Gujarat Factories Rules is a vast document that furnishes guidelines for the factory owners or employers in order to take care of the general well-being of the workers when they are at work. We have observed how the minimum wages, the hours of work, the safety rules, and facilities like washrooms and lunchrooms have to be taken care of by the employers.
The document is a guidebook that addresses employers from diverse industries functioning in the state of Gujarat. The industries covered under the factories' rules are textile, wood-working machinery, rubber mills, power-press, and so on.
In compliance with the Factories Rules, the employers need to fill in and submit certain forms when they need to apply for permissions for various tasks such as construction or retention of buildings. We shall be learning about all the 37 forms applicable in various scenarios.
Forms
All 36 forms with the sub-forms are included in the following sections. Let’s check them here:
Form No. 1
The form no. 1 is prescribed under Rule 3 and is used for applying for permission for construction, extension, and using any building as a factory.
Signature of the applicant
Name of the applicant (in block letters)
Telephone Number
Date:
Form No. I-A: Certificate of Stability
This is prescribed Under Rule 3-C and is called a Certificate of stability. Here are the details you need to provide to submit the form:
- Name of the Factory process
- Village, town, and district where the factory is situated.
- Entire postal address of the factory.
- Name of the factory’s Occupier
- Nature of manufacturing process that will be carried out in the factory
- The number of floors where the workers will be employed.

If the worker is employed at a company, then they must provide the name and address of the company.
Form No. 1-B
This is a form prescribed under Rule 68-1. It is the format of application to the site appraisal committee.
- Name and address of the applicant
- Site ownership data
2.1 Revenue details of the site including Survey No. or Plot No. and so on.
2.2 Here, you must indicate whether or not the site is classified as forest. If so, is there approval of the Central Government in accordance with section 5 of the Indian Forest Act, 1927.
2.3 Whether or not the proposed site attracts the provision of section 3(2)(v) of the Environment (Protection) Act. 1989, E.P. Act, 1989. If so, the nature of the restrictions.
2.4 Local authority under whose jurisdiction the site is located.
- Site plan:
3.1 Site plan with clear demarcation of boundaries and the proposed total area that will be occupied and showing the following details near the proposed site.
a. Indicate if there is a historical monument, in the vicinity.
b. Names of neighboring manufacturing units and human habitat. Also, inform about any educational and training institutions, storage of liquid Petroleum Gas (L.P.G.), petrol installations, and any other hazardous substances in the vicinity. You must also include their distances from the proposed unit.
c. Water sources (rivers, canals, streams, dams, and so on.) are in the vicinity.
d. Nearest hospitals, civil defense stations, fire stations, and police stations and the corresponding distances.
e. Pipelines for water, high tension electrical transmission lines, gas, oil, or sewage, railway lines, jetties, roads, stations, and other similar installations.
3.2 Details of soil conditions and depth at which hard strata were obtained.
3.3 Counter map of the area showing nearby hillocks and differences in levels.
3.4 Plot plan of the factory showing the roads within, entry and exit points, water drains, and so on.
- Project Report
4.1 An overview of the special characteristics of the project.
4.2 Status of the organization (Public or private, Government, Semi-Government, etc.) 4.3 Maximum number of individuals that are likely to work in the factory.
4.4 Maximum amount of power and water requirements and source of their supply.
4.5 Block diagram of the building and installation in the proposed supply.
4.6 Details of housing colony, hospitals, schools, and other infrastructural facilities proposed.
- The suggested manufacturing unit/organizational factory's structure.
5.1 Organizational diagrams for the proposed business in general
- Departments of health, safety, and environmental protection, and their ties to departments of preparation and technology
5.2 Health and Safety Policy Proposed
5.3 Allocation of area for waste
5.4 percent on safety, health, and environmental protection.
- Weather information for the location:
6.1 Average minimum and maximum temperatures, humidity, and wind speeds during the last ten years.
6.2 Wind direction changes throughout the year The highest water level ever recorded in the area during floods.
6.3 The area's lightning and adimic data
- Links of Communication
7.1 Telephone/telex-wireless and other communication facilities for external communication are available.
7.2 Proposed internal communication facilities
- Information on the manufacturing process
8.1 Diagram of the process flow.
8.2 Brief Process and technology
8.3 Critical process parameters include pressure rise, temperature rise, and runaway reactions.
8.4 Other critical external impacts with safety implications, such as water intrusion, contact with incompatible compounds, and sudden power failure Highlights of the safety/pollution control mechanisms or measures built into the production technology.
- Hazardous Materials Information
9.1 Quantities of raw materials, intermediates, manufacturing, and byproducts (Enclose Material Safety Data Sheet to expect of each hazardous substance.)
9.2 Proposed storage facilities for raw materials, intermediates, products, and by-products (maximum quantities to be stored at any time)
9.3 Materials inflow transportation methods, amounts, and most likely routes
9.4 Proposed safety measures for the following:
– Material handling;
– Internal and external transportation; and - Disposal (packing and forwarding of finished products)
- Waste and Pollution Disposal/Disposal Information
10.1 Characteristics and amounts of major pollutants (gases, liquids, and solids) (average and peak loads)
10.2 Solid waste generation, quality and quantity, treatment and disposal methods
10.3 Anticipated air, water, and soil pollution hazards, as well as suggested controls, such as effluent treatment and disposal.
- Information on Process Hazards
11.1 You will need to attach a copy of the environmental impact assessment report.
11.2 You will need to attach a copy of the risk assessment study report.
11.3 Any published (open or classified) reports on accident situations/occupational health dangers or similar plants elsewhere if any are available (within or outside the country)
- Information on suggested workplace safety and health measures:
12.1 Firefighting facilities, as well as the minimum amount of water, CO2, and/or other firefighting measures required to respond to crises.
12.2 Specifics of proposed in-house medical facilities
- Emergency preparedness information
13.1 Arrangements proposed If applicable, for a mutual aid agreement with a group of nearby factories.
- Any further pertinent information
The applicant's name and signature
Form No. 2
The form is prescribed under Rule 4 and is called Application for Registration and Grant or Amendment of License and Notice of Occupation. Additionally, the form must be submitted in triplicate.


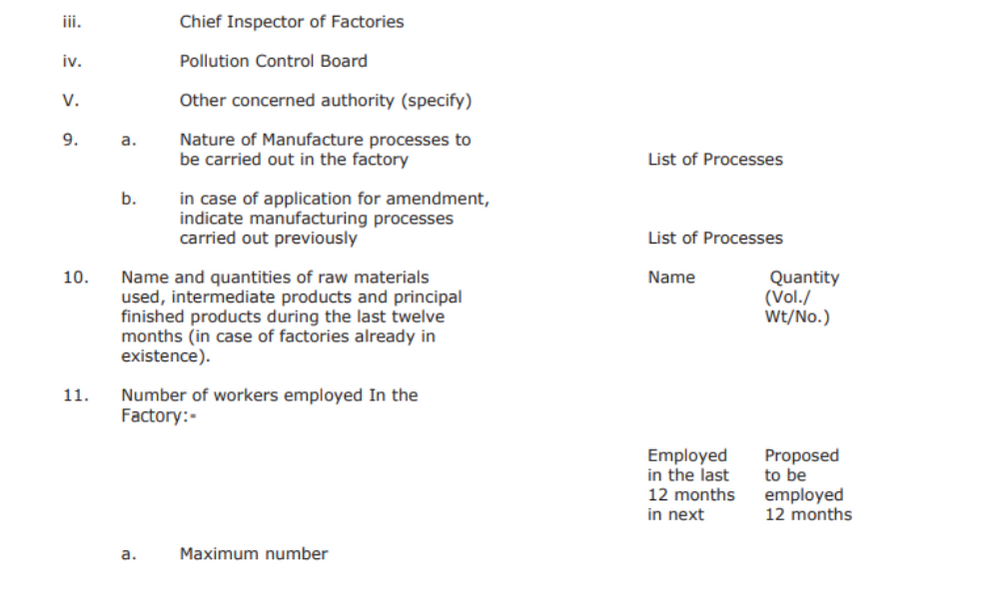

- You must mention what is the application for.
a. Is it for registration, grant of a license, and notice of occupation? Mention Yes or No.
b. Is it for amendment of license? Mention Yes or No.
- a. Provide the applicant’s name
b. Provide the following details:
i. Is the factory already registered? Select Yes or No.
ii. If yes, provide the registration number.
iii. Also, include license number
- Next, you must provide the full name and address of the factory
a. Factory’s name
b. Address
- Furnish the following details:
a. Distance from the nearest police station
b. Distance from the nearest railway station
c. Distance from the nearest public hospital
- Provide entire details of the manager’s name and residential address
- Provide entire details of the occupier’s name and residential address, along with their designation
- Provide entire details of the name and residential address of the owner of the building premises that refer to in section 93.
- Here, you must provide reference numbers, and dates on which the plans were approved. You must also provide approval dates from officers for the disposal of waste.
The authority details would include the State government, local authority, chief inspector of the factory, pollution control board, and any other authority.
- a. Here, mention the nature of the manufacturing process.
b. If your application is for amendment, mention the previous manufacturing process
- Mention the names and the quantities of the raw materials utilized in the manufacturing process
- Mention the number of workers employed in the factory
a. Maximum number of employees
b. The number of employees generally employed
- Mention the nature and total amount of H.P. (power)
a. Installed
b. Proposed installations
- Mention the amount of fees paid
The form must be signed by the occupier or the manager.
Form No. 3
This form is prescribed under the Rules 4 and 7 and is used as an application for renewal of license.

You shall need to furnish the following details here:
- Factory’s name
- Address of the factory
- Full communication address
- A manufacturing process flowchart along with briefing them about raw materials, the products, various stages involved, methods of storage, and quantities of finished products. You must also mention how the handling, loading, and transportation will take place. Also, mention the methods of waste disposal and ways to control and eliminate it.
- Mention the maximum number of employees working at any given time.
- Inform about the power in horsepower.
- Add information about the period for which the license is applied for. It should not be more than two years.
- Occupier’s name and residential address
- Manager’s name and residential address
- Amount of fees being paid by you.
- Finally, add your signature with the date of application.
Form No. 3-A
This is a form prescribed in Rule 12A and serves as a notice of change of manager. Let’s see the details you need to include with this form.
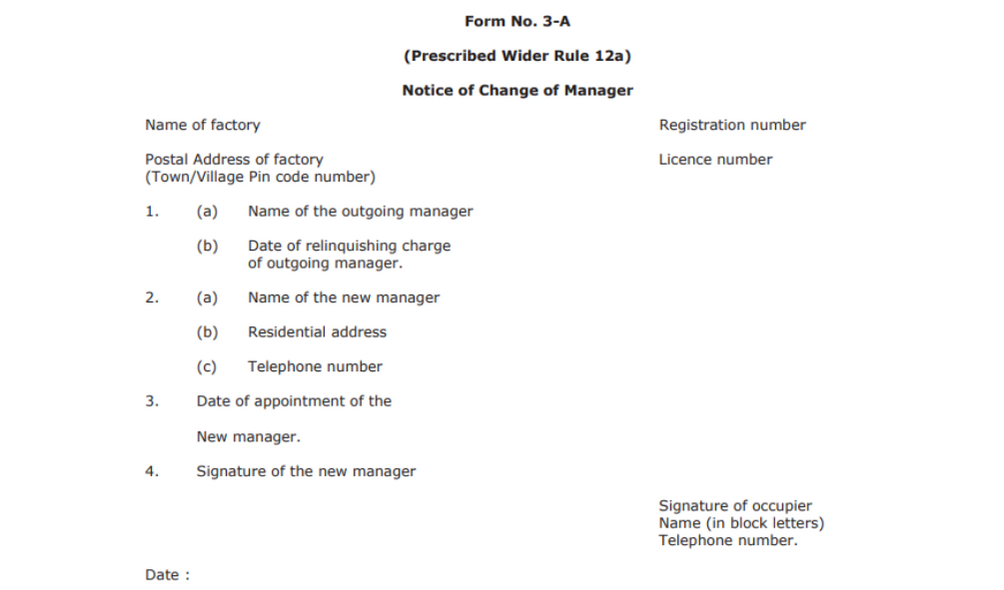
At the top left corner of the form, write the name of the factory along with its address. Also, provide the registration number and its license number.
- a. Name of the outgoing manager
b. Date of relinquishment of the outgoing manager
- a. Name of the new manager
b. Residential address of the new manager
c. telephone number of the new manager
- Appointment date of the new manager
- Signature of the new manager
Form No. 4
This form comes under the Directorate Industrial Safety and Health of Gujarat and is prescribed under Rule 5. It is used for applying for a license to operate as a factory.

The applicant must add the registration number and license number at the top left and right corners respectively. Fill in the blanks appropriately in the form. The form mentions that the license is issued for the maximum number of employees employed at any given time of the year and the maximum installed B.H.P. at any given time of the year.
The form also mentions that the license is valid only up to December 31.
In the end, you will need to include the amount of fees paid, the place, and the date while applying.
Form No. 4-A
This is a form meant for the certificate of competency of a person or an institution for pursuing rule 2-A under Section 2-Ca along with Section 6 and 112/Section 28/ Section 29/ Section 4-I/Section 87.

This form is prescribed under Rule 2(A). It requires you to include information in the blanks provided in the form. The form certifies a competent person from the organization to carry out tests and inspections in the factory located in Gujarat. It also mentions the date of validity of the license.
This certificate is issued according to the following terms and conditions: -
- Tests, examinations, and inspections shall be conducted in compliance with the Act and the rules promulgated thereunder;
- Tests, examinations, and inspections must be conducted under the immediate guidance of a professional person or a person so approved by an institution recognized as such.
- If the person certified competent quits the organization listed in his application, the certificate of competency obtained in his favor is revoked.
- The Institution designated as a competent person must keep the Chief Inspector up to date on the names, designations, and qualifications of those authorized to conduct tests, examinations, and inspections.
Form No. 5
This form is prescribed under Rule 15 and is known as the Certificate of Fitness for Young. The following details are required in the form:

- Serial Number
- Name of the individual examined
- Father’s name
- Sex
- Residence
- Date of Birth
- Reference details include the following:
a. Name and address of the factory
b. Name of the manager
- Name of the manufacturing process in which the young person is set to be employed.
The form will carry a declaration by the certifying surgeon stating that they have personally examined the individual in question. They will also state if the individual is fit or unfit to join the manufacturing unit.
The form shall also carry the following information:
- The Certifying Surgeon must issue it and keep a copy for two years.
- According to the proviso to section 69 sub-section (2), the Certifying Surgeon providing his certificate should have firsthand knowledge of the location where the young person intends to work.
- This certificate is valid for one year from the date of issue, according to section 69(3) of the Act.
- If it’s a case of physical disability, the form should clearly depict the same.
- Remove anything that isn't applicable.
- A youngster (under the age of 15) or an adolescent (under the age of 18) is referred to as a young person.
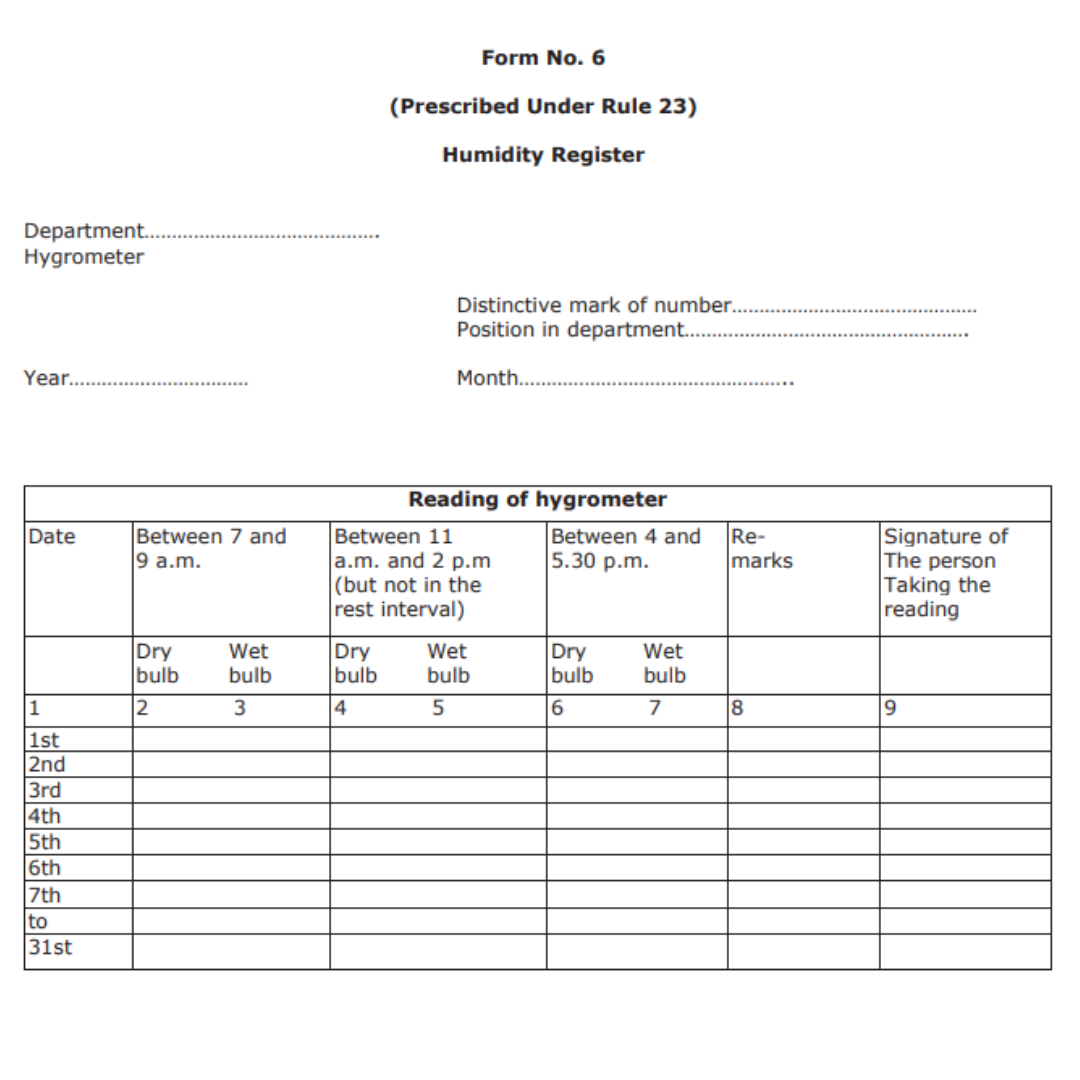
Form No. 6
The form is also known as the Humidity Register and is prescribed under Rule 23. The form is about taking down the readings of the hygrometer in a tabular format. The first column has the date, followed by the time in the second, third, and fourth columns. Finally, it has the remarks and signature of the individual who takes down the readings.
Form No. 7
The form is prescribed under rule 17 and is a record of lime washing, painting, and so on. The first column has the number, and name of the room along with the location of that room in the factory. The second column is about the part of the room being treated. The third column includes the nature of the treatment; whether it is varnished, painted, oiled, and so on. Next is the date of treatment followed by the remarks in the last column.
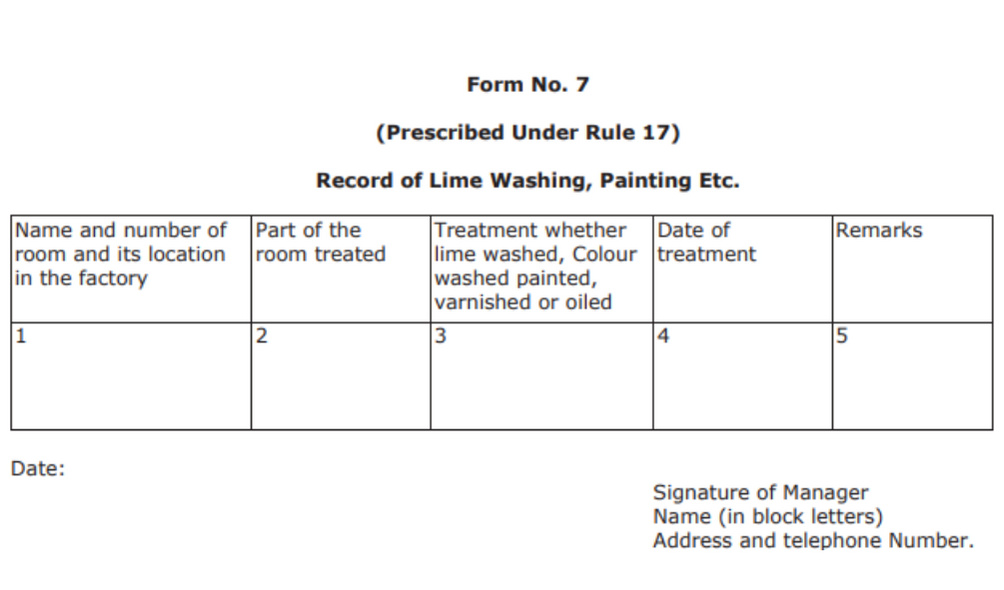
Finally, the form is signed by the manager.
Form No. 8
The form is prescribed under the 5(1)(c) of Schedule VI to Rule 54 and 55. The form is known as the register of workers employed for work near a piece of moving machinery. The form will require the following details:

- Worker’s name
- The serial number of the registered worker
- Father’s name
- Birthdate and age
- Nature of work
- Qualifications
- Date when the tight-fitting clothes were provided to the workers
- Remarks
All these details must be included by the manager. They also certify the mentioned individual has been trained to carry out the various tasks in the factory. The tasks may include shift belts, lubricating, and operating machines in motion. They must also include the thumb impression or the signature of the worker.
Form No. 9
This is the report of the examination of lifts and hoists and is prescribed under Rule 55. The top right corner of the form comprises the registration number, license number, and NIC code number. Let’s check the other details required in the form:


Owner or occupier of the premise
- Address of the owner
- a. Type of lift or hoist
b. Date of construction or reconstruction
- Mention if all the parts of the machines, lifts, and hoists are strong enough.
- Mention if the following parts of the hoists or lifts are working properly:
- Landing gates and cage gates
- Liftway or hoistway enclosure
- Other gate fastenings
- Interlocking
- Brakes
- Gearing parts
- Other electrical parts
- Suspension ropes, over-running devices
- Any other parts
- Name any parts that were inaccessible
- Name any repairs or renewals required
- Mention the maximum safe working load concerning the repairs specified in point 7.
- Mention any other relevant points.
Finally, the signature of the competent person states that they have thoroughly examined the hoist and lift.
Form No. 10
The form is prescribed under Rule 60 and is known as the report of examination of lifting machines, lifting tackles, and ropes. The form includes the following particulars:

- Occupier’s name
- Address of the factory
- Write down any distinct identity of the machine, chain, or rope.
- Mention the date on which the rope, chain, and machine were first used in the factory.
- Date when the examination was carried out under section 29(1)(a)(iii). Also, include the name of the person carrying out the examination.
- State the date and the number of the certificate of any test conducted under the sub-rule (1) of rule 60. It must also provide the name of the person issuing the certificate.
- If the chain and lifting tackle were subjected to sub-rule (5) of rule 60, the date of annealing or other heat treatment, as well as who performed it must also be added.
- Add details of any flaw discovered during the test or after annealing that affects the safe working load, as well as the procedures, are taken to correct the deficiency.
Finally, the signature and certification of the person concerned at the end of the form.
Form No. 11
The form is known as the Report of Examination of the plant or pressure vessel and is prescribed under Rule 61. You shall find space to put down the registration number, license number, and NIC code number which is as mentioned in the license.
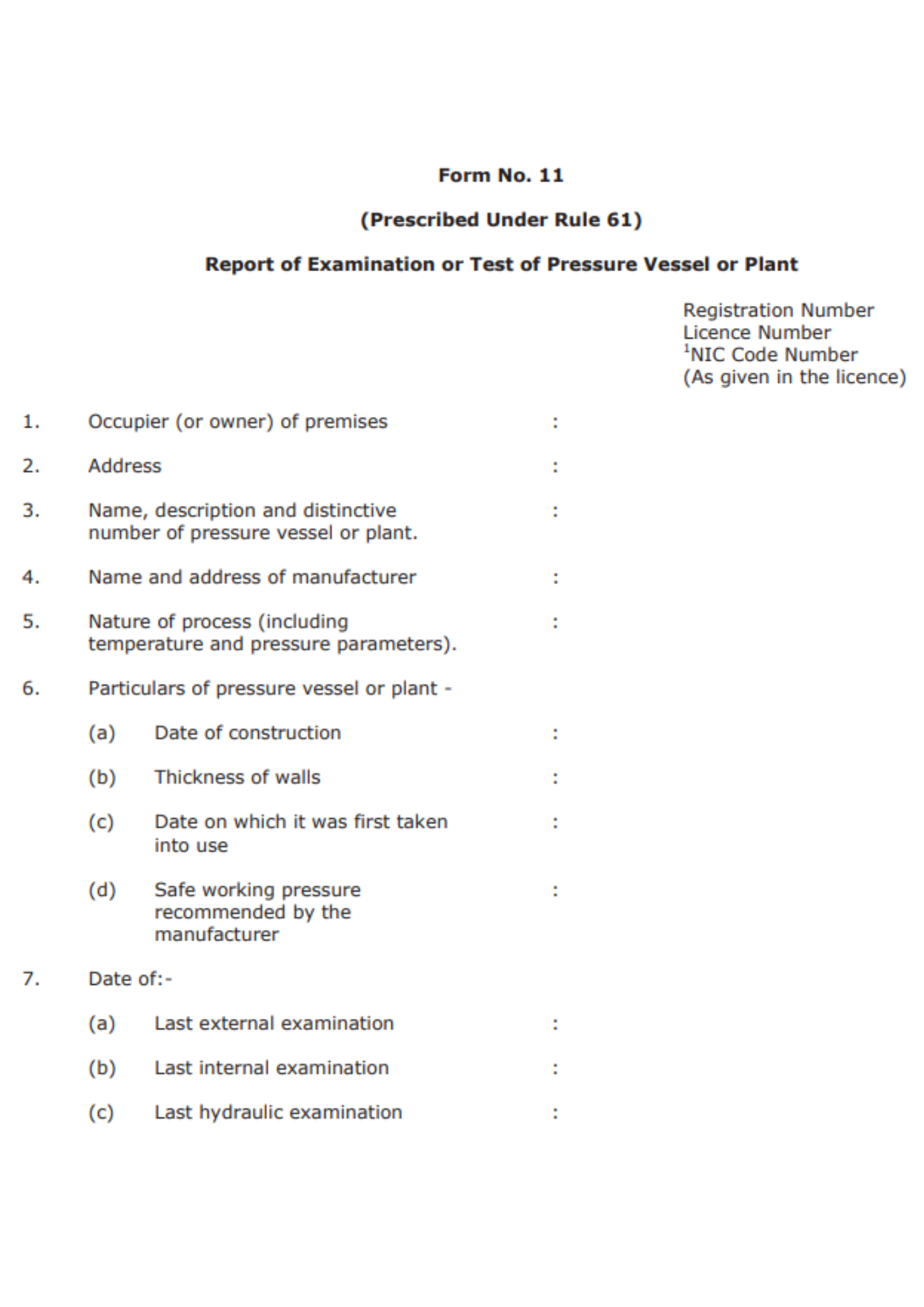


Provide the following details:
- Occupant (or property owner):
- Address:
- Pressure vessel or plant number, name, description, and distinguishing features
- Manufacturer's name and address:
- Process characteristics (such as temperature and pressure).
- Pressure vessel or plant specifics -
a) Date of construction
b) Wall thickness
c) Date it was initially used:
d) Recommended working pressure by the manufacturer
- Date of:
a) The most recent external inspection
b) The most recent internal examination
c) The most recent hydraulic examination
d) The most recent non-destructive ultrasonic
- Whether lagging was removed for examination reasons.
- Examinations that were carried out:
a) External examination (explain why it is not done six times a year)
b) Internal examination (explain why it is not done annually).
c) Hydraulic test: (explain reasons if this is not done every 2 or 4 years)
d) Non-destructive ultrasonic or other tests
- Pressure plant condition
a) Vessel
b) Piping
- Fittings and appliances in good working order
a) Pressure gauges
b) Safety device.
c) Check valve
d) Reducing valve (explain why if not required)
e) An extra safety valve (needed in the event that a reducing valve is required)
f) Other device: (in the case of jacketed vessels, please specify)
- After examination, a safe working pressure is recommended (specify the allowances made for working conditions such as heat, corrosion, and so on.)
- a) Required repairs (if any)
b) Timeframe for completing the repairs
c) Any other condition that the person conducting the examination believes is required for ensuring safe working conditions:
- Indicate the reason for the restricted working pressure: awaiting maintenance
- Calculate the safe operating pressure for a thin-walled pressure vessel or plant using the methods described in sub-rule 8.
- Lastly, mention any additional observations.
Form No. 11-A
The form comprises a report of examination of gasholders that are water-sealed. It is mandated under rule 61-A and at the top right corner needs you to add the registration number, license number, and NIC code number.




