What if your manufacturing process could be managed with a single system that optimizes everything from production planning to inventory control? This is exactly what the ERP Manufacturing Module offers. As manufacturers face increasing complexity in managing operations, the need for an integrated solution becomes vital. An ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) manufacturing module serves as a powerful tool that connects every aspect of your production line, ensuring seamless coordination and efficiency.
The ERP Manufacturing Module provides functionalities such as production scheduling, resource allocation, shop floor management, and quality control—all within one platform. This allows manufacturers to streamline processes, improve decision-making, and reduce waste, leading to better overall productivity. It also integrates with other key business functions like accounting and human resources, giving a 360-degree view of the entire manufacturing cycle.
One solution that stands out is Deskera ERP, designed to offer comprehensive features tailored to manufacturing businesses. Deskera’s ERP manufacturing module includes production planning, material requirements planning (MRP), inventory management, and demand forecasting. Additionally, its AI-powered assistant, David, helps with real-time data analytics and decision-making, making it an ideal choice for modern manufacturers seeking efficiency and agility.
In the following sections, we’ll dive deeper into the core functionalities of an ERP manufacturing module, explore its benefits, and look at how integrating this system can transform your manufacturing operations. Whether you're a small manufacturer or a large-scale operation, understanding how ERP manufacturing modules work is key to staying competitive in today’s market.
What is ERP Manufacturing Module?
An ERP Manufacturing Module is a specialized component of an ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system designed to manage and streamline all aspects of the manufacturing process. It integrates various production activities—such as production planning, scheduling, inventory management, and quality control—into a single platform, allowing businesses to optimize their operations more efficiently.
This module enables manufacturers to automate and manage key tasks like raw material procurement, work-in-progress tracking, resource allocation, and production forecasting. By providing real-time data and analytics, the ERP manufacturing module helps businesses reduce waste, minimize production downtime, and improve overall productivity.
It also facilitates better collaboration across departments like supply chain, finance, and human resources, ensuring that the entire production cycle is aligned with broader business goals.
In essence, an ERP manufacturing module centralizes the entire manufacturing operation, providing insights that lead to more informed decision-making and greater efficiency.
Core Features of the ERP Manufacturing Module
The core features of the ERP for manufacturers are designed to streamline manufacturing processes, improve efficiency, and enhance production quality. Below are the key features:
1. Production Planning and Scheduling
The module helps optimize production by planning resources, managing work orders, and scheduling tasks efficiently. It allows manufacturers to balance workloads, minimize bottlenecks, and maximize throughput while meeting production deadlines.
2. Inventory Management
Tracks raw materials, work-in-progress (WIP), and finished goods in real-time. It helps maintain optimal stock levels, avoid overstocking, and ensure materials are available when needed, reducing production delays.
3. Bill of Materials (BOM) Management
The module manages the bills of materials (BOM), which lists all raw materials, components, and assemblies required for production. It ensures accurate material requirements, helping avoid shortages or excesses during production runs.
4. Shop Floor Control
Provides real-time visibility into the shop floor by monitoring machines, workers, and processes. It tracks production progress, machine performance, and labor efficiency, allowing manufacturers to adjust processes as needed.
5. Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
Automates the procurement of materials based on demand forecasts, production schedules, and inventory levels. MRP helps ensure the timely availability of materials, minimizing production delays and reducing excess inventory.
6. Quality Management
Ensures consistent product quality by automating quality checks at various production stages. This feature helps manufacturers comply with industry standards and reduces defects by identifying issues early in the process.
7. Cost Control and Reporting
Tracks production costs, including labor, materials, and overheads, allowing for better cost management and profitability analysis. Detailed reports provide insights into production efficiency, resource utilization, and overall performance.
8. Maintenance Management
Schedules and tracks maintenance tasks for machinery and equipment to reduce downtime and avoid unexpected breakdowns. This feature helps ensure smooth production operations by maintaining equipment in optimal condition.
9. Supply Chain Integration
Integrates with supply chain management to synchronize procurement, production, and distribution processes. It enables seamless coordination with suppliers, ensuring timely material deliveries and optimized supply chain operations.
10. Real-time Data and Analytics
Provides real-time data on production performance, inventory levels, and resource utilization. Advanced analytics tools offer insights into operational efficiency, enabling manufacturers to make data-driven decisions.
These features help manufacturers enhance productivity, reduce costs, and maintain a competitive edge by automating and optimizing various aspects of the manufacturing process.
Benefits of Implementing ERP in Manufacturing
Implementing an ERP system in manufacturing offers numerous benefits that streamline operations and enhance overall efficiency. By incorporating a comprehensive manufacturing ERP system, businesses can optimize their production processes and improve decision-making.
Here are some key benefits:
1. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
One of the primary advantages of using the manufacturing module in ERP is the automation of manual processes. By integrating various functions—such as production planning, inventory management, and resource allocation—manufacturers can significantly reduce errors and repetitive tasks. This automation allows employees to focus on more critical areas of the business, leading to higher productivity.
2. Real-Time Data and Visibility
The manufacturing module of ERP provides real-time data on production activities, inventory levels, and supply chain performance. This enhanced visibility enables manufacturers to monitor their operations closely and respond quickly to any disruptions or changes in demand. Having access to real-time insights also improves decision-making, ensuring that resources are used effectively and production schedules are optimized.
