If you are going to enter the business world, you must know about the Shop and Establishment Act in India since this act is a vital move toward the promising business world. Here in this article, we have attempted to cover the nuts and bolts of the Act while we focus on one of its sections- The register of Fines.

The shop and Establishment Act is under state regulation, and each state has outlined its standards and guidelines for the equivalent. In this article, we will focus on Tamil Nadu.
Remember, the state government's outlined rules will contrast one state to another. Consequently, management for the state where enrollment is to be acquired should be followed.
This article covers the following:
- About Tamil Nadu Shops and Establishments Act
- The extent of the act
- Consequences of non-compliance to the act
- Register of Fines
- Form B
- Maintenance of Registers, Records, and Display of Notices
- How can Deskera assist you?
About the Tamil Nadu Shops and Establishments Act
The Tamil Nadu Shops and Establishments Act, 1947 and 1948 is relevant to every shop and business foundation in the areas advised by the Government of Tamil Nadu. The Act is sanctioned to safeguard workers' privileges and for the businesses' welfare.
The Act gives guidelines for the installment of wages, terms of administration, work hours, rest stretches, extra time work, opening and shutting hours, shut days, occasions, leaves, maternity leave and advantages, work conditions, rules for work of kids, records upkeep, and so on.
The act does not apply to the following organizations:
- Persons employed in any establishment in a position of management.
- Persons whose work involves traveling and persons employed as canvassers and caretakers.
- Establishments under the Central and State Governments, local authorities, the Reserve Bank of India, a railway administration is operating any railway as defined in clause (20) of Article 366 of the Constitution, and cantonment authorities.
- Establishments in mines and oil fields.
- Establishments in bazaars in places where fairs or festivals are held temporarily for a period not exceeding fifteen days at a time.
- Organizations that are not factories within the meaning of the Factories Act, 1948, are in respect of matters dealt with in this Act, governed by a separate law for the time being in force in the State.
The Extent of the Act
This act extends to the State of Tamil Nadu, including the Kanyakumari district and the Shencottah taluk of the Tirunelveli district and the territories specified in the Second Schedule to the Andhra Pradesh and Madras (Alteration of Boundaries) Act, 1959 Central Act 56 of 1959.
Applicable to all industrial and other establishments, including shops. Under this act, every employee in each calendar year has a holiday on 26th Jan, 15th Aug, two and Oct. and five other holidays for such festivals as the employer may specify in consultation with employees.
To submit a proposal for the specification of festivals if FORM No. I in duplicate along with a copy of the notice in FORM No.II to the Jurisdictional Inspector. To display the holiday list approved in FORM No.III in the premises of the establishment.
The employer should send to the Inspector a statement showing the holidays allowed in the calendar year under section 3 in FORM No. V and also display the same on the premises.
The employer should serve a Notice in FORM NO.V-A on the employee who is required to work on any holiday, not less than 24 hours before such holiday. Give twice the wages to employees who work on holidays or normal wages with a substitute holiday.
Consequences of Non-Compliance of the Act
Failure to comply with the provisions may attract imprisonment of up to 3 months or fine up to Rs. 500/- or both.
Register of Fines
The Commissioner of Labour and the Deputy Commissioners of Labour I and II, Madras, Salem, Coimbatore, Madurai, Tiruchirappalli, and Tirunelveli shall be the authority competent to approve, under sub-section 1 of section 35, acts and omissions in respect of which fines may be imposed and under sub-section 8 of section 35, the purposes to which the fines realized shall be applied.
Every employer requiring the power to impose fines in respect of any acts and omissions on the part of employed persons shall send to the Commissioner of Labour or to the Deputy Commissioner of Labour having jurisdiction over the area a list in English, in duplicate, clearly defining such acts and omissions.
In cases where the employer himself does not intend to be the sole person employed to impose fines, a list in duplicate, showing those appointments in his establishment the incumbents of which may pass orders imposing fines and the class of establishments on which the incumbent of each such appointment may impose fines.
A list showing the purpose to which the fines realized shall be applied. The Commissioner of Labour or the Deputy Commissioner of Labour having jurisdiction over the area may, on receipt of the list prescribed in sub-clause 1 or sub-clause 3 of clause b.
After such inquiry as you consider necessary, pass an order either (i) disapproving the list, or (ii) approving the list either in its original form or as amended by him in which case such list shall be considered to be an approved list.
Provided that an order disapproving or amending any list shall be passed unless the employer shall have been given an opportunity to show cause orally or in writing against such order.
