Delivering products of uncompromising quality has become a critical factor for businesses aiming to excel and retain customer loyalty in the dynamic marketplace. The ability to effectively track and monitor product quality across the entire supply chain has become paramount. In this pursuit, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems emerge as invaluable assets.
Startling statistics reveal that companies leveraging ERP systems for quality control witness an average reduction of 20% in product defects. Furthermore, these businesses report a noteworthy 25% improvement in customer satisfaction ratings. These figures underscore the immense impact ERP systems can have on consistently delivering superior products.
Functioning as centralized hubs, ERP systems seamlessly integrate key business functions, streamlining operations and empowering businesses to effortlessly track product quality. From establishing and monitoring quality parameters to implementing robust quality control processes, ERP systems offer comprehensive capabilities.
Real-time visibility into quality metrics and the ability to generate insightful reports and analytics further enable businesses to identify trends, proactively address issues, and drive continuous improvement.

In this article, we will delve into the strategic utilization of ERP systems for efficient product quality tracking. We will explore essential features, and implementation techniques, and share valuable insights to help businesses overcome challenges and unlock the full potential of ERP systems in achieving exceptional product quality.
- Significance of Product Quality Tracking in a Business
- Introduction to ERP and its Role in Managing Various Business Operations
- Understanding ERP's Role in Quality Control
- Setting Up Quality Parameters in the ERP System
- Implementing Quality Control Processes
- Real-Time Monitoring of Quality Metrics
- Generating Quality Reports and Analytics
- Integrating ERP with Other Quality Assurance Tools
- Ensuring Data Accuracy and Integrity
- Overcoming Challenges and Considerations
- Why Should Businesses Embrace ERP as a Comprehensive Solution for Quality Control and Improvement?
- Conclusion
- How can Deskera Help You?
- Key Takeaways
- Related Articles
Significance of Product Quality Tracking in a Business
product quality tracking plays a vital role in the success and sustainability of a company. Tracking and maintaining product quality throughout the production process is crucial for several reasons.
Firstly, meeting customer expectations is essential for any business. Customers have increasingly higher standards when it comes to product quality. By implementing effective quality tracking systems, businesses can ensure that their products consistently meet or exceed these expectations. Satisfied customers are more likely to become repeat customers and advocates for the brand, leading to increased customer loyalty and positive word-of-mouth.
Secondly, product quality directly affects a company's brand reputation. Customers associate quality products with reputable brands. By tracking product quality, businesses can uphold their brand image and build trust among consumers, establishing a competitive advantage in the market.
Tracking product quality also helps mitigate risks and reduce costs. Product defects can result in costly recalls, returns, and potential damage to a company's reputation. By proactively tracking quality metrics and identifying potential issues, businesses can take corrective actions early on, minimizing risks and saving costs in the long run.
Moreover, effective quality tracking ensures compliance with industry regulations and standards. Certain industries have strict regulations regarding product quality, and failure to comply can result in legal consequences or loss of market access. By tracking quality and maintaining documentation, businesses can demonstrate compliance during audits and certifications.
Product quality tracking also drives continuous improvement. By monitoring quality metrics and analyzing data, businesses can identify areas for enhancement and implement corrective actions. This leads to process optimization, increased efficiency, and ultimately, better product quality.
Furthermore, quality tracking strengthens relationships with suppliers. Collaborative quality tracking allows businesses to work closely with suppliers to ensure consistent quality across the supply chain. This fosters stronger partnerships and minimizes the risk of receiving subpar components or materials.
Thus, the significance of product quality tracking in a business cannot be overstated. It directly impacts customer satisfaction, brand reputation, cost reduction, regulatory compliance, and competitive advantage.
Introduction to ERP and its Role in Managing Various Business Operations
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have revolutionized the way businesses manage their operations, including product quality tracking. An ERP system is a comprehensive software solution that integrates various aspects of a company's operations, such as manufacturing, inventory management, finance, human resources, and customer relationship management.
In the context of product quality tracking, ERP systems provide a centralized platform that enables businesses to streamline and manage quality control processes effectively. By incorporating quality tracking modules and functionalities, ERP systems facilitate the monitoring and evaluation of product quality at various stages of the production cycle.
One of the key roles of an ERP system in quality tracking is the establishment of quality parameters specific to each product. These parameters define the standards and specifications that products must meet to be deemed of acceptable quality. ERP systems allow businesses to configure and customize these quality parameters, ensuring that they align with industry standards and customer requirements.
Once quality parameters are defined, an ERP system facilitates the implementation of quality control processes. It enables businesses to capture and track data related to product quality, such as inspection results, test reports, and non-conformance incidents. This data can be entered directly into the ERP system, providing real-time visibility into product quality metrics.
The integration of quality tracking modules within an ERP system also enables businesses to generate comprehensive reports and analytics. These reports provide insights into quality trends, identify recurring issues, and highlight areas for improvement. With access to this information, businesses can make data-driven decisions, take proactive measures to enhance product quality, and drive continuous improvement.
Furthermore, ERP systems can be integrated with other quality assurance tools, such as Statistical Process Control (SPC) software or Quality Management Systems (QMS). This integration enhances the capabilities of the ERP system, allowing businesses to leverage advanced statistical analysis, perform in-depth root cause analysis, and implement corrective and preventive actions effectively.
ERP systems play a crucial role in managing various business operations, including product quality tracking. They provide a centralized platform for establishing quality parameters, implementing quality control processes, capturing real-time quality data, generating insightful reports, and integrating with other quality assurance tools.
Leveraging the power of ERP in quality tracking enables businesses to ensure consistent product quality, drive improvement initiatives, and ultimately, enhance customer satisfaction.
Understanding ERP's Role in Quality Control
Within the realm of quality control, an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system assumes a pivotal role in streamlining and optimizing processes. By seamlessly integrating various business functions, an ERP system empowers businesses to establish effective quality control measures and track product quality throughout the production cycle.
In this section, we will explore the specific ways in which an ERP system contributes to quality control, ensuring that businesses can consistently deliver products of superior quality.
How ERP systems can be used to streamline quality control processes
ERP systems provide valuable tools and functionalities that can streamline quality control processes, ensuring efficient and effective tracking of product quality. Here are several ways ERP systems contribute to streamlining quality control:
- Centralized Data Management: ERP systems serve as centralized repositories for quality-related data, consolidating information from various departments and processes. This eliminates the need for multiple standalone systems and spreadsheets, enabling seamless access to real-time quality data.
- Standardized Quality Parameters: ERP systems allow businesses to define and establish standardized quality parameters for different products and processes. These parameters include specifications, tolerances, and criteria that determine acceptable quality levels. By centralizing and standardizing these parameters, ERP systems facilitate consistent quality control practices.
- Automated Quality Inspections: ERP systems enable the automation of quality inspections, reducing manual efforts and human errors. Inspection checklists, criteria, and workflows can be defined within the system, guiding inspectors through the inspection process and ensuring adherence to quality standards.
- Real-time Quality Monitoring: ERP systems provide real-time visibility into quality metrics by capturing data at each stage of the production process. This allows businesses to monitor quality performance, identify deviations, and take immediate corrective actions, thereby preventing quality issues from escalating.
- Non-Conformance Management: ERP systems offer robust non-conformance management capabilities. When a quality issue arises, the system can initiate workflows to investigate, document, and resolve the non-conformance incidents. This ensures that proper root cause analysis, corrective actions, and preventive measures are implemented in a timely manner.
