“Beware of little expenses. A small leak will sink a great ship.” - Benjamin Franklin
This is precisely what you are worried about, bringing you here to this article, hoping to get a complete understanding of expenses in accounting. While expenses in accounting sound like a very complex subject, it is a very important one at that.

This is because, without you understanding your expenses, your business functioning would continue to remain incomplete. In fact, without incurring expenses, you would not be able to generate revenue from your business.
Some of the most common expenses are:
- Factory leases
- Payment to suppliers
- Wages to employees
- Equipment depreciation
And so on. All of these and more are the costs that are incurred by your business not only to increase sales, solve customers’ pain points, increase customer retention, earn more gross profits and even net profits but also to increase the revenue earned from your business’s activities.
Further on, having a complete understanding of your expenses will also help you in identifying all those expenses that you can write off, hence reducing their taxable income and subsequently their tax liability.
ERP.AI enhances expense management by automatically categorizing and analyzing your business expenditures, uncovering spending trends, and identifying areas where costs can be reduced or optimized—all in real time.
Expenses in accounting are thus a very important part of your business’s functioning. This article is aimed at becoming your guide for understanding expenses in accounting.
What are Expenses in Accounting?
Expenses in accounting are the money spent or costs incurred by a business in an effort to generate revenue. Hence, expenses in accounting are the cost of doing business, including a sum of all the activities that will hopefully generate profit for you.
Some of the varied ways in which expenses are defined in accounting are:
- Office supplies use up the cash (asset)
- Depreciation expenses are a charge that reduces the book value of capital equipment like a machine or a building. This is done so in order to reflect its usage over a period of time.
- A prepaid expense, for example, a prepaid rent, is an asset that becomes a cash expense as the rent is used each month.
And so on.
A summary of all such expenses is included in your income statement as deductions from the total revenue. Therefore, for a given period, revenue minus expenses will provide you with the net profit earned by you.
However, when considering expenses for the double-entry bookkeeping system, expenses are just one of the five-main groups where all your financial transactions are recorded. The other four categories are revenue, owner’s equity, assets, and liabilities. Expenses in the double-entry bookkeeping system are recorded as a debit to a specific expense account. Simultaneously, the same amount’s credit entry also needs to be recorded, which will reduce your assets and increase your liabilities.
What needs to be noted here is that expenses like the purchase of land and equipment are not taken as simple expenses in accounting but rather as capital expenditures. This hence means that these assets are expended throughout their useful life through depreciation and amortization.
Differentiate Between Expenses and Expenditure
While expenditure is the payment or the incurrence of a liability, expenses represent the consumption of an asset. For example, your company has made an expenditure of $10,000 in cash to purchase a fixed asset. This asset, however, would be charged as an expense over the term of its useful life through depreciation and amortization.
Thus, while an expenditure tends to occur upfront, recognition of expenses incurred by your business is more likely to be spread over an extended period of time. However, there are always some other things to be considered during the accounting of your expenses. For example, the amount of your asset and the capitalization limit of your business.
Cost vs. Expenses in Accounting
In accounting, costs are used in reference to and specifically for business assets, especially for depreciable assets. The cost of an asset includes each cost that was involved in the buying, delivering, and setting up of the asset.
It also includes the cost incurred in training employees to use it. It is on your business’s balance sheet that the costs are accounted for. First, the original cost would be reported, then accumulated depreciation would be subtracted from it, with the result giving you the book value of your asset.
In contrast, expenses in accounting are used for determining profit. To calculate your business’s profit, your expenses would simply be subtracted from your income.
However, what needs to be remembered here is that your accountant would be looking at two types of expenses here- fixed expenses (those expenses that needs to be paid every month even if there is no sale) and variable expenses (those expenses which depend on your number of sales, and hence changes with changes in your level of sales).
The benefit of keeping track of both of your expenses while undertaking your accounting is that it will help you know the break-even point for your profit, hence giving you the levels at which you can maximize your profit margin.
Additionally, it will also give you valuable insights on where you can minimize your expenses and save your budget when you need to do so. Expenses are accounted for in your business’s income statement. In fact, as directed by your respective taxation governments, necessary business expenses can be deducted from your taxable income.