The employer shall display at or near the main entrance of the establishment a copy in English, together with a correct translation thereof, in the language of the majority of the persons employed therein of the list approved under clause C.
No fine shall be imposed by any person other than an employer or a person holding an appointment named in a list submitted under clause b. Any person desiring to impose a fine on a person employed or to make a deduction from his wages for damage or loss shall explain personally to the said person the act or omission, or damage or loss, in respect of which the fine or deduction is proposed to be imposed and the amount of the fine or deduction, which it is proposed to impose, and shall hear his explanation.
The charge in respect of which it is proposed to impose the fine or deduction and the explanation of the person concerned shall be reduced to writing, the signature of such person being obtained to the latter.
Every person other than the employer imposing a fine or directing the making of a deduction for damage or loss shall at once inform the employer of all particulars so that the register prescribed 1 in sub-rule 4 may be duly completed.
The employer of any establishment in respect of which he has obtained approval under sub-section 1 of section 35 to a list of acts and omissions in respect of which fines may be imposed, shall maintain a Register 2 prescribed under sub-rule 3.
Provided that the signature or thumb impression of the person employed shall be obtained in 4 the Register prescribed under sub-rule 4 immediately on the next working day following the last day of the month concerned.
At the beginning of the 1 Register prescribed under sub-rule 4, the approved purpose or purposes on which the fines realized are to be expended shall be entered and serially-numbered.
When any disbursements are made from the fines realized, deduct entry of the amount so expended shall be made in the 1 Register prescribed under sub-rule. The vouchers or receipts in respect of the expended amounts shall be serially numbered and kept separately, the serial number of each voucher or receipt and the amount to which it relates being noted in the remarks column of the register.
If more than one purpose has been approved, the entry of the disbursements shall also indicate the purpose for which it is made. Every employer shall maintain a Register of Fines, deductions for Damages or Loss, and Advances in Form P, Provided that the signature or thumb impression of the person employed shall be obtained in 4 Form P immediately on the next working day following the last day of the month concerned.
Every employer shall maintain a register of wages in Form R in the organization. Every employer shall issue a slip in Form T to every person employed every month, a day before the disbursement of wages or at least on the date of disbursement or if the wages are paid daily, along with the wages, duly signed by him or any other authorized person and also the signature of the concerned person employed shall be obtained.
The wage slip-issued copies shall be maintained by the employer and produced to the inspector on demand. Deductions for breach of contract. No deduction for breach of contract shall be made from the wages of an employed person under the age of fifteen.
No deduction for breach of contract shall be made from the wages of any employed person unless, there is provision in writing forming part of the term of the contract of employment requiring the employee to give notice of the termination of such employment and the period of notice does not exceed either, (i) fifteen days or the wage-period, whichever is less.
The period of notice which the employer is required to give of the termination of that employment; this rule has been displayed in English and in the language of the majority of the employed persons at or near the main entrance of the establishment and has been so displayed for not less than one month before the commencement of the absence in respect of which the deduction is made.
A notice has been displayed at or near the main entrance of the establishment giving the names of the persons from whose wages the deduction is proposed to be made, the number of days’ wages to be deducted and the conditions (if any) on which the deduction will be remitted.
Provided that where the deduction is proposed to be made from all the persons employed in any departments or sections of the establishment, it shall be sufficient in lieu of giving the names of the persons in such departments or sections, to specify the departments or sections affected.
No deduction for the breach of contract shall exceed the wages of the person employed for the period by which the notice of termination of service falls short of the period of such notice required by the contract of employment.
If any conditions have been specified in the notice displayed under clause C of sub-rule 2, no deductions for breach of contract shall be made from the wages of any person who has complied with those conditions.