- Supplier Quality Management: ERP systems facilitate supplier quality management by enabling businesses to track and evaluate the quality performance of suppliers. This includes monitoring supplier certifications, conducting audits, and managing non-conformance incidents related to supplier-provided materials or components.
- Document Control and Compliance: ERP systems support document control processes by managing quality-related documents, such as standard operating procedures (SOPs), work instructions, and quality manuals. This ensures that employees have access to up-to-date and approved documents, promoting compliance with quality standards and regulations.
- Reporting and Analytics: ERP systems offer robust reporting and analytics capabilities, allowing businesses to generate comprehensive quality reports. These reports provide insights into quality trends, performance metrics, and areas for improvement, facilitating data-driven decision-making and continuous quality enhancement.
By leveraging these features and functionalities, ERP systems streamline quality control processes, enabling businesses to proactively track and manage product quality. This ultimately leads to enhanced customer satisfaction, improved operational efficiency, and strengthened competitiveness in the market.
Key features and modules of an ERP system that facilitate quality tracking
An ERP system encompasses various features and modules that facilitate quality tracking and control. These key features and modules enable businesses to effectively monitor and manage product quality throughout the production process.
Here are some essential features and modules of an ERP system that support quality tracking:
Quality Management Module: The quality management module is specifically designed to handle quality control processes. It allows businesses to define quality parameters, conduct inspections, manage non-conformances, and track quality metrics. This module serves as the central hub for quality-related activities within the ERP system.
Document Control Module: The document control module ensures that quality-related documents, such as standard operating procedures (SOPs), work instructions, and quality manuals, are organized, version-controlled, and easily accessible. This module helps businesses maintain up-to-date and approved documentation, ensuring compliance with quality standards.
Supplier Management Module: The supplier management module enables businesses to track and evaluate the quality performance of suppliers. It allows businesses to manage supplier certifications, conduct audits, and record non-conformance incidents related to supplier-provided materials or components. This module ensures that suppliers meet quality requirements and contribute to overall product quality.
Inspection and Testing Module: The inspection and testing module provides functionalities to define inspection checklists, criteria, and workflows. It enables businesses to capture inspection results, conduct tests, and record measurements. This module streamlines the inspection process, reduces manual efforts, and ensures consistent adherence to quality standards.
Non-Conformance Management Module: The non-conformance management module helps businesses track and manage quality-related issues and non-conformance incidents. It allows for the initiation of investigation workflows, documentation of root causes, implementation of corrective actions, and monitoring of preventive measures. This module facilitates efficient handling of quality deviations and supports continuous improvement efforts.
Analytics and Reporting Module: The analytics and reporting module provides comprehensive reporting and analytical capabilities for quality tracking. It enables businesses to generate quality reports, analyze trends, and identify areas for improvement. This module offers insights into quality metrics, such as defect rates, customer complaints, and process variations, supporting data-driven decision-making.
Traceability and Recall Management: ERP systems often include features for traceability and recall management. These features track the movement of raw materials, components, and finished products throughout the supply chain. In the event of quality issues or recalls, businesses can quickly identify affected products, trace their origins, and take appropriate actions to mitigate risks.
By leveraging these features and modules, an ERP system provides businesses with the necessary tools to effectively track, monitor, and control product quality. The integration and centralized nature of these functionalities within an ERP system streamline quality tracking processes, enhance visibility, and enable continuous improvement efforts.
Setting Up Quality Parameters in the ERP System
In the context of quality tracking, establishing clear and standardized quality parameters is crucial for maintaining consistent product quality. An ERP system plays a pivotal role in this process, providing businesses with the tools and functionalities to define and configure quality parameters tailored to their specific products and processes.
This section explores the importance of setting up quality parameters within the ERP system and outlines the steps involved in ensuring consistency and standardization in product quality control.
Process of defining quality parameters specific to your products
The process of defining quality parameters specific to your products within an ERP system involves several key steps. These steps ensure that the quality parameters align with industry standards, customer requirements, and internal quality objectives.
Here is an overview of the process:
Understand Product Requirements: Begin by gaining a thorough understanding of the specific requirements and expectations for each product. This includes considering factors such as functionality, durability, safety, aesthetics, and any relevant industry regulations or standards.
Identify Critical Quality Characteristics: Identify the critical quality characteristics that directly impact the performance and satisfaction of customers. These characteristics are specific attributes or features of the product that need to be closely monitored and controlled to ensure consistent quality.
Establish Quality Metrics: Define the metrics that will be used to measure and assess the identified quality characteristics. This can include quantitative measurements, such as dimensions, weight, or performance indicators, as well as qualitative evaluations based on visual inspections or sensory assessments.
Set Acceptance Criteria: Determine the acceptable ranges or thresholds for each quality metric. These criteria define the acceptable limits within which the product should fall to be considered of satisfactory quality. They can be based on industry standards, customer specifications, or internal quality objectives.
Configure Quality Parameters in the ERP System: Utilize the quality management module of the ERP system to configure and input the defined quality parameters. This includes specifying the quality metrics, acceptance criteria, and any additional attributes or rules necessary for tracking and controlling product quality.
Test and Validate Quality Parameters: Conduct testing and validation to ensure that the defined quality parameters accurately reflect the desired product quality. This may involve sample testing, pilot runs, or comparison against reference samples or benchmarks.
Document Quality Parameters: Document the established quality parameters within the ERP system, creating a comprehensive record of the quality standards and specifications for each product. This documentation serves as a reference for quality control personnel and can be easily accessed and updated as needed.
Communicate and Train: Communicate the defined quality parameters to relevant stakeholders, including production teams, quality control personnel, and suppliers if applicable. Provide training and guidance on how to apply and monitor these parameters effectively within the ERP system.
By following these steps, businesses can define accurate and comprehensive quality parameters specific to their products. The utilization of an ERP system streamlines the process, ensuring consistency, standardization, and easy access to quality parameters for efficient quality tracking and control throughout the production cycle.
How to configure the ERP system to incorporate these quality parameters
Configuring the ERP system to incorporate quality parameters involves specific steps to ensure seamless integration and effective utilization. Here's a guide on how to configure the ERP system for quality parameter management:
Access the Quality Management Module: Navigate to the quality management module within the ERP system. This module is specifically designed to handle quality control processes and configuration.
Define Quality Metrics: Within the module, define the specific quality metrics that align with the critical quality characteristics identified for your products. This can include dimensions, specifications, performance indicators, or any other measurable attributes.
Set Acceptance Criteria: Specify the acceptance criteria for each quality metric. This involves determining the acceptable ranges, thresholds, or values that the product should meet to be considered of satisfactory quality. Input these criteria into the ERP system.
Configure Inspection Checklists: Create inspection checklists that correspond to the quality metrics and acceptance criteria. These checklists will guide the inspection process and ensure that all relevant quality parameters are assessed during inspections.
Establish Workflows: Define workflows within the ERP system to manage the flow of quality-related information and processes. This includes workflows for initiating inspections, documenting non-conformance incidents, conducting root cause analyses, implementing corrective actions, and verifying their effectiveness.
Integrate with Testing and Measuring Equipment: If applicable, integrate the ERP system with testing and measuring equipment. This allows for direct data capture and automatic transfer of measurement results into the system, reducing manual entry and minimizing human errors.
Implement Traceability Features: Utilize traceability features within the ERP system to track and record the movement of products, materials, and components throughout the production cycle. This helps ensure that quality parameters are consistently monitored at every stage.
Customize Reporting and Analytics: Customize the reporting and analytics functionalities of the ERP system to generate comprehensive reports and dashboards that provide insights into quality metrics, trends, and performance. This allows for data-driven decision-making and continuous improvement initiatives.
Train Users and Establish User Roles: Provide training to users who will be working with the quality management module of the ERP system. Familiarize them with the configuration, data entry, inspection processes, and reporting capabilities. Establish user roles and permissions to ensure appropriate access and data security.
Regularly Review and Update Parameters: Periodically review and update the quality parameters within the ERP system to reflect any changes in industry standards, customer requirements, or internal quality objectives. Maintain documentation and version control to track revisions.
By following these steps, businesses can effectively configure the ERP system to incorporate quality parameters and streamline quality control processes. The system will serve as a centralized platform for managing and tracking product quality, promoting consistency, standardization, and continuous improvement efforts.
Implementing Quality Control Processes
Once quality parameters have been defined and configured within the ERP system, the next crucial step is to implement effective quality control processes. This section focuses on the practical aspects of incorporating quality control measures within the organization, utilizing the capabilities of the ERP system.
From capturing real-time quality data to conducting inspections and managing non-conformance incidents, we will explore the essential steps and considerations involved in implementing quality control processes to ensure consistent product quality.
Steps involved in implementing quality control processes within the ERP system
Implementing quality control processes within the ERP system involves a series of steps to ensure effective and efficient monitoring and management of product quality. Here are the key steps involved in implementing quality control processes:
Plan and Define Quality Control Procedures: Start by developing a comprehensive plan that outlines the specific quality control procedures to be implemented. This includes determining the frequency and methods of quality inspections, establishing sampling plans, and defining the roles and responsibilities of the personnel involved.
Configure Inspection Checklists: Utilize the ERP system's inspection module to configure inspection checklists based on the defined quality parameters. These checklists should cover all critical quality characteristics and guide inspectors through the inspection process to ensure consistent evaluations.
Conduct Quality Inspections: Implement the defined quality control procedures by conducting regular inspections using the ERP system. Inspectors can use the system to record inspection results, enter measurements, and capture any non-conformances or deviations from the established quality parameters.
Capture Real-time Quality Data: Leverage the ERP system's capabilities to capture real-time quality data throughout the production process. This includes data such as inspection results, measurements, test reports, and any other quality-related information. Ensure that the system enables easy and accurate data entry for efficient tracking and analysis.
Manage Non-Conformance Incidents: Utilize the ERP system's non-conformance management module to effectively handle and track non-conformance incidents. When deviations from the defined quality parameters are identified, initiate workflows within the system to investigate the root causes, document corrective actions, and monitor their implementation.
Analyze Quality Trends and Performance: Utilize the reporting and analytics capabilities of the ERP system to analyze quality trends and performance metrics. Generate reports that provide insights into quality metrics, identify recurring issues, and highlight areas for improvement. Use this information to drive continuous improvement initiatives and enhance product quality.
Implement Corrective and Preventive Actions: Based on the analysis of quality data and identified trends, implement corrective and preventive actions as necessary. Utilize the ERP system to track and manage these actions, ensuring timely and effective resolution of quality issues and preventing their recurrence.
Continuously Monitor and Improve: Regularly review and monitor the effectiveness of the implemented quality control processes within the ERP system. Seek feedback from stakeholders, conduct internal audits, and utilize data-driven insights to identify areas for further improvement and optimization.
Leveraging the system's capabilities for inspections, data capture, non-conformance management, and analytics enables efficient tracking, analysis, and improvement of product quality. This ultimately leads to enhanced customer satisfaction, increased operational efficiency, and strengthened competitiveness in the market.
Importance of capturing data related to product quality at various stages of the production cycle
Capturing data related to product quality at various stages of the production cycle is of utmost importance for several key reasons:
Real-time Visibility: By capturing quality data throughout the production cycle, businesses gain real-time visibility into the quality performance of their products. This allows for timely identification of any deviations or issues that may arise, enabling prompt corrective actions to be taken.
Early Detection of Quality Issues: Capturing data at different stages of production enables early detection of quality issues. By monitoring quality metrics and comparing them against predefined parameters, businesses can quickly identify any abnormalities or trends that may indicate potential quality problems. This early detection allows for proactive measures to be taken, minimizing the impact on product quality.
Root Cause Analysis: The availability of comprehensive quality data facilitates effective root cause analysis. When a quality issue arises, businesses can trace back through the production cycle, analyzing the captured data to determine the underlying causes. This analysis enables businesses to address the root causes and implement targeted corrective actions, preventing similar issues from recurring in the future.
Process Optimization: Capturing quality data provides valuable insights into the performance of production processes. By analyzing this data, businesses can identify areas for process optimization, fine-tuning operations to enhance product quality. Continuous monitoring of quality data helps in identifying process inefficiencies, enabling businesses to make informed decisions and drive continuous improvement initiatives.
Supplier Evaluation and Collaboration: Quality data captured at different stages of the production cycle can also be used for evaluating the performance of suppliers. By analyzing supplier-specific quality metrics, businesses can assess the consistency and reliability of their suppliers' products or components. This data can then be used as a basis for collaboration and improvement discussions with suppliers, fostering stronger relationships and ensuring quality throughout the supply chain.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: Capturing quality data is essential for compliance with industry regulations and standards. Accurate and well-documented quality data serves as evidence of adherence to these requirements, enabling businesses to demonstrate compliance during audits or inspections. It also facilitates the implementation of quality control measures aligned with specific regulatory guidelines.
Continuous Improvement: Quality data serves as a foundation for continuous improvement efforts. By capturing and analyzing data at various stages of the production cycle, businesses can identify opportunities for enhancing product quality, streamlining processes, and optimizing resource allocation. This data-driven approach supports a culture of continuous improvement, fostering innovation and maintaining a competitive edge in the market.
Capturing data related to product quality at various stages of the production cycle is crucial for enabling real-time visibility and root cause analysis. It empowers businesses to maintain consistent and high-quality products, meets customer expectations, and stay ahead in a competitive market.
Real-Time Monitoring of Quality Metrics
Monitoring quality metrics in real time is a critical aspect of effective quality management. This section focuses on the significance of real-time monitoring within the context of product quality, highlighting how businesses can leverage the capabilities of an ERP system to capture and analyze quality data in real time.
How an ERP system enables real-time monitoring of quality metrics
An ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system provides businesses with robust capabilities to enable real-time monitoring of quality metrics. Here's how an ERP system facilitates real-time monitoring of quality metrics:
Centralized Data Repository: An ERP system serves as a centralized repository for all quality-related data, consolidating information from various stages of the production cycle. By integrating quality data with other relevant data sources, such as inventory, production, and sales, the ERP system enables real-time access to comprehensive quality metrics.
Automated Data Capture: With an ERP system, data capture can be automated, reducing manual entry and minimizing the risk of errors. Quality metrics can be captured directly from inspection tools, testing equipment, or integrated measuring devices, ensuring accurate and up-to-date data collection in real time.
