In today's fast-paced and competitive business landscape, small businesses are increasingly recognizing the value of implementing Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems to streamline their operations and stay ahead of the curve.
Despite the common perception that ERP systems are primarily tailored for large corporations, recent statistics reveal a significant uptake among mid-market enterprises, with over 80% of companies utilizing ERP solutions falling within this category.
This shift underscores the growing recognition of ERP systems as invaluable tools for organizations of all sizes, including small businesses, seeking to enhance efficiency, improve decision-making, and drive growth.
Among the diverse array of ERP solutions available, Deskera ERP stands out as a comprehensive and user-friendly option specifically designed to meet the needs of small and mid-sized businesses.
In this exploration of ERP for small businesses, we delve into the myriad benefits of ERP implementation, highlighting how Deskera ERP empowers small businesses to optimize their processes, boost productivity, and thrive in today's competitive market environment.
What is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Software?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software is a type of integrated management system that organizations use to manage and automate many of the business practices associated with the operations or production aspects of a company.
An ERP system helps streamline processes and information across the entire organization, ensuring that data flows seamlessly between different departments. This integration facilitates better coordination and collaboration within the company.
Key components of ERP software typically include:
- Finance and Accounting: Manages the general ledger, accounts payable and receivable, budgeting, and financial reporting.
- Human Resources (HR): Handles payroll, recruitment, employee records, and benefits administration.
- Manufacturing and Production: Oversees production planning, scheduling, and management, along with quality control and inventory management.
- Supply Chain Management: Manages procurement, inventory, order processing, and supplier relationships.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Manages sales, customer interactions, service requests, and marketing activities.
- Project Management: Tracks project schedules, resources, budgets, and performance metrics.
- Business Intelligence (BI): Provides analytics and reporting capabilities to help decision-makers analyze data and gain insights into business performance.
Importance of ERP Systems in Modern Business Operations
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems are crucial in contemporary business environments for several compelling reasons. Here’s an in-depth look at their importance:
Integration of Business Processes
- Unified System: ERP systems integrate various business functions, such as finance, HR, manufacturing, and supply chain, into a single, unified system. This integration ensures that all departments work with the same data and processes, reducing silos and improving coordination.
- Consistency and Accuracy: By maintaining a single source of truth, ERP systems ensure data consistency and accuracy across the organization, minimizing discrepancies and errors.
Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity
- Automation of Routine Tasks: ERP systems automate routine and repetitive tasks like order processing, payroll, and inventory management, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic activities.
- Streamlined Workflows: Automated workflows and standardized processes reduce the time and effort required to complete business tasks, leading to increased operational efficiency.
Improved Decision-Making
- Real-Time Data Access: ERP systems provide real-time access to critical business data, enabling managers and executives to make informed decisions quickly.
- Advanced Analytics and Reporting: Built-in analytics and reporting tools help businesses analyze performance metrics, identify trends, and gain actionable insights, driving better strategic planning.
Cost Savings
- Operational Efficiency: By streamlining processes and improving efficiency, ERP systems help reduce operational costs.
- Reduced IT Costs: An integrated ERP system can replace multiple disparate systems, reducing the costs associated with maintaining and integrating various software applications.
Scalability and Flexibility
- Adaptability: ERP systems are designed to grow with the business. They can accommodate new processes, additional users, and increased transaction volumes as the organization expands.
- Customizability: Many ERP systems offer customizable modules that can be tailored to fit the specific needs of different industries and business sizes.
Enhanced Collaboration
- Centralized Data Repository: By centralizing data, ERP systems facilitate better collaboration among departments. Employees can easily share information and work together on projects.
- Improved Communication: Integrated communication tools within ERP systems enhance internal communication, ensuring everyone is on the same page.
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management
- Compliance Management: ERP systems help businesses comply with industry standards and regulatory requirements by providing tools for accurate record-keeping, audit trails, and automated reporting.
- Risk Mitigation: By ensuring data accuracy and consistency, ERP systems reduce the risk of errors and fraudulent activities.
Better Customer Service
- Comprehensive Customer Data: ERP systems provide a holistic view of customer interactions and histories, enabling businesses to deliver personalized and efficient customer service.
- Efficient Order Fulfillment: Automated order processing and inventory management ensure timely and accurate order fulfillment, improving customer satisfaction.
Supply Chain Optimization
- Inventory Management: ERP systems provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, helping businesses maintain optimal stock levels and reduce carrying costs.
- Procurement and Supplier Management: Streamlined procurement processes and better supplier relationship management lead to more efficient supply chain operations.
