How can modern businesses streamline their operations to stay competitive in today's fast-paced market? The answer lies in leveraging advanced technology, and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are at the forefront of this transformation.
These systems integrate various business processes into a unified platform, providing a holistic view of operations and facilitating seamless management of tasks across different departments. In a world where agility and efficiency are crucial, ERP systems offer a strategic advantage by enabling businesses to coordinate and optimize their operations more effectively.
ERP systems centralize data from disparate sources, allowing for real-time access to critical information and enhancing decision-making capabilities. This centralization helps eliminate data silos and reduces the risk of errors associated with manual data entry.
By automating routine tasks, ERP systems streamline workflows and free up valuable time for employees to focus on more strategic activities. This improved efficiency not only accelerates business processes but also drives overall productivity, making ERP an indispensable tool for modern organizations.
Among the many ERP solutions available, Deskera ERP stands out for its comprehensive suite of features designed to cater to diverse operational needs. Deskera ERP provides a robust platform for managing everything from inventory and supply chain to finance and human resources.
Its intuitive interface and powerful analytics capabilities empower businesses to gain deeper insights into their operations, make informed decisions, and adapt quickly to changing market conditions. Deskera ERP’s flexibility and scalability make it a valuable asset for companies looking to streamline their processes and drive growth.
What is Operations Management?
Operations management is a critical function within an organization that focuses on overseeing, designing, and controlling the processes involved in producing goods and services.
It encompasses a range of activities aimed at optimizing efficiency, quality, and productivity to ensure that the organization's operations run smoothly and effectively.
Key Aspects of Operations Management:
- Process Design and Improvement: Operations management involves designing and refining processes to enhance productivity and quality. This includes setting up workflows, establishing best practices, and continuously improving processes to adapt to changing needs and technologies.
- Resource Management: Effective operations management requires the efficient allocation and utilization of resources, including human resources, materials, and equipment. It ensures that resources are used optimally to meet production goals and minimize waste.
- Supply Chain Management: Operations management plays a crucial role in managing the supply chain, which involves coordinating the flow of goods and services from suppliers to customers. This includes inventory management, procurement, and logistics to ensure timely delivery and cost-effectiveness.
- Quality Control: Ensuring that products and services meet established quality standards is a key aspect of operations management. This involves implementing quality control measures, conducting inspections, and addressing any issues that may affect product or service quality.
- Capacity Planning: Operations managers are responsible for planning and managing capacity to meet demand. This includes forecasting demand, adjusting production schedules, and managing workload to avoid bottlenecks and ensure efficient operation.
- Cost Management: Managing costs effectively is essential for maintaining profitability. Operations management involves budgeting, cost control, and identifying opportunities for cost savings without compromising quality.
In essence, operations management is about making strategic decisions to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of an organization’s processes. By focusing on these core areas, operations managers aim to deliver high-quality products and services, optimize resource use, and enhance overall organizational performance.
ERP in Operations Management
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) in operations management refers to the integration of various business processes and functions within an organization through a centralized software system.
ERP systems are designed to streamline and automate key operational activities, improving efficiency and providing a cohesive view of the entire organization.
Here’s a closer look at how ERP integrates with operations management:
- Integration of Business Processes: ERP systems unify disparate business functions such as inventory management, production planning, supply chain management, and human resources into a single platform. This integration ensures that all departments have access to consistent and accurate data, facilitating better coordination and decision-making.
- Centralized Data Management: One of the core functions of ERP in operations management is to centralize data from various sources. This centralization provides real-time visibility into operations, enabling managers to monitor performance, track key metrics, and make informed decisions based on up-to-date information.
- Automation of Routine Tasks: ERP systems automate routine operational tasks such as order processing, inventory tracking, and production scheduling. By reducing the need for manual intervention, ERP systems minimize errors, increase processing speed, and free up staff to focus on more strategic activities.
- Enhanced Visibility and Reporting: ERP systems offer advanced reporting and analytics capabilities that provide insights into operational performance. Users can generate comprehensive reports, analyze trends, and identify areas for improvement, helping to drive operational efficiency and effectiveness.
- Streamlined Supply Chain Management: In operations management, ERP systems facilitate better management of the supply chain by improving communication with suppliers, optimizing inventory levels, and enhancing logistics planning. This leads to more efficient procurement, reduced lead times, and lower operational costs.
- Improved Resource Allocation: ERP systems help in optimizing resource allocation by providing insights into resource utilization, capacity planning, and demand forecasting. This ensures that resources are allocated effectively to meet production needs and avoid bottlenecks.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Modern ERP systems are scalable and flexible, allowing businesses to adapt to changing operational needs and growth. They can be customized to fit specific industry requirements and expanded as the organization grows.
In summary, ERP in operations management enhances organizational efficiency by integrating and automating various processes, providing real-time data, and improving overall visibility and control. This leads to better resource management, streamlined operations, and a more agile and responsive business environment.
