced analytics and AI-driven supply chain management tools, are instrumental in optimizing these complex supplier networks.
Manufacturing ERP systems provide real-time visibility into supply chain operations, helping companies anticipate and mitigate disruptions. These systems enable manufacturers to make informed decisions, enhancing supply chain resilience.
Diversifying Supplier Base
Diversifying the supplier base is a critical strategy for enhancing supply chain resilience. By onboarding suppliers from different regions, manufacturers can mitigate risks associated with geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, and other disruptions. However, this approach requires careful management to balance the benefits of diversification with the added complexity and costs.
Recent trends in manufacturing technology, such as advanced analytics and AI-driven supply chain management tools, play a vital role in optimizing these complex supplier networks.
Manufacturing ERP systems provide real-time visibility into supply chain operations, enabling manufacturers to anticipate and mitigate potential disruptions more effectively. These systems facilitate informed decision-making, enhancing overall supply chain resilience.
Shifting to Product as a Service
One of the most promising recent trends in manufacturing is the shift towards offering products as a service (PaaS). This model involves charging fixed or usage-based prices, often through a subscription.
For instance, car manufacturers have begun offering vehicles as a service, where customers pay an upfront enrollment fee and a monthly subscription fee.
Unlike traditional leases, the automaker typically handles registration, taxes, insurance, roadside assistance, and maintenance, allowing customers to switch to new car models periodically.
The PaaS model extends beyond automotive manufacturing trends to include various industrial applications. Manufacturers of welding robots, for example, might offer a certain number of welds for a set price rather than selling the robots outright.
This approach provides several benefits, including more regular and predictable revenue streams, opportunities for cross-selling and upselling, and invaluable data on product usage that can inform future product development and revenue strategies.
Benefits of Product as a Service
The PaaS model, also known as XaaS (Anything as a Service), aligns with the broader manufacturing industry trends towards digital transformation.
It leverages the benefits of digital transformation in manufacturing by integrating cloud-based solutions, IoT, and advanced analytics.
This model not only improves customer satisfaction by offering flexible and cost-effective solutions but also enables manufacturers to gather data on customer usage patterns, leading to enhanced product innovation and personalized services.
Embracing Resilient and Optimized Supply Chains
As manufacturers continue to navigate the complexities of global supply chains, embracing resilience and optimization strategies will be crucial. Investing in recent trends in manufacturing technology, such as AI, IoT, and advanced analytics, can significantly enhance supply chain visibility and responsiveness.
By adopting a proactive approach to supply chain management and leveraging the latest manufacturing technology trends, companies can better withstand disruptions and maintain a competitive edge in the manufacturing industry.
Customization and Personalization
Customization and personalization have emerged as pivotal trends in the manufacturing industry in 2024.
As customer demands become increasingly sophisticated, manufacturers are shifting their focus toward creating tailored products and experiences.
This trend is driven by advancements in manufacturing technology and a growing emphasis on customer-centric approaches.
The Demand for Customization
Today's consumers expect products that cater to their specific needs and preferences.
This shift is particularly evident in the automotive manufacturing trends, where buyers increasingly seek vehicles with personalized features and configurations.
The ability to offer customization not only enhances customer satisfaction but also provides manufacturers with a competitive edge in a crowded marketplace.
Leveraging Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
Recent trends in manufacturing technology, such as additive manufacturing (3D printing), AI, and IoT, are enabling manufacturers to offer unprecedented levels of customization.
These technologies allow for the production of bespoke products on demand, reducing lead times and minimizing waste.
Manufacturing ERP systems play a crucial role in managing the complexity of customized production processes by providing real-time data and analytics to streamline operations.
Mass Customization
Mass customization is a strategy that combines the efficiency of mass production with the flexibility of customization. This approach allows manufacturers to produce a high volume of personalized products without compromising on cost or quality.
For instance, in the apparel industry, companies can offer custom-fit clothing by leveraging advanced manufacturing technology trends such as automated pattern cutting and digital fabric printing.
Personalization in the Automotive Industry
The automotive market trends are increasingly leaning towards personalization, with car manufacturers offering a wide range of customizable options.
Customers can choose from various interior and exterior features, such as color schemes, upholstery materials, and advanced infotainment systems.
