What’s the secret to staying competitive in today’s fast-paced manufacturing industry? The answer lies in efficiency—streamlining operations, reducing downtime, and making data-driven decisions. In today’s rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, the right ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system can be the difference between operational efficiency and bottlenecks that hinder growth.
As manufacturers face increasing complexity in managing supply chains, production schedules, and quality control, ERP systems have emerged as a vital tool to centralize data, streamline processes, and enhance decision-making. The global shift toward digital transformation has only intensified the need for robust ERP solutions that offer real-time insights and seamless integrations.
Choosing the ideal ERP system for your manufacturing business is no small task. With a wide range of options available, it’s important to consider the unique needs of your operations, such as scalability, customization, and industry-specific features.
From automating routine tasks to improving demand forecasting, the best ERP systems empower manufacturers to optimize production, reduce costs, and meet customer demands with greater accuracy. But how do you know which ERP system is the best fit for your organization?
To help you navigate this complex decision, we’ve compiled a list of the Top 10 Manufacturing ERP Systems that are transforming the industry in 2024. These systems offer a variety of features, from advanced inventory management to seamless integration with CRM and supply chain modules, making them ideal for manufacturers of all sizes. Whether you are a small business or a large enterprise, the right ERP can streamline operations and support future growth.
One such solution is Deskera ERP, a cloud-based system designed specifically for small and medium-sized manufacturers. Known for its affordability and ease of use, Deskera offers robust MRP (Material Requirements Planning) features, AI-powered insights, and advanced reporting capabilities.
With its mobile accessibility and AI assistant, Deskera helps manufacturers manage everything from demand forecasting to production planning, making it a standout choice for businesses looking to scale efficiently.
What is an ERP System in Manufacturing?
An ERP system in manufacturing is a comprehensive software solution that integrates and manages key business processes across various departments within a manufacturing organization. ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems serve as a centralized platform to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and provide real-time insights into production, inventory, supply chain, financials, and other critical areas.
In the context of manufacturing, ERP systems help automate and synchronize tasks such as material procurement, production planning, order management, quality control, and product delivery.
By consolidating data from different departments, ERP systems enable manufacturers to make informed decisions, optimize resource utilization, and reduce operational costs. Additionally, they support demand forecasting, inventory management, and compliance with industry regulations.
Overall, an ERP system in manufacturing provides a unified view of all operations, enhancing collaboration, reducing errors, and helping manufacturers adapt to market demands more effectively.
Key Features to Look for in a Manufacturing ERP System
When selecting an ERP system for manufacturing, it’s essential to ensure that it includes key features tailored to meet the specific needs of the industry.
Below are the most important features to consider:
1. Production Planning and Scheduling
- A manufacturing ERP should offer robust tools for managing production workflows, ensuring optimal resource allocation, and maintaining efficiency across production lines. It should also enable real-time monitoring of production schedules to minimize delays and adjust to unexpected changes.
2. Inventory Management
- Effective inventory management is crucial for manufacturers. The ERP system should track raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods. Features like real-time stock visibility, automated stock replenishment, and demand forecasting help in avoiding stockouts and overstock situations.
3. Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
- The ERP system should include MRP functionality to help manufacturers plan for the materials and components needed for production. This feature assists in maintaining optimal inventory levels, scheduling production runs, and improving lead times.
4. Supply Chain Management (SCM)
- A manufacturing ERP should integrate with the supply chain to streamline procurement, logistics, and supplier relationships. It should also provide real-time data on supplier performance and help in managing supply chain risks.
5. Quality Management
- Quality control features are essential to ensure that products meet industry standards and customer expectations. An ERP system should facilitate tracking defects, managing non-conformance reports, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
6. Financial Management
- Seamless financial integration is crucial for managing costs and profitability. Look for ERP systems with accounting, budgeting, and financial reporting capabilities tailored to manufacturing, such as cost tracking for materials, labor, and overhead.
7. Shop Floor Management
- The ERP system should offer tools to monitor real-time production activity on the shop floor, providing visibility into machine utilization, production output, and workforce productivity. This enables manufacturers to improve operational efficiency.
8. Compliance and Regulatory Management
- Manufacturing often involves strict regulatory requirements. An ERP system should have features that help manufacturers comply with industry standards and certifications, such as ISO, FDA, or environmental regulations.
9. Customization and Scalability
- Every manufacturing business has unique needs. The ERP system should be customizable to fit specific workflows and be scalable to accommodate growth or changes in production volume.