Types of Expenses in Accounting
While all types of expenses will affect your financial statements, they will affect your income statement the most. The five major headings under which expenses are reported on your income statement are:
- Cost of Goods Sold
- Operating Expenses
- Financial Expenses
- Extraordinary Expenses
- Non-Operating Expenses
However, there are more types of expenses that your business will incur and which are not recorded in your income statement directly. All these varied types of expenses in your business’s accounting are:
Cost of Goods Sold
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) is the costs incurred while acquiring raw materials and then turning them into finished goods. COGS, however, does not include selling and administrative costs as incurred by your whole company, nor does it include interest expense or loss on extraordinary items.
- For manufacturing firms, COGS includes direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead.
- For a service company, COGS is called the cost of services.
- For a company that sells goods and services, it is known as the cost of sales.
Operating Expenses- Selling/General and Administrative
Operating expenses are those expenses that are incurred while selling goods and services. It also includes advertising costs, your shop’s rent and salaries of your salespeople.
Under operating expenses, general and administrative costs are those expenses that are incurred while running the core line of your business. These involve R&D, executive salaries, travel and training, and IT expenses.
Financial Expenses
Financial expenses are incurred when your company borrows money from creditors and lenders. These are hence those expenses that are outside of your company’s core business line. For example, interest on money borrowed, loan origination fees.
Extraordinary Expenses
These are the expenses incurred outside your company’s regular business activities and during a large one-time event or transactions. For example, selling land, disposal of a significant asset, laying off of your employees, unexpected machine repairing or replacement.
Non-Operating Expenses
These are those expenses that cannot be linked back to operating revenue. One of the most common examples of non-operating expenses is interest expense. This is because while interest is the cost of borrowing money from a creditor or a bank, they are not generating any operating income. This makes interest payments a part of non-operating expenses.
Non-Cash Expenses
Under the accrual method of accounting, non-cash expenses are those expenses that are not paid for by cash directly. They are, however, recorded in your business’s income statement. For example, depreciation is a non-cash expense because it reduces your net profit while resulting in no cash outflow either. Its accounting transaction would be as follows:
- A debit to a depreciation expense account, a credit to contra asset account-i.e., accumulated depreciation
- On the balance sheet, the book value of that asset is decreased by accumulated depreciation.
Hence, expenses are those income statement accounts that are debited to an account, while a corresponding credit is booked to a contra asset or liability account.
Prepaid Expenses
When your business has paid for an expense in advance, it is not recognized as an expense but rather as an asset that is referred to as “prepaid expenses.” When the related expenses are incurred by your business, the prepaid expense account is credited, and the corresponding expense account is debited.
For example, your company paid its rent for the entire year in advance in January itself. At that time, this amount would be recorded as a prepaid rent asset account. At the end of each month, however, when a month’s worth of rent has already been incurred, a portion of prepaid rent will be credited, while simultaneously, rent expense will be debited as recognition of the rent expense incurred.
Accrued Expenses
When your business has incurred an expense but not yet paid for it, a corresponding liability account should be recognized, titled as “accrued expenses.” This will ensure that your expense is recorded in the same period in which it was incurred.
For example, if your company paid its rent for December 2021, in January 2022, and your company recorded rent only when it was actually paid, in that case, rent expense of the year 2021 will become the rent expense of the year 2022 overstated.
Fixed Expenses
They are those expenses that will not change over a period of time and are paid for as agreed in an agreement between the concerned parties. Even if fixed expenses do change, it would be only by a small margin. Also, fixed expenses are not dependent on the number of units you produce or sell. For example, rent, salaries, benefits, fixed wages.
Variable Expenses
These are those expenses that vary a lot, mostly from month to month, and are part of your company’s largest expenses chunk. Variable expenses are dependent on the number of units you produce or sell. For example, payroll of a company that hires a large amount of freelancers, overtime expenditure, commissions, etc.
How are Expenses Recorded in Accounting?
You would have to break down your business’s expenses and revenue in your income statement. However, there are several nitty gritty to be understood when accounting for your expenses.