Data Security
- Centralized Security Protocols: ERP systems offer robust security features to protect sensitive business data, including access controls, encryption, and regular security updates.
- Disaster Recovery: Many ERP systems include disaster recovery and backup solutions, ensuring business continuity in case of data loss or system failure.
In summary, ERP systems are indispensable in modern business operations due to their ability to integrate processes, enhance efficiency, improve decision-making, and support growth.
By providing a unified platform for managing all aspects of a business, ERP systems help organizations achieve greater agility, competitiveness, and long-term success.
Why Small Businesses Need ERP Systems
ERP implementation offers significant benefits for small businesses, enhancing efficiency, productivity, and decision-making. By integrating various business processes into a single system, ERP for small businesses provides the tools needed to streamline operations, improve customer service, and support growth.
Whether through on-premises solutions or cloud-based ERP software, small businesses can achieve greater agility and competitiveness in today's dynamic market environment.

Streamlined Operations
- Implementing ERP software for small businesses centralizes and integrates various business processes into a single system. This means that data from finance, HR, manufacturing, sales, and other departments are stored in one unified platform.
- This integration eliminates the need for multiple, disparate systems and reduces the time spent on manual data entry and reconciliation.
- For instance, ERP for small manufacturing businesses can link production schedules with inventory management, ensuring that materials are available when needed without excess stock.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
- ERP systems automate many routine tasks, which helps small businesses operate more efficiently.
- Tasks such as order processing, invoicing, and payroll are streamlined, reducing the time and effort required to complete these processes.
- This automation frees up employees to focus on more strategic, value-added activities.
- For example, cloud-based ERP software for small businesses can automate inventory tracking and reorder points, ensuring that stock levels are optimized without manual intervention.
Better Decision-Making
- With ERP for business, decision-makers have access to real-time data and advanced analytics. This comprehensive visibility into all business operations allows for more informed and timely decisions.
- The best ERP for small businesses provides customizable dashboards and reports that highlight key performance indicators (KPIs) and other critical metrics.
- For instance, managers can quickly assess financial health, monitor sales trends, and adjust strategies based on up-to-date information.
Enhanced Customer Service
- ERP systems improve customer service by providing a complete view of customer interactions and histories. This holistic view enables small businesses to respond more quickly and accurately to customer inquiries and issues.
- Additionally, ERP for small businesses can streamline order processing and delivery, ensuring that customers receive their products on time.
- Enhanced customer relationship management (CRM) features within the ERP system help track customer preferences and purchase history, allowing for personalized service.
Scalability
- As a small business grows, its operational needs become more complex. ERP systems are designed to scale with the business, accommodating new users, additional data, and more sophisticated processes.
- This scalability is particularly advantageous for small manufacturing businesses, which may expand their production lines or enter new markets.
- Cloud-based ERP software for small businesses offers flexible subscription models, making it easier to scale up or down based on current needs.
Cost Savings
- While the initial investment in an ERP system can be significant, the long-term cost savings often outweigh these upfront expenses.
- ERP for small businesses reduces the need for multiple software licenses and maintenance costs associated with disparate systems. Operational efficiencies gained from streamlined processes and automation translate into lower labor costs and reduced waste.
- For example, ERP for small manufacturing can optimize production schedules and resource allocation, leading to lower operational costs.
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management
- ERP systems help small businesses stay compliant with industry standards and regulatory requirements by providing tools for accurate record-keeping and reporting.
- Automated audit trails and documentation ensure that businesses can easily track and report financial transactions, HR activities, and other critical processes.
- This capability is particularly important for small manufacturing businesses that must adhere to stringent quality and safety regulations.
Inventory and Supply Chain Management
- Effective inventory and supply chain management are critical for small businesses to maintain optimal stock levels and reduce carrying costs.
- ERP for small manufacturing businesses provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, allowing for better planning and forecasting.
- Automated procurement processes ensure timely reordering of materials, preventing stock outs or overstock situations.
- Additionally, ERP systems can manage supplier relationships, track order status, and streamline procurement workflows.
Financial Management
- ERP systems integrate financial management modules that handle accounting, budgeting, and cash flow management.
- This integration ensures that all financial data is accurate and up-to-date, facilitating better financial planning and analysis.
- Small businesses can generate detailed financial reports, monitor expenses, and manage cash flow more effectively.
- Cloud-based ERP software for small businesses offers the added benefit of real-time financial data access from anywhere, enhancing financial oversight.