This level of personalization not only meets individual preferences but also enhances the overall driving experience.
Benefits of Customization and Personalization
The benefits of digital transformation in manufacturing extend to customization and personalization.
By integrating IoT and AI, manufacturers can gather and analyze data on customer preferences, enabling them to offer more targeted and relevant products. This approach leads to higher customer satisfaction, increased customer loyalty, and greater lifetime value.
Challenges and Solutions
While customization and personalization offer significant advantages, they also present challenges. Managing the complexity of customized production can strain traditional manufacturing processes.
However, the adoption of recent trends in manufacturing technology, such as advanced analytics and machine learning, can help manufacturers overcome these challenges by optimizing production schedules, reducing lead times, and ensuring quality control.
The Future of Customization and Personalization
As we look to the future, customization and personalization will continue to be at the forefront of manufacturing industry trends. Manufacturers will increasingly leverage digital tools and technologies to deliver tailored products that meet the unique needs of their customers.
The trend towards customization and personalization is not limited to consumer products but extends to industrial manufacturing trends, where businesses seek customized solutions to enhance their operations and meet specific requirements.
Advanced Robotics and Automation
Advanced robotics and automation are rapidly transforming the manufacturing industry, making them integral to the latest manufacturing industry trends.
These technologies are enhancing productivity, reducing labor costs, and improving workplace safety, aligning with broader trends in manufacturing technology.
Rising Adoption Rates
While automation has long been a part of the manufacturing landscape, recent years have seen a significant uptick in the adoption of robots, cobots (collaborative robots), drones, and autonomous vehicles.
According to the Association for Advancing Automation, North American orders for workplace robots surged by 25% in the second quarter of 2022 compared to the previous year.
Despite a slight decline in orders early in 2023, the global market for industrial robots is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.5% from 2023 to 2030, as reported by Grand View Research.
Similarly, the global cobot market, which was valued at $475 million in 2020, is expected to reach $8 billion by 2030, reflecting a dramatic expansion from ABI Research.
Automation in Agriculture and Food Production
One of the most dynamic sectors embracing advanced robotics is agriculture and food production. IMARC's report highlights that the global agricultural robotics market is anticipated to increase from $7.6 billion in 2022 to $21.1 billion by 2028, reflecting a CAGR of 18.4% for this period.
Agricultural robots are poised to revolutionize the industry by handling tasks from planting to weeding and harvesting, showcasing the profound impact of automation on industrial manufacturing trends.
Lights-Out Factories
In broader manufacturing, the concept of "lights-out" factories is gaining traction. These facilities operate with minimal human intervention, often functioning entirely in the dark.
This model of advanced robotics and automation minimizes human error and maximizes efficiency, setting new standards for manufacturing technology trends.
The shift towards lights-out operations highlights the ongoing evolution in manufacturing processes, driven by the integration of sophisticated robotic systems and automation tools.
Benefits of Advanced Robotics
The benefits of incorporating advanced robotics into manufacturing processes are substantial. These technologies not only reduce labor costs but also enhance safety and productivity.
By automating repetitive and hazardous tasks, manufacturers can improve overall workplace safety and ensure more consistent product quality.
Additionally, advanced robotics support the trend towards greater customization and personalization by enabling precise and flexible manufacturing processes.
The Future of Robotics and Automation
As we look to the future, advanced robotics and automation will continue to be at the forefront of trends in manufacturing.
The integration of these technologies is expected to drive further innovations in manufacturing ERP systems, providing real-time insights and optimizing production processes.
The continued growth of the robotics market, coupled with advancements in AI and machine learning, will further enhance the capabilities of manufacturing automation.
Cybersecurity in Manufacturing
Cybersecurity has become a crucial focus for the manufacturing industry in 2024, driven by the rapid advancement of manufacturing technology and the increasing sophistication of cyber threats.
As manufacturers embrace digital transformation and integrate technologies such as IoT, AI, and advanced robotics, ensuring robust cybersecurity measures is essential to protect sensitive data, maintain operational integrity, and safeguard against potential disruptions.
The Growing Importance of Cybersecurity
The rise of recent trends in manufacturing technology has introduced new vulnerabilities to industrial systems.