For example, if you have purchased an asset at an amount that is less than the capitalization limit of your business, then it is to be recorded as an expense in one go. However, if the purchase amount of your asset is higher than your business’s capitalization limit, then it has to be recorded as an asset and charged to expense later on when the asset is being used.
The most common transactions that accounting for expenses tend to involve are:
- Debit to expense, credit to cash- Reflects a cash payment.
- Debit to expense, credit to accounts payable- Reflects a purchase made on credit.
- Debit to expense, credit to asset account- Reflects the charging of expense on an asset. For example, charging depreciation on a fixed asset.
- Debit to expense, credit to other liabilities account- Reflects a payment that does not involve trade payables like interest payment on a loan, accrued expense, etc.
Therefore, based on whether you are following the accrual method of accounting or cash method of accounting, your bookkeeper or accountant will record your expenses accordingly.
Cash Method of Accounting
When your business is following the cash method of accounting, your expenses will be recorded only when actual cash has been paid. For example, a utility expense incurred by your business in April would be recorded as an expense in April itself if you are following the accrual basis of accounting. However, because you are following the cash method of accounting, that expense would be recorded in May, when you paid actual cash for covering it.
Accrual Method of Accounting
In contrast, if your business is following accrual accounting, then the expense for the goods or service will be recorded when its legal obligation is fulfilled, i.e., when the services have been provided, and the goods have been received.
Accrual accounting is based on the matching principle- which means that expenses are recognized in the same time period in which related revenues are recognized. This ensures that accurate profits get reflected during each accounting period.
For example, if your goods are sold in February, then the related cost of goods sold as well as revenue will get recorded in the same month. In fact, under this method of accounting, if your business has incurred a minor amount of expense that will not be used for a long period of time, the whole amount would be recorded as an expense at once. This will save your accounting staff the hassle of having to treat it as an asset and then track and record its expenses.
An Example of Expenses and Its Accounting
When looking at Amazon’s 2017 Income Statement, which lists their main categories of expenses, you would be able to see that Amazon has separated its costs into 2 categories:
- Operating Expenses - the cost of sales, marketing, fulfillment, technology, and content, general and administrative, etc.
- Non-Operating Expenses - interest expense (and income), other expenses (and income)
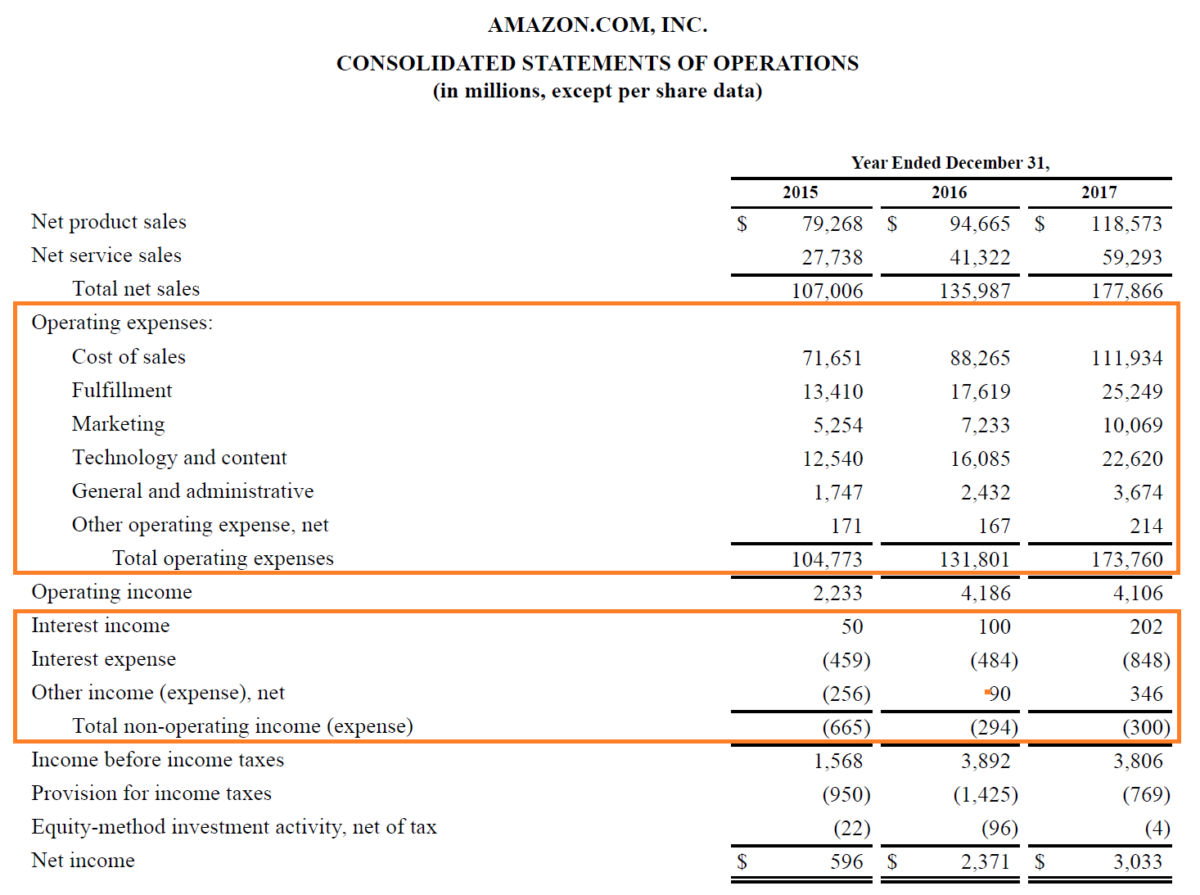
Amazon has even charged a provision of income taxes as per the income tax bracket it is applicable for. Additionally, it has even accounted for its equity method investment activity.