Real-Time Reporting and Dashboards: The reporting and dashboard functionalities of an ERP system enable real-time visualization of quality metrics. Customizable reports and interactive dashboards provide instant access to quality data, allowing stakeholders to monitor key performance indicators, track trends, and identify potential quality issues promptly.
Alerts and Notifications: An ERP system can be configured to generate alerts and notifications based on predefined thresholds or deviations from quality parameters. This functionality enables real-time alerts when quality metrics exceed or fall below acceptable limits, ensuring immediate attention and action to mitigate potential quality concerns.
Statistical Process Control (SPC) Analysis: ERP systems often incorporate statistical process control (SPC) tools that enable real-time analysis of quality metrics. SPC techniques, such as control charts and trend analysis, help identify patterns, variations, and outliers in quality data, enabling proactive decision-making to maintain consistent product quality.
Integration with Quality Management Modules: ERP systems typically offer dedicated quality management modules that streamline quality control processes. These modules allow for the configuration of quality metrics, acceptance criteria, and inspection checklists, making it easier to track and monitor quality metrics in real time.
Mobile Access: Many modern ERP systems provide mobile access, allowing authorized users to monitor quality metrics on the go. This mobility feature enables real-time monitoring and decision-making, even when away from the office or production floor, enhancing responsiveness and agility in quality management.
Integration with IoT and Sensors: In advanced ERP systems, integration with Internet of Things (IoT) devices and sensors further enhances real-time monitoring capabilities. IoT devices and sensors can collect data directly from production equipment, machinery, or even products themselves, providing instant visibility into quality metrics and enabling proactive quality management.
Real-time access to comprehensive quality data allows organizations to detect issues promptly, make informed decisions, implement corrective actions swiftly, and maintain consistent product quality throughout the production cycle.
Advantages of having access to up-to-date quality information and the impact on decision-making
Having access to up-to-date quality information offers several advantages and has a significant impact on decision-making within an organization. Here are some key advantages:
Timely Issue Identification: Up-to-date quality information enables businesses to identify quality issues promptly. By monitoring quality metrics in real time, organizations can quickly detect deviations or trends that indicate potential quality problems. This early identification allows for immediate action to address the issues before they escalate, minimizing the impact on product quality and customer satisfaction.
Proactive Decision-Making: Access to up-to-date quality information empowers organizations to make proactive decisions. With real-time visibility into quality metrics, decision-makers can assess the current state of product quality and take proactive measures to optimize processes, address potential bottlenecks, and improve overall quality performance. This proactive approach helps prevent quality issues before they occur, reducing costs associated with rework, scrap, and customer complaints.
Data-Driven Insights: Up-to-date quality information provides data-driven insights for decision-making. By analyzing real-time quality data, decision-makers can gain a comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing product quality. These insights help in identifying patterns, root causes, and areas for improvement. Data-driven decision-making enhances the accuracy and effectiveness of decision-making processes, leading to more informed and impactful quality management strategies.
Continuous Improvement: Access to up-to-date quality information supports continuous improvement initiatives. By continuously monitoring quality metrics, organizations can track the effectiveness of implemented quality control measures and evaluate the impact of process improvements. Up-to-date quality information facilitates the identification of opportunities for optimization, allowing organizations to drive continuous improvement in product quality and overall business performance.
Supplier Collaboration and Evaluation: Having access to up-to-date quality information enables effective collaboration and evaluation of suppliers. By sharing quality data with suppliers in real time, organizations can establish a transparent and collaborative relationship. Suppliers can leverage this information to address quality issues promptly, make necessary improvements, and ensure consistent supply of high-quality materials or components.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Up-to-date quality information plays a crucial role in meeting customer expectations. By closely monitoring quality metrics and taking prompt corrective actions when necessary, organizations can ensure that products meet or exceed customer requirements. This, in turn, leads to higher customer satisfaction, increased loyalty, and a positive brand reputation.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: Access to up-to-date quality information helps organizations comply with industry regulations and standards. By maintaining accurate and up-to-date quality records, businesses can demonstrate compliance during audits or inspections. This ensures that products meet the necessary regulatory requirements and helps maintain good standing in the industry.
Having access to up-to-date quality information empowers organizations to identify issues promptly, make proactive decisions, gain data-driven insights, drive continuous improvement, enhance supplier collaboration, ensure customer satisfaction, and meet compliance requirements.
Generating Quality Reports and Analytics
In the pursuit of continuous improvement and effective quality management, the ability to generate comprehensive quality reports and perform insightful analytics is invaluable. This section explores the significance of generating quality reports and conducting analytics within an ERP system.
By leveraging the data captured throughout the production cycle, businesses can transform raw quality data into meaningful information, enabling evidence-based decision-making, identification of trends, and strategic quality improvements.
From standardized quality reports to advanced analytics techniques, we delve into how organizations can harness the power of their ERP system to derive actionable insights and drive continuous enhancement of product quality.
Reporting capabilities of an ERP system for quality tracking
The reporting capabilities of an ERP system play a crucial role in quality tracking and management. Here are some key reporting features and functionalities that enable organizations to effectively track and monitor product quality:
Standardized Quality Reports: An ERP system provides predefined templates and standardized quality reports that offer a consistent format for presenting quality-related information. These reports include metrics such as defect rates, non-conformance incidents, inspection results, and adherence to quality parameters. Standardized reports facilitate easy comparison and analysis of quality data across different products, batches, or time periods.
Customizable Reports: ERP systems allow businesses to create customized reports tailored to their specific quality tracking requirements. Users can select relevant quality metrics, define filters, and specify report layouts to focus on the most critical aspects of product quality. Customizable reports provide flexibility in presenting information based on unique business needs and enable in-depth analysis of quality trends and performance.
Real-Time Reporting: ERP systems enable real-time reporting, allowing stakeholders to access up-to-date quality information as it is captured within the system. Real-time reports provide instant visibility into quality metrics, ensuring that decision-makers have the most current information to make informed decisions and take timely actions to address quality concerns.
Drill-Down Capabilities: ERP systems offer drill-down capabilities that allow users to navigate from summary-level reports to detailed information. Users can drill down into specific quality metrics, inspection records, or non-conformance incidents for a more granular view. This functionality enables root cause analysis, facilitates troubleshooting, and supports targeted improvement efforts.
Trend Analysis: ERP systems enable trend analysis by presenting quality data over time. Trend reports help identify patterns, variations, and long-term quality trends. By tracking quality metrics over specific time periods, organizations can assess the effectiveness of quality improvement initiatives, evaluate the impact of process changes, and make data-driven decisions for further enhancements.
Comparative Analysis: ERP systems facilitate comparative analysis by providing the ability to compare quality metrics across different products, production lines, or locations. Comparative reports enable benchmarking, identification of best practices, and performance evaluation. This analysis helps organizations identify areas for improvement and drive consistent quality standards across the organization.
Dashboard Views: ERP systems often include interactive dashboards that provide a consolidated view of quality metrics. Dashboards present key performance indicators (KPIs), graphical representations, and visualizations of quality data in real time. These user-friendly interfaces enable stakeholders to quickly assess the overall quality status, identify trends, and gain insights at a glance.
Ad Hoc Reporting: ERP systems support ad hoc reporting capabilities, allowing users to create on-the-fly reports based on specific quality-related queries or analysis requirements. Ad hoc reporting empowers users to explore quality data, generate custom views, and extract valuable insights that may not be available through standard reports.