10. Business Intelligence and Analytics
- Real-time analytics and reporting tools are essential for data-driven decision-making. ERP systems should offer insights into performance metrics, production efficiency, and market trends to help manufacturers stay competitive.
By prioritizing these features, manufacturers can choose an ERP system that optimizes their operations, improves efficiency, and supports long-term business growth.
Key Challenges Solved by Manufacturing ERP Systems
In the fast-paced world of manufacturing, businesses face numerous challenges that can affect productivity, profitability, and overall competitiveness. Managing complex operations manually or with outdated systems often leads to inefficiencies, data inaccuracies, and poor decision-making.
Fortunately, manufacturing ERP systems are designed to address these challenges by providing robust solutions that streamline operations, automate processes, and enhance real-time visibility.
Below are some of the most pressing challenges in manufacturing and how ERP systems can effectively solve them:
Lack of Real-Time Data and Visibility
Manufacturers often struggle with outdated or inaccurate information that can delay decision-making and reduce operational efficiency. Manufacturing ERP systems provide real-time data from all departments, allowing businesses to monitor operations as they happen.
This includes tracking production progress, inventory levels, and sales orders, enabling manufacturers to react quickly to changing demands and make data-driven decisions.
Inefficient Inventory Management
Maintaining the right level of inventory is critical to prevent costly overstocking or stockouts. A manufacturing ERP system solves this issue by offering advanced inventory tracking, real-time inventory levels, and automated reordering.
This ensures that the right materials are always available for production, optimizing inventory control and reducing costs.
Manual and Redundant Processes
Relying on manual processes is time-consuming and prone to errors, especially in a complex manufacturing environment. ERP systems automate key processes such as order processing, production planning, and procurement.
Automation not only reduces the risk of human error but also frees up employees to focus on more strategic tasks, ultimately improving efficiency and reducing operational costs.
Challenges with Production Scheduling
Efficient production scheduling is essential to meet customer demands while minimizing downtime. Without a centralized system, scheduling is often done in silos, leading to delays and bottlenecks.
ERP systems offer tools that integrate production planning with inventory and capacity management. This allows manufacturers to schedule production more effectively, optimize machine usage, reduce downtime, and ensure on-time delivery.
Difficulty Meeting Regulatory Compliance
Manufacturers must comply with a range of industry regulations, whether related to safety standards, environmental laws, or product quality. ERP systems help track compliance by automating documentation and reporting processes, as well as maintaining a digital audit trail. This simplifies regulatory compliance and reduces the risk of fines or product recalls.
Siloed Departments and Poor Collaboration
When different departments operate on separate systems or rely on manual communication, it can lead to a breakdown in collaboration and poor coordination.
ERP systems integrate all departments into a single platform, allowing for seamless communication and real-time data sharing. This enhances collaboration across production, procurement, sales, and finance, improving overall workflow and business alignment.
Inaccurate Demand Forecasting
Accurate demand forecasting is essential for managing production schedules, inventory levels, and supply chain operations. Many manufacturers struggle with inaccurate forecasts due to a lack of real-time data and analysis tools.
ERP systems address this challenge by offering advanced forecasting capabilities that use historical data, market trends, and real-time inputs to predict demand. This enables manufacturers to better align production with customer needs, reducing waste and improving service levels.
Implementing a manufacturing ERP system effectively addresses these common challenges, leading to increased operational efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced business agility. By optimizing processes and providing real-time insights, ERP systems empower manufacturers to stay competitive in a demanding industry.
Benefits of Using Manufacturing ERP Systems
By leveraging a manufacturing ERP system, companies can boost operational efficiency, improve customer relations, and support long-term growth with scalable technology that adapts to changing business needs.
The benefits of using manufacturing ERP systems are:
Streamlined Operations
ERP systems automate and integrate critical processes such as production planning, procurement, inventory control, and order management, improving overall efficiency.
Enhanced Visibility and Real-Time Insights
Gain access to real-time data from all departments. This allows for better coordination between teams and improved decision-making based on live data analytics.
Cost Reduction
ERP systems help optimize resource usage, reduce inventory costs, and minimize waste by automating routine tasks and accurately forecasting demand and production needs.
Improved Compliance and Traceability
ERP software supports compliance with industry standards, government regulations, and quality controls, ensuring accurate records of materials, processes, and finished goods. This is crucial for audits and certifications.
Scalability and Flexibility
ERP systems can scale alongside your business growth, accommodating increasing workloads, product lines, and production complexity without the need for significant reconfiguration.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Advanced reporting and business intelligence tools offer actionable insights, empowering executives and managers to make strategic decisions to improve operational efficiency and profitability.