Form B
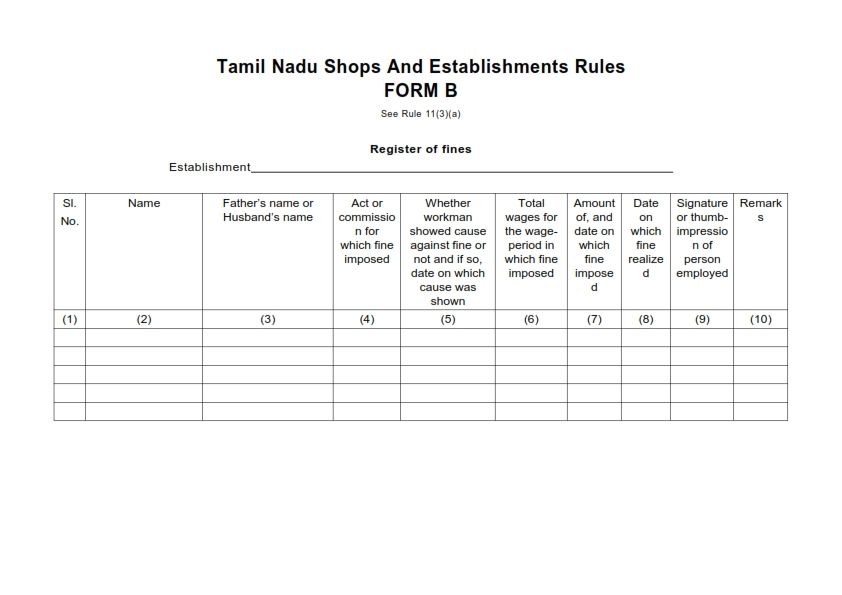
Maintenance of Registers and Records and Display of Notices
Every employer shall maintain a Register of Employment in Form Q. Every employer shall exhibit in his establishment in a conspicuous place a notice in 4 Form S showing the names of the persons employed, daily periods of work, rest interval, and weekly holiday and send a copy of the same to the Assistant Inspector of Labor having jurisdiction over the area before commencement of work by the persons employed therein.
No employer shall require or allow any person employed to work in his establishment without exhibiting a notice in 4 Form S in respect of him and without sending a copy of it to the Assistant Inspector of Labor concerned and shall not require or allow him to work otherwise than in accordance with the periods of work and weekly holiday shown therein.
Provided that the persons employed may be required to work overtime in accordance with the provisions of the Act if entries showing the periods of such overtime work are made before commencement of such work in the employment register.
Provided further that in exceptional circumstances and due to unforeseen reasons when a notice of change could not be sent to the Assistant Inspector of Labor prior to allowing or requiring any person/persons employed to work otherwise than in accordance with the notice in 1 Form S, it will be deemed sufficient compliance with the rules, if the notice of change has been exhibited simultaneously while so allowing him to work subject to the payment of overtime wages, in accordance with the provisions of the Act and Rules, entries being made to the employment register.
Every employer shall exhibit in his establishment a notice containing such extracts of the Act and these Rules in English and in the language of the majority of the persons employed by him as the Government may direct.
Any notice required to be exhibited under these rules shall be exhibited in such a manner that can be readily seen and read by any person whom it affects and shall be renewed whenever it becomes defaced or otherwise ceases to be clearly legible.
In any register or record which an employer is required to maintain under these rules, the entries relating to any day shall be made on such day. The registers, records, and notices relating to any calendar year shall be preserved till the end of the next calendar year.
Save as otherwise provided in sub-rule 5, all registers, records, and notices required to be maintained, exhibited, or given under this rule shall be either in English or in the language of most of the people employed in the establishment.
Every employer shall maintain a visit book in which an inspector visiting the establishment may record his remarks regarding any defects that may come to light at the time of his inspection and shall produce it whenever required to do so by any Inspector having jurisdiction.
The registers, records, and notices maintained or exhibited under these rules shall always be available in the establishment. They shall be produced or caused to be produced for inspection at all reasonable hours by any Inspector having jurisdiction.
How Can Deskera Assist You?
Deskera People has the tools to help you manage your payroll, leaves, employee onboarding process, and managing employee expenses, all in a single system. Features like a flexible payment schedule, custom payroll components, detailed reports, customizable pay slips, scanning and uploading expenses, and creating new leave types make your work simple.
Key Takeaways
- Remember, the state government's outlined rules will contrast one state to another.
- This act extends to the whole of the State of Tamil Nadu, Kanyakumari district, the Shencottah taluk of the Tirunelveli district, and the territories specified in the Second Schedule to the Andhra Pradesh and Madras.
- Failure to comply with the provisions may attract imprisonment of up to 3 months or a fine up to Rs. 500/- or both.
- A list showing the purpose to which the fines realized shall be applied.
- No fine shall be imposed by anyone other than an employer or a person holding an appointment named in a list submitted under clause b.
- A list showing the purpose to which the fines realized shall be applied.
- Any person desiring to impose a fine on a person employed or to make a deduction from his wages for damage.
- Or loss shall explain personally to the said person the act or omission, or damage or loss, in respect of which the fine or deduction is proposed to be imposed.
Related Articles:















