Have you ever wondered what’s holding your manufacturing processes back from achieving peak efficiency? In today’s fast-paced world, manufacturers face growing pressure to optimize their operations, reduce costs, and deliver products faster.
The key to unlocking this efficiency lies in leveraging technology, and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solutions are rapidly becoming the go-to strategy for manufacturing leaders. By shifting to cloud-based systems, manufacturers can streamline their operations, improve collaboration, and gain real-time insights that drive smarter decision-making.
SaaS solutions have revolutionized various industries, and manufacturing is no exception. These cloud-based platforms offer flexibility, scalability, and accessibility, making them an ideal choice for modern manufacturers. With SaaS, companies can avoid the hefty upfront investments associated with traditional on-premise software, while still benefiting from continuous updates and innovations.
Whether it’s managing inventory, optimizing production schedules, or improving communication across departments, SaaS platforms provide the tools manufacturers need to stay competitive in an increasingly complex market.
One leading player in the SaaS space is Deskera, which offers an all-in-one solution tailored specifically for manufacturing. Deskera’s platform integrates features like inventory management, production planning, accounting, and advanced reporting, all accessible from a single dashboard.
With its mobile accessibility and AI-driven insights, Deskera enables manufacturers to monitor and manage their operations in real-time, improving efficiency across the board. By adopting Deskera, manufacturers can enhance productivity, reduce errors, and ensure smoother workflows throughout their production cycle.
As manufacturers continue to face rising demand and operational challenges, implementing SaaS solutions can be a game-changer. In the following sections, we’ll explore the key benefits of adopting SaaS in manufacturing, from improving production efficiency to enhancing supply chain visibility and reducing costs.
What is SaaS in Manufacturing?
SaaS (Software as a Service) in manufacturing refers to cloud-based software solutions specifically designed to optimize various aspects of manufacturing operations.
Instead of relying on traditional, on-premise software that requires physical installation, licensing, and maintenance, SaaS solutions are hosted in the cloud and delivered over the internet on a subscription basis.
This model allows manufacturers to access and use software tools without the need for extensive infrastructure, reducing upfront costs and simplifying IT management.
Key Characteristics of SaaS in Manufacturing
Here are the key characteristics of SaaS in manufacturing:
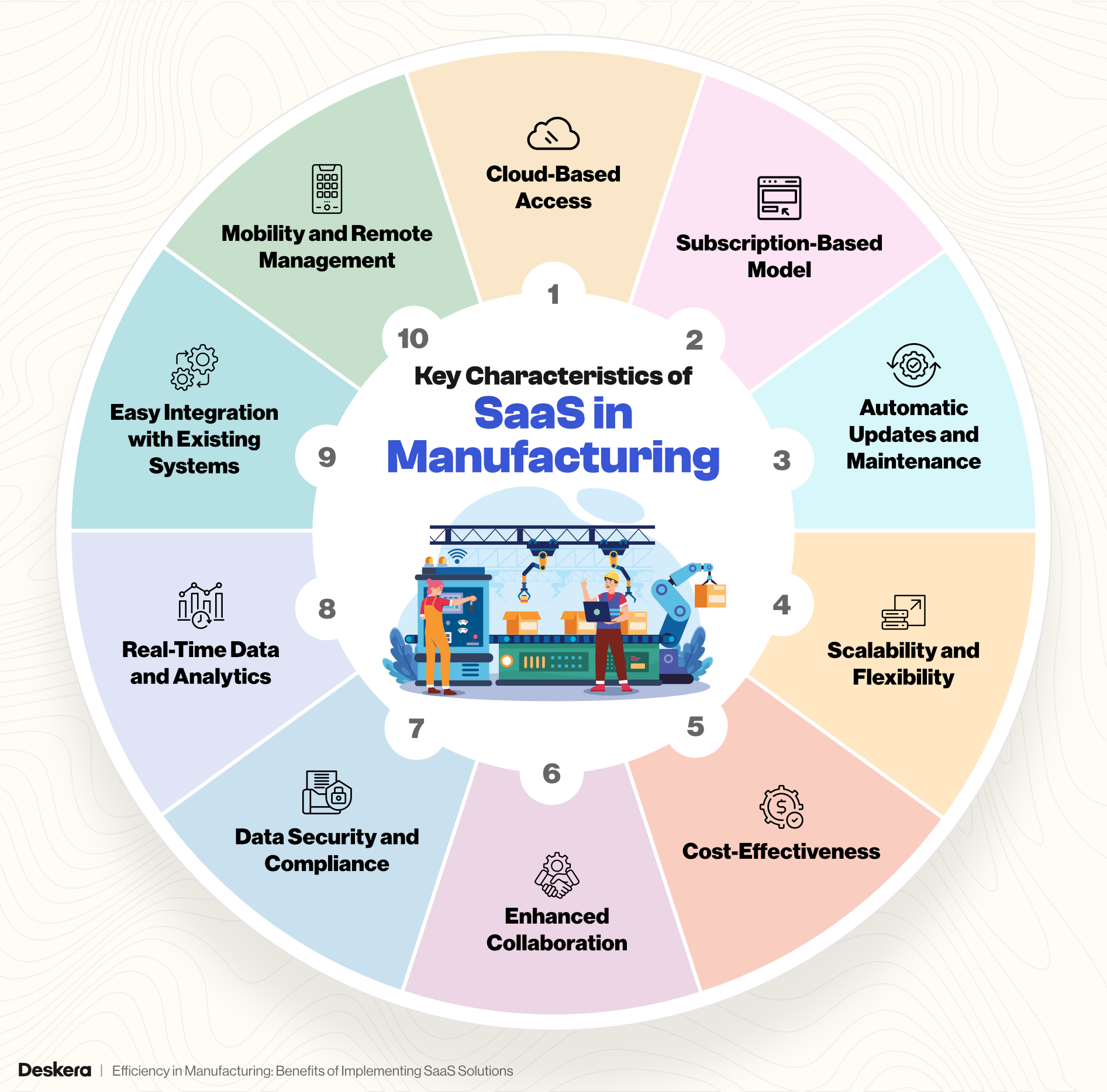
1. Cloud-Based Access
- SaaS solutions are hosted on remote servers in the cloud, enabling manufacturers to access their software from any device with an internet connection. This accessibility facilitates remote management of production lines, inventory, and other key operations.
- It ensures that manufacturing teams at different locations can collaborate effectively without being restricted by on-premise systems.
2. Subscription-Based Model
