Goods and Services Tax (GST) is also known as indirect tax or consumption tax in India on the supply of goods and services. It is a comprehensive, multistage, and also known as destination-based tax.

Goods and Services Tax (GST) is also known as indirect tax or consumption tax in India on the supply of goods and services. It is a comprehensive, multistage, and also known as destination-based tax. The GST in India is comprehensive because it has subsumed almost all the indirect taxes except a few state taxes.
GST will be imposed at every step in the production process, and a refund will be possible in the various production stages other than the final consumer. It will be collected from the point of consumption and not a point of origin.
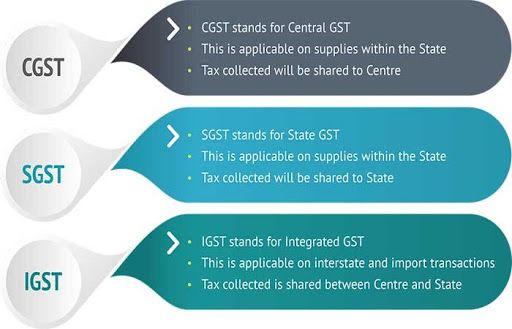
Types of GST
There are three types of GST,
1. Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST),
2. State Goods and Services Tax (SGST),
3. Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST),
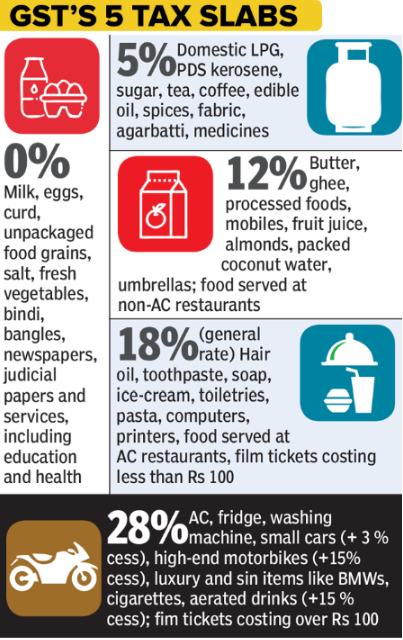
GST Rates and Slabs
Who is liable to pay GST?
The registered GST businesses whose turnover exceeds Rs. Forty lakhs* (Rs 10 lakhs for North East and hill states) is required to register as an average taxable person.
Some businesses must register for GST irrespective of the turnover, and they are:
- E-commerce operators and sellers
- Input service distributors
- Interstate supplier of Goods and Services
- On behalf of a taxable person Agents supplying
- Any entity or individual under the GST Act required to deduct tax deducted at source (TDS)
- Any foreign entities running a business in India or individuals registered outside India are liable to pay tax in India due to their business operation.
If you are a GST-registered business, you are required to fill in the GSTIN field. It is a fifteen-digit number given in a certificate of registration to an applicant. It is a unique identification number assigned to a business or person registered under the GST Act.
When creating an account as a GST-registered business, you will have to make sure that you input the accurate information of your business address. These include the address line, city, state, and zip code as the tax will vary depending on the place of supply.
GSTIN Format
GST under Deskera Books
Let say you are not required to register GST When creating an account with Deskera Books; you have an option too, tick on the checkbox 'No' when prompted with the question 'Is your business registered for GST?'
If you are a GST-registered business, you have an option to fill in the GSTIN field. You can choose more than one field that applies to your organization. Selecting the right field enables us to compute the accurate Goods and Service Tax that you'll have to pay to the Government.
GST Codes: HSN & SAC Codes
What are HSN codes?
HSN stands for the Harmonized System of Nomenclature. This code is used for the classification of goods systematically. HSN is a six-digit code developed by the World Customs Organization (WCO) and is used to classify more than 5,000 products for tax purposes.
The HSN code structure consists of 21 sections, 99 chapters with 1244 headings, and 5224 subheadings. The section and chapter stand for the broad categories of goods, whereas the headings and subheadings describe the details of the product.
The structure for HSN Codes to be declared are:
- If the taxpayer's annual turnover below 1.5 crores is not required to follow HSN.
- Taxpayers will have to use 2-digit HSN code if the annual turnover is above 1.5 crores but below five crores.
- The businesses will have to use a four-digit HSN code whose yearly turnover exceeds five crores.
- The businesses that deal with Import and Export will follow Eight-digit HSN code.
What is SAC code?