- Occupant (or property owner):
- Address:
- Name, description, and distinctive features: number or letter, and gas holder type
- Manufacturer's name and address:
- a) The number of lists
b) Maximum cubic meter capacity:
c) Gas holder pressure: when the gas container is full of gas
- Gas to be held in the holder's name
- Was it an internal or external examination?
- Gasholder parts examination: using electronic or other precise devices, or cutting sample discs, and the findings of the examination
- Information on the state of
a) Crown:
b) grips and cups, as well as side sheeting
c) a guiding device (carts, rollers, pines, guide rails, or ropes)
d) Tank and
e) Any other structures:
(bracing, framing, and columns)
- Information on the location of the lift at the time of the assessment.
- Whether the tank: and lists were found to be adequately level for safe working, and if not, what steps were taken to correct the problem.
- When and by whom was the examination performed?
- a) Are all fixtures and appliances in good working order and condition?
b) Any necessary repairs and the timeframe in which they should be completed.
c) Any other condition that the person conducting the examination considers necessary for ensuring safe working conditions.
- Add any other observations made.
Finally, the competent person in charge will sign the document certifying that the gasholder has been carefully examined and that the report presents all the data concerning the machine accurately.
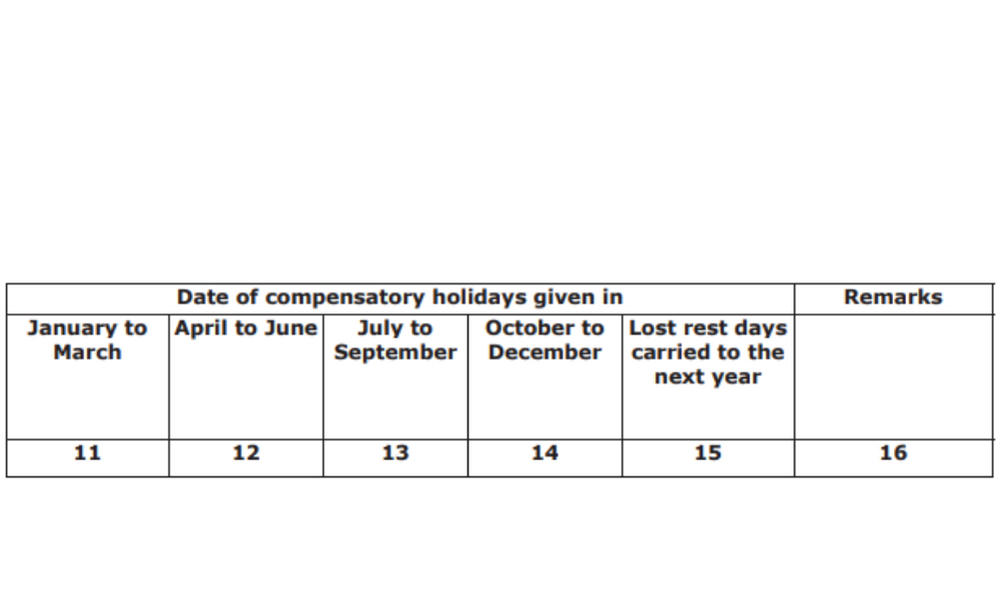
Form No. 12
Register of Compensatory Holidays is form 12 which is mandated under Rule 84. There are 16 columns in the tables of the form. The name and description of each column are as follows:
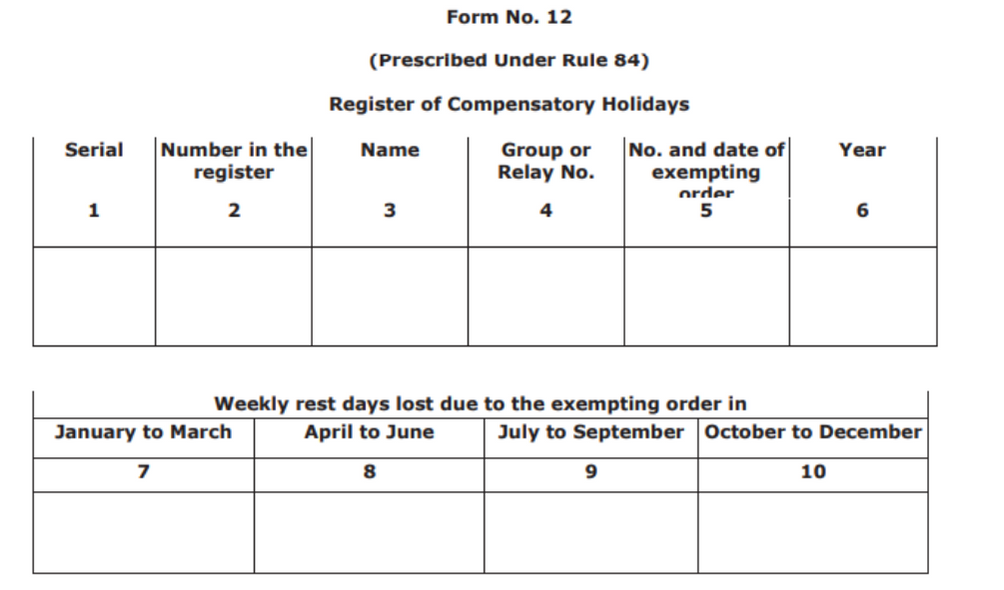
- Serial Number
- Number in the register
- Name
- Relay number or group number
- Number and date of the exempting order
- Year
- Weekly loss of rest days due to exempting order from January to March
- Weekly loss of rest days due to exempting order from April to June
- Weekly loss of rest days due to exempting order from July to September
- Weekly loss of rest days due to exempting order from October to December
- Date of compensatory holidays given from January to March
- Date of compensatory holidays given from April to June
- Date of compensatory holidays given from July to September
- Date of compensatory holidays given from October to December
- The number of lost rest days that will be carried to the next year
- Mention any relevant remarks
Form No. 13
This is the overtime register for the exempted workers and is prescribed under Rule 85. The information in this form is also presented in a table format and the various fields in the table are summarized as follows:
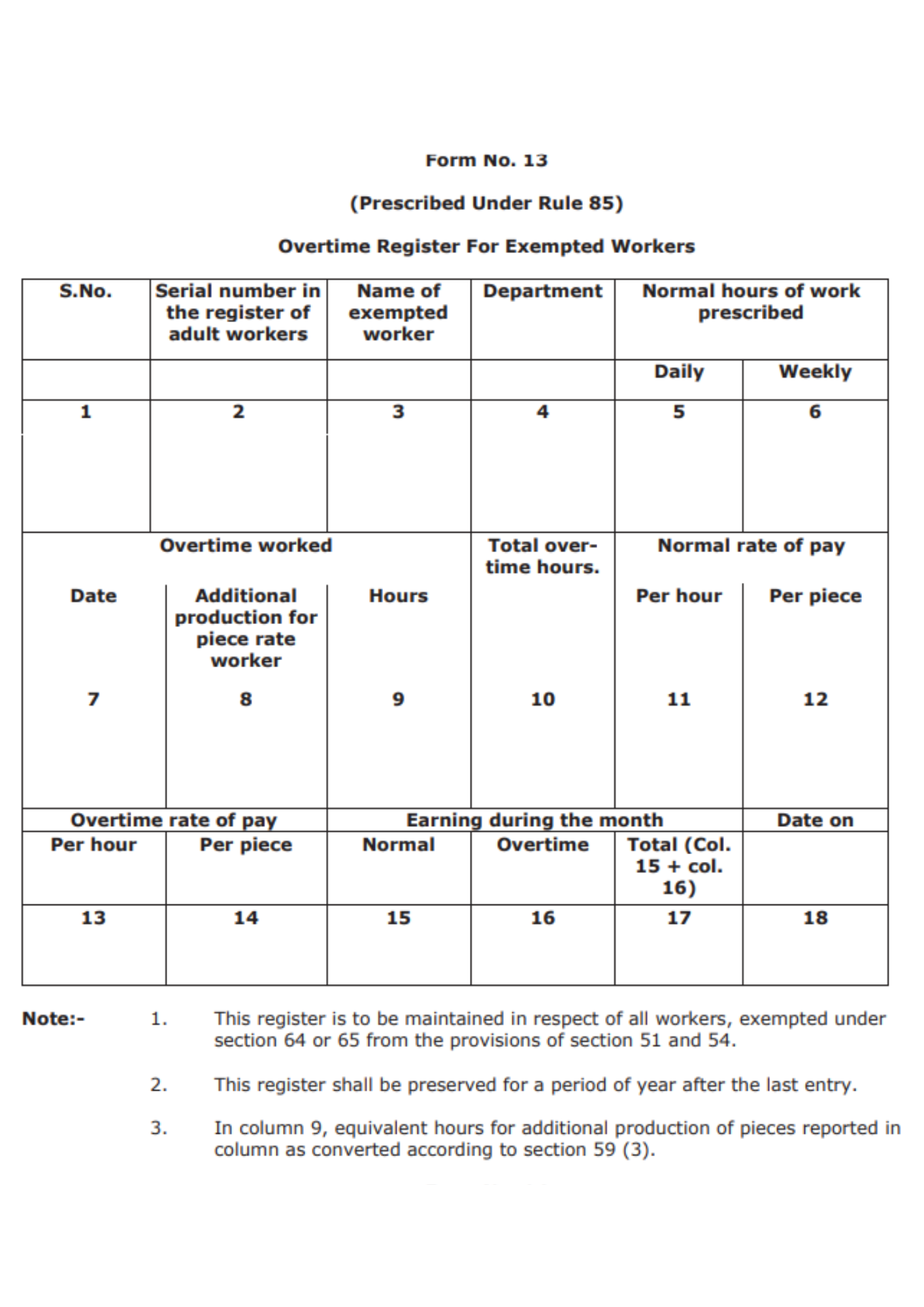
- Serial Number
- Serial number in the register of adult workers
- Name of the exempted worker
- Department of the worker
- Normal daily work hours of the worker
- Normal weekly work hours of the worker
- Date of the overtime work
- Additional production for piece-rate worker
- Hours of overtime work
- Mention the total overtime hours
- The normal rate of pay per hour
- The normal rate of pay per piece
- Overtime rate of pay per hour
- Overtime rate of pay per piece
- Normal earning during the month
- Overtime earning during the month
- Total of Column 15 and Column 16
- Date
- This register must be kept for all workers who are excluded from the provisions of sections 51 and 54 under sections 64 or 65.
- This register must be kept for a year after the last entry has been made.
- In column 9, convert equivalent hours for increased manufacturing of parts listed in column 3 to section 59 hours (3).
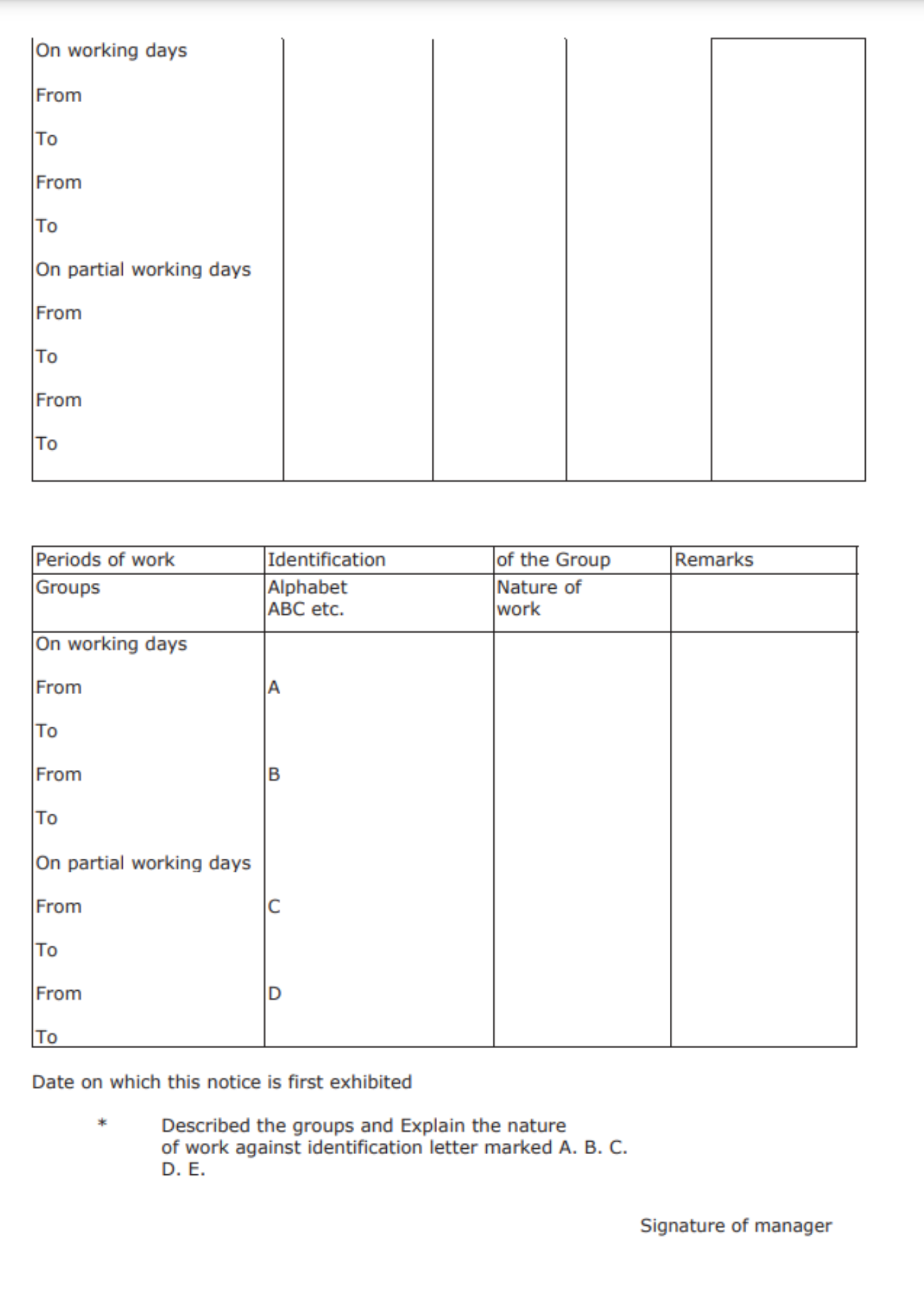
Form No. 14
This form is for Notice of Period Of Work For Adult Workers is prescribed under Rule 87. We find the following mentioned fields in the form:
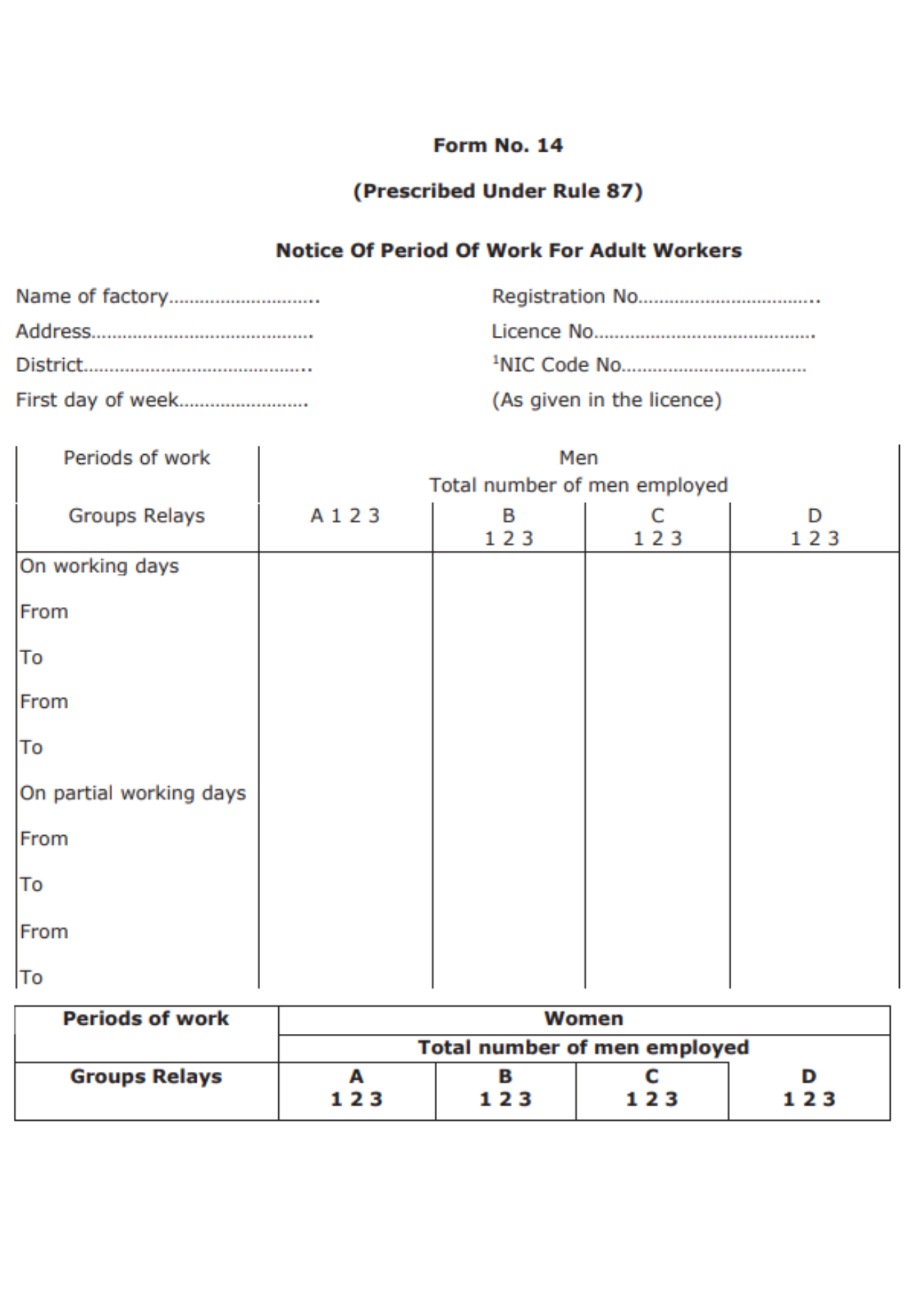
- Name of factory
- Registration No
- Address
- License Number
- District
- NIC Code No
- First day of the week (As mentioned in the license)
Once you have filled in this information, you will find a table that comprises the fields such as Periods of work for Men and Periods of work for Women. The form will be filled out by the manager of the factory and also signed by them.
Form No. 15
Prescribed under Rule 88, the form is about registering adult workers. The table in the form comprises the following fields:
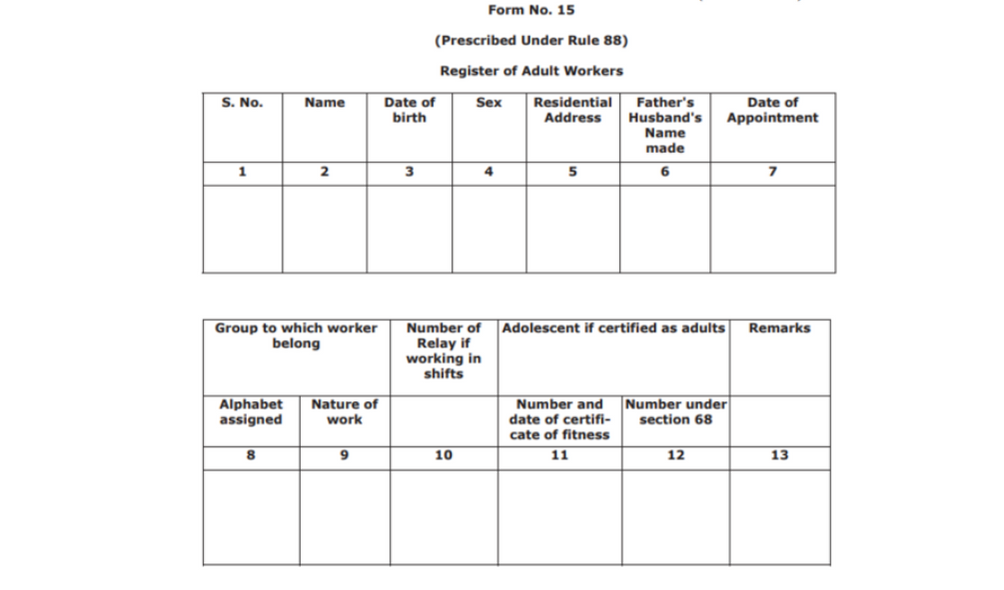
- Serial number
- Name
- Date of birth
- Sex
- Residential address
- Father’s or Husband’s name
- Date of appointment
- Group of the worker
- Number of relays if the workers are working in shifts
- Enter information is the adolescents are certified as adults
- Add any relevant remarks of applicable
Form No. 16
Notice of period of work for the child workers is what this form is all about. It is prescribed under Rule 92. The top of the form requires the manager to fill out the following information:
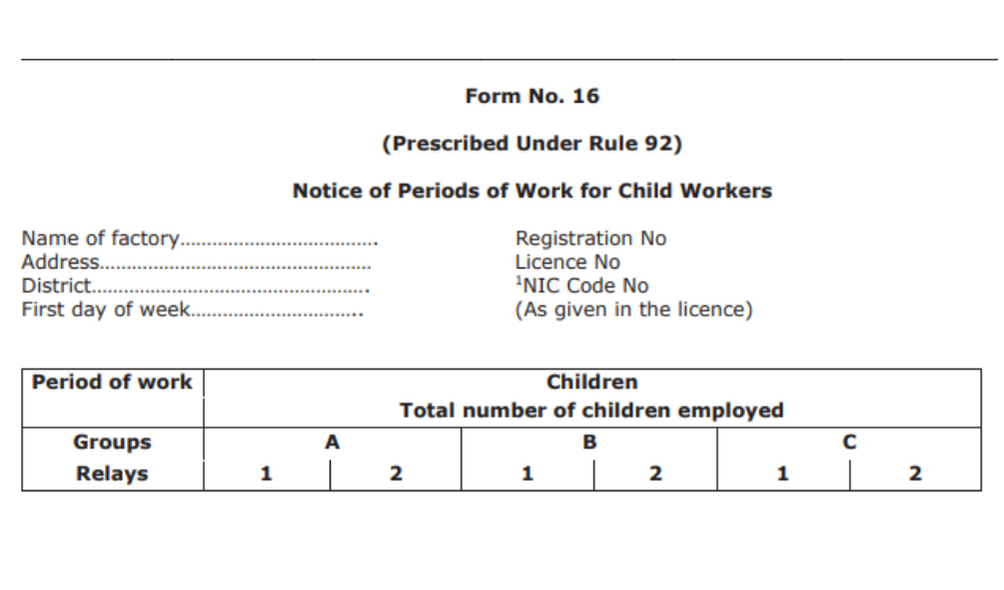
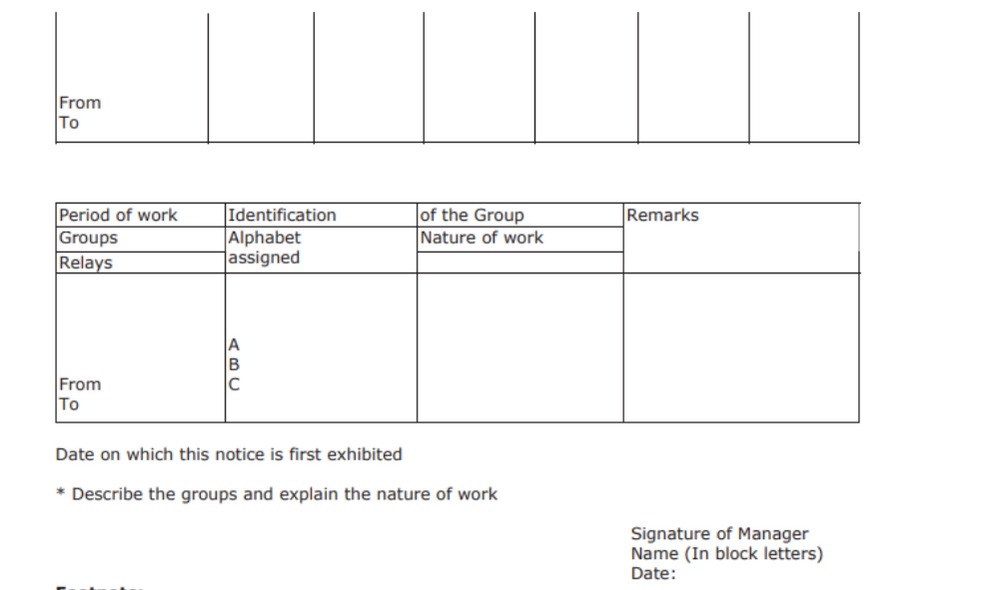
- Name of factory
- Registration No
- Address
- License No
- District
- NIC Code No First day of the week (As provided in the license)
The form consists of 2 tables with the following fields:
- The total number of children employed with the factory
- Mention the relay in the three columns A, B, and C
The manager must describe the groups and also explain the nature of their work. Lastly, the manager is required to sign the document along with the date.
Form No. 17
This is the form of the register of child workers and comes under Rule 93. Here are the fields that need to be filled into the form:
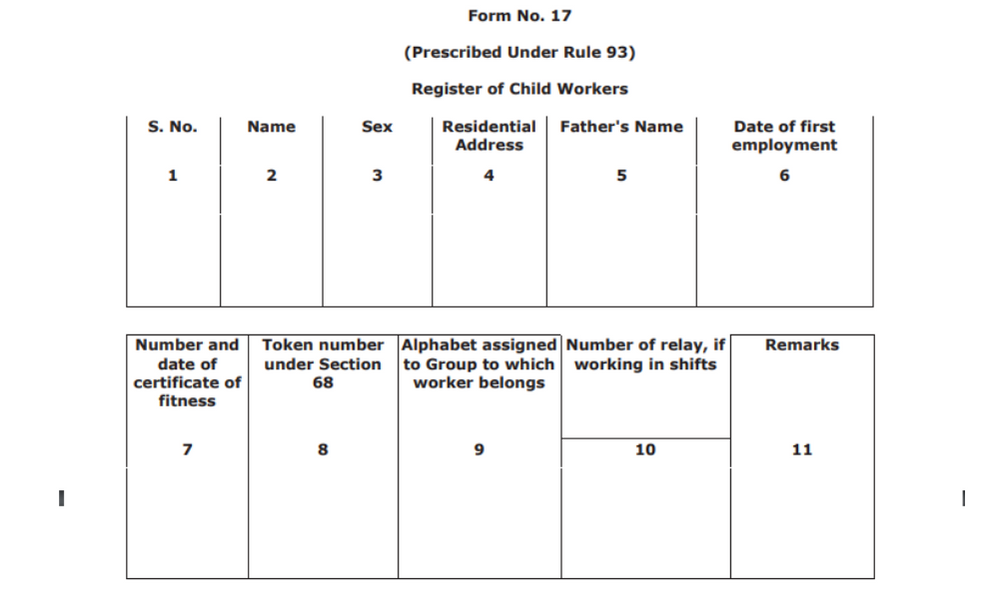
- Serial number
- Name
- Sex
- Residential address
- Father’s name
- Date of first employment
- Number and the date on which the certificate of fitness was provided
- Mention the token number placed under section 68
- Mention the number of relays if the workers are working in shifts
- Add any other relevant remarks
Form No. 18
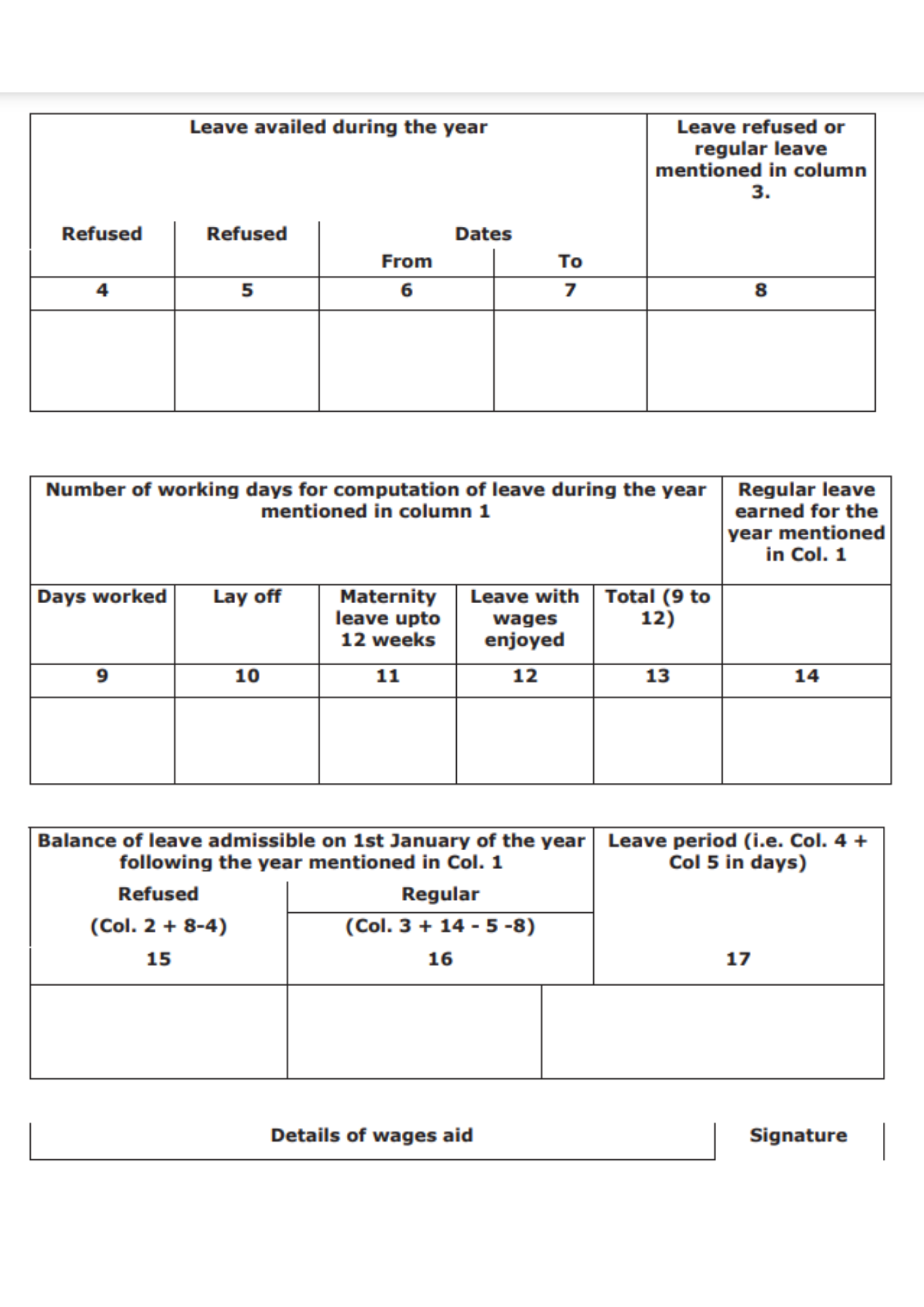
This is the register of leave with wages and is prescribed under the Rule 94. Let’s check the fields you will encounter here:

- Name
- Gender
- Name of Father / Husband
- Worker's serial number in the Register
- Department
- Designation
- Start date of employment
- Date of discharge/dismissal: resignation, retirement, or death while in service
- In such cases, the date of payment in lieu of: leave with salary due
- Whether leave was denied in conformity with the arrangement under section 79 (8)
After providing this data, the table consists of the fields as mentioned here:
- Calendar year of service
- Refused Leave due as on 1st January of the year in column 1
- Regular Leave due as on 1st January of the year in column 1
- Refused Leave availed during the year
- Refused Leave availed during the year (both columns 4 and 5 will have this data)
- Mentioned starting date
- Mention the end date
- Enter the leave refused or regular leave mentioned in column 3.
- Days worked
- Lay off
- Mention the maternity leaves
- Leaves enjoyed with wages
- Total of columns 9 to 12.
- Regular leave earned for the year mentioned in column 1
- Refused Balance of leave admissible on 1st January of the year following the year mentioned in Column 1
- Regular Balance of leave admissible on 1st January of the year following the year mentioned in Column 1
- Mention the total of columns 4 and 5 in days
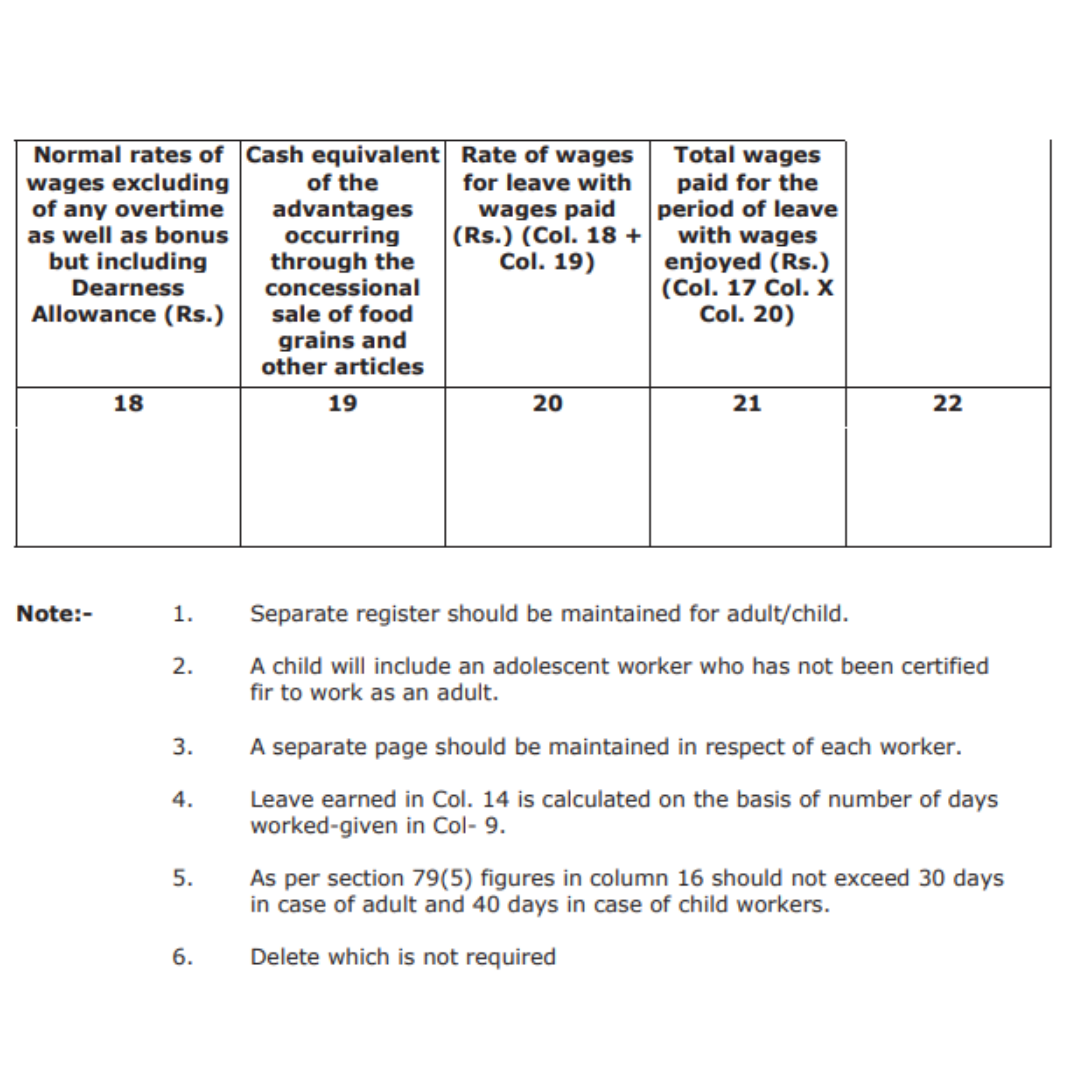
- Mention the normal rates of wages excluding any overtime and bonus but including Dearness Allowance
- The monetary equivalent of the benefits gained from the concessional sale of food grains and other items
- The wage rate for workers on paid leave
- Total pay paid during the leave time plus wages received
The form also includes the following notes:
- Separate registration for adults and children should be kept.
- An adolescent worker who has not been certified to work as an adult will be considered a child.
- For each employee, a separate page should be kept.
- The number of days worked in Col. 9 is used to compute the amount of leave earned in Col. 14.
- Figures in column 16 should not exceed 30 days for adult workers and 40 days for minor workers, according to section 79(5).
- Remove anything that isn't necessary.
Form No. 19
This form shall be the same as the "Register of Leave with Wages" which is Form No. 18. However, it must be completed separately for each worker on a thick bound sheet. The form is also known as the Leave Book, mandated under Rule 95.
Form No. 20
This is the Health Register prescribed under Rule 15. As this is a health register, the information will be provided by the certifying surgeon.
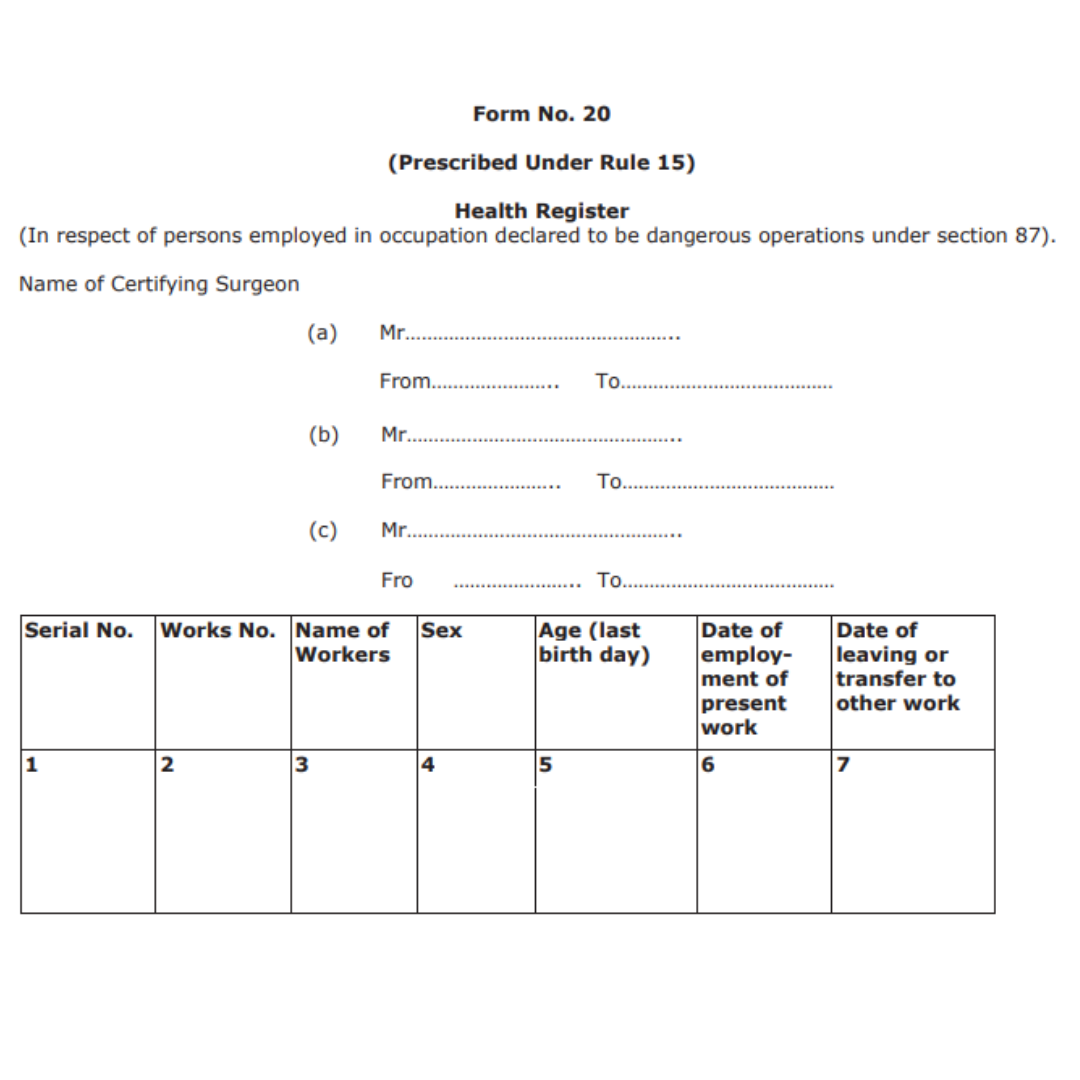
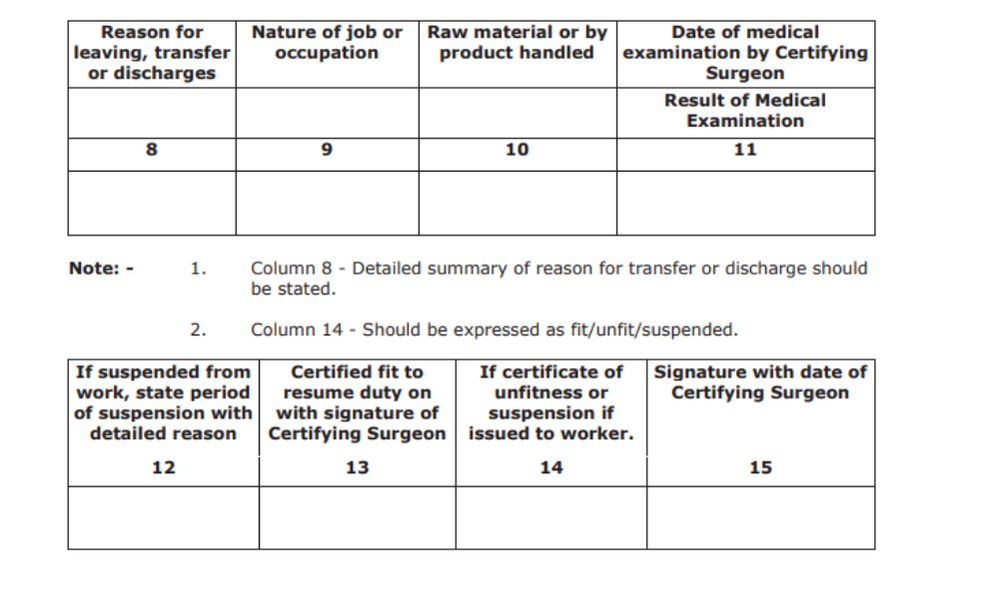
- Name of the certifying surgeon
- Serial number
- Work
- Number of the worker
- Sex
- Age
- Date of employment of the current format of work
- Date of transfer or leaving for another work
- Reason for leaving
- Kind of job or occupation
- Name of the raw material or product
- Date and reason of medical examination
- If suspended from work, explain why and for how long.
- Signature of the certifying surgeon with their certification of fitness
- Information about suspension or unfitness
- Signature of certifying surgeon with date
Form No. 21
Mandated under Rule 103, Report of Accident Including, Dangerous Occurrence Resulting In Death Or Bodily Injury is the form 21.
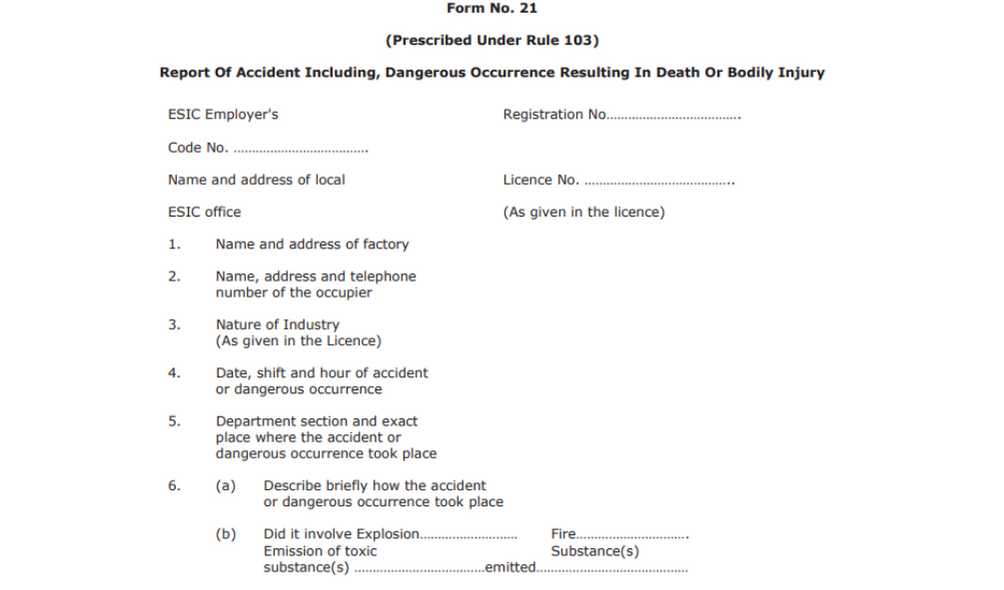
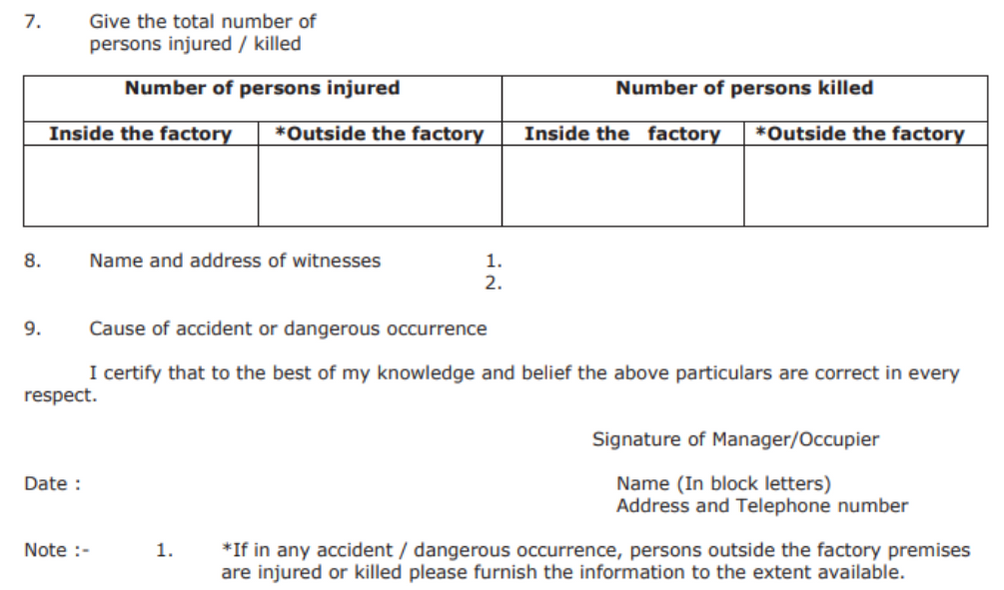