Employee Management
- ERP systems include HR modules that manage employee information, track attendance, process payroll, and handle benefits administration.
- This comprehensive management leads to better resource planning and employee satisfaction.
- ERP for small businesses can automate HR processes, reducing administrative burdens and ensuring compliance with labor laws.
- Enhanced HR analytics help businesses understand workforce trends, manage talent more effectively, and plan for future staffing needs.
Collaboration and Communication
- ERP systems improve internal communication and collaboration by providing a unified platform where employees can share information and work together more effectively.
- Centralized data storage ensures that all team members have access to the same information, reducing misunderstandings and duplication of effort.
- Cloud-based ERP software for small businesses enables remote access, allowing teams to collaborate seamlessly regardless of location.
Key Features to Look for in an ERP System for Small Businesses
When selecting ERP software for small business needs, it's essential to focus on features that align with your operational requirements and growth goals.
Here are the key features to consider:
User-Friendly Interface
- ERP systems should be intuitive and easy to navigate, ensuring that all users, regardless of technical expertise, can quickly learn and use the software.
- A user-friendly interface minimizes training time and helps employees adapt to the new system smoothly.
- Look for ERP for small businesses that offer customizable dashboards and role-based access to streamline daily operations.
Customizability and Flexibility
- Every small business has unique processes and needs. The best ERP for small businesses will offer customizable modules and workflows that can be tailored to fit specific requirements.
- This flexibility allows businesses to configure the ERP system to support their unique operations without significant modifications.
Integration Capabilities with Existing Tools
- An ERP system should integrate seamlessly with the existing tools and software your business uses, such as CRM, e-commerce platforms, and accounting software.
- ERP for small manufacturing, for instance, should integrate with production planning and inventory management tools to ensure smooth operations across all departments.
Scalability Options
- As your business grows, your ERP system should be able to scale accordingly. Look for ERP software for small businesses that can handle increasing data volumes, additional users, and more complex processes without compromising performance.
- Cloud-based ERP software for small businesses often provides scalable solutions that can grow with your business needs.
Mobile Accessibility
- In today’s mobile-first world, having access to your ERP system on the go is crucial. ERP for business should offer robust mobile applications or responsive web interfaces that allow users to access essential functions and data from their smartphones or tablets, ensuring productivity even outside the office.
Security Features
- Data security is paramount for any business. Ensure that the ERP system you choose has strong security measures, such as data encryption, user authentication, and regular security updates.
- Cloud-based ERP software for small businesses often includes advanced security protocols managed by the provider, offering peace of mind.
Support and Training Resources
- Implementing a new ERP system requires adequate support and training. Choose an ERP for small businesses that offer comprehensive training resources, including user manuals, video tutorials, and live support.
- Additionally, look for vendors that provide ongoing customer support to help resolve any issues promptly.
Cost Considerations (Upfront and Ongoing)
- The cost of ERP software for small businesses can vary widely. Evaluate both the upfront costs (such as licensing and implementation fees) and ongoing costs (such as maintenance, support, and subscription fees for cloud-based solutions).
- Ensure that the ERP system provides good value for its cost and fits within your budget.
Robust Reporting and Analytics
- The ability to generate detailed reports and analyze data is a critical feature of any ERP system.
- ERP for small businesses should include powerful reporting tools that provide insights into financial performance, sales trends, inventory levels, and other key metrics.
- These tools help in making data-driven decisions to enhance business growth.
Inventory and Supply Chain Management
- For small manufacturing businesses, effective inventory and supply chain management features are essential.
- Look for ERP systems that offer real-time tracking of inventory levels, automated reordering, and supplier management tools.
- These features help maintain optimal stock levels and ensure efficient supply chain operations.
Financial Management
- An integrated financial management module is crucial for maintaining accurate financial records and managing budgets.
- ERP software for small businesses should include comprehensive accounting features such as general ledger, accounts payable and receivable, budgeting, and financial reporting.
- Cloud-based ERP systems often provide real-time financial data access, facilitating better financial oversight.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- A built-in CRM module helps manage customer interactions and relationships more effectively. ERP for business should track customer orders, service requests, and preferences, enabling personalized service and improved customer satisfaction.
- This integration ensures that sales, marketing, and customer service teams have a complete view of customer activities.
ERP Software Selection Process
Choosing the right ERP software for your small business is a significant decision that requires careful consideration and thorough evaluation.
By conducting a systematic selection process, you can identify an ERP solution that enhances efficiency, supports growth, and drives long-term success for your business.
Here's a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the selection process:
Assess Business Needs and Processes
- Identify the specific challenges and pain points your business faces.
- Evaluate existing processes and workflows to determine areas for improvement.
- Define your goals and objectives for implementing an ERP system, such as streamlining operations, improving efficiency, or supporting business growth.
Research ERP Vendors
- Compile a list of potential ERP vendors that offer solutions tailored to small businesses.
- Evaluate each vendor's reputation, experience, and track record in serving businesses similar to yours.
- Consider factors such as industry expertise, customer reviews, and awards or certifications.
Evaluate Demos and Trial Versions
- Request demos or trial versions of ERP software from shortlisted vendors.
- Test the functionality and usability of the software to ensure it meets your business requirements.
- Involve key stakeholders from different departments in the evaluation process to gather diverse perspectives.
Consider Total Cost of Ownership
- Assess the total cost of ownership (TCO) of each ERP solution, including upfront costs, implementation fees, and ongoing expenses.
- Compare pricing models, such as perpetual licensing, subscription-based pricing, or pay-per-user models.
- Factor in potential costs for customization, training, support, and upgrades over the long term.
Seek Customer References and Testimonials
- Reach out to existing customers of the ERP vendors to gather feedback and insights about their experiences.
- Ask specific questions about implementation timelines, challenges faced, and overall satisfaction with the software.
- Consider visiting reference sites or attending user group meetings to learn more about real-world usage scenarios.
Ensure Vendor Support and Training
- Evaluate the level of support and training provided by each ERP vendor.
- Inquire about available support channels, response times, and service level agreements (SLAs).
- Assess the quality and availability of training resources, such as user manuals, documentation, online courses, and in-person training sessions.
Assess Integration Capabilities
- Determine how well the ERP software integrates with existing tools and systems used in your business, such as CRM, accounting software, or e-commerce platforms.
- Evaluate the ease of integration and any potential limitations or customization requirements.
Consider Customizability and Flexibility
- Assess the degree of customizability and flexibility offered by each ERP solution.
- Determine whether the software can be tailored to fit your specific business processes and requirements without extensive modifications.
- Consider future scalability and the ability to adapt to changing business needs over time.
Evaluate Security Features
- Prioritize data security and compliance requirements when selecting an ERP system.
- Assess the security features offered by each vendor, such as data encryption, role-based access controls, and regular security updates.
- Inquire about compliance certifications and adherence to industry standards for data protection.
Finalize Decision and Implementation Plan
- Compile all evaluation criteria and feedback gathered during the selection process.
- Conduct a final review and comparison of ERP vendors based on their suitability for your business needs.
- Select the ERP software that best aligns with your goals, requirements, and budget constraints.