Key Components of ERP Systems for Operations Management
Understanding the key components of ERP systems is crucial for leveraging their full potential in operations management. These components work together to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and provide a comprehensive view of business operations.
By integrating various functionalities into a single platform, ERP systems enable businesses to manage their operations more effectively and adapt to changing needs.
1. Core Modules
Inventory Management
- Purpose: Manages stock levels, tracks inventory movement, and ensures optimal inventory levels.
- Features: Real-time inventory tracking, automated reordering, and stock level alerts.
Production Planning
- Purpose: Coordinates and manages production processes to ensure efficient manufacturing.
- Features: Scheduling, work order management, and resource allocation.
Supply Chain Management
- Purpose: Oversees the flow of goods from suppliers to customers, optimizing procurement and logistics.
- Features: Supplier management, demand forecasting, and logistics coordination.
Order Management
- Purpose: Manages customer orders from entry to fulfillment, ensuring timely and accurate processing.
- Features: Order tracking, customer communication, and invoicing.
2. Integration Capabilities
Financial Management
- Purpose: Integrates financial processes with operational data for accurate financial reporting and analysis.
- Features: General ledger, accounts payable/receivable, and financial reporting.
Human Resources Management
- Purpose: Manages employee data, payroll, and benefits within the ERP system.
- Features: Recruitment, employee records, and performance management.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Purpose: Enhances customer interactions and improves service delivery by integrating customer data.
- Features: Contact management, sales tracking, and customer support.
3. Data Management and Analytics
Real-Time Data Access
- Purpose: Provides instant access to operational data for timely decision-making.
- Features: Dashboards, real-time reporting, and data visualization.
Advanced Reporting
- Purpose: Generates detailed reports and analyses to monitor performance and identify trends.
- Features: Custom report creation, trend analysis, and KPI tracking.
4. Automation and Workflow Management
Automated Processes
- Purpose: Reduces manual intervention by automating routine tasks and processes.
- Features: Workflow automation, task reminders, and automated alerts.
Workflow Optimization
- Purpose: Streamlines and optimizes business workflows to enhance operational efficiency.
- Features: Process mapping, task sequencing, and bottleneck identification.
5. Scalability and Customization
Scalability
- Purpose: Adapts to the growing needs of the business by accommodating increased data and users.
- Features: Modular design, flexible configurations, and capacity expansion.
Customization
- Purpose: Tailors the ERP system to meet specific business requirements and industry standards.
- Features: Customizable modules, user-defined fields, and integration with third-party applications.
By exploring these components, businesses can better understand how ERP systems support efficient operations management, enhance decision-making, and drive overall performance.
The Role of ERP in Operations Management
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems play a pivotal role in operations management by integrating various business functions and processes into a unified platform. This integration enhances the efficiency, accuracy, and visibility of operations, driving overall organizational success.
Here’s a detailed look at the critical roles ERP systems play in operations management:
1. Streamlining Processes
ERP systems streamline business processes by automating routine tasks and coordinating activities across different departments.
By providing a centralized platform for managing operations, ERP systems reduce the complexity and redundancy associated with traditional, siloed approaches.
This streamlining results in smoother workflows, faster processing times, and a more cohesive operational strategy.
2. Centralizing Data
One of the key benefits of ERP systems is their ability to centralize data from various sources within the organization. This centralized data repository ensures that all departments have access to accurate and up-to-date information, which is crucial for effective decision-making.
By eliminating data silos and ensuring data consistency, ERP systems facilitate better collaboration and communication across the organization.
3. Enhancing Visibility and Reporting
ERP systems provide enhanced visibility into operational performance through comprehensive reporting and analytics tools. Users can generate real-time reports, track key performance indicators (KPIs), and analyze trends to gain insights into various aspects of the business.
This improved visibility allows managers to make informed decisions, identify potential issues, and proactively address challenges.
4. Optimizing Resource Management
Effective resource management is a core function of ERP systems in operations management. ERP systems help organizations optimize the allocation of resources such as labor, materials, and equipment.
By providing tools for demand forecasting, inventory management, and production planning, ERP systems ensure that resources are used efficiently and that operational capacities are aligned with business needs.
5. Improving Supply Chain Coordination
ERP systems enhance supply chain management by integrating procurement, inventory, and logistics functions. This integration improves communication with suppliers, streamlines order processing, and optimizes inventory levels.
As a result, businesses can reduce lead times, minimize stockouts and overstock situations, and achieve better coordination with their supply chain partners.
6. Facilitating Scalability and Flexibility
As businesses grow and evolve, ERP systems offer the scalability and flexibility needed to adapt to changing operational requirements. ERP systems can be customized and expanded to accommodate new processes, additional users, and increased data volumes. This scalability ensures that the ERP system continues to support the organization’s operational needs as it grows.
7. Enhancing Compliance and Risk Management
ERP systems help organizations manage compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards.
By providing tools for tracking and documenting processes, ERP systems facilitate adherence to compliance requirements and reduce the risk of non-compliance.