3. Better Inventory and Resource Management
One of the features of the manufacturing module in ERP is its robust inventory management system. It helps manufacturers maintain optimal inventory levels by tracking raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods. This reduces the risk of stockouts or overstocking, resulting in smoother production cycles and lower storage costs. Additionally, efficient resource management ensures that labor, machinery, and materials are allocated effectively.
4. Cost Reduction and Financial Control
A manufacturing ERP module integrates financial management tools that track production costs in real-time, including labor, materials, and overheads. This allows businesses to better control their expenses, identify cost-saving opportunities, and improve overall profitability. By reducing waste, production downtime, and inefficiencies, ERP systems help manufacturers lower their operational costs.
5. Improved Quality Control
Quality management is another critical component of the manufacturing module in ERP. Automated quality checks throughout the production process ensure that products meet the required standards and regulatory compliance. This reduces the likelihood of defects and recalls, helping manufacturers maintain high levels of customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
6. Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
An integrated manufacturing ERP system promotes better collaboration across departments by centralizing data and processes. Whether it’s production, procurement, or finance, all teams work from the same platform, leading to smoother communication and fewer misunderstandings. This also helps in faster response times to market changes or customer demands.
7. Scalability and Flexibility
The manufacturing ERP module is designed to grow with your business. As manufacturing needs evolve, the system can be scaled to handle increased production volumes, new product lines, or changes in operational strategy. The flexibility of the manufacturing module in ERP ensures that businesses can adapt quickly to market demands without needing to overhaul their entire system.
8. Regulatory Compliance and Reporting
In industries where strict regulations and standards must be met, the manufacturing module of ERP helps businesses stay compliant. It automates the tracking and reporting of production processes, quality standards, and material usage, ensuring that manufacturers meet industry regulations such as ISO, FDA, or OSHA standards. ERP systems also provide detailed audit trails, making compliance reporting seamless and transparent.
9. Seamless Integration with Other Business Functions
One of the standout features of the manufacturing module in ERP is its ability to integrate seamlessly with other critical business functions such as finance, sales, procurement, and human resources. This integration ensures that all departments are aligned, enabling smooth data flow and improving cross-functional collaboration. It also provides a unified platform for managing the entire business, reducing data silos and boosting overall efficiency.
10. Better Demand Forecasting
The manufacturing ERP module leverages advanced analytics and historical data to predict future demand accurately. This improves production planning, helps maintain optimal inventory levels, and ensures that manufacturers can meet customer orders without delays. By anticipating demand fluctuations, businesses can minimize production downtime and avoid the costs associated with last-minute adjustments or rush orders.
11. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
A well-implemented manufacturing module in ERP contributes directly to higher customer satisfaction. With more accurate production schedules, better quality control, and timely delivery of products, manufacturers can meet customer expectations consistently. The transparency and traceability that ERP systems provide also build trust with customers by ensuring product quality and timely service.
12. Reduced Downtime and Improved Maintenance
The manufacturing ERP module includes maintenance management tools that help track the condition of machinery and equipment. By scheduling preventive maintenance and monitoring equipment in real-time, manufacturers can reduce the risk of unexpected breakdowns and minimize downtime. This not only keeps production lines running smoothly but also extends the lifespan of expensive machinery.
13. Improved Supplier and Vendor Management
Another significant benefit of the manufacturing module of ERP is the improvement in supplier and vendor relationships. By integrating supply chain data with the manufacturing process, ERP systems enable businesses to manage supplier contracts, track vendor performance, and ensure timely procurement of raw materials. This creates stronger, more reliable relationships with key suppliers, leading to better pricing, availability, and on-time deliveries.
14. Customizable Workflows and Automation
The features of the manufacturing module in ERP often include workflow customization, allowing manufacturers to automate specific processes that match their unique business needs. Whether it's automating repetitive tasks or creating custom production workflows, ERP systems improve operational efficiency by ensuring that critical tasks are completed with minimal manual intervention.
Challenges Addressed by ERP in Manufacturing
Implementing an ERP system in manufacturing addresses a wide range of challenges, helping businesses streamline operations and improve overall efficiency.
Below are some of the key challenges resolved by an ERP manufacturing module:
1. Complex Production Processes
Managing complex production processes involving multiple departments, machinery, and timelines can be overwhelming. The manufacturing module of ERP integrates all these processes into a single platform, providing better coordination and minimizing production delays. It ensures that each phase of the production cycle is synchronized, from raw material procurement to finished goods.
2. Inefficient Inventory Management
One of the biggest challenges in manufacturing is maintaining optimal inventory levels—having too much stock leads to excess costs, while too little causes production delays.
The manufacturing ERP module addresses this by offering real-time inventory tracking, demand forecasting, and automated material requirements planning (MRP), ensuring materials are available when needed without overstocking.
3. Limited Visibility and Data Silos
In many manufacturing environments, data is often scattered across various departments, leading to poor visibility and delayed decision-making. An ERP manufacturing module centralizes data, providing real-time insights into production performance, inventory levels, costs, and more.
This improved visibility helps managers make data-driven decisions faster and ensures alignment between different departments like finance, procurement, and operations.
4. Production Downtime and Maintenance Issues
Unexpected equipment breakdowns can halt production, leading to lost revenue and missed deadlines. ERP systems address this by offering maintenance management tools that track equipment performance and schedule preventive maintenance. This reduces unplanned downtime and ensures that machinery is running optimally, contributing to a more efficient manufacturing process.
5. Quality Control Challenges
Maintaining product quality while scaling production can be a challenge. The manufacturing module in ERP helps automate quality control processes, ensuring that quality checks are performed consistently at every stage of production. This minimizes defects and ensures compliance with industry standards, resulting in higher-quality products and fewer customer returns.
6. Compliance with Industry Regulations
Manufacturers often have to navigate complex regulatory requirements, from safety standards to environmental regulations. The ERP manufacturing module helps manage compliance by automating reporting and ensuring that all processes meet industry standards. It creates audit trails and tracks certifications, helping manufacturers avoid penalties and stay compliant with legal regulations.
7. Lack of Real-Time Data for Decision-Making
Without real-time data, decision-making can be slow and reactive, leading to missed opportunities or inefficient production processes. ERP systems solve this by providing live data from the shop floor, allowing manufacturers to track performance metrics like machine utilization, labor efficiency, and production progress. This enables proactive decision-making and faster responses to changing market conditions.
8. High Production Costs
Controlling production costs is a constant challenge for manufacturers. An ERP manufacturing module helps by tracking labor, materials, and overhead costs in real-time, allowing businesses to identify inefficiencies and reduce waste. The system also offers cost analysis and reporting features that help manufacturers optimize resource allocation and achieve better cost control.
9. Inconsistent Supplier Management
Managing relationships with multiple suppliers can be complex, especially when trying to ensure timely deliveries of raw materials. ERP systems address this by integrating supplier management into the overall production planning process. The manufacturing module of ERP allows businesses to monitor supplier performance, track lead times, and manage procurement contracts more effectively, leading to smoother operations.
10. Scaling Operations
As manufacturing businesses grow, managing an expanding production line becomes increasingly difficult. The manufacturing ERP module offers scalability, allowing manufacturers to adapt their systems to handle increased demand, new products, or expanded operations. Whether you’re adding new production lines or entering new markets, ERP systems ensure that processes remain efficient as the business scales.
11. Communication Gaps Between Departments
Manufacturing operations often involve coordination between multiple departments, such as production, sales, procurement, and finance. Poor communication between these departments can lead to delays and errors.
ERP systems centralize communication by ensuring that all departments are connected on a single platform, allowing for smooth information sharing and reducing misunderstandings.
Types of ERP Manufacturing Modules
There are various types of ERP manufacturing modules designed to address specific aspects of the manufacturing process. Each module serves a unique function, helping manufacturers streamline operations, improve efficiency, and optimize resource management.
Below are the primary types of manufacturing modules in ERP:
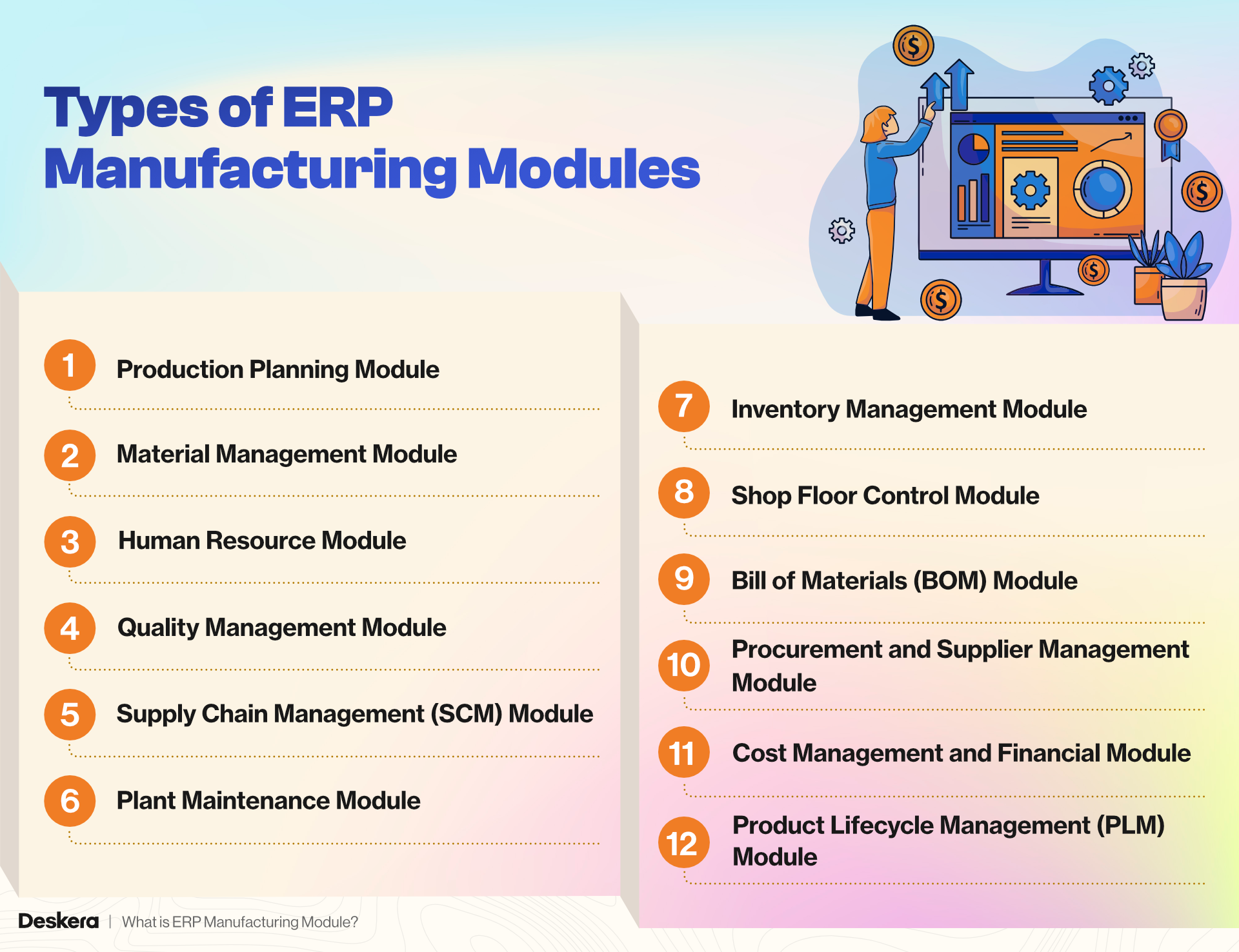
1. Production Planning Module in ERP
The production planning module in ERP helps manufacturers efficiently plan and schedule production activities. It forecasts demand, allocates resources, and optimizes the use of labor and machinery to ensure smooth production processes. This module allows for real-time adjustments based on changing demands or disruptions, ensuring that deadlines are met and production runs efficiently.
2. Material Management Module in ERP
The material management module in ERP focuses on the procurement and management of materials throughout the production process. It tracks raw materials, components, and finished goods, ensuring optimal inventory levels are maintained.
By automating inventory replenishment and integrating with production planning, this module helps prevent overstocking and stockouts, thereby reducing costs and enhancing operational efficiency.
3. Human Resource Module in ERP
The human resource module in ERP manages all aspects of workforce management, including recruitment, training, payroll, and performance management.
In manufacturing, this module ensures that the right personnel are available for production tasks and helps track labor costs associated with manufacturing processes. By integrating HR with production scheduling, manufacturers can optimize labor allocation and improve workforce productivity.
4. Quality Management Module
The quality management module in ERP is responsible for maintaining high product quality throughout the manufacturing process. It automates quality checks at various stages of production to ensure compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements.
This module helps manufacturers track quality-related data, identify defects early, and implement corrective actions to enhance product quality and reduce customer returns.
5. Supply Chain Management (SCM) Module
The SCM module manages the entire supply chain, from procuring raw materials to delivering finished goods to customers. It integrates procurement, inventory, and logistics to ensure smooth supply chain operations.
The manufacturing module of ERP enables manufacturers to manage supplier relationships, track lead times, and optimize the flow of materials throughout the supply chain.
6. Plant Maintenance Module in ERP
The plant maintenance module in ERP focuses on maintaining and managing manufacturing equipment and facilities. It schedules preventive maintenance, tracks machine performance, and logs repair histories to minimize downtime.
By ensuring that equipment is in optimal condition, this module helps manufacturers reduce unexpected breakdowns and extend the lifespan of machinery, contributing to more efficient production processes.
7. Inventory Management Module
The inventory management module is essential for tracking and controlling inventory levels across various stages of the manufacturing process. It monitors raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods to ensure that manufacturers have the necessary resources when needed.
By automating inventory tracking and replenishment, this module helps prevent stockouts and overstock situations, reducing carrying costs and enhancing operational efficiency.
8. Shop Floor Control Module
The shop floor control module provides real-time monitoring and management of production activities on the shop floor. It tracks machine performance, labor efficiency, and the progress of production orders, allowing manufacturers to identify bottlenecks and improve overall operational efficiency. This module integrates with other manufacturing modules in ERP to ensure that production goals are met and resources are utilized effectively.
9. Bill of Materials (BOM) Module
The BOM module manages the detailed list of materials, components, and instructions required to manufacture a product. It helps manufacturers keep track of the raw materials and subassemblies needed for production, ensuring accurate cost estimates and efficient resource planning. The BOM module integrates with inventory, procurement, and production planning to streamline operations.
10. Procurement and Supplier Management Module
This module handles purchasing and supplier management activities. It automates purchase orders, monitors supplier performance, and ensures that materials are procured at competitive prices.
By integrating with inventory and production planning, this module helps manufacturers maintain strong supplier relationships and ensure the timely availability of raw materials.
11. Cost Management and Financial Module
This module tracks production costs, including labor, materials, and overhead expenses. It helps manufacturers monitor and control costs throughout the production cycle, providing detailed reports and insights for better financial planning.
By integrating with other ERP manufacturing modules, the cost management module ensures that businesses can maintain profitability and reduce waste.
12. Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) Module
The PLM module manages the entire lifecycle of a product, from initial design to production and end-of-life. It integrates with other ERP modules to track product changes, manage design data, and streamline the manufacturing process.
This module helps manufacturers reduce time-to-market and improve product quality by maintaining accurate design information and ensuring seamless collaboration across departments.
Emerging Trends in ERP Manufacturing Modules
As technology continues to evolve, ERP manufacturing modules are adapting to meet the changing needs of the manufacturing sector.
Here are some emerging trends shaping the future of ERP in manufacturing:
1. Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
The integration of AI and ML into ERP manufacturing modules is revolutionizing how manufacturers analyze data and make decisions. These technologies enable predictive analytics, allowing manufacturers to anticipate demand fluctuations, optimize inventory levels, and improve production scheduling. AI-driven insights help identify inefficiencies in manufacturing processes, enabling continuous improvement and cost reduction.
2. IoT and Smart Manufacturing
The Internet of Things (IoT) is becoming increasingly prevalent in manufacturing environments. IoT-enabled devices collect real-time data from machines and production lines, which can be integrated into ERP systems.
This connectivity allows manufacturers to monitor equipment health, track production progress, and analyze performance metrics.
As a result, manufacturers can implement proactive maintenance strategies and respond quickly to production issues, enhancing overall efficiency.
3. Cloud-Based ERP Solutions
Cloud-based ERP solutions are gaining traction in the manufacturing sector due to their scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. These solutions enable manufacturers to access real-time data from anywhere, facilitating remote collaboration and decision-making.
Additionally, cloud-based ERP systems are easier to implement and maintain, reducing the burden on IT resources and allowing manufacturers to focus on core operations.
4. Enhanced User Experience and Customization
Modern ERP systems are increasingly focused on user experience (UX) and customization. Manufacturers are demanding intuitive interfaces that simplify navigation and reduce training time for employees.
ERP vendors are responding by offering customizable dashboards and modules tailored to specific manufacturing processes. This trend allows manufacturers to create a system that aligns with their unique workflows, enhancing overall productivity.
5. Focus on Sustainability and Circular Economy
As sustainability becomes a priority for businesses, ERP manufacturing modules are incorporating features that support sustainable practices. This includes tools for tracking material usage, waste reduction, and energy consumption.
Additionally, ERP systems are facilitating circular economy practices by enabling manufacturers to manage the lifecycle of products, including recycling and reusing materials. This trend not only helps manufacturers comply with environmental regulations but also appeals to eco-conscious consumers.
6. Blockchain for Enhanced Traceability
Blockchain technology is emerging as a powerful tool for enhancing traceability in manufacturing. By creating a decentralized and immutable ledger, blockchain enables manufacturers to track the origin of materials and components throughout the supply chain.
This level of transparency is crucial for compliance with regulations and for building consumer trust. Integrating blockchain with ERP systems can streamline processes like supplier verification and quality assurance.
7. Mobile ERP Solutions
The demand for mobile access to ERP systems is increasing as manufacturers seek to empower their workforce with real-time data on the go.
Mobile ERP solutions allow employees to access critical information, manage tasks, and collaborate from anywhere, enhancing responsiveness and productivity.
This trend is particularly beneficial for shop floor managers and field technicians who require immediate access to information to make informed decisions.
8. Focus on Cybersecurity
As manufacturing systems become more interconnected, the risk of cyber threats increases. ERP vendors are prioritizing cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data and ensure system integrity.
This includes implementing robust security protocols, regular system updates, and employee training on cybersecurity best practices. Manufacturers are increasingly aware of the importance of safeguarding their systems against potential breaches.
9. Collaborative ERP Systems
Collaborative ERP systems are emerging to facilitate better communication and collaboration among different departments and stakeholders within the manufacturing process.
These systems enable cross-functional teams to work together more effectively, share data, and streamline workflows. By fostering collaboration, manufacturers can improve decision-making, enhance innovation, and accelerate time-to-market for new products.
10. Data-Driven Decision Making
The trend toward data-driven decision-making is transforming how manufacturers operate. ERP manufacturing modules are increasingly equipped with advanced analytics tools that provide actionable insights based on historical and real-time data.
Manufacturers are leveraging these insights to optimize processes, enhance productivity, and drive strategic initiatives, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and competitiveness.
ERP Manufacturing Module vs. Standalone Manufacturing Software
In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing technology, businesses often face a critical decision: whether to implement an ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) manufacturing module or to invest in standalone manufacturing software.
Both options offer unique advantages and challenges, and understanding their differences is essential for making an informed choice.
Here’s a detailed comparison of ERP manufacturing modules and standalone manufacturing software.
1. Integration and Scope
- ERP Manufacturing Module: An ERP manufacturing module is part of a broader ERP system that integrates various business functions, such as finance, human resources, supply chain, and customer relationship management. This integrated approach ensures that data flows seamlessly across departments, providing a holistic view of operations. For instance, production planning in the manufacturing module can automatically inform inventory management and procurement processes.