- ESIC Employer's Registration No
- Code No.
- Name and address of local ESIC office
- Licence No.
- Factory's name and address
- Occupier's Name, address, and telephone number
- Industry's nature (As given in the Licence)
- Date, shift, and hour of the accident or dangerous occurrence
- Department section and the exact place where the accident or dangerous occurrence took place
- (a) Describe briefly how the accident took place
- Explosion
- Fire
- Emission of toxic Substance
- Inform about the number of individuals injured or killed
- Name and addresses of witnesses
- Cause of accident
- Signature of the manager certifying the accuracy of the details in the form.
The following details will be provided by the inspector of the factories:
- Date of report receipt
- District
- a) Number assigned to injury-causing accident
b) The number of dangerous incident
- The investigation's start date
- Accident classification
- a) Cause
b) Industry
c) dangerous operation
d) dangerous process
e) occupation
- Any relevant remarks
Signature of the inspector with a date at the left bottom corner of the form.
Annexure Particulars of Persons Injured, Killed
- Provide details of injured/killed person
a) Name
b) Age
c) Sex
d) Serial Number in the register of adult workers
e) Address
f) Precise occupation
g) Nature of job
- Cause of injury
- Details of the injury
a) Fatal
b) Non-fatal
c) Inform if the injured individual had been disabled for a span of over 48 hours
d) Injured part of the body
- a) Mention what exactly the injured person was doing at the time of the accident
b) Mention if the work placed under the hazardous category
- a) mention the hour when the injured person commenced the work
b) mention if the wages in part or full were payable to the worker on the day of dangerous incident
- Mention the details in case the incident occurred while traveling via the employer’s vehicle
a) was the injured person traveling as a passenger to his place
b)did the injured person have the permission of the employer
c) was the transport being carried out by the employer or their behalf
d) Inform whether or not the vehicle was being operated in the ordinary course of a public transport service
- Clarify if the accident was a result of an emergency
a) nature
b) was the injured person employed for the purpose of the employer’s business
- a) Mention the details about the hospital, doctors, and clinics from where the injured person received their treatment
b) Inform about the dispensary selected by the injured person.
Form No. 21-A
This is about reporting a dangerous occurrence that did not result in physical injury and is mandated under Rule 103.



- Name and address of factory
- Occupier’s name, address, and telephone number
- Manager’s name
- Nature of Industry
- Department, Section, and the exact place where the dangerous occurrence took place
- Date, shift, and hour of dangerous occurrence.
a) Type of dangerous occurrence (See overleaf)
b) Did it Involve Explosion
- Mention the exact details of the incident.
The manager signs the document certifying that all the details provided are accurate. The next part of the form is to be completed by the inspector of the factories.
- Date of receipt of the report
- District
- (a) Number allotted to the dangerous occurrence that does not involve injuries and/or death
b) Number allotted to "Major accident" that does not involve reportable injuries and/or death
- Date of investigation
- Cause
- Provide the NIC Code as given in the license
- Give the result of the investigation.
Schedule
The following types of harmful events, whether or not they result in personal injury or disability:
- A plant is used to hold or deliver steam under pressure greater than atmospheric pressure bursts.
- A crane, derrick, winch, hoist, or other devices that are used to raise or lower people or goods, or any part thereof, collapses or fails, or a crane overturns.
- Explosion, bursting leakage, or escape of any molten metal, hot alcohol, or gas inflicting physical injury or damage to any room or place where people work, or fire in rooms of cotton pressing factories when a cotton opener is used.
- Explosion of a vessel used for the containment of any gas or gases or any liquid or solid at a pressure greater than atmospheric pressure as a result of gas compression.
- Any floor, gallery, roof, bridge, tunnel, wall, building, or other structure collapses or subsides.
NIC stands for National Industrial Classification.
Form No. 22
This form is about notifying of poisoning or disease and is prescribed under Rule 104. It requires the following details:



- Factory’s name and address
- Occupier's name, address, and telephone number
- Nature of Industry
- Particulars of affected worker:-
a) Name
b) Age
c) Sex
d) Serial number as per Register of Adult/Child worker
e) Address
f) Precise occupation
g) Nature of job
- Nature of poisoning/disease. Provide the serial number and name.
- a) Name the harmful agent that caused poisoning
b) Provide the tentative date of start and end of exposure of the workers to the harmful process
- Mention if the case has been taken to a certified surgeon or doctor.
All the details must be provided and duly signed by the manager of the factory. This notice should be forwarded to the following authorities as soon as possible:
- Chief Inspector of Factories
- Certifying Surgeon
- Medical Inspector
- ESIC's Administrative Medical Officer
Extract from the 1948 Factories Act (Section 89):
When a manufacturing worker gets one of the diseases listed in the Schedule, the factory management must notify the appropriate authorities in the manner and within the timeframe provided.
Schedule: List of Notifiable Diseases
- Poisoning caused by any kind of lead or its derivatives is known as lead poisoning.
- Tetra-ethyl lead poisoning
- Phosphorous toxicity and its complications.
- Mercury toxicity and its complications
- Manganese toxicity and its complications.
- Arsenic poisoning and its complications.
- Nitrous oxide poisoning.
- Poisoning with carbon disulfide.
- Benzene toxicity, including poisoning from any homolog, their nitro or amide derivatives, or their sequelae.
- Chrome ulceration and its complications
- Anthrax.
- Silicosis.
- Mention poisoning that is caused by halogens or halogen derivatives of aliphatic hydrocarbons.
- Due to - pathological manifestation
a) radium or other radioactive materials:
b) x-rays
- Skin cancer
- Anemia caused by toxins
- Toxic jaundice as a result of poisoning.
- Mineral oils and substances with a mineral oil base cause oil acne or dermatitis.
- Byssinosis.
- Asbestosis.
- Contact dermatitis is produced by direct contact with chemicals and paints in the workplace. Primary irritants and allergy sensitizers are both on the rise.
- Noise-induced hearing loss is number
- Beryllium poisoning
- Carbon monoxide (CO).
- Pneumoconiosis in coal mines.
- Phosgene poisoning
- Occupational cancer
- Poisoning with isocyanates.
- Toxic nephritis.
Form No. 23
This is the abstract of the Factories Act of 1948 along with Gujarat Factories Rules, 1963. The form is mandated under Rule 106. Let’s look through the interpretation of diverse terms used in the document.
Factory: It is a premise described as follows:
i) where more than ten workers are working, or were working, on any day in the previous twelve months in any part of which a manufacturing process is being carried out with the aid of power OR
ii) where more than twenty workers are working, or were working, on any day in the previous twelve months in any part of which a manufacturing process is being carried out without the help of power, or is ordinarily carried out.
Note: A mine subject to operation 1[of the Mines Act, 1952 (XXX of 1952)] or a railway operating shed are not included.
Worker refers to someone who is employed in any manufacturing process, whether for pay or not, who cleans any component of the machinery or premises utilized in a manufacturing process, or who does any other form of labor related to the manufacturing process or the subject of the manufacturing process.
Manufacturing: Any process for making, modifying, mending, adorning, packing, oiling, rinsing, cleaning, demolishing, or otherwise treating any article for its use, sale, transport, or disposal, or other similar procedures.
- Hours of Work as defined in Sections 51 and 54 (Adults): No adult worker shall be compelled or permitted to work in a factory for over 48 hours per week or 9 hours per day.
(The minimal limit may be exceeded in order to allow shift changes, with the Chief Inspector's prior consent.)
- Relaxation of Work Hours for Adults as defined in Section 64:
Adults' normal working hours may be shortened in some extraordinary instances, such as workers performing emergency repairs: in preparatory or complementary work that must be done outside the factory's normal working hours, in work that is so intermittent that the time spent not working while on duty usually exceeds the time spent resting; in work that must be done continuously 2 [x x x] in making or supplying articles of primary necessity that must be made or supplied every day; in work that must be done every day for technical reasons.
Except in the case of emergency repairs, the relaxation shall not exceed the following limits:
- I the total number of hours worked in any one day shall not exceed;
- the total overtime work shall not be more than 50 in any one quarter;
- the total number of hours of rest intervals shall not be more than 12 in any one day.
The restrictions of clauses 1 and 2 of subsection 4, section 64 will not apply where a shift worker has not reported to work and another worker had to work for the whole day or a significant part of the day as indicated by the government.
Ordinary limits on working hours for adults may be reduced for any or all adult workers in any factory for a time or periods not exceeding 3 months in any year to allow the firm to deal with an unusually high volume of work.
Payment for Extra-Section 59
Workers working for over 9 hours in a day or more than 48 hours in a week are entitled to double his or her regular rate of pay for overtime work.
Exemption of Supervisory Staff - Section 64
Chapter VI of the Act-Working hours of adults is not applicable to persons holding a position of supervision or management or working in a confidential position in a factory in any work that must be carried on continuously for technical reasons, subject to the conditions set forth in the Schedule attached to the Manual.
Weekly Holiday for Adults -Section 25
Adult workers shall not be required or allowed to work in a factory on the first day of the week unless they have; or will have; a full day off on one of the three days immediately before or after the said day; the factory manager has delivered a notice to the inspector's office, before the said day or the substituted day, whichever is earlier, of his intention to require the worker to work on the said day.
Intervals for Rest for Adults - Sections 55 and 56
The periods of work of adult workers in a factory each day shall be fixed in such a way that no period shall exceed 5 hours before he has had an interval for rest of at least half an hour, and that his intervals for rest shall not spread over more than 10 1/2 hours in any day or, with the Chief Inspector's written permission, 12 hours 4 minutes. This is subject to State Government regulation and the Chief Inspector may exempt any factory by written order for the reasons mentioned therein, provided that the total number of hours worked by a worker without any gap is not more than six.
Sections 61, 71, and 99 prohibit double employment
No child or adult worker, with the exception of specified conditions, should be forced or allowed to work in any factory on any day when he has already worked in another industry.
If a child works in a factory on a day when he has already worked in another factory, the child's parent or guardian, or a custodian receives any direct benefit from his wages and is subject to a fine of up to Rs. 50, unless it would seem to the court that the child did so without such person's consent.
Prohibition of employment of children younger than 14 based on Section 67
No kid under the age of fourteen shall be required or permitted to work in any factory.
Section 71 defines the Hours of Work for children
No youngster shall be engaged or authorized to labor in a factory for more than 4 1/2 hours per day or night (between 10 p.m. and 6 a.m.). All children employed in a factory shall be confined to two shifts, each of which shall not overlap or span more than 5 hours, and each child shall be assigned to just one of the relays.
The regulation relating to weekly holidays applies to child laborers as well, and no exceptions to this rule can be made in the case of any child.
Women's Employment Prohibition based on Section 66
Women must not be employed in any factory for over 9 hours on any day or between the hours of 7 p.m. and 6 a.m. under any circumstances.
Leave with Wages based on Sections 79, 80, and 83 and the rules
Every worker who has worked in a factory for 240 days or more in a year is entitled to paid leave for a number of days calculated as follows:
i) in case of an adult, one day for every twenty days of labor completed during the preceding calendar year.
(ii) one day for every fifteen days of employment accomplished by him during the previous calendar year if he is a child;
Cleanliness as given in Section 11
In a factory, all walls, sides, and tops of tunnels and staircases must be kept white-washed or color washed. White-washing or color-washing must be done at least once every fourteen months. Every workroom's flooring must be cleaned at least once a week, either by washing with disinfectant or using another method.
Disposal of Wastes and Effluents as mentioned in Section 12
Every plant must make effective measures for the disposal of wastes and effluents generated by the manufacturing process.
Ventilation and Temperature-Section 13
Every plant shall make effective and appropriate provisions for providing and maintaining enough ventilation by the circulation of fresh air in every workroom, as well as a temperature that will provide workers with fair conditions of comfort and prevent injury to their health.
Overcrowding as mentioned in Section 16
Only if an exemption has been approved, there must be at least 350 cubic feet of space in every workroom of a factory in operation on April 1, 1949, and at least 500 cubic feet of space in every factory built after that date for every worker. While doing so, any space more than 14 feet above the level of the room's floor will not be considered.
Lightening as described in Section 17
Every factory where workers work or pass through must have sufficient and appropriate illumination, whether natural or artificial or both.
Drinking water as described in Section 18
Effective measures must be made in every factory to provide and maintain a sufficient supply of clean drinking water at acceptable sites, conveniently located for all workers engaged within. In any factory with more than 250 regular employees, the drinking water must be chilled using ice or other efficient techniques during hot weather. Cooled drinking water will be available in every canteen, lunchroom, and restroom, as well as at strategically placed locations throughout the workplace.
Latrines and Urinals under Section 19
Every factory must offer sufficient latrine and urinal facilities of the prescribed type that are conveniently located and available to workers at all times while they are on the job. These should be separate for males and females. Every latrine must be covered and partitioned to ensure privacy, as well as have a good door and fastenings. A sweeper will be hired, whose major responsibility will be to keep the latrines, urinals, and washing stations clean.
Spittoons as mentioned in Section 20
In every factory, there must be a sufficient number of spittoons of the type prescribed in convenient locations, and they must be kept clean and sanitary. Within the confines of a factory, no one may spit except in the spittoons supplied for that purpose. Spitting in violation of this law is penalized with a fine of five rupees.
Safety
Fencing of Machinery as mentioned under Section 21
Every manufacturing unit comprises dangerous machine parts, such as a prime mover and a flywheel attached to a primary mover, and so on. These shall be surrounded by significant safeguards while the sections of machinery are in action.
Work on Machinery in Motion under Section 22
Women or young people should not be asked to clean, lubricate, or tweak any part of the prime mover while it is moving. The purpose of this is to prevent them from any injury.
Employing young people on Dangerous Machinery
Under section 23, young people will not be allowed to work on any dangerous machinery. It will only be handled by a person who has received professional training and has enough knowledge about the same.
The casing of New Machinery under Section 26
All electrically-driven machines installed after 1st April 1949 that have belts, screws on a revolving shaft, wheel, and spindle, must be guarded to prevent any mishaps. All spur and any other toothed friction gearing that does not require regular adjustment while in motion must be entirely enclosed, unless it is placed in such a way that it is as safe.
Forbidding Women and Children near Cotton Openers as prescribed under Section 27
Women or children should not be employed in areas where the cotton opener is deployed.
24A. Lifting Machines, Ropes, Chains, and Lifting Tackles based on Section 29
Every movable or fixed part of a lifting machine and all the chains must be of standard quality and good strength. They must be thoroughly maintained and adequately examined by a competent person at least once a year.
Excess Weight as prescribed under Section 34
Women or young children must not be allowed to carry weights beyond a certain limit. The chart below presents the limits.
Protection of Eyes in Section 35
The workers who are required to work involving risks to the eyes must be provided with protective eye gear.
Precautions to take in case of fire, based on Section 38
All factories must have provisions of protection in case of fire for the people employed in the vicinity. The doors and the windows must facilitate easy escape. The exits on these doors and windows must be clearly marked with signs to guide the employees. If there are warnings or alarms, they must be clearly audible to the workers.
Welfare
Washing Facilities as described in Section 42
All factories must provide adequate washing facilities with soap and brushes to keep the areas clean. Female workers must be provided a separate and compartmentalized area to avoid visibility to anyone.
Facilities for Drying Clothes based on Section 43 and rules
When the workers, working in dangerous operations, are not wearing a set of clothes, they should be provided with enough space to dry their extra pair of clothes.
Facilities for Sitting based on Section 44
All the factories that require the workers to stand and work for long hours, must provide facilities for sitting and resting in between intervals.
First Aid and Ambulance Room based on Section 45
All factories must provide readily accessible first aid boxes managed with the prescribed contents. The factories must also train a reliable person for the use of the first aid kit who shall always be available during work hours.
Every factory comprising 500 workers or more must have an ambulance room of the prescribed size along with all the mandated equipment. It should be overseen by a medical practitioner or another qualified person.
Canteens, as defined in Section 46 and rules
The occupier of the factory must provide a canteen in a factory that usually employs 250 or more people. Food, drink, and other products offered in the canteen shall be sold on a non-profit basis, with pricing set by a Canteen Managing Committee appointed by the Manager and made up of an equal number of people nominated by the occupier and chosen by the workers.
Shelters, Lunch Rooms, and Rest Rooms as described in Section 47
Every factory with over 150 workers must provide and maintain adequate restrooms, as well as a proper lunchroom with drinking water where workers can consume meals.
Creches described in Section 48 and Rules
An appropriate room for the use of children under the age of six years must be maintained in any factory where more than 50 women workers are normally employed. The creche must be suitably equipped and provided, including one suitable cot or cradle with all essential bedding for each child. It must also include at least one chair or equivalent sitting for the mother to use while feeding or visiting her child, and a sufficient stock of appropriate toys.
Welfare Officers described in Section 49
Welfare officers must be employed in a factory with 500 or more workers.
Special Provisions
Dangerous Operations explained in Section 87 and Rules
Employing women, children, and adolescents is forbidden in areas and operations that have been declared dangerous or hazardous. These are described as follows:
- the production of aerated water and operations related to it:
- electrolytic plating or oxidation of metal articles using an electrolyte containing chromic acid or other chromium compounds;
- manufacture and restoration of electric accumulators;
- glass manufacture;
- metal grinding or glazing;
- manufacture and treatment of lead and certain lead compounds;
- production of gas from dangerous petroleum as defined in clause
Section 2 of the Petroleum Act of 1934
- Liming or tanning of raw hides and skins, and operations incidental thereto;
- cleaning or smoothing of goods by a jet of sand, metal shot, grit, or other abrasive driven by a blast of compressed air or steam;
- manufacture or recovery of sodium, potassium, or ammonium bichromate;
- manipulation of nitro or amino compounds;
- manipulation of acids and alkalis;
- manufacture of bangles and other articles from cinematograph films and acetone, tetrachloroethene, and other toxic and inflammable solvents:
- operations involving the production, usage, or evolution of carbon disulfide and hydrogen sulfide, as well as
- the production and manipulation of harmful pesticides.
- Notice of Accidents as explained in Section 88 and Rules
There could be fatal incidents in a factory that cause injury or death of a worker and keep them away from work for 48 hours or more. These incidents can be of the following types:
- Apart from plants covered by the Indian Boilers Act, the bursting of a vessel used for containing steam under pressure greater than atmospheric pressure;
- A crane, derrick, hoist, winch, or other appliance used in lifting or lowering persons or commodities, or any part thereof, collapsing or failing, or a crane overturning;
- An explosion or fire that causes damage to any place where people are employed, or a fire in a cotton pressing factory room where a cotton opener is being used;
- The explosion of a container utilized for the storage of any gases, liquid, or solid at a pressure greater than atmospheric pressure as a result of gas compression;
- If any floor gallery, tunnel, wall, or building forming part of a factory or within the compound of a factory collapses, the factory manager must immediately notify the Chief Inspector.
A notice must also be issued to the District Magistrate or the Subdivisional Officer, as well as the Officer-in-Charge of the nearest Police Station if the accident is deadly.
Notice of Certain Diseases based on Section 89 and Rules
In the case of occurrence of any diseases within the factory, the manager must notify the Chief Inspector about the same. If it is serious in nature, then the manager must also notify the District Magistrate or Sub-divisional officer or inform the nearest police station.
No charge for Facilities and Conveniences as explained in Section 114
Workers will not be charged for any facilities provided to them in the factory by the occupier.
Power of Inspectors as described in Sections 9 and 82
Inspectors have the authority to inspect factories at any time and may demand to see the registers, certificates, and other documents as required by the Act and Rules.
Any Inspector may bring legal action on behalf of a worker to recover any sum due from an employer under the regulations relating to leave with wages that have not been paid.
Obligations of Workers on the basis of Sections 97 and 111
No factory worker shall attempt the following:
- Deliberately tamper with or abuse any appliance provided in the factory for the aim of obtaining the health, safety, or welfare of the workers therein;
- deliberately endanger themselves or others; or
- deliberately ignore using appliance provided for the purpose of safeguarding the health, safety, or welfare of the workers there
Any factory worker violates any of these provisions will be subject to imprisonment for a period of up to three months, a fine of up to Rs. 100, or both. Any factory worker who violates any provision of the Act will be subject to a fine of up to Rs. 20.
Certificates of Fitness based on Sections 68, 70, and 98
Any child who has completed the 14th year or is an adolescent will not be allowed to work in the factory without a fitness certificate. The fee for the certificate will be paid by the occupier of the factory.
Registers, Notices, and Returns as described in Sections 61, 63, 72, 74, 79, 80, and 110
Manager of every factory shall maintain a register of adult workers in the prescribed form No. 15 and a register of child workers in the prescribed Form No. 17. Notice of periods of work for adults and a notice of periods of work for children in the prescribed forms No. 14 and 16 shall be correctly maintained and displayed in every factory.
Form No. 24
Master Form In Respect Of The Factories Act, 1948, Payment Of Wages Act, 1936, Maternity Benefit Act, 1961, Workmen's Compensation Act, 1923 And As Applicable To Registered Factories Covered Under The Factories Act, 1948
Part A as Prescribed Under clause (1) of Rule 107
- a) Factory’s registration number
b) License number
c) Section of the Act under which the factory is covered (select the appropriate option):
Section 2 (m)(i)
Section 2 (m)(ii)
Section 85-Chemical
Section 85-Non Chemical
- Factory’s name
- Occupier’s name
- Manager’s name
- District
- Address of the Factory with Pincode
- Industry
a) nature of the industry, NIC code number
b) Sector of the industry: Select the appropriate one:
Joint sector
Public sector
Private sector
Co-operative sector
c) In the case of MAH or Major Accident Hazard, submit the following information
- a) Number of days worked in the factory in a year
b) Number of working weeks in the year
Total attendance in a year
a) Adults: Men and Women
b) Adolescents: Male and Female
c) Children: Boys and Girls
Average workers employed daily
a) Adults: Men and Women
b) Adolescents: Male and Female
c) Children: Boys and Girls
The total number of hours worked including overtime but not rest Interval
a) Adults: Men and Women
b) Young People: Male and Female
The average number of hours worked per week
a) Adults: Men and Women
b) Young People: Male and Female
In the case where the factories carry out dangerous processes described in Section 87, furnish the following information:
In the case where the factories carry out dangerous processes described in Section 2(cb), furnish the following information
Leave with Wages
Total workers employed during the year (see note J)
a) Adults: Men and Women
b) Young People: Male and Female
The number of workers who were eligible for annual leave with wages during the year
a) Adults: Men and Women
b) Young People: Male and Female
The number of workers who were granted leave (see note K)
a) Adults: Men and Women
b) Young People: Male and Female
a) Total number of people dismissed or discharged during the year
b) The number of employees for whom compensation in lieu of leave was paid
Safety Officers (See Note L)
a) Is the factory advised that Safety Officers will be appointed under section 40-B(1)(i)?
Yes or No
b) Is the factory under section 40-B(1)(ii) (for factories except those in (a) above) notified for the appointment of Safety officers?
Yes or No
c) Number of appointed safety officers
Health and Safety Policy
The information must be provided only by the following:
a) Factories that come under section 2(cb) of section 87 of Act
b) Factories except in ‘a)’ but registered under:
i) Section 2(M)(1) 50 or more workers
ii) Section 2(M)(ii), 100 or more workers
Has the factory formed a Health and Safety Policy? If yes, include a copy of the same.
Safety Committee
(Information to be provided only by (1) hazardous process and (ii) other factories employing more than 250 workers)
- Is a safety committee appointed?
- Emergency Plan (Information to be furnished by factories covered under 2(cb). (See explanatory note 'M')
- Medical Facilities: Information must be provided only by Factories employing factories with less than 200 or lesser employees that come under section 2(cb) or 87.
- Competent supervisors
- industrial hygienists,
- Canteens, creches and shelter rooms are some of the other information which must be provided by the factories.
Part B under the Payment of Wages Act of 1936
Information like the days worked, total wages paid, the gross amount paid, and deductions must be entered under this section.
Part C under the Maternity Benefit Act of 1961 and E.S.I.C. Act, 1948
- Information like the name, qualifications, and type of employment of the Medical officer.
- Enter any information about any nearby hospital, its number of beds, lady doctors, midwives, and creche.
- The number of Welfare officers appointed
- Accidents
- dangerous occurrences
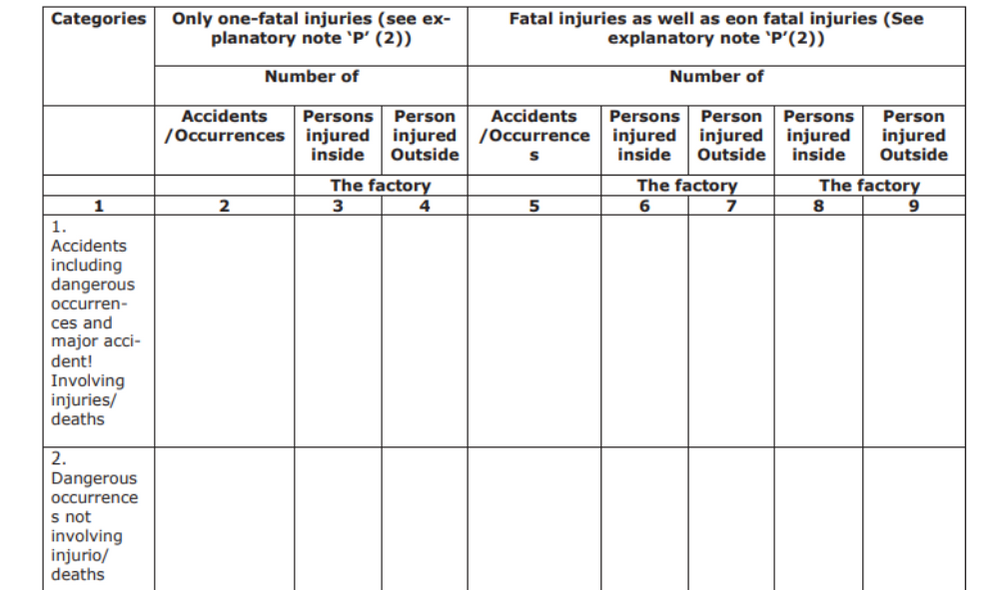
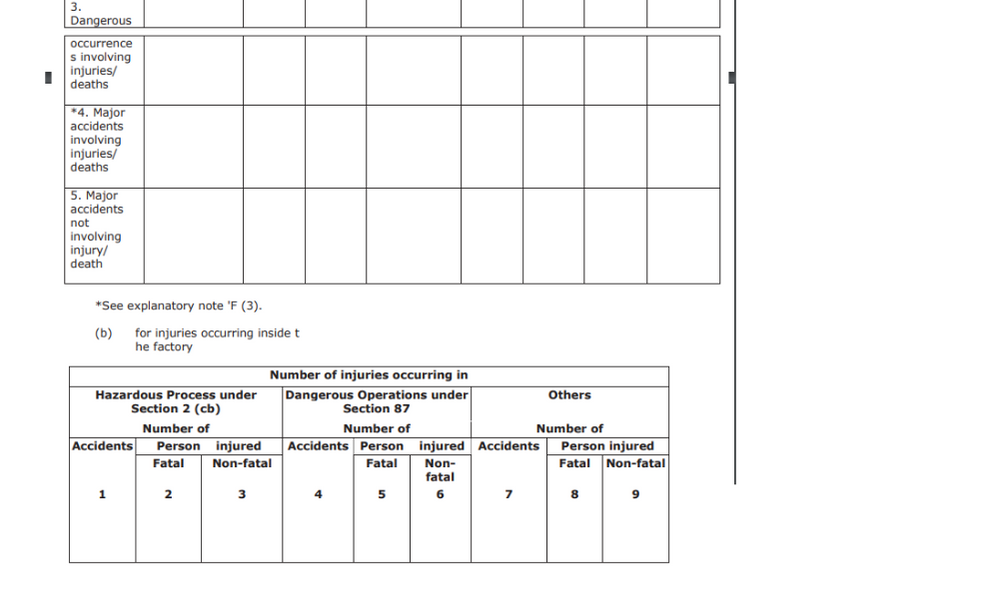
Part B (Under the Payment of Wages Act of 1936)
- Number of Mandays worked by adults and young people
- Total wages paid, including deductions, for those earning less than Rs.1600 per month on the following accounts under Section 7(2) of the Payment of Wages Act, 1936
- Gross amount paid as payment to persons earning less than Rs. 1600 per month, including the deductions made under section 7(2) of the Act on the following accounts
- Deductions-number of cases and amount realized.
- Balance of Fines fund
Part -C Maternity Benefit Act 1961 & E.S.I.C. Act of 1948
- Name, qualification, employment type of the Medical Officer
- Information about the hospital attached to the factory
- Average permanent or temporary women working with the factory
- Number of cases of miscarriage for which the leaves were granted
- Number of women who died before or after delivery
- Complete set of particulars and reasons for the action taken under serials 39(6). 39(9), 40(2). 40(4). 41(3). 41(4)
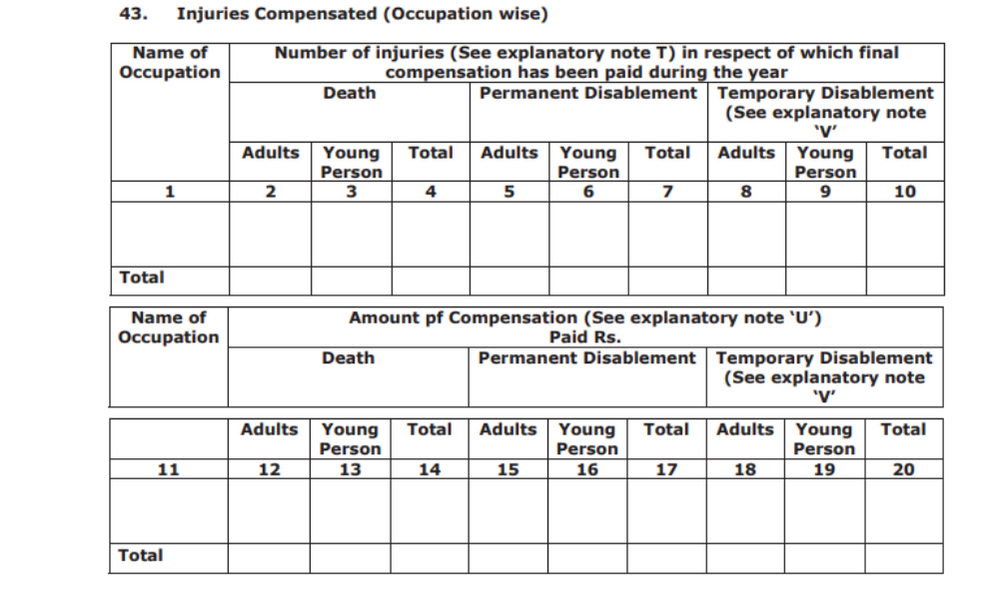
- Injuries Compensated (Occupation wise)
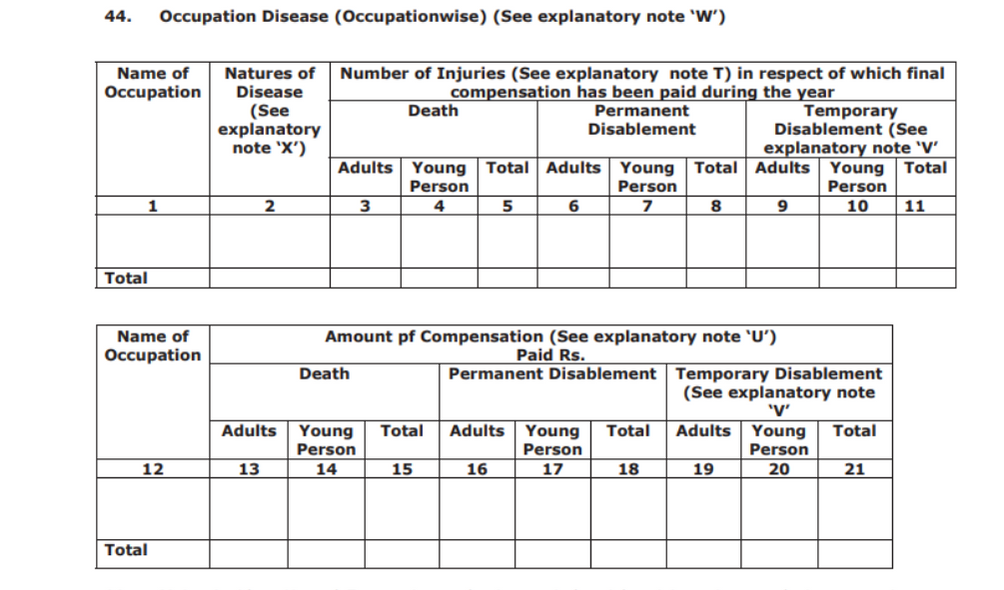
Details about occupation Disease:
Form No. 25
This is a form that is prescribed under Clause 2, Rule 107, and is called as the form for Half Yearly Return.


The form requires the details of the products actually manufactured including the kind of repairs. Also include the NIC Code.
The term Public sector implies an establishment owned or managed by the government.
In co-operative sector, establishment is managed by a co-operative society that is enrolled under Cooperative Societies Act of 1912.
Form No. 26
This is a form for applying for Grant of Certificate of Competency to a Person under Sub-rule 3 of rule 2A. The form is prescribed under rule 2A.
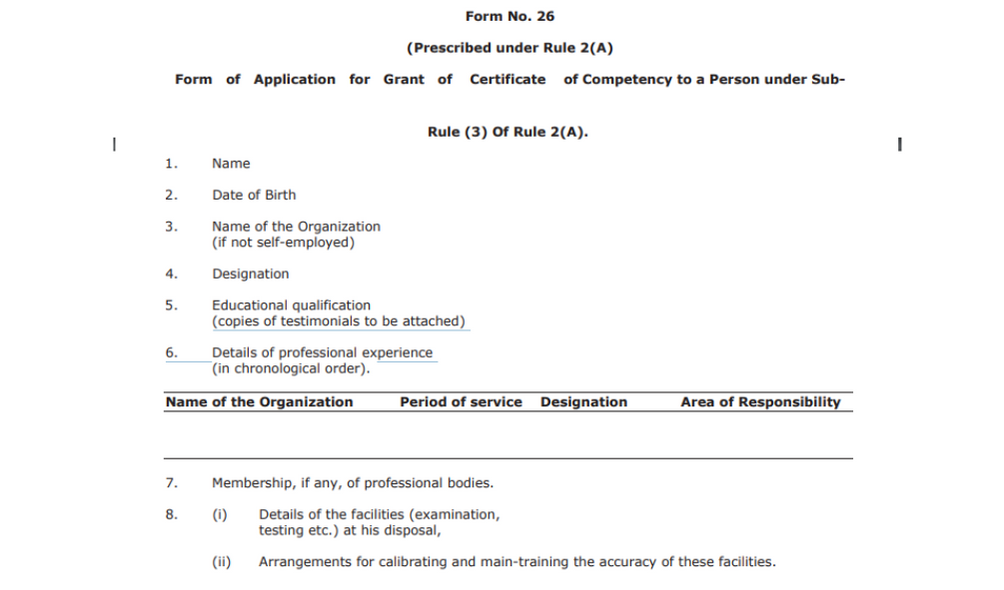


It requires the following information:
1. Name
2. Date of Birth
3. Name of the Organization (in the case of self-employment)
4. Designation
5. Educational qualification
6. Details of professional experience (chronologically provided).
7. Membership of the professional bodies.
8. Details of the facilities provided
9. Reason for seeking competency certificate
10. Inform if the applicant is a competent person
11. Provide any other relevant information.
12. Declaration by the applicant
Form No. 26-A
This is the test report of the fume extraction system and is prescribed under the Rule 102. The details required by the form are as follows:
1. System's description
2. Hood: Provide details of the hood such as its serial number, capture velocities, volume exhausted, statics pressure, and so on.
3. Total pressure drop
4. Transport velocity in Dust/Fume
5. Air cleaning device
6. Fan
7. Fan motor
8. Information of any defects
Finally the document must be signed and attested by the competent person monitoring the system.
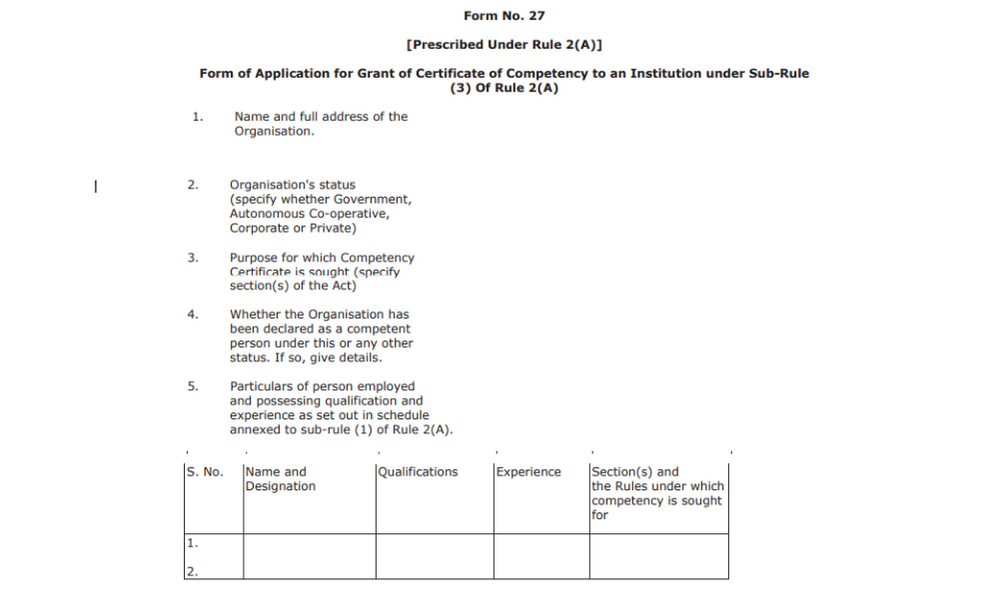
Form No. 27
Prescribed Under Rule 2(A), the form is for applying for competency certificate by an institution. Here is what shall be needed:
- Company's full name and address
- Company's status (mention whether co-operative, private, government)
- Reason for seeking competency
- Has the company been declared competent
- details of the person with experience and qualification based on sub-rule(1) of rule 2a
- Details of the arrangements for the maintenance
- Provide any other relevant information
- Declaration by the applicant.