With the adoption of manufacturing ERP systems, connected devices, and cloud-based solutions, manufacturers are more exposed to cyber threats than ever before.
Cybersecurity in manufacturing is no longer just about protecting IT infrastructure but also about securing operational technology (OT), which includes everything from control systems to industrial networks.
Key Cybersecurity Threats
Manufacturers face several key cybersecurity threats, including ransomware attacks, data breaches, identity thefts, and cyber-espionage.
These threats can lead to significant financial losses, operational downtime, and damage to a company’s reputation. As manufacturing technology trends evolve, the complexity of cyber threats continues to increase.
For example, cybercriminals may target vulnerabilities in IoT devices or exploit weaknesses in connected supply chain systems to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Strategies for Enhancing Cybersecurity
To address these cybersecurity challenges, manufacturers must implement comprehensive strategies that encompass both IT and OT security.
This includes deploying advanced security solutions, conducting regular vulnerability assessments, and ensuring robust data encryption and access controls.
Integrating cybersecurity best practices into manufacturing ERP systems and other critical infrastructure is essential for protecting against potential breaches.
- Adopting Advanced Security Technologies: The use of AI and machine learning can enhance threat detection and response capabilities. These technologies help identify and mitigate cyber threats in real-time, providing manufacturers with a proactive approach to cybersecurity.
- Regular Training and Awareness: Educating employees about cybersecurity best practices and potential threats is crucial. Regular training can help prevent phishing attacks and ensure that staff are aware of their role in maintaining cybersecurity.
- Implementing Robust Access Controls: Limiting access to sensitive data and systems to authorized personnel only helps reduce the risk of insider threats and accidental breaches. Multi-factor authentication and strong password policies are essential components of a secure access control strategy.
- Ensuring Compliance with Industry Standards: Adhering to industry standards and regulations, such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework or ISO/IEC 27001, can help manufacturers establish a solid cybersecurity foundation and demonstrate their commitment to protecting sensitive information.
The Role of Cybersecurity in Digital Transformation
As manufacturers continue to adopt digital transformation initiatives, such as integrating IoT and automation into their operations, cybersecurity must be a top priority.
The benefits of digital transformation in manufacturing are substantial, including increased efficiency and improved decision-making.
However, these benefits can only be realized if cybersecurity measures are in place to protect against potential threats.
Future Trends in Cybersecurity
Looking ahead, cybersecurity will remain a critical aspect of manufacturing industry trends. As the adoption of smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 technologies grows, so will the need for advanced cybersecurity solutions.
The focus will shift towards protecting complex, interconnected systems and ensuring that cybersecurity measures evolve in tandem with technological advancements.
Human-Machine Collaboration
Human-machine collaboration stands at the forefront of manufacturing industry trends in 2024, reflecting a significant shift in how humans and machines interact in the industrial environment.
As manufacturers embrace advanced robotics, automation, and other recent trends in manufacturing technology, the synergy between human operators and machines is becoming increasingly crucial for optimizing productivity, enhancing safety, and driving innovation.
The Evolution of Human-Machine Interaction
The integration of advanced robotics and automation into manufacturing processes has transformed traditional workflows.
Modern manufacturing technology trends emphasize the importance of human-machine collaboration, where robots, cobots (collaborative robots), and automated systems work alongside human operators.
This collaboration is not only reshaping the manufacturing industry but also setting new standards for efficiency and operational excellence.
Benefits of Human-Machine Collaboration
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: One of the primary benefits of human-machine collaboration is the significant boost in efficiency and productivity. Robots and automation systems handle repetitive, high-precision tasks, while human operators focus on complex decision-making and oversight. This combination enables faster production cycles, higher accuracy, and reduced operational downtime.
- Enhanced Workplace Safety: Advanced robotics and automation contribute to a safer work environment by taking over hazardous tasks. Collaborative robots, or cobots, are designed to work alongside humans without the need for safety cages, reducing the risk of injuries and creating a safer workplace. This trend is particularly relevant in automotive manufacturing trends, where safety and precision are paramount.
- Improved Quality Control: The use of robotics and automation in manufacturing processes enhances quality control by ensuring consistent and precise execution of tasks. Human operators can monitor these systems and make real-time adjustments as needed, ensuring that products meet the highest quality standards.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Human-machine collaboration offers greater flexibility in manufacturing processes. Robots and automation systems can be reprogrammed or reconfigured to accommodate changes in production requirements, while human operators can quickly adapt to new tasks and technologies. This adaptability is essential for meeting the dynamic demands of manufacturing trends 2024.
Implementing Effective Collaboration Strategies
To maximize the benefits of human-machine collaboration, manufacturers must focus on several key strategies:
- Training and Upskilling: Ensuring that human operators are well-trained and skilled in working with advanced robotics and automation systems is crucial. Training programs should emphasize the interaction between humans and machines, focusing on how to effectively operate, monitor, and troubleshoot automated systems.
- Integration of Manufacturing ERP Systems: Integrating manufacturing ERP systems with robotics and automation technologies provides real-time data and insights, facilitating smoother collaboration between human operators and machines. This integration enhances decision-making, process optimization, and overall operational efficiency.
- Continuous Improvement and Innovation: Manufacturers should continuously assess and refine their human-machine collaboration strategies. Leveraging feedback from operators and analyzing performance data can help identify areas for improvement and drive innovation in manufacturing processes.
The Future of Human-Machine Collaboration
As we look to the future, human-machine collaboration will continue to be a defining trend in the manufacturing industry.
Advances in AI, machine learning, and robotics will further enhance the capabilities of automated systems, while human operators will play a critical role in overseeing, guiding, and optimizing these technologies.
The evolving landscape of industrial manufacturing trends will increasingly rely on the effective integration of human and machine efforts to achieve greater efficiency, innovation, and success.
Building the Factory of the Future
The vision for the factory of the future is marked by remarkable advancements in automation, efficiency, and data integration.
As manufacturing technology trends evolve, the factory of tomorrow will feature an array of cutting-edge technologies, including drones, AI, IoT, and robotics, which will collectively minimize human error and enhance operational accuracy.
With these advancements, there will be a shift from manual labor to more analytical and strategic roles, as smart factories leverage data to drive decisions and optimize performance.
The Role of Modern ERP Systems
At the heart of the smart factory's success lies a robust back-office infrastructure, supported by modern enterprise software.
The transition to Industry 4.0, characterized by increased automation and connectivity, hinges on the effective use of ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems, along with SCM (Supply Chain Management) and PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) tools.
Many manufacturers are grappling with outdated legacy systems that are fragmented and challenging to update, exacerbated by complexities introduced through mergers and acquisitions.
Modernizing ERP systems is a crucial step for manufacturers seeking to capitalize on the benefits of smart manufacturing.
Moving ERP systems to cloud-based platforms provides several advantages, including access to regular updates, enhanced security features, and the ability to scale applications based on demand.
Cloud ERP solutions offer integrated suites that combine finance, manufacturing, and other functions, delivering comprehensive visibility and streamlined operations across the enterprise.
Leveraging Data-Driven Decision-Making
Manufacturing processes generate vast amounts of data, necessitating sophisticated analytics tools to extract actionable insights.
For instance, an offshore oil platform can produce up to 2 terabytes of data daily from hundreds of thousands of sensors, as highlighted by Cisco. This data is crucial for predictive maintenance, operational efficiency, and safety.
As the volume of data grows, manufacturers are increasingly focusing on analytics software to enhance forecasting, manage inventory, and preempt supply chain disruptions.
According to Deloitte, 60% of companies prioritized analytics in 2023 to improve their ability to predict shortages and optimize resource allocation. Moreover, a 2023 LNS Research report noted that 37% of manufacturers identified data quality as a critical area for improvement.
Digital twins—virtual replicas of physical manufacturing systems—are another significant technology enabling data-driven decision-making.
These digital models allow manufacturers to simulate various scenarios, from supply chain fluctuations to equipment performance, providing valuable insights that inform production planning and quality assessment.
By utilizing digital twins, manufacturers can make well-informed decisions and optimize both their operations and end products before committing to physical changes.
The Future of Manufacturing
The factory of the future will blend advanced robotics, cloud-based ERP systems, and data analytics to achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency and innovation.
By embracing these trends and technologies, manufacturers can enhance operational precision, streamline processes, and remain competitive in a rapidly evolving industry landscape.