- Standalone Manufacturing Software: In contrast, standalone manufacturing software is specifically designed to address manufacturing processes without the integration of other business functions. While it may offer robust features tailored to manufacturing, it often lacks the cross-departmental integration found in ERP systems. This can lead to data silos, where information is not easily shared across departments, potentially hindering collaboration and decision-making.
2. Customization and Flexibility
- ERP Manufacturing Module: ERP systems tend to be less flexible when it comes to customization, as they are designed to support a wide range of industries and processes. However, many modern ERP solutions offer configurable options that allow businesses to tailor certain functionalities to their specific needs. This balance of standardization and customization can be beneficial for businesses looking for proven best practices.
- Standalone Manufacturing Software: Standalone solutions often provide more flexibility and customization options tailored to specific manufacturing needs. Businesses can select features that align closely with their unique processes, allowing for a highly specialized solution. However, this can also mean that companies may need to invest more time and resources in implementation and ongoing maintenance.
3. Cost Considerations
- ERP Manufacturing Module: Implementing an ERP manufacturing module typically involves a higher upfront cost due to the complexity of the system and the extensive functionalities it offers. However, it can lead to long-term savings by reducing inefficiencies, improving inventory management, and enhancing overall operational performance.
- Standalone Manufacturing Software: Standalone manufacturing software generally has lower initial costs and may be more accessible for small to mid-sized manufacturers. However, businesses should consider potential hidden costs related to integration with other systems, training, and ongoing support. If companies eventually decide to integrate standalone solutions into a larger ERP system, they may face additional costs and complexities.
4. User Experience and Training
- ERP Manufacturing Module: ERP systems often come with a steeper learning curve due to their comprehensive functionalities and integrated nature. Organizations may require extensive training to ensure employees can navigate the system effectively. However, once trained, users benefit from having a unified platform that provides a complete view of operations.
- Standalone Manufacturing Software: Many standalone solutions offer user-friendly interfaces and streamlined functionalities, making them easier for employees to adopt quickly. This can lead to faster implementation times and less disruption to operations. However, users may find it challenging to access other necessary business information if the standalone software does not integrate with other systems.
5. Scalability
- ERP Manufacturing Module: ERP systems are designed with scalability in mind, making them suitable for growing businesses. As a company expands, it can easily add new modules or functionalities to accommodate increasing complexity. This scalability is particularly beneficial for manufacturers looking to expand operations, enter new markets, or diversify product lines.
- Standalone Manufacturing Software: While some standalone solutions can also scale, they may require additional investments or system changes as the business grows. Companies may find themselves needing to transition to an ERP system in the future to support their expanding operations, leading to additional costs and effort.
6. Reporting and Analytics
- ERP Manufacturing Module: ERP systems typically come equipped with advanced reporting and analytics capabilities that allow manufacturers to track key performance indicators (KPIs), monitor production efficiency, and identify trends across the organization. This data-driven approach supports informed decision-making at all levels of the business.
- Standalone Manufacturing Software: Standalone solutions often offer robust reporting tools specific to manufacturing processes. However, without integrated data from other departments, the insights may be limited to manufacturing metrics only. This can lead to a lack of visibility into overall business performance, making it harder to make strategic decisions.
How to Choose the Right ERP Manufacturing Module
Selecting the right ERP manufacturing module is a critical decision that can significantly impact your organization’s operational efficiency, data management, and overall success. With numerous options available, it’s essential to approach this selection process methodically.
Here are key factors to consider when choosing the right ERP manufacturing module for your organization:
1. Identify Your Business Needs
- Assess Current Processes: Begin by evaluating your existing manufacturing processes and identifying pain points or areas for improvement. Consider factors such as inventory management, production scheduling, and quality control. Understanding your specific needs will help you pinpoint which functionalities are essential in an ERP manufacturing module.
- Future Growth: Consider your business’s growth trajectory. Choose a module that can scale with your operations, accommodating increased production volumes, additional product lines, or new market demands. A flexible ERP system will support your evolving needs.
2. Evaluate Core Features
- Key Functionalities: Review the core features of various ERP manufacturing modules, such as production planning, inventory management, quality control, and supply chain integration. Ensure that the module you select includes functionalities that align with your specific manufacturing processes.
- Customization Options: Check if the ERP system allows for customization to tailor features to your unique requirements. A module that can adapt to your workflows can enhance user experience and overall efficiency.
3. Integration Capabilities
- Seamless Data Flow: Choose an ERP manufacturing module that can integrate with other critical business systems, such as finance, HR, and customer relationship management (CRM). This integration is vital for ensuring seamless data flow across departments, facilitating better collaboration and decision-making.
- Third-Party Integrations: Additionally, consider whether the module supports integration with third-party applications or tools that your organization currently uses. This flexibility can enhance the overall functionality of the ERP system.
4. User Experience and Accessibility
- User-Friendly Interface: An intuitive interface is crucial for employee adoption and productivity. Evaluate the user experience by requesting demos or trials of the ERP manufacturing module to ensure it is easy to navigate and use.
- Mobile Accessibility: Consider whether the ERP system offers mobile access, allowing users to access critical information and manage tasks on the go. This feature can be particularly beneficial for shop floor managers and field personnel.