- Manufacturers pay for SaaS solutions on a subscription basis, typically monthly or annually, rather than making a large, upfront capital investment. This pay-as-you-go model allows businesses to manage their cash flow more effectively.
- Costs are predictable, and manufacturers can scale the service based on usage needs, reducing wasteful spending on unnecessary resources.
3. Automatic Updates and Maintenance
- SaaS providers manage software updates, patches, and routine maintenance, meaning manufacturers always have access to the latest features without needing to worry about upgrading or maintaining software.
- This ensures minimal downtime and reduces the need for dedicated IT resources.
4. Scalability and Flexibility
- SaaS platforms can easily grow alongside manufacturing operations. Manufacturers can add more users, integrate additional modules, or expand functionality without substantial IT overhead.
- As production needs change, businesses can scale their SaaS subscriptions up or down, providing the flexibility to adapt to market shifts or operational demands.
5. Cost-Effectiveness
- By eliminating the need for extensive IT infrastructure, such as servers and hardware, SaaS solutions significantly reduce initial capital expenses.
- SaaS also lowers operational costs by reducing the need for in-house IT personnel to maintain, support, and update software systems.
6. Enhanced Collaboration
- SaaS enables better collaboration across teams and locations by providing real-time data access and shared dashboards. For example, plant managers, suppliers, and production teams can work together seamlessly through shared platforms.
- This also extends to external partners, like suppliers, who can access relevant data to align their deliveries and services with manufacturing needs.
7. Data Security and Compliance
- SaaS providers implement robust security measures, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and automatic backups, to ensure the protection of sensitive manufacturing data.
- Many SaaS solutions comply with industry standards and regulations, providing manufacturers with built-in tools to manage compliance with laws like GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO certifications.
8. Real-Time Data and Analytics
- SaaS platforms provide real-time access to data, allowing manufacturers to track and monitor performance metrics across the production cycle. This real-time insight enables faster decision-making and better management of supply chains, inventories, and production schedules.
- Advanced analytics features allow manufacturers to extract actionable insights from data, improving productivity and efficiency.
9. Easy Integration with Existing Systems
- Many SaaS platforms are designed to integrate with existing enterprise systems, such as ERP, MRP, or CRM solutions. This helps manufacturers avoid disruptions by ensuring that new SaaS tools can complement and enhance current workflows.
- Open APIs and plug-and-play functionality make it easier for SaaS solutions to interact with legacy systems.
10. Mobility and Remote Management
- SaaS solutions offer mobile-friendly interfaces, allowing users to manage operations on the go. Plant managers and executives can monitor production, inventory, and even make adjustments remotely.
- This is especially valuable for manufacturing environments that require flexibility in managing multiple sites, global supply chains, or hybrid work models.