As the industry continues to advance, the integration of these technologies will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of manufacturing.
Microfactories and DEI
The manufacturing landscape is evolving rapidly, with microfactories and diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) initiatives emerging as pivotal trends in 2024.
These developments are reshaping production processes and fostering a more inclusive industry environment, reflecting the broader shifts in manufacturing technology and practices.
Modernizing Through Microfactories
Microfactories represent a transformative shift in manufacturing. Unlike traditional large-scale factories, microfactories are small, highly automated facilities designed to be more flexible and cost-efficient. This model allows manufacturers to respond more swiftly to market demands and customize production processes with greater ease.
A notable example is Arrival, an electric vehicle startup that gained significant attention in 2020 with a $110 million deal with Hyundai and a substantial order for 10,000 electric vans from UPS. Arrival is leveraging the microfactory model to revolutionize vehicle production.
The company plans to build over 1,000 microfactories worldwide by 2026, underscoring the growing appeal of this approach. These microfactories, being smaller and less expensive than traditional factories, align well with the broader goals of digital transformation and manufacturing efficiency.
Leveraging Advanced Technologies
Microfactories are a key component of smart manufacturing, driven by Industry 4.0 technologies. The integration of IoT, AI, and robotics into these facilities enhances operational efficiency and flexibility. IoT devices monitor equipment performance, AI optimizes production schedules, and robotics automate tasks, reducing downtime and operational costs.
The benefits of microfactories extend to sustainability as well. Their localized production model minimizes transportation needs, contributing to lower carbon emissions. This aligns with recent trends in manufacturing technology, where digital tools and automation play a crucial role in achieving environmental and efficiency goals.
Prioritizing Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI)
Simultaneously, the manufacturing industry is placing increasing emphasis on DEI. According to the Manufacturing Institute, 64% of manufacturers view DEI efforts as a critical focus for their organizations. This shift is driven by the recognition that a diverse and inclusive workforce fosters innovation and strengthens competitive advantage.
In response, the National Association of Manufacturers and the Manufacturing Institute have introduced the Pledge of Action. This initiative aims to advance equity and inclusion by committing to 50,000 tangible actions and creating 300,000 job opportunities for minorities by 2030.