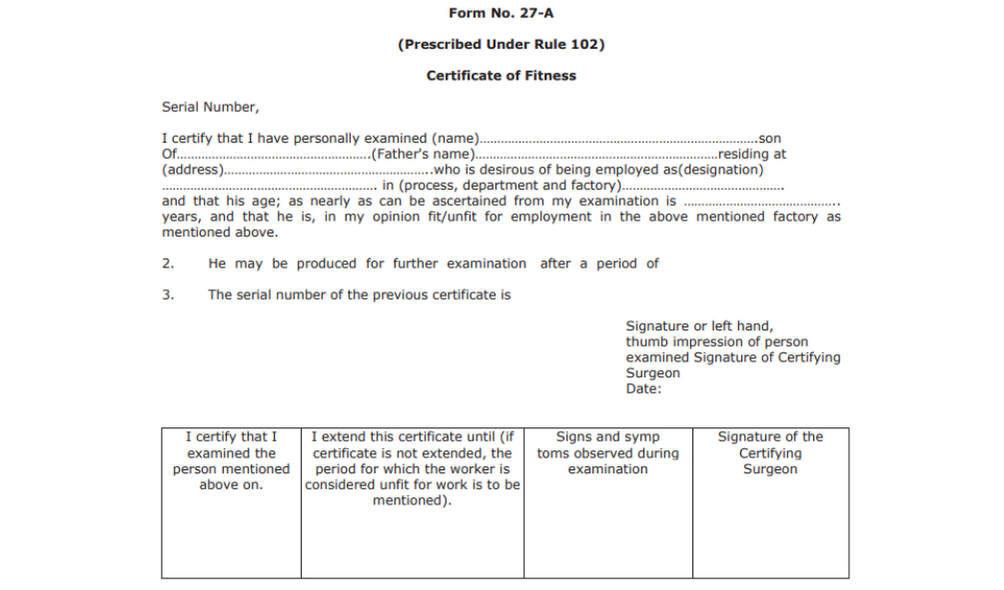
Form No. 27-A
This is the certificate of fitness as prescribed under rule 102. Here are the particulars of the form:
The form is certified and signed by a certifying surgeon. The surgeon mentions that they have examined the person seeking the fitness certificate and provides their report.
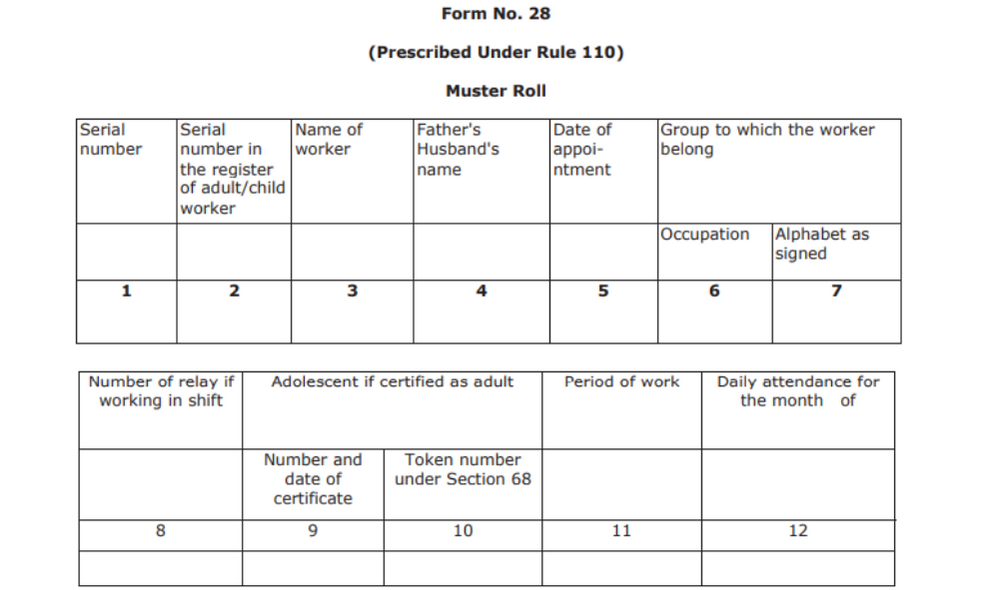
Form No. 28
This is the muster roll as prescribed under the Rule 110. Here are the fields to be provided in the form:
- Serial number
- Serial number of the child or adult worker
- Worker's name
- Father's or husband's name
- Appointment date
- Group of the worker and their occupation
- Alphabet assigned
- Number of relay
- Number of certificate
- Token
- Span of work
- Daily attendance for the month
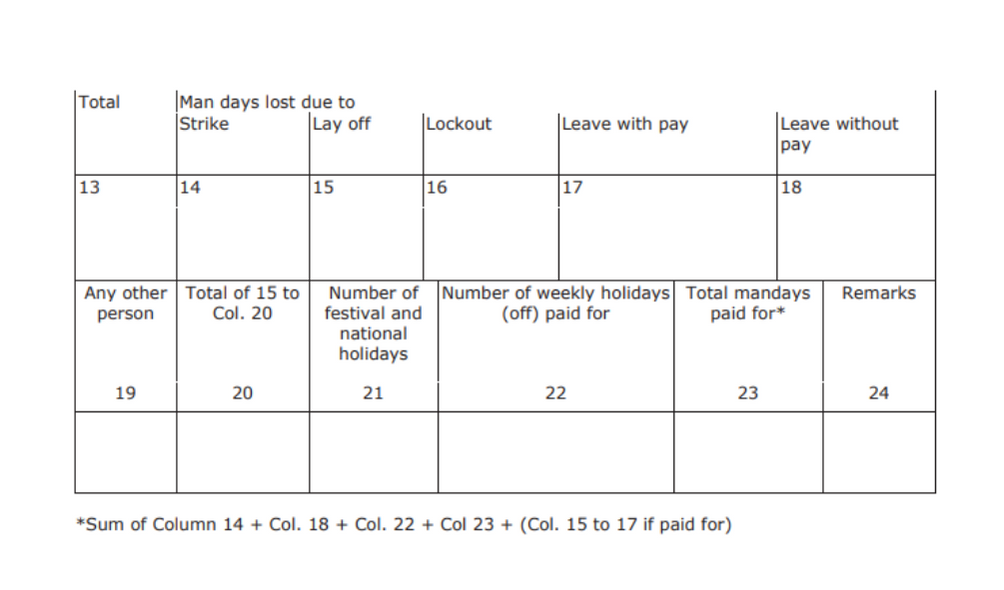
- Total
- Mandays lost due to strike
- Layoff
- Lockout
- Leave with pay
- Leave without pay
- Any other person
- Add up the digits from columns 15 to 20
- Number of national holidays
- Number of paid weekly holidays
- Total paid mandays
- Add any relevant remarks
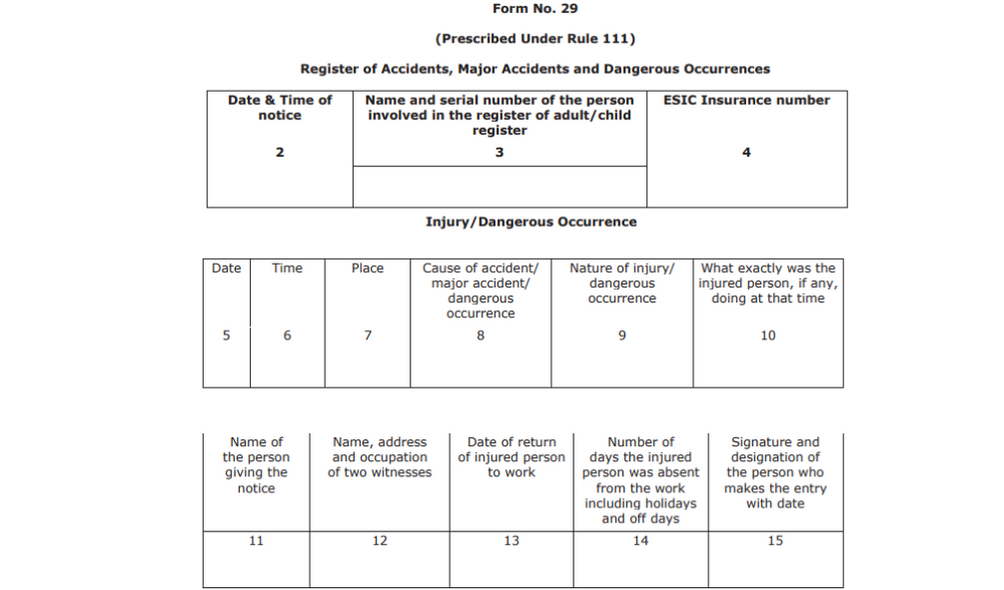
Form No. 29
This is the register of accidents and dangerous incidents prescribed under Rule 111. The form needs details such as cause, nature and exact details of the dangerous incident. It will also ask about the date, time, place of the incident. Mention what the injured person did at the time of the incident. If there are witnesses, add in their details and finally, sign of the person who makes the entry.
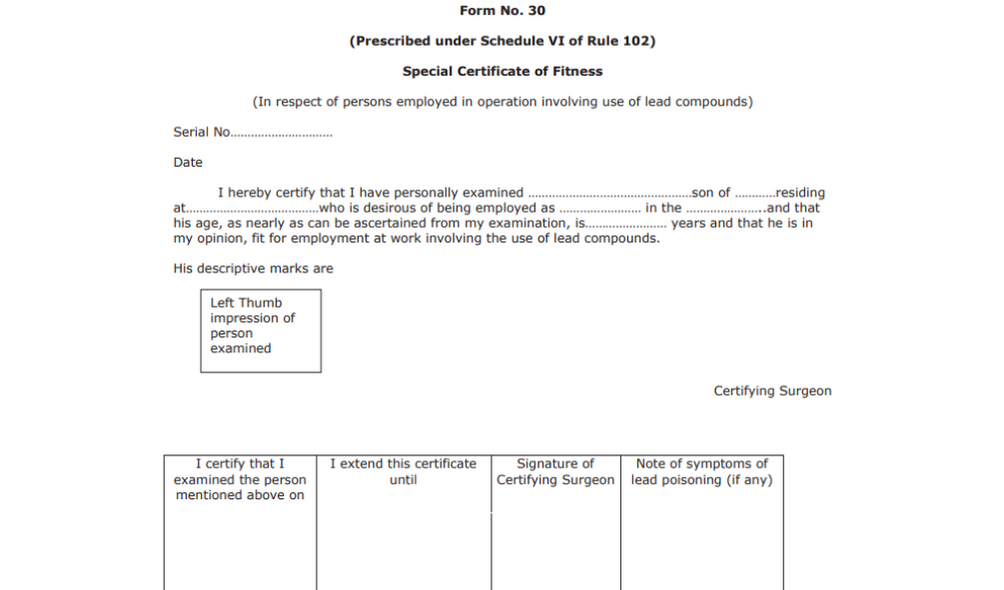
Form No. 30
This is the special certificate of fitness and prescribed by the Rule 102, schedule 6.
Form No. 31
This is the inspection book and prescribed under Rule 112.
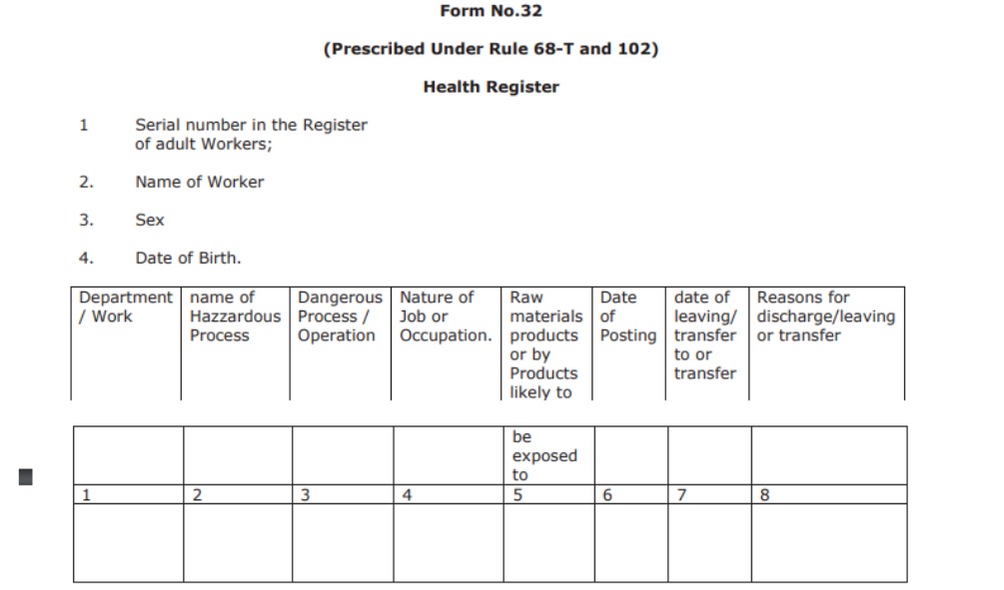
Form No. 32
This is the health register prescribed under the Rule 68-T and 102. Mention the following in the form:
Department, nature of work, raw materials, date of posting and leaving, and also provide the reasons for discharge or transfer of the worker.
Form No. 33
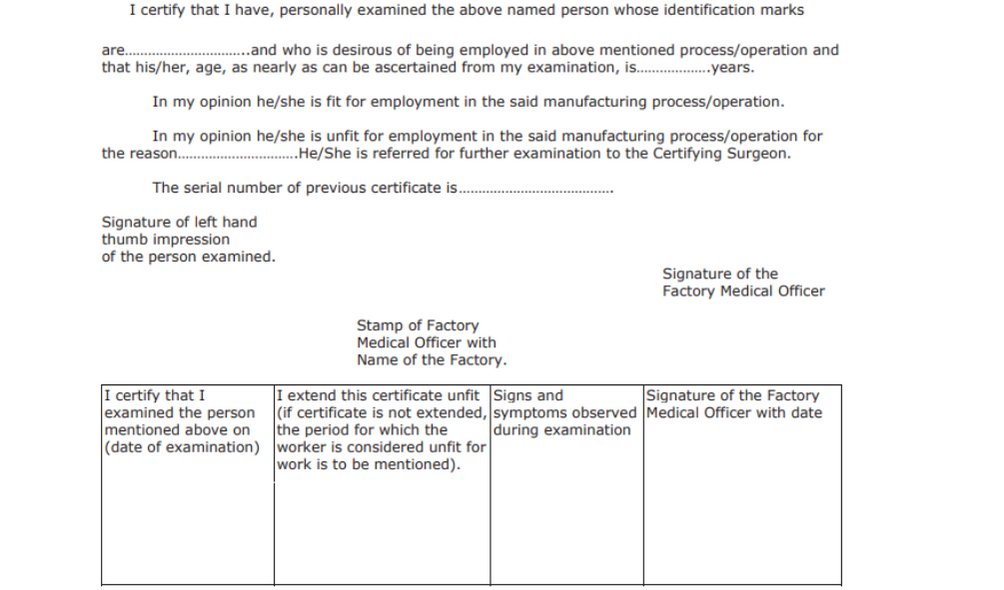
This form is Certificate Of Fitness for Employment In Hazardous Process And Operations. It is prescribed in Rule 68-T and 102.
Apart from the primary details of the worker, the form offer a certification from the factory medical officer. They certify the worker to be fit or unfit upon their thorough examination.
Form No. 34
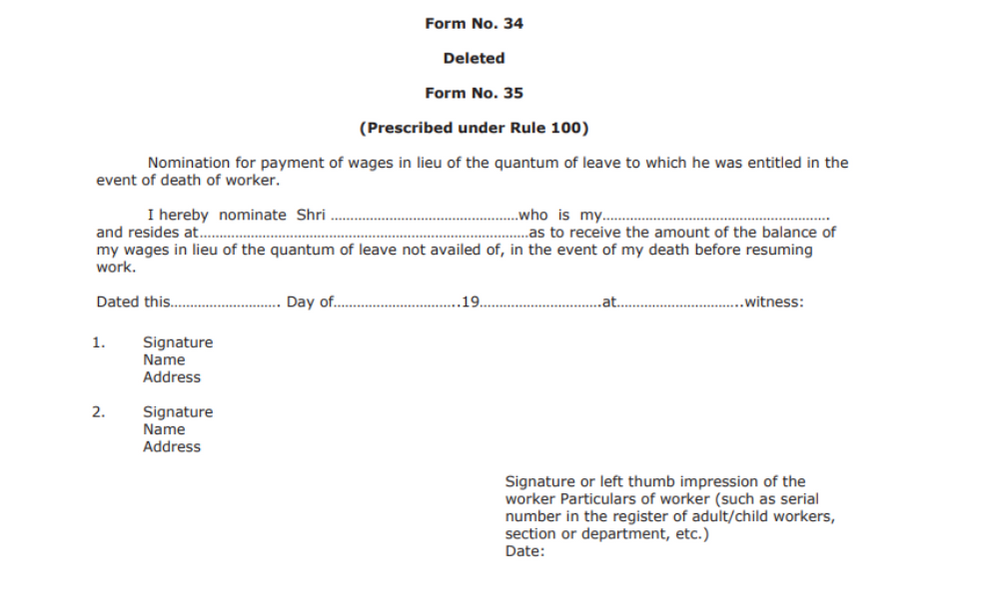
Form number 34 has been deleted.
Form No. 35
The form enables a person to nominate for payment of wages in lieu of leaves in event of death of a worker.
Form No. 36
The form requires the basic information of the workers such as name, address, date of birth, date of joining, and the latest photo of the worker.

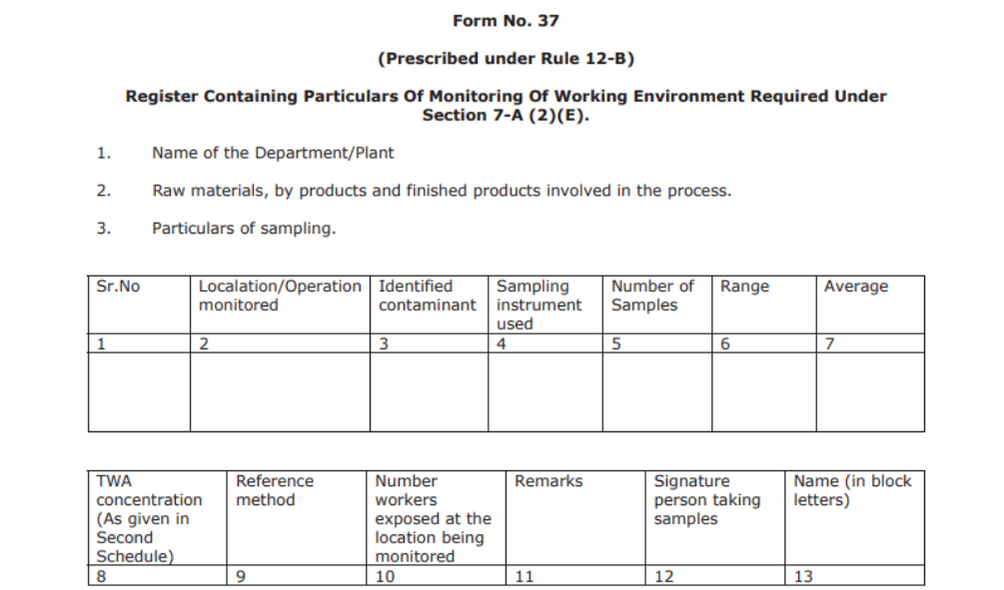
Form No. 37
This is a register that contains particulars of supervision of the work environment under the section 7A (2)(E).
It will require the name of the department monitored along with the particulars of the sampling.
How can Deskera Help You?
Payroll management and employee management are integral to any organization. If you are looking for a comprehensive and automated tool to manage payroll, employees, expenses, and contractor management, Deskera People could be the apt solution.
Key Takeaways
The article sums up the forms required for various applications based in the Gujarat Factories Rules 1963. Forms must be submitted by either the manager, occupier, the medical officer, or any other competent person who has duly and responsibly filled in the forms.
Related Articles