Standardized and customizable reports, real-time reporting, drill-down capabilities, trend analysis, comparative analysis, dashboard views, and ad hoc reporting all contribute to transforming quality data into actionable insights, driving continuous improvement, and ensuring consistent product quality.
How to generate customized reports and analytics to gain insights into product quality trends and areas for improvement
Generating customized reports and analytics within an ERP system allows organizations to gain valuable insights into product quality trends and identify areas for improvement.
Here are the steps involved in generating customized reports and analytics:
Identify Key Quality Metrics: Determine the specific quality metrics that are most relevant to your organization and align with your quality objectives. These metrics could include defect rates, non-conformance incidents, customer complaints, inspection results, or any other parameters that define product quality.
Define Reporting Requirements: Clearly define the reporting requirements based on the identified quality metrics. Specify the data elements, filters, and time periods necessary for generating meaningful reports. Consider the specific needs of different stakeholders, such as managers, quality control teams, or production supervisors, and ensure that the reports cater to their requirements.
Select Report Generation Tools: Explore the reporting capabilities within your ERP system. Identify the tools or modules that allow for customized report generation and analytics. These tools may include report builders, query builders, or ad hoc reporting features. Familiarize yourself with the functionalities and options available within the ERP system to leverage them effectively.
Design Report Templates: Create customized report templates that align with your reporting requirements. Determine the layout, format, and visualization options that will best represent the quality data. Consider using charts, graphs, and tables to present the information in a visually appealing and easily understandable manner. Ensure that the reports provide the necessary level of detail for analysis.
Select Data Sources: Determine the relevant data sources within the ERP system that contain the quality data you need for analysis. These sources could include inspection records, non-conformance logs, production data, or customer feedback. Identify the fields and attributes that need to be included in the reports to capture the required information accurately.
Define Filters and Parameters: Specify the filters and parameters that will help narrow down the data for analysis. These filters may include product categories, production lines, time periods, or specific quality thresholds. Applying appropriate filters ensures that the reports focus on the relevant data and provide insights specific to the desired scope.
Generate and Review Reports: Utilize the reporting tools within the ERP system to generate the customized reports based on the defined templates, data sources, and filters. Review the reports for accuracy and relevance. Pay attention to the quality metrics, trends, and any anomalies that may indicate areas for improvement or deviations from quality standards.
Perform Analytics and Interpretation: Analyze the generated reports to gain insights into product quality trends and areas for improvement. Look for patterns, correlations, or outliers in the data. Interpret the findings to understand the underlying causes of quality issues or identify opportunities for enhancing product quality. Use data visualization techniques to aid in the interpretation and communicate the findings effectively.
Take Action and Continuous Improvement: Based on the insights derived from the customized reports and analytics, develop action plans to address identified quality issues or improvement areas. Implement corrective actions, process changes, or training programs as needed. Monitor the impact of these actions through ongoing quality tracking and iterate the reporting and analytics process to drive continuous improvement.
The ability to tailor reports to specific requirements enables evidence-based the decision-making, facilitates targeted quality management strategies, and supports the continuous enhancement of product quality.
Integrating ERP with Other Quality Assurance Tools
To further enhance the capabilities of an ERP system in tracking product quality, integration with other quality assurance tools is vital. This section explores the significance of integrating ERP with complementary quality assurance tools and technologies.
This integration facilitates data exchange, streamlines processes, and enables a more comprehensive and efficient approach to quality control. From harnessing the power of data analysis to automating testing procedures, we delve into how integrating ERP with other quality assurance tools optimizes quality management and fosters continuous improvement.
Benefits of integrating the ERP system with other quality assurance tools, such as Statistical Process Control (SPC) software or Quality Management Systems (QMS)
Integrating the ERP system with other quality assurance tools, such as Statistical Process Control (SPC) software or Quality Management Systems (QMS), offers numerous benefits for organizations.
Here are some key advantages of integrating ERP with these tools:
- Enhanced Data Analysis and Insights: Integration allows for seamless data exchange between the ERP system and quality assurance tools. By combining the data captured by the ERP system with the analytical capabilities of SPC software or QMS, organizations gain deeper insights into product quality trends, process variations, and potential improvement opportunities. Advanced statistical analysis techniques enable the identification of root causes, correlations, and patterns that may not be readily apparent from ERP data alone.
- Streamlined Quality Control Processes: Integration facilitates the automation and streamlining of quality control processes. Data generated by quality control equipment or testing procedures can be directly captured and integrated into the ERP system, eliminating the need for manual data entry. This not only saves time but also minimizes the risk of errors or discrepancies in data recording. Real-time integration ensures that quality control data is instantly available within the ERP system for analysis, decision-making, and immediate action.
- Improved Traceability and Compliance: Integrating the ERP system with QMS or other compliance-focused tools enhances traceability and compliance management. Quality-related data, including product specifications, testing results, non-conformance incidents, and corrective actions, can be seamlessly linked to the relevant processes and documentation within the QMS. This integration enables efficient tracking of quality-related activities, adherence to regulatory requirements, and easier preparation for audits or inspections.
- Holistic Quality Management: Integrating ERP with other quality assurance tools enables a holistic approach to quality management. The ERP system serves as the central repository for all quality-related data, while the additional tools provide specialized functionalities for specific quality control aspects. This integration allows for a comprehensive view of quality across the organization, enabling stakeholders to monitor, analyze, and improve quality throughout the entire value chain.
- Real-Time Decision-Making: Integration ensures that quality-related data is readily available in real time, enabling faster and more informed decision-making. By having access to real-time quality data from the ERP system and supplementary tools, decision-makers can quickly assess quality performance, identify issues, and take proactive measures to maintain or enhance product quality. Real-time decision-making is particularly crucial in fast-paced industries where immediate action is required to mitigate quality risks and ensure customer satisfaction.
- Collaborative Quality Management: Integration fosters collaboration among various teams involved in quality management. With ERP integration, quality-related information can be shared seamlessly across departments, such as production, quality control, and procurement. This collaboration facilitates proactive problem-solving, cross-functional decision-making, and a shared understanding of quality goals and metrics. Integration also enables effective communication and collaboration with external stakeholders, such as suppliers or customers, for seamless quality management across the supply chain.
Integrating the ERP system with quality assurance tools. These include SPC software or QMS brings several advantages, including enhanced data analysis and insights, streamlined quality control processes, improved traceability and compliance, holistic quality management, real-time decision-making, and collaborative quality management.
This integration optimizes the quality management ecosystem, enabling organizations to drive continuous improvement, maintain high product quality standards, and achieve operational excellence.
How these integrations can further enhance the ability to track and maintain product quality
The integrations between an ERP system and quality assurance tools have a significant impact on the ability to track and maintain product quality.
Here's how these integrations further enhance the quality tracking and maintenance capabilities:
Comprehensive Data Visibility: The integrations enable the consolidation of quality-related data from multiple sources into a centralized platform, such as the ERP system. This provides a holistic view of product quality by incorporating data from quality control equipment, testing procedures, and supplementary tools. The comprehensive data visibility allows for a more accurate and thorough assessment of quality performance throughout the production cycle.
Real-Time Data Capture and Analysis: The integrations facilitate real-time data capture from quality assurance tools into the ERP system. As quality-related data is instantly available, organizations can track quality metrics, monitor performance, and identify issues in real time. Real-time data analysis helps in detecting deviations or variations from quality standards promptly, enabling timely interventions to maintain product quality and prevent potential quality-related risks.