In summary, SaaS solutions in manufacturing offer accessibility, scalability, cost efficiency, and enhanced collaboration, making them an ideal choice for modern manufacturers aiming to improve operational efficiency while reducing IT complexities.
Common SaaS Applications in Manufacturing
Here are some common SaaS applications in manufacturing that help streamline various aspects of operations and improve efficiency:
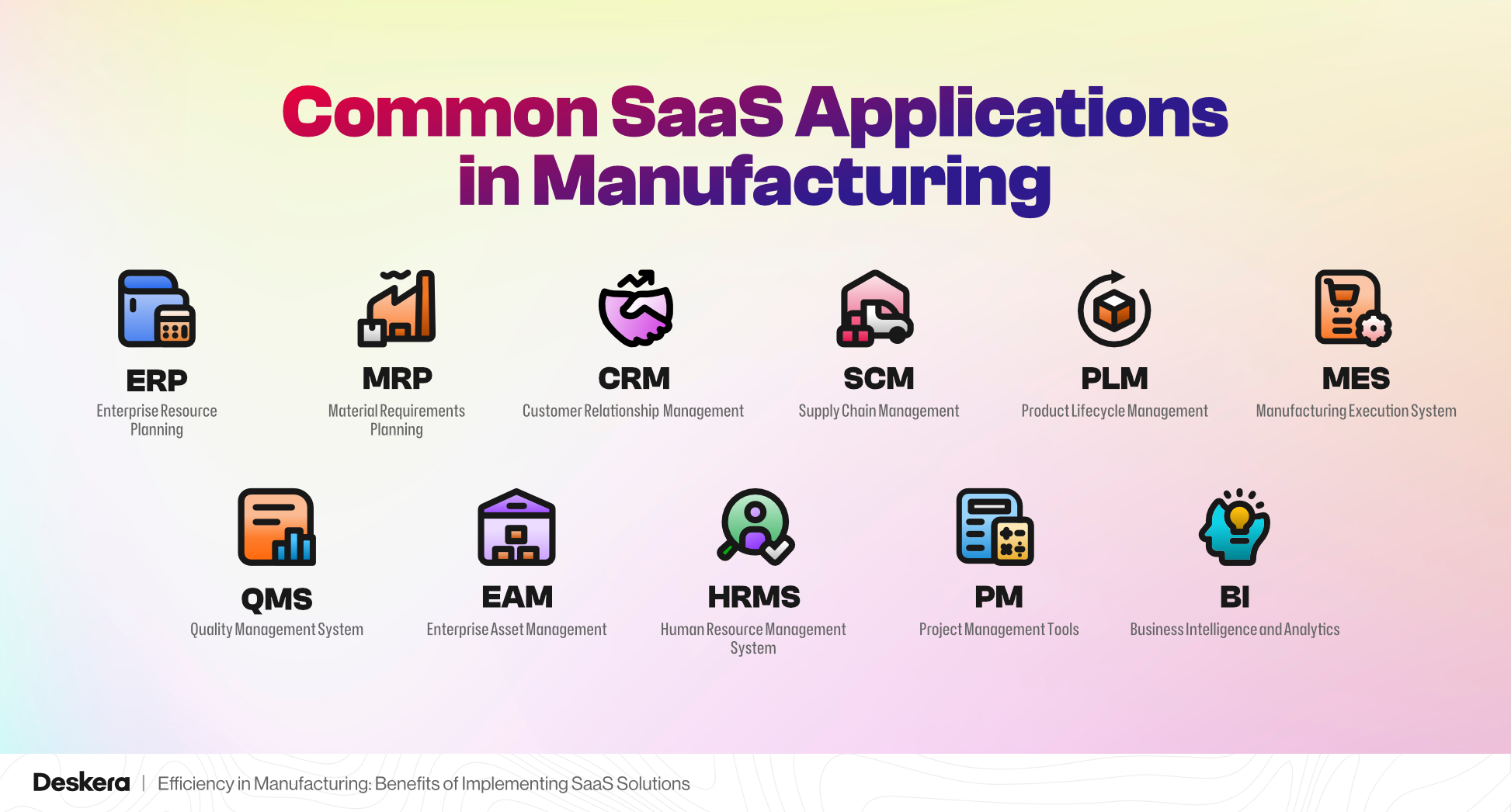
1. ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning)
- Functionality: SaaS-based ERP solutions integrate multiple business functions, such as production planning, procurement, inventory management, accounting, human resources, and customer relationship management (CRM).
- Benefits: With real-time data access, SaaS ERP helps manufacturers monitor and manage their operations efficiently. It allows for better coordination across departments and ensures data consistency.