Improved Customer Satisfaction
By automating order management and ensuring accurate inventory levels, ERP systems help meet customer demand more effectively, resulting in timely deliveries and increased customer satisfaction.
Better Collaboration Across Teams
With an integrated system, various departments—such as production, sales, finance, and procurement—can collaborate more effectively, breaking down silos and ensuring everyone works with the same accurate data.
Supply Chain Optimization
ERP systems enhance visibility into the entire supply chain, helping companies to better manage relationships with suppliers, reduce lead times, and optimize procurement processes.
Enhanced Inventory Management
With real-time inventory tracking and automated reordering, ERP software prevents overstocking and stockouts, improving cash flow and ensuring efficient inventory control.
Top 10 Manufacturing ERP Systems for 2024
1. Deskera Manufacturing ERP
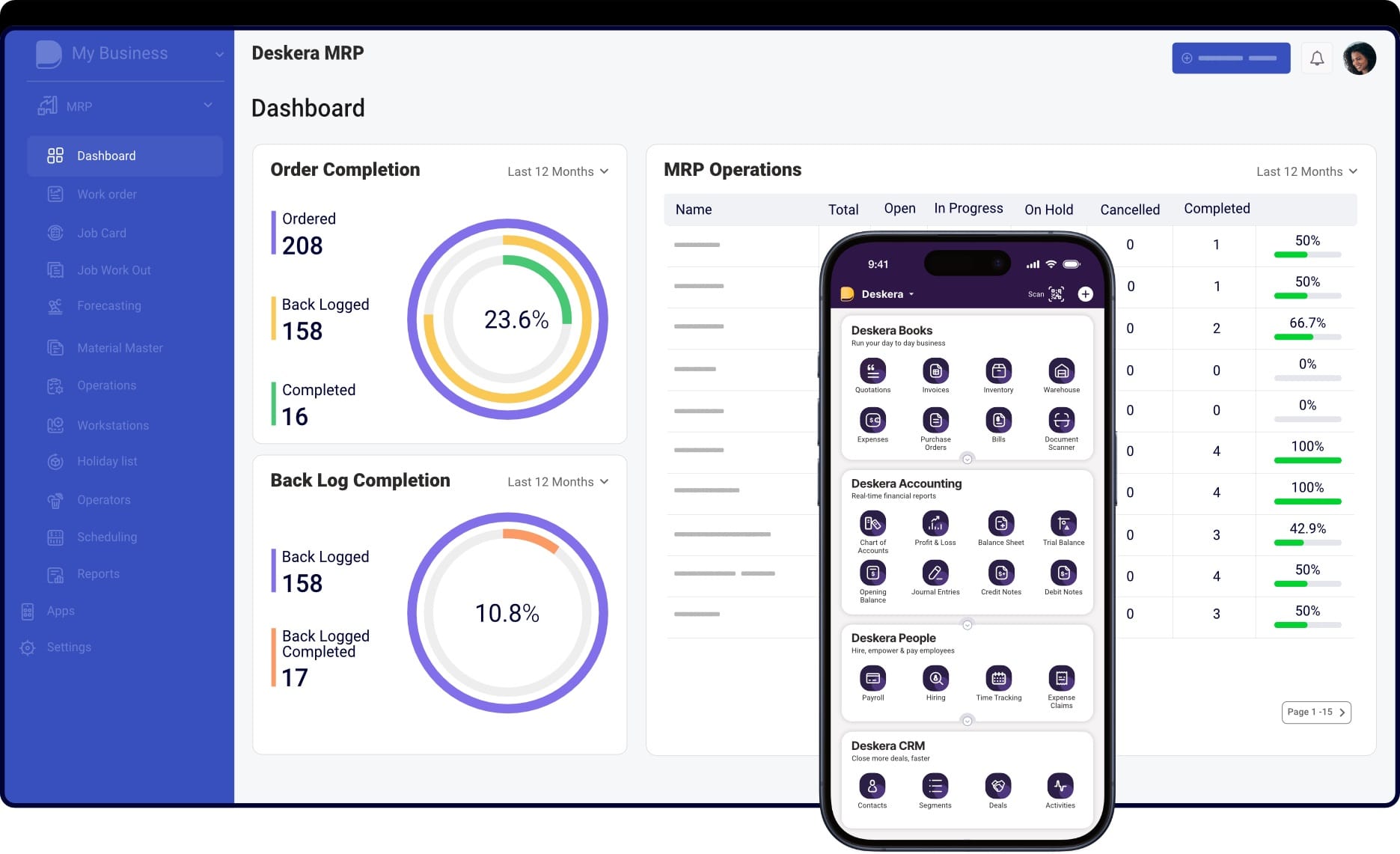
Overview:
Deskera is a comprehensive cloud-based ERP system designed for small and medium-sized manufacturers. With its wide range of tools, it enables manufacturers to manage inventory, streamline production processes, and enhance decision-making through real-time data analytics.
Its affordability and scalability make it one of the best ERP systems for manufacturing, especially for companies seeking growth.
Key Features:
- Material Requirements Planning (MRP): Efficient management of raw materials, production schedules, and inventory levels.
- Production Planning & Scheduling: Automate workflows and track every phase of production for increased efficiency.
- AI Assistant David: Automates routine tasks and offers predictive insights to help businesses optimize their operations.
- Mobile Accessibility: Manage your entire manufacturing operations from anywhere with mobile-friendly access.
- Inventory Management: Real-time inventory tracking with automated stock updates and reorder notifications.
- Advanced Order Management: Streamline order processing from multiple channels, including integrated pick-pack-ship functionalities.
- Procurement Automation: Manage purchase orders and vendor performance with RFQs and scorecards.
- Business Intelligence and Reporting: Get actionable insights through customizable dashboards and advanced reporting tools.
- Project Accounting: Track project-specific costs and profitability in real time.
Advantages:
- Affordable, making it suitable for small and medium businesses.
- Strong focus on demand forecasting and inventory management.
- AI Assistant David enhances productivity through automation and data-driven insights.
- Easy-to-use interface.
Disadvantages:
- Has no features for document management
- Offers no free versions
2. Odoo
Overview:
Odoo is a modular, open-source ERP system that caters to manufacturers of all sizes. Its flexibility makes it a low-cost manufacturing ERP software solution, especially for businesses looking to customize their operations.
Key Features:
- Customizable modules for inventory, manufacturing, sales, and CRM.
- Production planning and work center control.
- Real-time cost tracking for materials and labor.
Advantages:
- Highly customizable with an open-source framework.
- Affordable for small businesses.
Disadvantages:
- Requires more technical expertise for customization.
- Advanced features may require additional modules, increasing the cost.
3. Epicor ERP
Overview:
Epicor is one of the best ERP systems for manufacturing industries, especially for mid-sized manufacturers. It offers a comprehensive solution focused on optimizing production efficiency, quality control, and compliance.
Key Features:
- Strong inventory and supply chain management tools.
- Advanced production planning and scheduling.
- Quality management and compliance tracking.
Advantages:
- Industry-specific solutions for various manufacturing sectors.
- Scalable for mid-sized to large enterprises.
Disadvantages:
- Higher implementation costs.
- Requires significant customization for smaller manufacturers.
4. Acumatica
Overview:
Acumatica is a cloud-based ERP system that delivers robust solutions for manufacturing, offering flexibility in both deployment and integration. It is widely regarded as one of the best ERP software for manufacturing due to its intuitive interface and scalability.
Key Features:
- Production management with BOM (Bill of Materials) and routing.
- Inventory management and order fulfillment.
- Real-time visibility into operations via a centralized dashboard.
Advantages:
- Scalable for growing businesses.
- Flexible deployment options (cloud, hybrid, or on-premise).
Disadvantages:
- Pricing may be prohibitive for smaller manufacturers.
- Complex customization may require third-party support.
5. Oracle NetSuite ERP
Overview:
Oracle NetSuite is a powerful cloud-based ERP system, providing manufacturers with extensive capabilities for managing financials, production, and supply chains. Its global reach makes it ideal for multinational manufacturing operations.
Key Features:
- Supply chain management and advanced financials.
- Manufacturing execution system (MES) integration.
- Real-time visibility into the entire production lifecycle.
Advantages:
- Comprehensive suite of tools for large enterprises.
- Strong integration with other Oracle products.
Disadvantages:
- Expensive for small to medium-sized manufacturers.
- Complex setup and longer implementation times.
6. Microsoft Dynamics 365
Overview:
Microsoft Dynamics 365 is an ERP and CRM platform that integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft products. It’s a popular ERP system for the manufacturing industry due to its flexibility, advanced analytics, and integration capabilities.
Key Features:
- AI-powered demand forecasting.
- Real-time production scheduling.
- Integration with Microsoft Office and Power BI for analytics.
Advantages:
- Familiar interface for users already using Microsoft products.