- Develop a detailed implementation plan, including timelines, resource allocation, training schedules, and change management strategies.
How can Deskera Help Small Businesses as an ERP System?
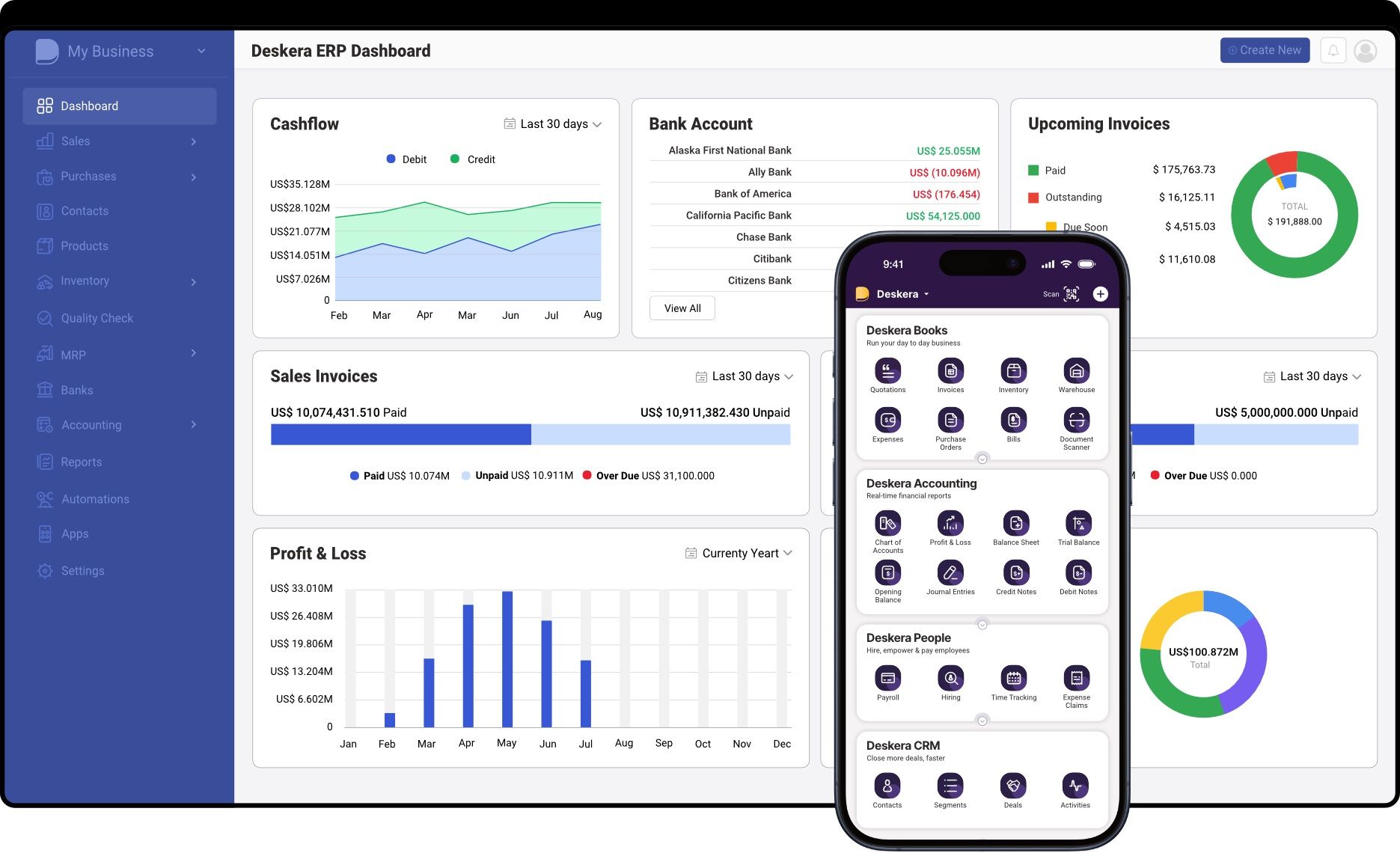
Deskera offers an ERP system tailored specifically for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), providing a comprehensive suite of tools to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and support growth.
Here's how Deskera can help small businesses as an ERP system:
Unified Platform for Business Operations
Deskera provides a unified platform that integrates various business functions, including finance, HR, CRM, inventory management, and project management. By centralizing data and processes in one system, Deskera eliminates the need for multiple disparate systems, reducing complexity and improving collaboration across departments.
Streamlined Operations and Efficiency
With Deskera ERP, small businesses can automate routine tasks and workflows, such as order processing, invoicing, payroll, and inventory management. This automation helps streamline operations, reduce manual errors, and improve overall efficiency, allowing employees to focus on more strategic activities.
Real-Time Insights and Reporting
Deskera offers robust reporting and analytics tools that provide real-time insights into business performance. Small businesses can generate customizable reports and dashboards to track key metrics, monitor trends, and make data-driven decisions quickly. This visibility enables proactive management and helps identify areas for improvement.
Scalability and Flexibility
Deskera's ERP system is designed to scale with small businesses as they grow. Whether it's adding new users, expanding into new markets, or introducing new products, Deskera can accommodate changing business needs without disruption. The system's flexibility allows businesses to customize workflows and modules to fit their unique requirements.
Cost-Effective Solution
Deskera offers affordable pricing plans tailored for small businesses, making it a cost-effective ERP solution. With Deskera, small businesses can access enterprise-grade features and functionality without the high upfront costs typically associated with traditional ERP systems. Additionally, Deskera's subscription-based model ensures predictable monthly expenses, making budgeting easier for SMBs.
Easy Implementation and User-Friendly Interface
Deskera's ERP system is designed for ease of use, with a user-friendly interface that requires minimal training for employees to get started. The system's intuitive design and straightforward setup process make implementation quick and hassle-free, allowing small businesses to start seeing benefits sooner.
Enhanced Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Deskera includes CRM functionality to help small businesses manage customer interactions and relationships more effectively. With Deskera CRM, businesses can track leads, manage contacts, automate marketing campaigns, and provide personalized customer service, ultimately driving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Cloud-Based Accessibility
Deskera's ERP system is cloud-based, meaning it can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection. This flexibility allows small business owners and employees to work remotely, collaborate in real-time, and access critical business information on the go, increasing productivity and agility.