The pledge highlights the industry’s commitment to improving DEI and reflects a broader trend towards creating supportive and equitable work environments.
Integrating Trends for Future Success
As the manufacturing industry embraces microfactories and DEI initiatives, it is setting the stage for a more agile, equitable, and sustainable future. These trends not only enhance operational efficiency but also promote a more inclusive and innovative industry landscape.
By integrating advanced technologies with a strong commitment to DEI, manufacturers can navigate the complexities of the modern industrial environment and thrive in 2024 and beyond.
How can Deskera ERP Help You with Manufacturing?
Deskera ERP offers a comprehensive suite of features tailored to enhance various aspects of manufacturing operations.
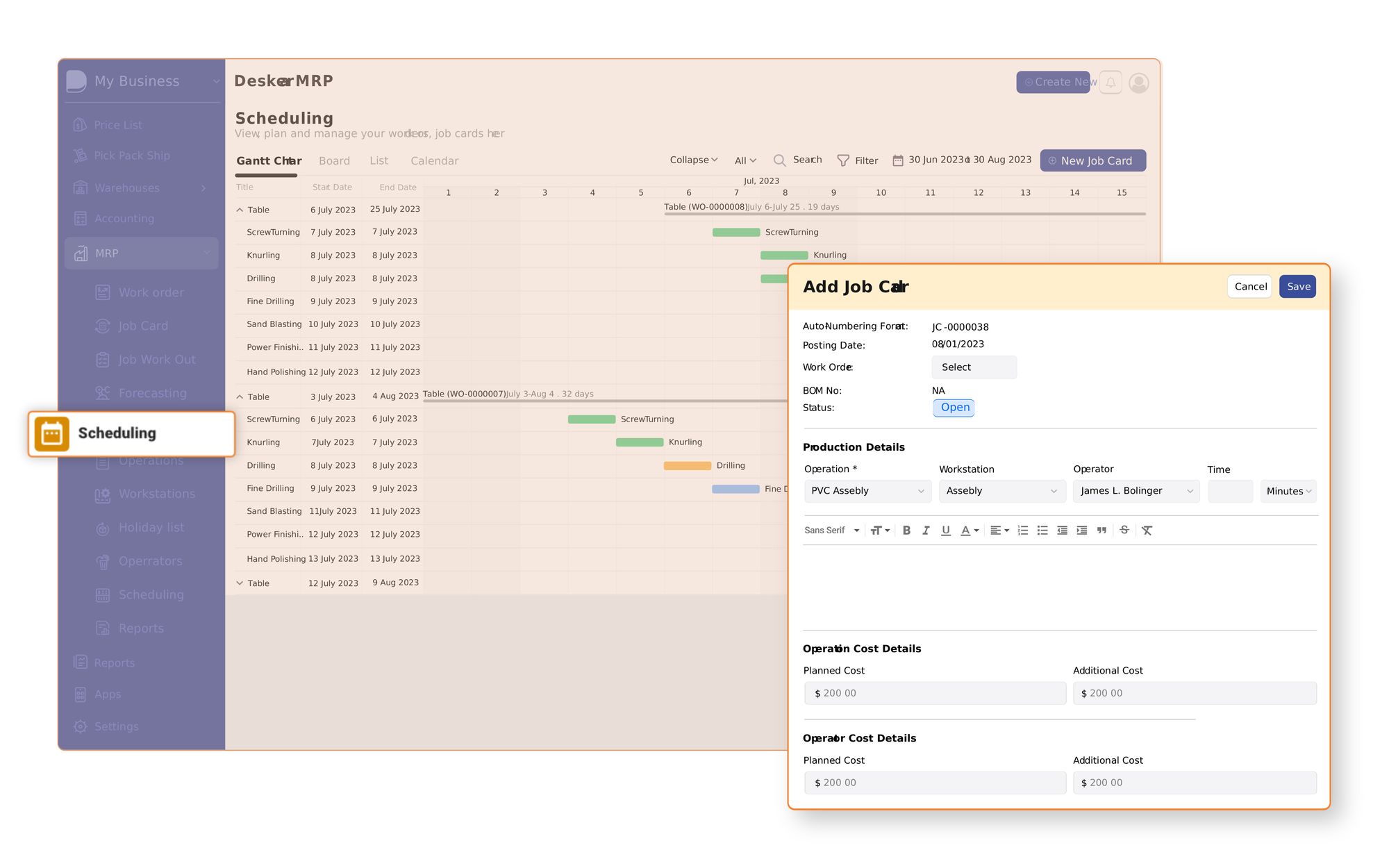
Here’s how Deskera ERP can significantly benefit manufacturing businesses:
1. Streamlined Production Planning
Deskera ERP provides robust tools for production planning and scheduling, enabling manufacturers to efficiently manage their production processes. The system integrates data from different departments, such as inventory and sales, to optimize production schedules, minimize downtime, and ensure timely order fulfillment.
2. Real-Time Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is crucial in manufacturing. Deskera ERP offers real-time tracking of raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods. This visibility helps prevent stockouts and overstocking, reduces carrying costs, and ensures that materials are available when needed for production.
3. Enhanced Quality Control
Quality control is vital for maintaining product standards. Deskera ERP includes features for monitoring and managing quality throughout the manufacturing process. The system helps in setting quality benchmarks, tracking defects, and implementing corrective actions to ensure that products meet quality standards.
4. Integrated Supply Chain Management
Deskera ERP’s supply chain management tools streamline the procurement process, manage supplier relationships, and ensure timely delivery of materials. By integrating supply chain data with production schedules, manufacturers can optimize their procurement strategies and reduce lead times.
5. Comprehensive Financial Management
Manufacturers can benefit from Deskera ERP’s financial management capabilities, which include budgeting, accounting, and financial reporting. The system provides insights into production costs, profit margins, and overall financial performance, helping manufacturers make informed financial decisions.
6. Data-Driven Decision-Making
Deskera ERP leverages data analytics to offer valuable insights into various aspects of manufacturing operations. With real-time data and advanced reporting tools, manufacturers can analyze performance metrics, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions to enhance operational efficiency.