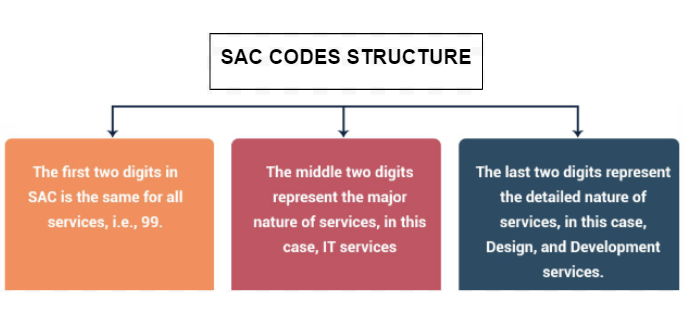
SAC stands for Servicing Accounting Code and is used to classify services instead of goods. This code provides the recognition, measurement, and taxation of services. All these services start with a number 99, making it easy to differentiate between HSN and SAC codes.
Structure of SAC codes
Conclusion
In India, an eight-digit HSN/SAC code is used instead of a six-digit code. The first two digits stand for the chapter in which the goods or services will list in the Code List. The next two digits are the chapters, and the next two digits are for products. The last two digits are further classification of the product.HSN/SAC codes exist for each commodity in more than 200 countries, and the code remains the same for almost all goods. In some countries, HSN numbers can vary a little because it depends entirely on the nature of the items classified.
HSN codes and SAC codes are internationally recognizable. With these codes and a standard structure, the government can quickly analyze the purchase and sale of the commodities and decide on macroeconomic policies. HSN/SAC codes helped to classify the products and mapped them to the right tax codes plus the Cess amount based on the India GST regime.
How do HSN/SAC codes apply using Deskera Books?
When creating a product on Deskera, select the product as taxable, and you have an option available to choose the HSN/SAC of the products. Once you have entered the HSN/SAC code, the tax rate will be auto-populated based on the code you have input.
GST Cess
As compared to other countries, in India, the tax system is unique and different. If you have your own business in India, you have come across this term known as 'GST Cess.'
So, what is a 'GST Cess?' Let us start by explaining the word 'cess.' According to the dictionary, Cess means levy or tax. Thus, Cess is a form of tax that is charged/levied to the taxpayer over and above the base tax liability.
Why is Compensation Cess Implemented?
The Government created the compensation cess to ensure that the states get the tax revenue they need to operate. This charge is usually on certain types of goods, and you must pay it in addition to any required GST. This Cess applies to inter-state sales, intrastate sales, and imports. It does not apply to exports. The Government will collect, then distribute the Cess to states to help them meet minimum revenue levels. This helps to ensure that manufacturing-heavy states have enough money to operate.
Products with Compensation Cess and rates
How is Compensation Cess calculated?
For example, Company XYZ supplies one car that is worth Rs. 10,0000/- to A&T Company in the same state, Maharashtra. Taking into consideration the cess rate is 3%, and on a car, the GST rate applicable is 28%.
Compensation Cess on Deskera Books
You can input the compensation cess description for that particular product while creating a new product using Deskera Books.
Input Tax Credit (ITC)
ITC is the credit where a taxpayer can claim if he has already paid taxes on the input. Let's take an example. A manufacturer pays Rs. 100 as tax when he purchases the inputs. And, he pays Rs. 200 as a tax on the output. Hence, in this case, the manufacturer needs to pay only the difference between both the amounts, i.e., Rs. 100. It is known as the Input Tax Credit
Documents and forms to submit for application
Any applicant who wants to claim ITC under GST will need to provide the following documents:
- Issued invoice by the supplier
- Bill supply issued by the supplier
- An issued debit note by the supplier to the recipient
- Bill of entry
- Invoice issued similar to Bill of Supply, in cases where the total amount is less than Rs. 200 or reverse charge mechanism is applicable
- An invoice or credit note to be issued by the Input Service Distributor(ISD) as per the invoice rules under GST.
ITC Reversal under GST
In certain situations, the ITC claim can be reversed, for claiming ITC is satisfied. Reversal of ITC means the credit of inputs utilized earlier would now be added to the output tax liability, effectively nullifying the credit claimed earlier. Payment of interest may also be required depending upon when such reversal has been done.
Scenarios of ITC reversal
Below are some of those scenarios where ITC is reversible
How does ITC Reversal apply using Deskera Books?