Secure and Reliable Infrastructure
Deskera prioritizes data security and reliability, providing robust security measures to protect sensitive business information. With encryption, regular backups, and data redundancy, Deskera ensures that small businesses' data is safe and accessible at all times, giving peace of mind to business owners.
Compliance and Regulatory Support
Deskera helps small businesses stay compliant with industry regulations and standards by providing tools for accurate record-keeping, audit trails, and regulatory reporting. With Deskera, SMBs can ensure compliance with tax laws, accounting standards, and other regulatory requirements, minimizing the risk of non-compliance penalties.
Key Takeaways
The implementation of an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system offers small businesses a multitude of benefits that contribute to their overall success and growth.
These are:
1. Streamlined Operations
- Integrated Processes: ERP systems integrate various business functions (finance, HR, sales, inventory, etc.) into a single system, eliminating the need for multiple disparate systems and ensuring smooth and consistent operations across departments.
- Reduction of Redundancy: By consolidating data and processes, ERP systems reduce redundancy and duplication of efforts, leading to more efficient operations.
2. Improved Efficiency and Productivity
- Automation: Automating routine tasks such as order processing, invoicing, payroll, and inventory management reduces manual work and errors, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic tasks.
- Standardized Processes: ERP systems enforce standardized business processes, ensuring consistency and improving overall efficiency.
3. Better Decision-Making
- Real-Time Data Access: ERP systems provide real-time access to accurate and up-to-date information, enabling small businesses to make informed decisions quickly.
- Advanced Analytics: Built-in analytics and reporting tools help businesses analyze performance metrics, identify trends, and gain actionable insights, which support strategic planning and decision-making.
4. Enhanced Customer Service
- Comprehensive Customer Information: ERP systems offer a 360-degree view of customer interactions and histories, allowing businesses to deliver personalized and efficient customer service.
- Faster Response Times: With real-time data access and streamlined processes, businesses can respond to customer inquiries and orders more quickly, improving customer satisfaction.
5. Scalability
- Growth Support: ERP systems are designed to scale with the business. As a small business grows, the ERP system can accommodate new processes, additional users, and higher transaction volumes without requiring significant changes.
- Flexibility: Many ERP solutions offer modular functionality, allowing businesses to add new features and capabilities as needed.
6. Cost Savings
- Operational Efficiency: By streamlining processes and improving efficiency, ERP systems help reduce operational costs.
- Reduced IT Costs: Implementing an ERP system can eliminate the need for multiple software applications, reducing IT maintenance and support costs.
7. Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management
- Accurate Record-Keeping: ERP systems provide tools for accurate and consistent record-keeping, helping businesses comply with industry standards and regulatory requirements.
- Audit Trails: Comprehensive audit trails and reporting capabilities support compliance and reduce the risk of errors and fraud.
8. Improved Inventory and Supply Chain Management
- Real-Time Inventory Tracking: ERP systems provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, helping businesses maintain optimal stock levels, reduce carrying costs, and prevent stockouts or overstock situations.
- Efficient Procurement: Streamlined procurement processes and better supplier relationship management lead to more efficient supply chain operations.
9. Financial Management
- Comprehensive Financial Reporting: ERP systems integrate financial management modules that handle accounting, budgeting, and cash flow management, providing accurate financial reports and insights.
- Enhanced Financial Control: Improved financial control and visibility help businesses manage their finances more effectively, supporting better budgeting and forecasting.
10. Employee Management
- HR Functionality: ERP systems manage employee information, track attendance, process payroll, and handle benefits administration, leading to better resource planning and employee satisfaction.
- Improved Productivity: By automating HR processes, ERP systems free up HR staff to focus on strategic initiatives like talent development and employee engagement.
11. Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
- Centralized Data: A centralized data repository facilitates better collaboration among departments, as employees can easily share information and work together on projects.
- Unified Communication Tools: Integrated communication tools within ERP systems enhance internal communication, ensuring everyone is aligned and informed.
In essence, ERP implementation is not just an investment in technology; it's an investment in the future of the business. By embracing ERP systems, small businesses can position themselves for sustainable growth, operational excellence, and continued success in the years to come.
Deskera offers a comprehensive ERP solution tailored to the needs of small businesses, providing the tools and functionality needed to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and support growth. With its user-friendly interface, affordability, scalability, and cloud-based accessibility, Deskera helps small businesses compete more effectively in today's dynamic market environment.
Related Articles