7. Improved Compliance and Reporting
Manufacturers often face regulatory compliance requirements. Deskera ERP helps ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations by providing tools for accurate reporting, documentation, and audit trails. This reduces the risk of non-compliance and simplifies the reporting process.
8. Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
Deskera ERP fosters better communication and collaboration across different departments. With a unified platform, teams can access real-time information, share updates, and collaborate on projects more effectively, leading to improved coordination and efficiency.
9. Customizable and Scalable Solutions
Deskera ERP offers customizable modules that can be tailored to meet specific manufacturing needs. As businesses grow or change, the system can be scaled and adapted to accommodate new processes, products, or markets.
10. Cloud-Based Accessibility
Being a cloud-based ERP solution, Deskera ERP provides manufacturers with the flexibility to access the system from anywhere, at any time. This cloud infrastructure supports remote work, real-time updates, and seamless integration with other digital tools and platforms.
Key Takeaways
The manufacturing industry in 2024 is marked by transformative trends like:
- Digital Transformation and Industry 4.0 Technologies: The manufacturing sector is undergoing a significant digital transformation driven by Industry 4.0 technologies. The integration of IoT, AI, machine learning, and cloud computing is enhancing efficiency, agility, and productivity. Real-time data analysis and smart manufacturing systems are paving the way for predictive maintenance, reduced downtime, and improved operational efficiency.
- Rise of Microfactories: Microfactories are emerging as a transformative trend in manufacturing. These compact, modular facilities offer cost-effective solutions and flexibility in production, especially in the automotive sector. With companies like Arrival leading the way, the adoption of microfactories is expected to increase, facilitating localized production and reducing shipping costs.
- Focus on Sustainability and Green Manufacturing: Environmental sustainability is a major trend, with manufacturers striving for carbon neutrality and incorporating eco-friendly practices. The adoption of renewable energy sources, smart building technologies, and electric vehicles aligns with broader environmental goals. Efforts to improve sustainability not only benefit the planet but also enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
- Importance of Supply Chain Resilience and Optimization: The need for resilient and optimized supply chains has become crucial in response to recent disruptions. Manufacturers are reshoring operations, diversifying their supplier base, and exploring "product as a service" models to improve supply chain flexibility and efficiency.
- Customization and Personalization: The trend towards customization and personalization is reshaping manufacturing. Consumers' growing demand for tailored products is driving manufacturers to implement flexible production systems that can handle bespoke orders efficiently. The focus is on balancing customization with cost-effectiveness and operational efficiency.
- Advanced Robotics and Automation: Robotics and automation continue to revolutionize manufacturing processes. The increased adoption of robots, cobots, and autonomous vehicles is driving productivity, reducing labor costs, and enhancing workplace safety. The market for industrial robots and cobots is expected to grow substantially, with applications extending across various sectors, including agriculture.
- Cybersecurity in Manufacturing: As digital transformation accelerates, cybersecurity becomes a critical concern. Manufacturers are investing in robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data and maintain operational integrity. The integration of cybersecurity with manufacturing processes is essential for safeguarding against cyber threats and ensuring data privacy.
- Human-Machine Collaboration: The collaboration between humans and machines is evolving, with advanced technologies enhancing worker capabilities and productivity. Human-machine interaction is becoming more seamless, improving efficiency and fostering a safer work environment. The focus is on leveraging technology to complement human skills and optimize manufacturing processes.
- Leveraging Data-Driven Decision-Making: Data-driven decision-making is becoming a cornerstone of modern manufacturing. The use of data analytics, digital twins, and real-time insights helps manufacturers optimize production, forecast demand, and improve overall operational efficiency. The ability to analyze and act on large volumes of data is critical for maintaining a competitive edge.
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI): The push for greater diversity, equity, and inclusion is gaining momentum in the manufacturing industry. Efforts to improve DEI are seen as essential for fostering innovation and attracting talent. Programs and pledges aimed at enhancing workforce diversity and creating equitable job opportunities are shaping the future of manufacturing.
Also, Deskera ERP equips manufacturers with the tools needed to optimize production processes, manage inventory efficiently, ensure quality control, and make informed decisions. Its comprehensive features and cloud-based platform help manufacturers stay competitive in the evolving industrial landscape.
Related Articles