How AI Streamlines Financial Management
AI-powered systems help streamline everything from tracking expenses to managing budgets and analyzing spending patterns. With automation and intelligent data analysis, businesses gain clarity and control over their financial health.
It also enables faster reporting and greater accuracy across finance functions. Whether you're a small business or an established enterprise, integrating AI into your financial workflows improves consistency, transparency, and strategic focus—making financial management simpler, smarter, and more scalable.
How Can Deskera Help You With Accounting of Your Expenses?
To make accounting of your expenses a hassle-free process, you should use Deskera Books. Deskera Books is online accounting software that will make your processes of financial reporting and auditing easier, faster, and more efficient.
Deskera Books also comes with pre-configured tax codes, accounting rules, and charts of accounts. This will make sure you do not miss out on the benefits from tax-deductible expenses. Additionally, it will keep track of all your expenses and keep your financial statements and financial KPIs updated in real-time.
Lastly, you can even make your bookkeepers or accountants, or CPAs a part of your Deskera Books account by giving them access through an invitation link. Hence, with Deskera Books, you can focus on other activities of your business like winning customer loyalty, increasing sales, and getting positive customer feedback, while the software takes care of all your accounting needed for reporting and compliance.
Key Takeaways
Expenses in accounting are incurred for earning revenue either immediately or in the near future- depending on the type of expenses you have incurred and the type of business that you own.
Usually, expenses are accounted for in your business’s income statement. However, there are some which are non-cash expenses like depreciation, in which case they are accounted for in other relevant financial statements.
The several types of expenses are:
- Cost of Goods Sold
- Operating Expenses
- Financial Expenses
- Extraordinary Expenses
- Non-Operating Expenses
- Non-Cash Expenses
- Prepaid Expenses
- Accrued Expenses
- Fixed Expenses
- Variable Expenses
When it comes to accounting, depending on whether you are following a cash method of accounting or an accrual method of accounting, the accounting of your expenses gets determined, with the type of expense also playing an important role in how it will be accounted for.
What also needs to be noted is that while all expenses that your business will incur cannot be tax-deductible expenses, some would be. These expenses include depreciation, amortization, salaries, rent, wages, marketing, advertising, promotion, etc. Which expenses are tax-deductible and which are not vary from region to region and country to country. The best way thus to have an efficient accounting of your expenses is through using Deskera Books.
Related Articles