When creating a product, there is an option on Deskera Books to indicate if the Input Tax Credit (ITC) is blocked or reversed under the ITC Adjustment in the Accounting section.
From the drop-down box from the ITC adjustment field, select either ITC is blocked, or ITC is reversed. ITC is blocked for general insurance, repair, and maintenance services related to motor vehicles, servicing, work contract services related to construction, etc.
GST Composition Scheme
It is a hassle-free compliance scheme for small taxpayers. In the Composition Scheme, a registered taxable person whose aggregate turnover does not exceed one crore and 75 lakhs for the particular category states can pay tax at a lesser rate.
The tax rates applicable under this scheme are as follows,
Who is eligible for a composition scheme?
A taxpayer can opt for composition scheme whose turnover is below Rs 1.5 crore*. In the case of North-Eastern states and Himachal Pradesh, the limit is now Rs 75* lakh.
As per the CGST Act, 2018, a composition dealer can also supply services to the extent of Rs.5 lakhs or 10% percent of turnover, whichever is higher.
Advantages and disadvantages of registering under the GST composition scheme
How does GST Composition Scheme apply using Deskera Books?
On Deskera Books, while creating an organization, you can select if your business 'Is Registered for Composition scheme?' You need to choose the below-mentioned applicable category of businesses,
- 1% - For Traders and Manufacturers
- 2% - For Manufacturers: GSTIN has lowered the rate for manufacturers to 1%
- 5% - For Restaurant Sector
- 6% - For Suppliers of Services or Mixed Suppliers)
GST Reverse Charge
Reverse Change is a process under GST in which the receiver makes the payment of GST instead of the supplier. In typical cases, the supplier is the one who pays tax on supplies, but in case of reverse charge, the role gets reversed. Here, the buyer pays taxes directly to the Government. Reverse charge mechanism happens in the case of import and other notified supplies.
When is Reverse Charge applicable?
The Reverse Charge is applicable in case of:
- Services offered by an E-commerce aggregator/operator
- Here the liability to pay taxes lies on the recipient of the services. If the recipient has no physical presence in the taxable area, the E-commerce operator will be liable to pay the tax.
- The reverse charge will be applicable if a dealer is not registered under GST and supplies goods to a registered buyer,
- Supply of specific products and services decided by the government some of these goods and services are cashew nuts (not shelved or peeled), tobacco leaves, silk yarn, raw cotton, old and used goods, GTA services, legal services by an advocate, etc.
How does GST Reverse Change apply using Deskera users?
Using Deskera Books when you create a new company, you can indicate that your business 'Enables reverse charge in sales transactions,' which will apply to all the sales transactions.
Special Economic Zone under GST
The Special Economic Zone (SEZ) in India came to inception on April 1, 2000. All the businesses that operate in this zone can enjoy simpler tax and easier legal compliance's. The main objective is to provide a hassle-free environment for exports internationally and enhance foreign investment.
List of SEZ Zones in India
How does GST Work in the SEZ zone?
One of the main advantages of conducting business in the SEZ zone is tax benefits. You'll be charged zero-rated supply if you're supplying goods and services to any companies in the Special Economic Zone. Zero-rated supply means any goods and supplies sold by the companies that are free from Goods and Services Tax (GST).
The advantages suppliers gained from supplying goods to SEZ zones are:
- They can claim Input Tax Credit for supply under bond or LUT without payment of IGST.
- They can request a refund of taxes paid for supply on payment on IGST.
Businesses in the SEZ zones have to pay IGST to supply goods, services, or both to anyone as it's considered an inter-state supply.
If businesses supply goods and services to a Domestic Tariff Area (DTA), it will be considered as export to the DTA area. Hence, customs duties and other import duties are payable by the person receiving the supplies in DTA.
How does the Special Economic Zone apply using Deskera users?
Using Deskera Books when you create a new organization, you have an option to indicate if your company is located or 'involved in the Special Economic Zone or Overseas Trading.' Providing the right information is crucial for accurate computing Goods and Service Tax (GST).
Different types of GST Returns?
GST Return
A registered person/business has to file a document or report containing details about the income to the tax authorities every calendar month. This document or statement is known as GST Return. The GST Return should include purchases, sales, output GST on sales, and input tax credit. This return needs to be filled with the tax administrative authorities to pay the tax to the Government. It is essential for every business registered under GST to file GST returns.
Different types of GST Returns.