Additionally, ERP systems support risk management by providing insights into potential operational risks and enabling proactive mitigation strategies.
Benefits of ERP in Operations Management
Implementing an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system in operations management offers a multitude of benefits that enhance efficiency, accuracy, and overall effectiveness.
Here’s a detailed look at the key advantages of ERP systems:
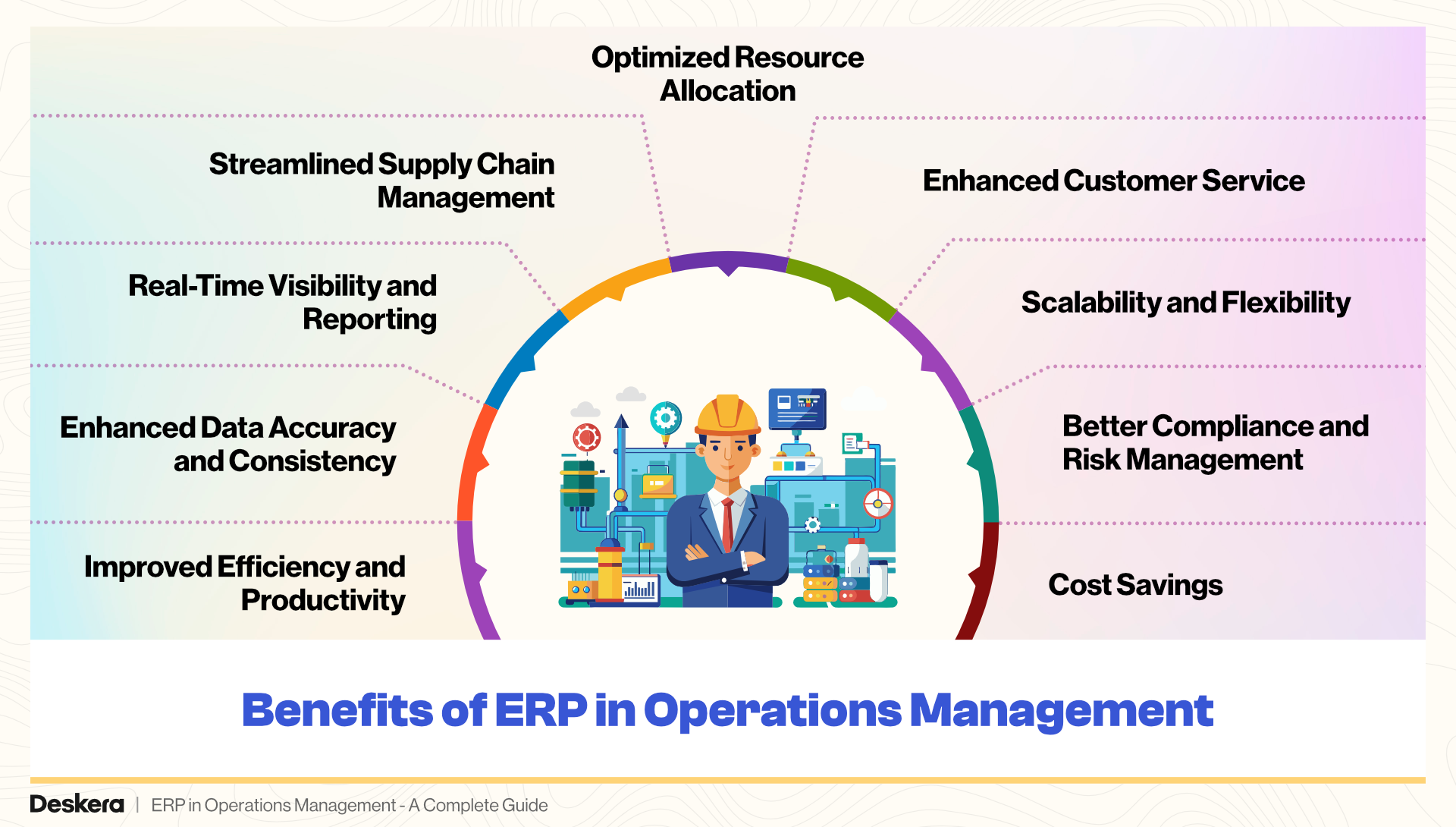
1. Improved Efficiency and Productivity
ERP systems streamline business processes by automating routine tasks and integrating various functions into a unified platform. This automation reduces manual intervention, minimizes errors, and accelerates workflow processes.
As a result, organizations experience increased operational efficiency and productivity, allowing employees to focus on more strategic activities and core business functions.
2. Enhanced Data Accuracy and Consistency
By centralizing data from different departments into a single system, ERP ensures data accuracy and consistency across the organization.
This centralized approach eliminates data silos and reduces the risk of discrepancies that can occur when using multiple, disconnected systems.
Accurate and consistent data improves decision-making and ensures that all departments operate with the same information.
3. Real-Time Visibility and Reporting
ERP systems provide real-time access to operational data and advanced reporting capabilities. This visibility allows managers and executives to monitor performance, track key metrics, and analyze trends in real time.
With up-to-date information at their fingertips, decision-makers can respond quickly to changes, identify potential issues, and make informed decisions that drive business success.
4. Streamlined Supply Chain Management
Effective supply chain management is facilitated by ERP systems through better integration of procurement, inventory, and logistics functions.
ERP systems optimize inventory levels, improve order processing, and enhance communication with suppliers.
This streamlining leads to reduced lead times, fewer stockouts, and lower inventory holding costs, resulting in a more efficient and responsive supply chain.
5. Optimized Resource Allocation
ERP systems help organizations manage and allocate resources more effectively. By providing tools for demand forecasting, production planning, and resource tracking, ERP systems ensure that resources are used efficiently and are aligned with business needs.
This optimization helps prevent overutilization or underutilization of resources, improving overall operational effectiveness.
6. Enhanced Customer Service
With integrated customer relationship management (CRM) capabilities, ERP systems improve customer service by providing a comprehensive view of customer interactions and transactions.
This integration allows businesses to manage orders more effectively, track customer preferences, and provide timely support. Enhanced customer service leads to higher customer satisfaction and customer loyalty.
7. Scalability and Flexibility
ERP systems are designed to scale with the growth of the organization. They can be customized and expanded to accommodate new processes, additional users, and increased data volumes.
This scalability ensures that the ERP system continues to support the organization’s evolving operational needs and adapts to changes in the business environment.
8. Better Compliance and Risk Management
ERP systems assist organizations in maintaining compliance with industry regulations and standards by providing tools for tracking and documenting processes.
This functionality reduces the risk of non-compliance and helps organizations manage operational risks more effectively.
Additionally, ERP systems support risk management by providing insights into potential risks and enabling proactive mitigation strategies.
9. Cost Savings
By automating processes, reducing manual tasks, and improving resource management, ERP systems contribute to significant cost savings. Efficient operations lead to reduced operational costs, minimized errors, and optimized resource utilization.
Additionally, the improved supply chain management and inventory control facilitated by ERP systems contribute to lower overall expenses.
How ERP Works in Operations Management
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are integral to modern operations management, providing a comprehensive framework for integrating and optimizing various business processes.
Here’s an overview of how ERP systems work in operations management:
1. Centralized Data Integration
ERP systems centralize data from various departments and functions into a unified database. This centralization ensures that all departments, such as finance, inventory, production, and sales, have access to the same, up-to-date information.
By integrating data across different functions, ERP systems eliminate data silos and ensure consistency, which enhances communication and decision-making across the organization.
2. Automated Processes
One of the core functionalities of ERP systems is the automation of routine tasks. ERP automates various operational processes, such as order processing, inventory management, and financial transactions. This automation reduces manual data entry, minimizes errors, and speeds up transaction processing.
For example, when a sales order is entered into the system, ERP automatically updates inventory levels, generates invoices, and triggers shipping processes.
3. Real-Time Data Access
ERP systems provide real-time access to operational data, allowing managers and executives to monitor performance and make informed decisions. Through dashboards and reporting tools, users can view real-time metrics, track key performance indicators (KPIs), and analyze trends.
This real-time visibility helps organizations respond quickly to changes, identify potential issues, and adjust strategies as needed.
4. Integrated Workflow Management
ERP systems facilitate integrated workflow management by coordinating activities across different departments.
For example, when a customer places an order, the ERP system coordinates with inventory management to check stock levels, with production planning to schedule manufacturing, and with logistics to arrange delivery.
This integration ensures that all processes are aligned and that the workflow is streamlined, improving overall operational efficiency.
5. Resource Planning and Optimization
ERP systems support resource planning and optimization by providing tools for demand forecasting, capacity planning, and inventory control.
ERP helps organizations forecast future demand based on historical data and market trends, plan production schedules to meet this demand, and manage inventory levels to avoid overstocking or stockouts.
This planning and optimization ensure that resources are used efficiently and aligned with business needs.
6. Enhanced Communication and Collaboration
ERP systems enhance communication and collaboration within the organization by providing a shared platform for data and processes. Employees across different departments can access the same information, collaborate on projects, and share insights. This improved communication reduces the risk of misunderstandings and ensures that everyone is working towards common goals.
7. Scalability and Customization
ERP systems are designed to be scalable and customizable, allowing organizations to adapt the system to their specific needs and growth.
Organizations can add new modules or functionalities as their requirements evolve and customize the system to fit their unique processes and industry standards.
This scalability ensures that the ERP system continues to support the organization’s operational needs as it expands.
8. Compliance and Risk Management
ERP systems help manage compliance and risk by providing tools for tracking and documenting processes. These features ensure that organizations adhere to industry regulations and standards.
ERP systems also support risk management by providing insights into potential risks and enabling proactive measures to mitigate them.
Implementation Considerations for ERP Systems in Operations Management
Implementing an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system is a significant decision that can profoundly impact an organization’s operations management.
Successful ERP implementation requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure that the system aligns with the organization’s needs and delivers the desired benefits.
Here are crucial considerations to keep in mind:
1. Choosing the Right ERP System
Selecting the right ERP system is critical for effective operations management. Here are key factors to consider when choosing an ERP system:
- Business Requirements: Assess the specific needs of your organization, including the size, industry, and unique operational challenges. Ensure the ERP system can address these requirements and scale with your business.
- Functionality: Evaluate the core functionalities of the ERP system, such as inventory management, production planning, and financial management. Choose a system that offers the features essential for your operations.
- User-Friendliness: Consider the ease of use and user interface of the ERP system. A system that is intuitive and user-friendly will facilitate smoother adoption and reduce the learning curve for employees.
- Vendor Reputation: Research the reputation of ERP vendors, including their track record, customer support, and post-implementation services. Opt for a vendor with a proven history of successful ERP implementations.
- Cost: Analyze the total cost of ownership, including licensing, implementation, customization, and ongoing maintenance costs. Ensure the ERP system fits within your budget while meeting your operational needs.
2. Customization and Integration
Customization and integration are crucial for ensuring that the ERP system aligns with your existing processes and maximizes its value:
- Customization: Tailor the ERP system to fit your organization’s specific processes and workflows. Customization allows the system to address unique business requirements and optimize operations according to your needs.
- Integration: Ensure the ERP system integrates seamlessly with existing software and systems within your organization. This integration facilitates data flow between systems, reduces duplication of efforts, and improves overall efficiency.
- Data Migration: Plan for the migration of data from existing systems to the new ERP system. Accurate and complete data migration is essential for maintaining data integrity and ensuring continuity in operations.
- Testing: Conduct thorough testing of the ERP system before full deployment. Testing helps identify and address potential issues, ensuring that the system functions as expected and meets your operational requirements.
3. Training and Support
Effective training and ongoing support are vital for the successful implementation and utilization of an ERP system:
- Training: Provide comprehensive training for employees to ensure they understand how to use the ERP system effectively. Training should cover all relevant functionalities and processes, tailored to different user roles within the organization.
- Support: Establish a support structure for addressing any issues that arise during and after implementation. This support may include technical assistance, troubleshooting, and regular updates to ensure the system remains effective and secure.
- Change Management: Implement a change management strategy to help employees adapt to the new ERP system. Communicate the benefits of the system, involve key stakeholders in the implementation process, and address any concerns or resistance.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and assess the performance of the ERP system. Seek feedback from users, identify areas for improvement, and make necessary adjustments to enhance the system’s effectiveness.
Challenges and Solutions in ERP Implementation
Implementing an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system can transform operations management, but it also comes with its set of challenges.
Understanding these challenges and knowing how to address them effectively is crucial for ensuring a successful ERP implementation.
Here’s a look at common challenges faced during ERP implementation and usage, along with practical solutions and best practices to overcome them.
Common Challenges
- Resistance to Change
- Issue: Employees may resist adopting new systems due to comfort with existing processes or fear of the unknown.
- Impact: Resistance can hinder the successful implementation and integration of the ERP system.
- Data Migration Issues
- Issue: Migrating data from legacy systems to the new ERP system can be complex and prone to errors.
- Impact: Poor data migration can lead to inaccuracies, data loss, and operational disruptions.
- Customization and Integration Difficulties
- Issue: Customizing the ERP system to fit specific business needs and integrating it with existing systems can be challenging.
- Impact: Inadequate customization and integration can result in misalignment with business processes and inefficiencies.
- Underestimating Costs and Timelines
- Issue: Organizations often underestimate the total cost of ownership and the time required for implementation.
- Impact: Underestimating costs and timelines can lead to budget overruns and project delays.
- Insufficient Training and Support
- Issue: Inadequate training and support can leave users struggling to effectively utilize the ERP system.
- Impact: Poor user proficiency can reduce the effectiveness of the ERP system and hinder its benefits.
- Inadequate Change Management
- Issue: Failing to manage the change process effectively can lead to confusion and resistance among employees.
- Impact: Ineffective change management can result in a lack of buy-in and incomplete adoption of the ERP system.
Solutions and Best Practices
- Implement a Comprehensive Change Management Strategy
- Solution: Develop a robust change management plan that includes clear communication, stakeholder involvement, and support for employees throughout the transition.
- Best Practice: Engage employees early in the process, provide regular updates, and offer incentives to encourage adoption and acceptance of the new system.
- Plan and Execute Thorough Data Migration
- Solution: Prepare a detailed data migration plan that includes data cleansing, mapping, and validation to ensure accuracy and completeness.
- Best Practice: Conduct multiple rounds of testing and validation to identify and resolve data issues before the full migration.
- Prioritize Customization and Integration
- Solution: Work closely with ERP vendors and consultants to customize the system according to your specific needs and ensure seamless integration with existing applications.
- Best Practice: Define clear requirements and objectives for customization and integration, and perform rigorous testing to confirm that all systems work together effectively.
- Develop a Realistic Budget and Timeline
- Solution: Create a comprehensive project plan with realistic estimates for costs and timelines, including contingencies for unexpected issues.
- Best Practice: Regularly review and adjust the budget and timeline as needed, and maintain open communication with stakeholders to manage expectations.
- Provide Extensive Training and Ongoing Support
- Solution: Implement a thorough training program that covers all aspects of the ERP system, and establish a support structure for addressing user questions and issues.
- Best Practice: Offer continuous learning opportunities and updates to keep users proficient with the system, and provide accessible support channels for prompt assistance.
- Adopt Best Practices for Change Management
- Solution: Use change management best practices to facilitate a smooth transition, including clear communication, employee involvement, and feedback mechanisms.
- Best Practice: Develop a change management team to oversee the transition, address concerns, and ensure that the ERP system aligns with organizational goals.
By proactively addressing these challenges with well-planned solutions and best practices, organizations can overcome common obstacles in ERP implementation and maximize the benefits of their ERP systems.
Future Trends in ERP and Operations Management
The landscape of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and operations management is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and shifting business needs. Staying ahead of these trends is crucial for organizations looking to leverage ERP systems for competitive advantage and operational efficiency.
Here’s a look at some of the key future trends shaping ERP and operations management:

1. Increased Adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are set to revolutionize ERP systems by enhancing their capabilities and decision-making processes.
AI can automate routine tasks, predict future trends, and provide advanced analytics, while ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and insights.
This integration will enable more accurate forecasting, improved resource management, and enhanced operational efficiency.
- Trend: AI-powered ERP systems will increasingly offer predictive analytics, intelligent automation, and enhanced data-driven decision-making.
- Impact: Organizations will benefit from smarter, more responsive ERP systems that can adapt to changing business conditions and optimize operations more effectively.
2. Integration of Internet of Things (IoT) Technologies
The Internet of Things (IoT) involves connecting devices and sensors to gather and exchange data in real time.
In ERP systems, IoT integration will provide valuable insights into operations by monitoring equipment performance, inventory levels, and supply chain processes.
This real-time data will enable better decision-making and proactive management of operations.
- Trend: IoT-enabled ERP systems will offer real-time monitoring and analytics capabilities, enhancing visibility and control over operational processes.
- Impact: Improved data accuracy and timeliness will lead to better resource management, reduced downtime, and more efficient supply chain operations.
3. Growth of Cloud-Based ERP Solutions
Cloud-based ERP solutions continue to gain traction due to their scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
The shift to the cloud allows organizations to access ERP systems from anywhere, reduces the need for on-premises infrastructure, and supports remote work and collaboration.
Cloud ERP solutions are also more agile, enabling faster updates and integration with other cloud-based tools and applications.
- Trend: The adoption of cloud-based ERP systems will increase, with a focus on hybrid and multi-cloud strategies to enhance flexibility and scalability.
- Impact: Organizations will benefit from reduced IT costs, increased accessibility, and the ability to scale ERP solutions according to their evolving needs.
4. Focus on Enhanced User Experience and User Interface (UX/UI)
As ERP systems become more integral to daily operations, there is a growing emphasis on improving the user experience and user interface (UX/UI).
Modern ERP solutions are designed to be more intuitive, user-friendly, and customizable, with features such as dashboards, mobile access, and personalized workflows. Enhancing UX/UI will drive higher user adoption and satisfaction.
- Trend: ERP vendors will focus on developing user-centric interfaces with customizable dashboards, mobile capabilities, and streamlined workflows.
- Impact: Improved UX/UI will lead to greater user engagement, reduced training time, and increased productivity.
5. Advancements in Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology offers secure, transparent, and immutable record-keeping capabilities.
In ERP systems, blockchain can enhance supply chain management, contract management, and financial transactions by providing a secure and verifiable way to track and record transactions.
This technology can help reduce fraud, improve traceability, and ensure data integrity.
- Trend: The integration of blockchain technology into ERP systems will support secure and transparent transaction processing and data management.
- Impact: Organizations will benefit from enhanced security, reduced risk of fraud, and improved transparency in supply chain and financial processes.
6. Emphasis on Data Privacy and Compliance
With increasing regulations and concerns around data privacy, ERP systems will need to incorporate robust data protection and compliance features.
Organizations will focus on ensuring that their ERP systems adhere to regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, and other industry-specific standards.
This emphasis on data privacy will be crucial for maintaining trust and avoiding regulatory penalties.
- Trend: ERP systems will integrate advanced data protection measures and compliance features to address evolving privacy regulations and standards.
- Impact: Enhanced data privacy and compliance capabilities will help organizations manage regulatory requirements effectively and protect sensitive information.