Proactive Quality Control: Integrating quality assurance tools with the ERP system enables proactive quality control. With real-time data and analytics, organizations can establish control limits, define quality thresholds, and set up automated alerts or notifications to trigger immediate actions when quality parameters exceed predetermined levels. This proactive approach allows for early detection and resolution of quality issues, minimizing the impact on product quality and customer satisfaction.
Advanced Analytics and Insights: Integrations with statistical analysis software or other advanced analytics tools enable organizations to delve deeper into quality data. By leveraging sophisticated analysis techniques, such as Statistical Process Control (SPC), predictive analytics, or machine learning algorithms, organizations can uncover hidden patterns, correlations, or anomalies in quality data. These insights provide valuable information for process optimization, root cause analysis, and continuous quality improvement initiatives.
Closed-Loop Corrective Actions: Integrations facilitate closed-loop corrective actions by linking quality-related issues, non-conformances, or customer complaints with the appropriate corrective and preventive actions (CAPAs) within the ERP system. When quality issues are identified, the integrated system enables the seamless initiation, tracking, and resolution of CAPAs. This closed-loop approach ensures that quality improvements are implemented effectively, and the impact of corrective actions is monitored to prevent recurrence.
Data-Driven Decision-Making: The integrations enable data-driven decision-making in quality management. By combining data from various sources and applying advanced analytics, organizations can make informed decisions based on objective insights. Decision-makers can assess quality trends, identify areas for improvement, and prioritize quality initiatives based on data-driven evidence. This data-driven approach minimizes subjective decision-making and promotes a culture of continuous improvement.
Improved Collaboration and Communication: Integrations foster collaboration and communication among different teams involved in quality management. With shared access to quality-related data and real-time visibility into quality performance, cross-functional teams can collaborate effectively to address quality issues, share best practices, and implement quality improvements. Enhanced collaboration strengthens the alignment of quality goals across departments and promotes a culture of shared responsibility for maintaining product quality.
These integrations empower organizations to effectively monitor quality, detect issues early, implement timely corrective actions, and continuously enhance product quality throughout the value chain.
Ensuring Data Accuracy and Integrity
In the realm of tracking product quality, data accuracy and integrity play a vital role. This section explores the significance of maintaining accurate and reliable data within an ERP system for effective quality tracking. From data entry to data validation and ongoing data maintenance, we delve into the key practices and strategies that organizations can employ to ensure data accuracy and integrity.
By establishing robust data management processes and leveraging data validation techniques, organizations can rely on accurate and trustworthy information for making informed decisions, identifying quality trends, and implementing targeted quality improvements.
Importance of data accuracy and integrity in quality tracking
Data accuracy and integrity are of utmost importance in quality tracking within an organization. Here are key reasons highlighting their significance:
Reliable Decision-Making: Accurate and reliable data serves as the foundation for making informed decisions regarding product quality. Quality tracking involves analyzing various metrics, identifying trends, and taking appropriate actions. If the data used for analysis is inaccurate or incomplete, it can lead to flawed decision-making and ineffective quality control strategies. By ensuring data accuracy and integrity, organizations can rely on trustworthy information to drive decision-making and implement targeted quality improvements.
Effective Problem Identification: Accurate data is crucial for identifying quality issues and deviations from established standards. By tracking and analyzing quality data, organizations can pinpoint specific areas or processes that require attention. However, if the data is unreliable, it can mask underlying problems or create false positives, leading to wasted resources and ineffective problem-solving efforts. Data accuracy and integrity enable organizations to identify genuine quality issues and take prompt corrective actions.
Continuous Improvement Initiatives: Quality tracking serves as a basis for continuous improvement initiatives. Organizations need accurate data to measure performance, track progress, and evaluate the effectiveness of quality improvement efforts. Inaccurate data can provide a distorted picture of quality performance, hindering the identification of improvement opportunities and impeding progress. Accurate and reliable data, on the other hand, allows organizations to measure the impact of their initiatives and make data-driven adjustments for ongoing quality enhancement.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: Many industries are subject to stringent regulatory requirements related to product quality. Accurate and reliable data is essential for meeting these compliance obligations. Regulatory bodies often conduct audits or inspections to ensure adherence to quality standards. Inaccurate or unreliable data can lead to compliance issues, penalties, and damage to the organization's reputation. By prioritizing data accuracy and integrity, organizations can confidently demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements.
Trustworthy Reporting and Analysis: Quality tracking involves generating reports, analyzing trends, and presenting findings to stakeholders. To ensure that these reports and analyses are trustworthy, it is essential to have accurate and reliable data as the basis. Stakeholders, including management, customers, or regulatory authorities, rely on these reports to assess quality performance, make informed decisions, and evaluate the organization's commitment to quality. Data accuracy and integrity are fundamental to maintaining the trust and credibility of the quality tracking process.
Efficient Data Integration and Interoperability: Data accuracy and integrity are crucial when integrating quality tracking data with other systems or tools within the organization's infrastructure. Integrated systems, such as ERP, QMS, or SPC software, rely on accurate data exchange to provide a holistic view of quality performance. Inaccurate or inconsistent data can lead to integration issues, data conflicts, or misinterpretation of quality metrics. Ensuring data accuracy and integrity allows for seamless integration, interoperability, and reliable data flow across different systems.
Organizations must establish robust data management processes, implement data validation techniques, and prioritize data integrity to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information used for quality tracking
Best practices for data entry, validation, and verification within the ERP system
Best Practices for Data Entry, Validation, and Verification within the ERP System
Standardized Data Entry Procedures: Establish standardized procedures for data entry to ensure consistency and accuracy. Define clear guidelines and formats for entering data into the ERP system, including required fields, data types, and units of measurement. Train employees on these procedures to maintain uniformity in data entry across the organization.
Data Validation Rules: Implement data validation rules within the ERP system to enforce data integrity. Set up validation rules that automatically check the accuracy, completeness, and validity of entered data. These rules can include range checks, format checks, mandatory field checks, or cross-referencing with existing data to identify potential errors or inconsistencies.
Real-Time Error Detection and Correction: Enable real-time error detection and correction mechanisms within the ERP system. Validate data entered in real time to provide immediate feedback to users about potential errors or inconsistencies. Implement alerts or warnings to prompt users to correct data entry mistakes promptly. This ensures that errors are caught and resolved at the earliest stage, minimizing the impact on subsequent quality tracking processes.
Data Verification and Review Processes: Establish verification and review processes to ensure the accuracy and reliability of data. Conduct regular data reviews to identify discrepancies, outliers, or patterns that may indicate data quality issues. Assign responsibilities for data verification and review to designated personnel who are responsible for conducting thorough checks, validating data against source documents, and addressing any identified issues.
User Access Control and Security: Implement user access controls and security measures to prevent unauthorized access or modifications to data. Define user roles and permissions within the ERP system, granting access only to authorized individuals. This minimizes the risk of data manipulation or tampering that could compromise the accuracy and integrity of quality tracking data.
Data Auditing and Logging: Enable data auditing and logging features within the ERP system to track data changes and maintain an audit trail. This helps in identifying and investigating any data anomalies, discrepancies, or unauthorized modifications. Regularly review audit logs to ensure data integrity and identify any potential data entry or validation issues.