- Strong analytical capabilities.
Disadvantages:
- Expensive for small businesses.
- Customization can be complex and require external support.
7. Infor CloudSuite Industrial (SyteLine)
Overview:
Infor’s CloudSuite Industrial is specifically tailored to manufacturing. It provides end-to-end visibility across production lines, from procurement to product delivery, and supports various manufacturing modes.
Key Features:
- Comprehensive inventory and supply chain management.
- Demand forecasting and scheduling.
- Strong support for mixed-mode manufacturing.
Advantages:
- Flexible deployment options.
- Great for complex manufacturing operations.
Disadvantages:
- High cost for smaller companies.
- Implementation can be time-consuming.
8. JobBOSS2
Overview:
JobBOSS2 is a manufacturing ERP system designed for job shops and custom manufacturers. It offers real-time tracking of jobs, costs, and materials, making it ideal for manufacturers that focus on small-batch or custom production.
Key Features:
- Real-time job tracking and costing.
- Shop floor management with mobile capabilities.
- Inventory and purchasing management.
Advantages:
- Strong focus on job shop manufacturing.
- User-friendly and quick implementation.
Disadvantages:
- Limited scalability for large enterprises.
- Lacks some advanced features like predictive analytics.
9. Sage X3
Overview:
Sage X3 offers advanced functionality for managing complex manufacturing processes. It is a great fit for manufacturers in process and discrete industries looking for robust ERP systems that handle production, distribution, and financials.
Key Features:
- Advanced supply chain and inventory management.
- Process manufacturing and quality control tools.
- Multi-location and multi-currency support.
Advantages:
- Strong financial and supply chain management tools.
- Great for large, multinational manufacturers.
Disadvantages:
- Steep learning curve.
- Expensive for smaller businesses.
10. SAP Business One
Overview:
SAP Business One is a popular ERP system for small and medium-sized manufacturers looking for a simplified, yet powerful ERP solution. It is designed to integrate various aspects of production and business management into one system.
Key Features:
- Inventory and production management.
- Financial accounting and reporting.
- Real-time data analytics and forecasting.
Advantages:
- Scalable and customizable to business needs.
- Strong reporting tools with real-time analytics.
Disadvantages:
- Costly compared to other ERP systems for small businesses.
- Requires SAP expertise for effective customization.
By exploring the top 10 manufacturing ERP systems, manufacturers can find solutions that align with their specific needs. Whether looking for low-cost manufacturing ERP software or high-end solutions, these systems offer a range of options to optimize production, manage inventory, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
How to Choose the Right ERP for Your Manufacturing Business
Selecting the ideal ERP system for your manufacturing operations requires careful consideration of several factors:
Understand Your Business Needs
Assess the specific requirements of your manufacturing processes—inventory management, production scheduling, supply chain coordination, and financial tracking.
Customization and Flexibility
Choose an ERP that can be customized to fit your unique workflows and can scale as your business grows.
Industry-Specific Features
Ensure the ERP includes features tailored to manufacturing, such as Material Requirements Planning (MRP), demand forecasting, and quality control.
Ease of Use and Integration
Look for an intuitive interface and easy integration with existing systems like CRM, supply chain management software, or financial tools.
Cloud vs. On-Premise
Decide between a cloud-based or on-premise solution based on your infrastructure and security needs. Cloud ERP systems are generally more flexible and easier to update.
Vendor Support and Training
Ensure that the ERP vendor provides adequate customer support, training, and ongoing maintenance to facilitate smooth implementation and continuous updates.
Cost vs. ROI
Compare the upfront costs, subscription fees, and maintenance costs with the potential return on investment. A low-cost manufacturing ERP system may not provide the full range of features you need, while higher-tier systems might offer greater long-term value.
Compliance and Security
Ensure the ERP system helps meet industry-specific compliance and data security regulations, protecting sensitive information and enabling traceability.
Future-Proof Technology
Select a system that integrates the latest technologies such as AI, IoT, or machine learning to ensure long-term innovation and adaptability.
By considering these factors, you can find the best ERP system for manufacturing that will align with your business goals, streamline operations, and enhance productivity.
Effective Strategies for Implementing a Manufacturing ERP System
Successfully implementing an ERP system in manufacturing requires a well-structured approach to ensure smooth integration, minimize disruptions, and achieve long-term benefits.
Manufacturing ERP systems bring immense value by streamlining operations, improving data accuracy, and enhancing decision-making, but without a strategic rollout, companies may face operational setbacks.