5. Cost Considerations
- Budget Assessment: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including licensing fees, implementation costs, maintenance, and support. Ensure that the ERP manufacturing module aligns with your budget while providing the necessary features and functionalities.
- ROI Expectations: Consider the potential return on investment (ROI) that the ERP system can deliver. A higher initial cost may be justifiable if the system can significantly enhance efficiency, reduce operational costs, and improve productivity.
6. Vendor Reputation and Support
- Research Vendors: Investigate the reputation of ERP vendors by reviewing customer testimonials, case studies, and industry rankings. A reputable vendor is more likely to provide a reliable and effective solution.
- Support and Training: Evaluate the level of support and training offered by the vendor. Adequate training ensures that your team can effectively utilize the system, and responsive support is essential for addressing any issues that may arise post-implementation.
7. Compliance and Security Features
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the ERP manufacturing module helps you meet industry-specific regulations and compliance standards. Features such as traceability, documentation, and reporting can be crucial in maintaining compliance.
- Data Security: Consider the security measures in place to protect sensitive business data. Look for features like user access controls, data encryption, and regular security updates to safeguard your information.
8. Implementation Process
- Timeline and Resources: Understand the implementation process and timeline for the ERP manufacturing module. A clear plan with defined milestones can help ensure a smooth transition.
- Change Management: Consider the change management strategies the vendor offers to support your team during the implementation phase. Effective communication and training can ease the transition and foster user acceptance.
How Deskera Can Help You?
Deskera offers a comprehensive suite of tools designed to enhance business operations across various domains, making it particularly beneficial for manufacturers.
Here’s how Deskera can help you streamline processes, improve efficiency, and drive growth:
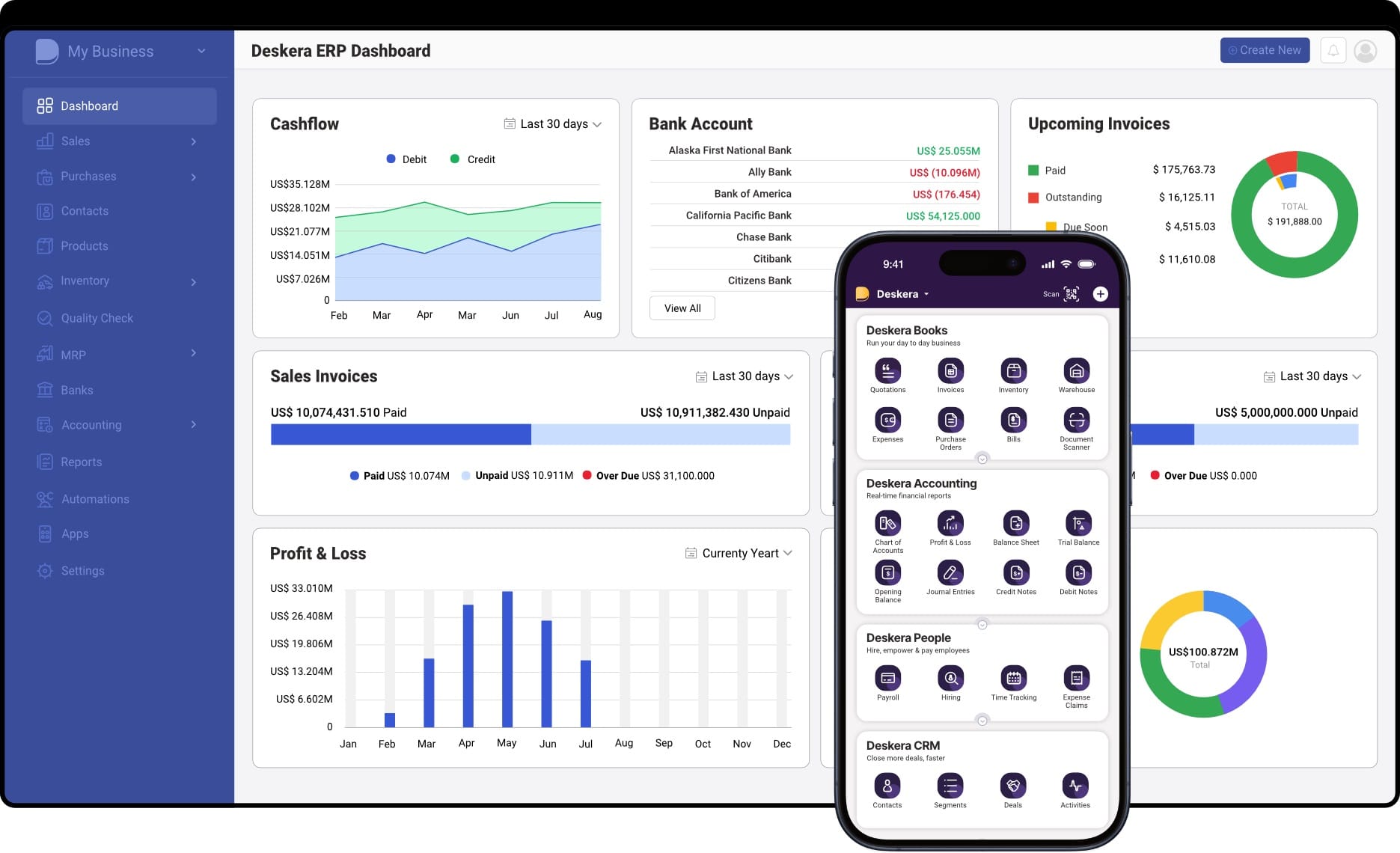
1. Integrated ERP Solutions
- Holistic View of Operations: Deskera’s ERP platform integrates various business functions, including inventory management, production planning, finance, and human resources. This integration provides a unified view of your operations, facilitating better decision-making and collaboration across departments.