Data Cleansing and Maintenance: Implement regular data cleansing and maintenance activities to keep the data clean and up to date. Identify and remove duplicate or outdated records, perform data deduplication, and correct any inaccuracies or inconsistencies. Set up data maintenance schedules to periodically review and update data to ensure its accuracy and reliability over time.
Training and Education: Provide training and education to employees on the importance of accurate data entry and the best practices for data validation and verification. Make sure employees are aware of the impact of data quality on quality tracking processes and the overall success of the organization. Offer ongoing training programs to keep employees updated on data entry procedures and techniques.
Continuous Improvement: Continuously monitor and improve data entry, validation, and verification processes. Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of data validation rules, review data quality reports, and seek feedback from users. Identify areas for improvement and implement necessary changes to enhance data accuracy and integrity within the ERP system.
By following these best practices for data entry, validation, and verification within the ERP system, organizations can ensure the accuracy, reliability, and integrity of quality tracking data. This, in turn, enables effective decision-making, reliable analysis, and continuous improvement initiatives based on trustworthy information.
Overcoming Challenges and Considerations
Implementing an ERP system for quality tracking brings numerous benefits, but it also comes with its own set of challenges. This section sheds light on the common obstacles organizations may encounter and explores key considerations to overcome them successfully.
From addressing data integration complexities to managing system customization and user adoption, understanding and proactively addressing these challenges are crucial for a smooth and effective implementation of an ERP system for quality tracking. By taking the necessary steps to overcome these hurdles, organizations can unlock the full potential of ERP in enhancing their quality management processes and achieving their quality objectives.
Common challenges businesses may face when using an ERP system for product quality tracking
Implementing an ERP system for product quality tracking can bring about significant improvements in quality management processes. However, businesses may encounter certain challenges during this implementation. It is important to be aware of these challenges and take proactive measures to address them.
Here are some common challenges businesses may face when using an ERP system for product quality tracking:
Data Integration Complexity: Integrating data from various sources and systems into the ERP system can be complex. Data may come from quality control equipment, testing procedures, and other sources. Ensuring smooth data integration requires careful planning, data mapping, and establishing standardized data interfaces to maintain data consistency and accuracy.
System Customization: Every business has unique quality tracking requirements. Customizing the ERP system to align with specific quality processes and metrics can be challenging. It may involve configuring workflows, creating custom fields, or integrating additional modules. Balancing customization needs with system stability and future upgrades requires careful consideration.
User Adoption and Training: Implementing an ERP system for quality tracking requires user adoption and training. Employees need to understand how to effectively use the system, enter data accurately, and leverage its features for quality monitoring and analysis. Overcoming resistance to change, providing comprehensive training programs, and ongoing user support are crucial for successful adoption.
Data Quality and Accuracy: Maintaining data quality and accuracy is critical for effective quality tracking. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to misleading insights and flawed decision-making. Establishing data validation rules, implementing data cleansing processes, and ensuring ongoing data integrity are essential to mitigate data quality issues.
Organizational Alignment: Implementing an ERP system for quality tracking often involves cross-functional collaboration. Achieving organizational alignment and securing buy-in from different departments can be challenging. Clear communication, involving stakeholders in the implementation process, and showcasing the benefits of the system are key to fostering alignment and cooperation.
Change Management: Implementing an ERP system for quality tracking represents a significant organizational change. Resistance to change and fear of disruption can pose challenges. Effective change management strategies, including stakeholder engagement, communication, and addressing concerns, are crucial for minimizing resistance and fostering a positive transition.
System Scalability: As businesses grow and evolve, the scalability of the ERP system becomes crucial. Ensuring that the system can accommodate increasing data volumes, user demands, and new quality tracking requirements is essential. Regular system assessments, capacity planning, and selecting an ERP system that can scale with the business are vital considerations.
Continuous Improvement: Implementing an ERP system for quality tracking is not a one-time project. It requires continuous improvement to optimize quality processes and adapt to changing business needs. Creating a culture of continuous improvement, regularly reviewing system performance, and incorporating user feedback are important for ongoing success.
By understanding these common challenges and proactively addressing them, businesses can overcome hurdles in implementing an ERP system for product quality tracking. With proper planning, robust change management strategies, and ongoing support, organizations can harness the full potential of the ERP system to enhance their quality management practices and achieve their quality objectives effectively.
Tips and recommendations to overcome these challenges effectively
In this section, we shall go through the tips and recommendations to overcome challenges using an ERP.
Thorough Planning: Start with a comprehensive planning phase that includes defining quality objectives, identifying key stakeholders, and assessing the organization's current quality processes. This will help in setting clear goals, understanding system requirements, and anticipating potential challenges.
Engage Stakeholders: Involve key stakeholders from different departments throughout the implementation process. Their input and involvement will increase acceptance and facilitate smoother integration of the ERP system into existing quality management processes.
Seek Vendor Expertise: Collaborate closely with the ERP system vendor or implementation partner. Leverage their expertise to understand best practices, receive guidance on system customization, and gain insights on how to address specific challenges related to quality tracking.
Prioritize Data Migration and Integration: Develop a well-defined strategy for data migration and integration. Ensure that data from various sources is cleansed, standardized, and mapped accurately to fit the ERP system's data structure. Conduct thorough testing to verify the accuracy and reliability of integrated data.
Training and Change Management: Invest in comprehensive training programs to educate employees on using the ERP system for quality tracking. Offer hands-on training, workshops, and user support to foster user adoption and minimize resistance to change. Communicate the benefits and address concerns throughout the implementation process.
Continuous User Support: Provide ongoing user support to address user queries, system-related issues, and enhance user proficiency. Create user manuals, FAQs, and a dedicated support team to assist users in utilizing the ERP system effectively for quality tracking.
Data Governance and Quality Control: Establish data governance practices and quality control measures to ensure data accuracy and integrity. Define data validation rules, conduct regular data audits, and implement data cleansing processes to maintain high-quality data within the ERP system.
Regular System Evaluation and Improvement: Continuously evaluate the ERP system's performance in meeting quality tracking requirements. Solicit feedback from users, monitor system performance, and regularly assess the system's scalability. Identify areas for improvement and work with the vendor or implementation partner to optimize the system's functionality.
Foster a Culture of Continuous Improvement: Encourage employees to actively participate in the improvement of quality tracking processes using the ERP system. Implement feedback mechanisms, regularly review quality metrics, and promote a culture that values continuous improvement in quality management.
Collaborate with Quality Assurance Tools: Integrate the ERP system with other quality assurance tools, such as Statistical Process Control (SPC) software or Quality Management Systems (QMS), to leverage their combined functionalities. This integration can enhance the accuracy, efficiency, and effectiveness of quality tracking processes.
By implementing these tips and recommendations, businesses can effectively overcome challenges associated with using an ERP system for product quality tracking. This will facilitate a smoother implementation process, increase user adoption, and maximize the benefits of the ERP system in enhancing overall quality management practices.
Why Should Businesses Embrace ERP as a Comprehensive Solution for Quality Control and Improvement?
Investing in product quality tracking brings numerous benefits. It enables businesses to detect quality deviations early, minimizing the risk of defective products reaching customers. Timely identification of quality issues allows for prompt corrective actions, reducing costs associated with product recalls, returns, and customer complaints.
Moreover, effective quality tracking strategies provide valuable insights into process efficiencies, enabling organizations to optimize their production workflows and reduce waste.
To prioritize and invest in effective product quality tracking strategies, businesses should consider the following:
Implement an Integrated Quality Management System: Adopting an integrated Quality Management System (QMS) or leveraging the quality modules of an ERP system can streamline quality tracking processes. These systems enable organizations to capture, analyze, and report quality-related data in a centralized manner, facilitating better decision-making and continuous improvement.
Define Clear Quality Metrics and Parameters: Establishing clear quality metrics and parameters specific to each product is essential. Define measurable criteria to assess product quality at different stages of the production cycle. This allows for accurate monitoring and comparison against established benchmarks.
Leverage Technology and Automation: Embrace technology solutions such as ERP systems, Quality Control software, and automation tools to enhance accuracy, efficiency, and traceability in quality tracking. These tools facilitate real-time data collection, analysis, and reporting, empowering businesses to make data-driven decisions and proactively manage quality issues.
Promote a Culture of Quality: Foster a company culture that values and prioritizes product quality. This requires active engagement from top management to frontline employees. Encourage cross-functional collaboration, provide training on quality tracking processes, and recognize and reward individuals and teams for their contributions to quality improvement.
Continuously Monitor and Analyze Quality Data: Regularly monitor and analyze quality data to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement. Use statistical process control techniques, trend analysis, and root cause analysis to gain insights into quality performance and make data-driven decisions.
Engage Suppliers and Partners: Collaborate closely with suppliers and partners to ensure their commitment to delivering quality materials and services. Establish quality agreements, conduct audits, and foster strong communication channels to maintain a high level of quality throughout the supply chain.
Seek Customer Feedback: Actively seek customer feedback to understand their perceptions of product quality. Incorporate customer feedback into quality tracking processes to identify areas for improvement and drive customer-centric quality initiatives.
Investing in effective product quality tracking strategies is an investment in the long-term success and sustainability of the business. By prioritizing product quality, businesses can strengthen their brand reputation, increase customer loyalty, and differentiate themselves in the market. Furthermore, a focus on quality leads to continuous improvement, operational efficiencies, and ultimately, higher profitability.
Conclusion
Implementing an ERP system for product quality tracking can revolutionize the way businesses manage and monitor their quality processes. By leveraging the power of ERP, organizations can streamline quality control, enhance data accuracy, and make data-driven decisions to improve overall product quality.
Throughout this article, we have explored various aspects of using ERP for quality tracking, from understanding its role in managing business operations to configuring the system, implementing quality control processes, and generating insightful reports and analytics.
However, we also acknowledge the challenges that businesses may encounter during the implementation of an ERP system for quality tracking. From data integration complexities to user adoption and system customization, these hurdles require careful consideration and proactive measures for successful implementation.
To overcome these challenges, we have provided valuable tips and recommendations, emphasizing the importance of thorough planning, stakeholder engagement, training, and ongoing user support. Additionally, we highlighted the significance of data accuracy, continuous improvement, and integrating the ERP system with other quality assurance tools.
By effectively addressing these challenges and following best practices, businesses can unlock the full potential of ERP in tracking and maintaining product quality. This will lead to improved customer satisfaction, enhanced operational efficiency, and a competitive advantage in the market.
In conclusion, implementing an ERP system for product quality tracking is a transformative step for businesses seeking to achieve excellence in their quality management processes. With careful planning, strategic implementation, and a commitment to continuous improvement, organizations can leverage ERP to streamline quality control. They will also be in a position to drive better decision-making, and ultimately deliver high-quality products that meet and exceed customer expectations.
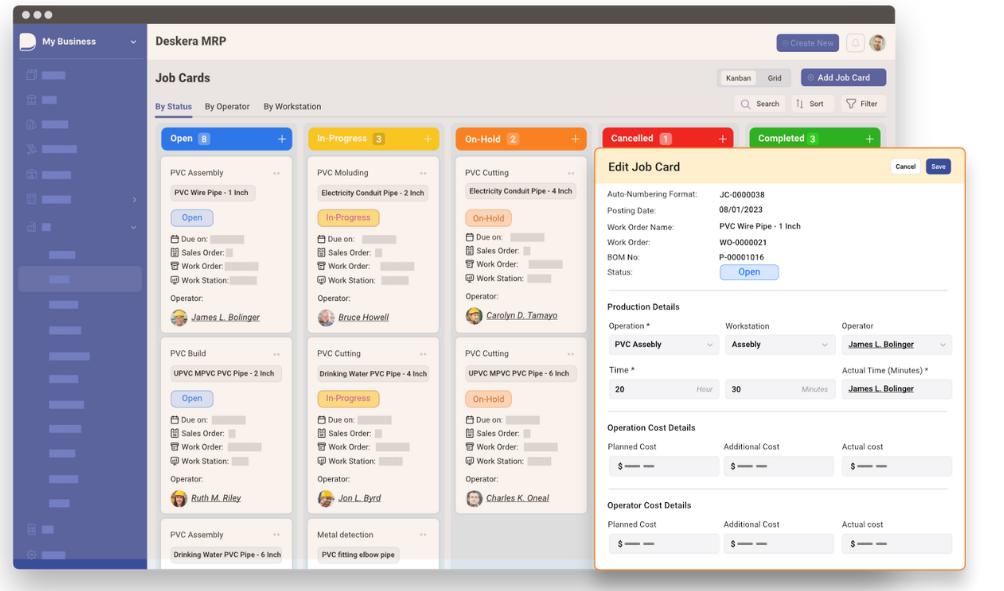
How can Deskera Help You?
Deskera ERP and MRP systems help you to keep your business units organized. The system's primary functions are as follows:
- Keep track of your raw materials and final items inventories
- Control production schedules and routings
- Keep a bill of materials
- Produce thorough reports
- Make your own dashboards
Deskera's integrated financial planning tools enable investors to better plan and track their investments. It can assist investors in making faster and more accurate decisions.
Deskera Books allows you to better manage your accounts and finances. Maintain good accounting practices by automating tasks like billing, invoicing, and payment processing.
Deskera CRM is a powerful solution that manages your sales and helps you close deals quickly. It not only enables you to perform critical tasks like lead generation via email, but it also gives you a comprehensive view of your sales funnel.
Deskera People is a straightforward tool for centralizing your human resource management functions.
Key Takeaways
- Product quality tracking is essential for long-term success and competitive advantage in today's business landscape.
- Effective quality tracking strategies help identify and address quality issues, ensuring customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Investing in product quality tracking minimizes the risk of defective products reaching customers, reducing costs associated with recalls and returns.
- An integrated Quality Management System (QMS) or ERP system with quality modules streamlines quality tracking processes.
- Clear quality metrics and parameters specific to each product should be defined for accurate monitoring and comparison.
- Technology solutions such as ERP systems, Quality Control software, and automation tools enhance accuracy, efficiency, and traceability in quality tracking.
- Promoting a culture of quality throughout the organization is crucial, with active engagement from management and continuous training for employees.
- Regular monitoring and analysis of quality data using statistical process control techniques and root cause analysis provide insights for improvement.
- Collaboration with suppliers and partners ensures quality throughout the supply chain.
- Seeking customer feedback and incorporating it into quality tracking processes drives customer-centric quality improvement initiatives.
Related Articles