7. Rise of Industry-Specific ERP Solutions
As industries become more specialized, there is a growing demand for ERP solutions tailored to specific sectors. Industry-specific ERP solutions offer features and functionalities designed to address the unique challenges and requirements of particular industries, such as manufacturing, healthcare, or retail.
- Trend: The development and adoption of industry-specific ERP solutions will increase, providing tailored functionalities and best practices for various sectors.
- Impact: Organizations will benefit from ERP systems that better align with their industry requirements, leading to improved efficiency and competitive advantage.
How Deskera ERP Can Help You with Operations Management
Deskera ERP is a robust platform designed to streamline and enhance various aspects of operations management. By integrating key functionalities and advanced features, Deskera ERP provides comprehensive support for managing and optimizing your operations.
Here’s how Deskera ERP can help you with operations management:
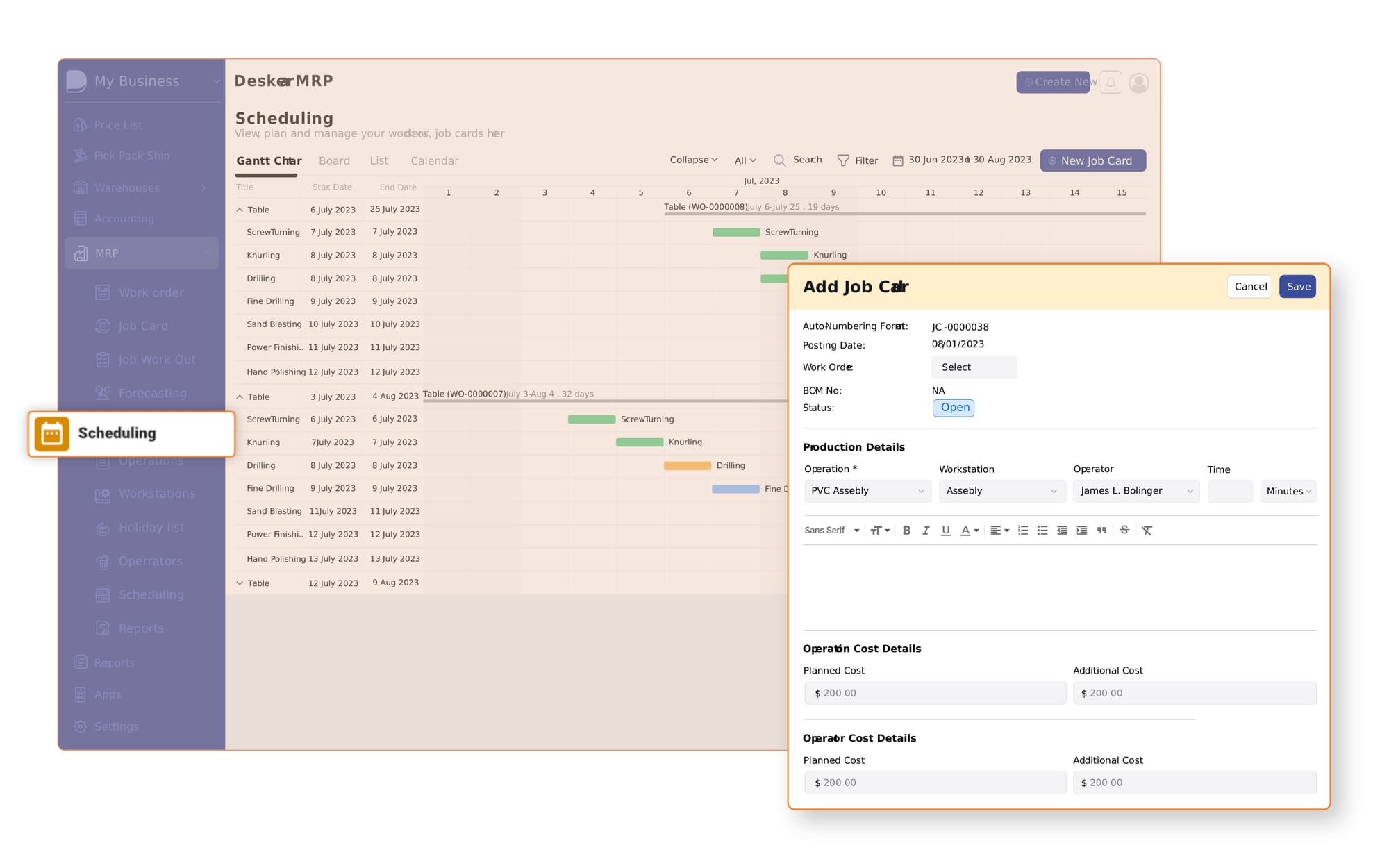
1. Centralized Data and Real-Time Insights
Deskera ERP centralizes data from various departments into a single, unified platform. This centralization ensures that all operational information is consistent and easily accessible. With real-time insights and dashboards, you can monitor performance metrics, track key performance indicators (KPIs), and make informed decisions based on up-to-date information.