- Customizable Modules: With customizable modules tailored to different business needs, Deskera allows you to configure the system according to your specific manufacturing processes. Whether you require a manufacturing module, inventory management, or HR functionalities, Deskera has the flexibility to meet your requirements.
2. Streamlined Inventory Management
- Real-Time Tracking: Deskera’s inventory management module offers real-time tracking of stock levels, enabling you to optimize inventory control and reduce carrying costs. You can easily monitor stock movements, set reorder points, and manage multiple warehouses efficiently.
- Demand Forecasting: By utilizing advanced analytics and demand forecasting features, Deskera helps you anticipate future inventory needs, ensuring that you have the right products available at the right time without overstocking.
3. Enhanced Production Planning
- Efficient Scheduling: Deskera enables efficient production scheduling, allowing you to allocate resources effectively and minimize downtime. You can create production orders, manage work orders, and optimize workflows to enhance overall productivity.
- Quality Control: The platform includes quality management features that allow you to set quality standards, conduct inspections, and maintain compliance with industry regulations, ensuring that your products meet the highest quality standards.
4. Improved Financial Management
- Comprehensive Financial Tools: Deskera’s financial management capabilities include budgeting, expense tracking, and financial reporting. You can gain insights into your financial performance, manage cash flow effectively, and make informed decisions based on real-time financial data.
- Automated Invoicing and Payments: The system automates invoicing and payment processes, reducing administrative burdens and improving cash flow management.
5. Scalability and Flexibility
- Support for Growth: Deskera is designed to grow with your business. Whether you are a small manufacturer or a large enterprise, the platform can scale to accommodate increased production demands, new product lines, and expanded operations.
- Cloud-Based Accessibility: Being a cloud-based solution, Deskera provides accessibility from anywhere, allowing you to manage your operations on the go and collaborate with team members remotely.
6. User-Friendly Interface
- Intuitive Design: Deskera features an intuitive and user-friendly interface that minimizes the learning curve for employees. Training and onboarding processes are simplified, enabling your team to quickly adapt to the system and maximize its potential.
- Mobile App Access: With mobile app capabilities, users can access key features and data from their smartphones or tablets, enhancing productivity and responsiveness.
7. Robust Analytics and Reporting
- Data-Driven Insights: Deskera provides advanced reporting and analytics tools that help you monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) and gain insights into various aspects of your operations. You can analyze trends, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions to optimize performance.
- Customizable Dashboards: The platform allows you to create customizable dashboards tailored to your specific needs, giving you a clear overview of your business metrics in real time.
8. Dedicated Support and Training
- Comprehensive Support: Deskera offers dedicated customer support and resources to assist you during and after the implementation process. Whether you have questions about system features or require technical assistance, their support team is available to help.
Key Takeaways
- The ERP manufacturing module is a crucial component of an ERP system, designed specifically to address the unique challenges of manufacturing operations. It streamlines processes, enhances productivity, and improves visibility across the entire manufacturing supply chain.
- Key features of the manufacturing module in ERP include production planning, inventory management, quality control, shop floor control, and materials management. These functionalities work together to optimize manufacturing processes and drive efficiency.
- Implementing a manufacturing ERP module can lead to numerous benefits, such as improved productivity, enhanced data accuracy, better inventory management, and compliance with industry regulations. These advantages contribute to overall business growth and operational efficiency.
- The ERP manufacturing module effectively tackles common challenges such as inefficient processes, lack of real-time data, difficulties in inventory management, and compliance issues. By providing a centralized system, it enhances visibility and control over operations.
- Various types of modules cater to different manufacturing needs, including materials management, human resources, production planning, plant maintenance, inventory management, and shop floor control. Each module serves a distinct purpose, contributing to a comprehensive ERP solution.
- ERP manufacturing modules help organizations meet compliance and industry standards by providing features that facilitate traceability, documentation, and reporting. This ensures adherence to regulations and enhances operational integrity.
- Current trends in ERP manufacturing modules include the integration of artificial intelligence, automation of processes, and increased focus on sustainability. These trends reflect the evolving landscape of manufacturing and the need for adaptive ERP solutions.
- Compared to standalone manufacturing software, an ERP manufacturing module offers greater integration capabilities, enabling seamless data flow across departments. This holistic approach enhances collaboration and improves decision-making.
- When selecting an ERP manufacturing module, businesses should consider factors such as their specific needs, core features, integration capabilities, user experience, vendor reputation, and cost. A well-informed decision can lead to significant improvements in operational efficiency.
Related Articles