- GSTR-1
- GSTR-2
- GSTR-2A
- GSTR-2B
- GSTR-3
- GSTR-3B
- GSTR-4
- GSTR-5
- GSTR-5A
- GSTR-6
- GSTR-7
- GSTR-8
- GSTR-9
- GSTR-9A
- GSTR-9B
- GSTR-9C
- GSTR-10
- GSTR-11
Due Dates of Filing GST Returns
Reports available Under Deskera Books
GSTR-1 Report under Deskera Books
GSTR-1 is a report about the monthly return of outward supplies that shows all the sales transactions of a business.
Using Deskera Books, users can now retrieve the GSTR-1 Report summary, which is mapped according to the Sell tab's transactions.
The GSTR-1 Report will reflect the details of the following fields, which segregate the tax amount in IGST, SGST, CGST, and Cess, and the amount is auto-populated based on the transactions in the Buy and Sell Module.
- B2B Invoices
- B2C Invoices (Small)
- B2C Invoices (Large)
- Credit and Debit Notes (Registered-9B)
- Credit and Debit Notes (Unregistered-9B)
- Export Invoice (6A)
- Tax Liability (Advance Payment)
- Adjustment of Advances
- Nil Rate Invoices - (8A, 8B, 8C, 8D)
- HSN Invoices
GSTR- 3B Report under Deskera Books
GSTR-2 involves the Report of details of purchases. GSTR-3B report consists of a monthly summary of sales and purchases, which is auto-populated by pulling the source of information from GSTR-1 and GSTR-2.
On the GSTR-3B Report page and you will come across the information of details such as:
- Section 3.1: Inward supplies and Outward supplies are liable to reverse charge
- Section 3.2: Interstate supplies made to an unregistered person, composition taxable person, and UIN holders.
- Section 4: Eligible ITC
- Section 5: Value of exempt, nil-rated and non-GST inward supplies
- Section 5.1: Interest and late fee payable
Here is the step-by-step guide for filing your GST Returns

Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) and Tax Collected at Source (TCS)
Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) is a process to keep an eye on the transactions of the supply of goods and services by making the buyer of such transactions deduct a small amount to be paid to the supplier and deposit the amount with the Government. In such a case, the supplier takes into account the deducted amount and makes the balance payment of tax to the Government.
Under the GST, TDS will be deducted at the rate of 2% on payments made to the supplier of taxable goods and services (1% CGST and 1% SGST in case of intrastate supply and 2% IGST in case of the inter-state supply). TDS will deduct on the taxable goods and services which exceed 2,50,000/-.
The following people/entities are liable to deduct TDS are:
- Government Agencies
- Local Authorities
- Department of Central Government
- Department of State Government
- An establishment of State and Central Government
- The person notified by the Central or State Government on the recommendation of the GST Council
Tax Collected at Source is a process where the tax is collected by the e-commerce operator when a supplier sells goods and services through its portal, and the payment received by the e-commerce operator. TCS will be charged and collected at the rate of 1% (0.5% CGST and 0.5% SGST) for intrastate supply and (IGST 1%) will be levied in case of inter-state supply. Every e-commerce operator must register under GST.
The sellers referred to as TCS are:
- Partnership Firms
- Central Government
- State Government
- Statutory Authority
- Local Authority
- Company
Similarly, there are only a few buyers that are liable to pay TCS to sellers such as:
- Public Sector Companies
- State Government
- Central Government
- Clubs (sports and social)
- Embassy of High Commission
The TCS has to deposit within seven days from the last month. There is a penalty for non-payment to the Government on the due date; then, he will be liable to pay interest of 1% per month.
Lastly, in simple words, TDS is an expense deducted by payer or buyer, and TCS, on the other hand, is an income collected by payee or seller.
TDS Sections and Rates
According to the Income Tax Act, in 1961, every person or company making a payment of certain kind above a specified threshold limit is applicable for deducting tax at source. The tax is to be deducted based on the provisions specified in the Act. The company deducting tax at source is called deductor, and the person or company who is receiving the payment after the deduction of tax at source is called the deductor. Link to TDS sections and rates
Refer below articles to know how TDS and TCS work in Deskera Books.


Refer to the video tutorial for, how to manage and set up India GST in Deskera Books.
Conclusion:
So with Deskera Books, has implemented GST taxation by using a simple, scalable account and financial management system that allows you to conduct business on a pan-India basis with a single Books system.