To maximize the return on investment and ensure that the system supports your business goals, it's essential to follow best practices throughout the implementation process.
Here are some detailed strategies to ensure effective ERP implementation in your manufacturing business:
Conduct a Detailed Needs Assessment
Start by thoroughly assessing your current manufacturing processes, identifying pain points, and determining what specific ERP features will address these gaps. Understanding your production flow, inventory needs, and supply chain challenges is key to selecting the right ERP system for your business.
Set Clear and Measurable Objectives
Outline specific goals that the ERP system should help you achieve. Whether it’s reducing lead times, enhancing inventory accuracy, or automating production scheduling, defining these objectives early on will guide the implementation process and help you measure success post-implementation.
Engage Stakeholders Early and Maintain Communication
Involve all key stakeholders from various departments such as production, finance, supply chain, and IT from the very beginning. Their feedback will be valuable in shaping the ERP implementation. Clear communication and collaboration between these departments ensure that all functional needs are addressed and reduce resistance to change.
Develop a Robust Training Program
Training is crucial to ensuring that employees can effectively use the new ERP system. Create a comprehensive training plan that includes hands-on sessions and follow-up support. Ensure that employees from every department understand how the system works and how it integrates with their daily tasks.
Phased Implementation for Minimal Disruption
Rather than implementing the entire ERP system at once, consider a phased rollout, beginning with critical processes like production and inventory management. This approach allows you to test the system, fix issues, and make improvements gradually without overwhelming your employees or risking major disruptions to operations.
Ensure Accurate Data Migration and Clean Up Existing Data
Data accuracy is vital to the success of any ERP implementation. Before migrating data into the new system, conduct a data audit to remove outdated, duplicate, or inaccurate information. Clean, accurate data will ensure smoother system functioning and more reliable reporting once the ERP goes live.
Continuous Monitoring, Evaluation, and Support
Post-implementation, establish a continuous monitoring process to evaluate system performance and user feedback. Address any technical issues quickly and make adjustments as necessary. Having ongoing support from the ERP vendor or an internal team ensures that any challenges are resolved efficiently, and new features can be optimized as they are introduced.
By following these detailed strategies, manufacturing businesses can implement ERP systems effectively, ensuring that the system not only fits their current needs but also supports future growth and innovation in a dynamic industry.
Key Takeaways
- Manufacturing ERP systems are essential tools that help businesses streamline operations, improve efficiency, and enable data-driven decision-making. These systems integrate key areas like inventory, production, and finance into one cohesive platform, ensuring that manufacturers can respond rapidly to market changes and customer demands.
- The most effective ERP systems for manufacturing in 2024—such as Odoo, Epicor, SAP Business One, and others—offer a wide range of functionalities to suit the diverse needs of manufacturers. These ERPs provide flexible solutions that integrate production, supply chain, and financial data, making them adaptable for businesses of different sizes and industries. Each ERP system has its strengths, whether it’s scalability, customization, or advanced automation features.
- Manufacturing ERP systems offer key benefits such as real-time visibility across operations, improved accuracy in inventory management, and enhanced production efficiency. These systems automate manual tasks, reduce human error, and help manufacturers comply with industry regulations. Additionally, they enable better forecasting, ensuring that businesses can anticipate demand and optimize production accordingly.
- When selecting an ERP for your manufacturing business, it's crucial to assess your company's specific needs, future growth potential, and the level of customization and support offered by the ERP provider. Prioritize systems that offer scalability, integration capabilities, and ease of use to ensure long-term alignment with your business goals. A good ERP should also provide comprehensive training and ongoing support for successful implementation.
- Effective implementation of an ERP system requires thorough planning and stakeholder engagement from the start. Key strategies include conducting a detailed needs assessment, setting clear objectives, providing extensive employee training, and adopting a phased rollout to minimize disruptions. Continuous monitoring post-implementation ensures that the system is optimized and able to meet evolving business needs.
- Manufacturing ERP systems address critical challenges such as siloed data, inefficient production scheduling, and poor inventory control. By centralizing data and automating workflows, ERPs enhance cross-departmental collaboration, streamline production processes, and improve demand forecasting accuracy. Moreover, they simplify compliance with regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of fines or operational setbacks.
- Deskera stands out for its user-friendly interface and robust features tailored for small to mid-sized manufacturers. It offers modules for production planning, inventory management, financial reporting, and an AI assistant named David, enhancing workflow automation and providing real-time insights for more informed decision-making. Its MRP features help manufacturers meet demand efficiently while controlling costs.
Related Articles