- Benefit: Improved data accuracy and real-time visibility into operations enhance decision-making and responsiveness.
2. Streamlined Workflow Automation
Deskera ERP automates routine operational processes, such as order processing, inventory management, and production scheduling. Automation reduces manual data entry, minimizes errors, and accelerates transaction processing. For instance, Deskera ERP automatically updates inventory levels when sales orders are processed, ensuring accurate stock management.
- Benefit: Increased efficiency and reduced operational errors through streamlined workflow automation.
3. Integrated Supply Chain Management
Deskera ERP offers integrated supply chain management features that help you manage procurement, inventory, and supplier relationships. The system enables you to track inventory levels, manage supplier orders, and forecast demand. By integrating these processes, Deskera ERP improves supply chain visibility and coordination.
- Benefit: Enhanced supply chain efficiency and better inventory control through integrated management features.
4. Advanced Production Planning
With Deskera ERP’s production planning capabilities, you can optimize manufacturing processes by scheduling production runs, managing work orders, and tracking production progress. The system provides tools for demand forecasting and capacity planning, ensuring that production aligns with market demand and resource availability.
- Benefit: Improved production efficiency and alignment with demand through advanced planning and scheduling tools.
5. Comprehensive Financial Management
Deskera ERP integrates financial management with operations, allowing you to manage budgets, track expenses, and generate financial reports. By linking financial data with operational processes, you gain a complete view of your organization’s financial health and operational performance.
- Benefit: Better financial oversight and control through integrated financial and operational management.
6. Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
Deskera ERP fosters collaboration and communication across departments by providing a shared platform for data and processes. Employees can access the same information, collaborate on projects, and share insights. This improved communication helps ensure that all teams are aligned and working towards common goals.
- Benefit: Enhanced teamwork and coordination through improved communication and information sharing.
7. Customizable and Scalable Solutions
Deskera ERP is customizable and scalable, allowing you to tailor the system to your specific operational needs and business growth. You can customize workflows, reports, and functionalities to fit your unique requirements and add new features or modules as your organization expands.
- Benefit: Flexibility to adapt the ERP system to your evolving needs and business growth.
8. Robust Reporting and Analytics
Deskera ERP provides robust reporting and analytics tools that enable you to generate detailed reports and analyze operational data. With built-in templates and customizable reports, you can gain insights into various aspects of your operations, such as inventory turnover, production efficiency, and sales performance.
- Benefit: Data-driven decision-making and performance monitoring through advanced reporting and analytics.
9. Mobile Accessibility
Deskera ERP offers mobile accessibility, allowing you to manage operations and access critical information from anywhere. The mobile app ensures that you stay connected and can make decisions on the go, whether you’re on-site or working remotely.
- Benefit: Greater flexibility and accessibility through mobile ERP capabilities.
10. AI-Powered Assistance
Deskera ERP features an AI Assistant, named David, which provides intelligent support for various tasks. AI-driven features, such as predictive analytics and automated recommendations, help optimize operations and enhance decision-making.
- Benefit: Enhanced operational efficiency and strategic insights through AI-powered assistance.
Key Takeaways
- ERP systems are essential for modern businesses looking to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and remain competitive. By integrating various business processes into a unified platform, ERP solutions help optimize operational management and decision-making.
- Operations management involves overseeing and controlling the production and delivery of goods and services. It includes planning, organizing, and optimizing resources to ensure efficient operations that meet organizational goals.
- ERP in operations management refers to using Enterprise Resource Planning systems to manage and optimize functions such as production, inventory, and supply chain processes. ERP systems provide a comprehensive approach to integrating and automating these functions for improved efficiency and coordination.
- Key components of ERP systems for operations management include modules for supply chain management, production planning, inventory control, and financial management. These components work together to provide a holistic view of operations and enhance overall efficiency.
- ERP systems are crucial for operations management as they centralize data, automate workflows, and integrate various processes. This integration enables real-time insights, improved decision-making, and enhanced operational efficiency.
- The benefits of ERP in operations management include increased operational efficiency, streamlined processes, better resource management, and enhanced data accuracy. ERP systems contribute to higher productivity and cost savings through automation and integration.
- ERP systems function by integrating various operational functions into a single platform, providing real-time data, and automating routine tasks. This integration allows for improved coordination, accurate forecasting, and efficient management of resources and processes.
- When implementing an ERP system, it's important to consider factors such as choosing the right system, customizing and integrating it with existing processes, and providing adequate training and support. Proper planning and execution in these areas are crucial for successful ERP implementation.
- Common challenges in ERP implementation include resistance to change, data migration issues, and customization difficulties. Addressing these challenges with effective change management, thorough data migration planning, and strong customization strategies can ensure a successful deployment.
- Future trends in ERP and operations management include increased adoption of AI and ML, integration of IoT technologies, growth of cloud-based solutions, and advancements in data privacy and compliance. Staying informed about these trends will help organizations leverage new technologies and maintain a competitive edge.
Related Articles