2. MRP (Material Requirements Planning)
- Functionality: SaaS-based MRP systems assist manufacturers in planning production, managing inventory, and scheduling deliveries of raw materials based on demand forecasts and production schedules.
- Benefits: These solutions reduce overstocking, prevent stockouts, and ensure that the necessary materials are available when needed, optimizing the production process.
3. CRM (Customer Relationship Management)
- Functionality: CRM solutions enable manufacturers to manage interactions with customers, track sales pipelines, process orders, and manage after-sales services.
- Benefits: By centralizing customer data, SaaS CRM improves customer service, boosts sales performance, and strengthens customer relationships.
4. SCM (Supply Chain Management)
- Functionality: SaaS-based SCM platforms help manufacturers manage their supply chain from end to end, including sourcing, procurement, production, and distribution. They provide real-time visibility into supply chain activities.
- Benefits: SCM solutions optimize procurement, enhance supplier relationships, and improve demand forecasting, leading to better supply chain efficiency and cost savings.
5. PLM (Product Lifecycle Management)
- Functionality: SaaS PLM solutions manage the entire lifecycle of a product, from design and development to manufacturing and eventual disposal. They facilitate collaboration between design, engineering, and production teams.
- Benefits: PLM tools improve time-to-market by streamlining product design processes and ensuring that teams can collaborate effectively, reducing errors and design rework.
6. MES (Manufacturing Execution System)
- Functionality: SaaS-based MES solutions track and document the production process in real-time, offering insight into performance, production schedules, and quality control.
- Benefits: These solutions enhance productivity by minimizing downtime, reducing waste, and improving quality control processes on the shop floor.
7. QMS (Quality Management System)
- Functionality: SaaS QMS tools ensure compliance with quality standards and help manage the entire quality control process. This includes document control, corrective actions, audits, and process validation.
- Benefits: QMS solutions help manufacturers maintain product quality, reduce defects, and ensure regulatory compliance with minimal paperwork and manual processes.
8. EAM (Enterprise Asset Management)
- Functionality: SaaS EAM solutions manage and monitor a manufacturer’s physical assets, such as machinery, equipment, and vehicles, ensuring they remain in good working condition through preventive maintenance.
- Benefits: These solutions minimize downtime by predicting equipment failures and scheduling maintenance, improving the overall efficiency of production lines.
9. HRMS (Human Resource Management System)
- Functionality: HRMS solutions help manage the workforce in a manufacturing setting by automating tasks such as payroll, attendance tracking, performance evaluation, and training.
- Benefits: By centralizing HR data and automating administrative tasks, HRMS tools improve employee productivity, reduce errors, and enhance workforce management.
10. Project Management Tools
- Functionality: SaaS-based project management solutions allow manufacturers to plan, execute, and monitor projects such as product launches, equipment installations, or process improvements.
- Benefits: These tools enhance collaboration, improve resource allocation, and ensure timely project delivery within budget.
11. BI (Business Intelligence) and Analytics
- Functionality: SaaS BI tools provide manufacturers with real-time analytics and dashboards, offering insights into key performance indicators (KPIs) such as production efficiency, cost control, and quality metrics.
- Benefits: These solutions enable data-driven decision-making by analyzing trends, optimizing operations, and identifying areas for improvement.
In conclusion, SaaS applications cover every aspect of manufacturing, from production planning and inventory control to customer management and business intelligence. These tools help manufacturers streamline operations, improve collaboration, and drive efficiency through the power of cloud-based solutions.
Benefits of SaaS in Manufacturing
Here are the key benefits of implementing SaaS in manufacturing:
1. Cost Efficiency
- SaaS eliminates the need for upfront investments in hardware, software licenses, and IT infrastructure. Manufacturers pay only for what they use on a subscription basis, converting capital expenditures into operational expenditures.
- Lower IT costs, as software updates, maintenance, and security are handled by the SaaS provider, reducing the need for in-house IT staff.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
- SaaS solutions can easily scale to meet the growing needs of a manufacturing business. Whether expanding production lines, adding new users, or increasing storage, manufacturers can scale their SaaS services without the need for additional hardware or IT resources.
- Flexibility to add or remove services and features as business needs evolve, ensuring manufacturers always have the right tools for their current operations.
3. Improved Collaboration and Accessibility
- SaaS platforms are accessible from any device with an internet connection, allowing teams from different locations to collaborate in real-time. This is particularly useful for manufacturers with multiple facilities or remote teams.
- Teams, suppliers, and partners can easily access and share data, ensuring seamless coordination across the entire supply chain and production process.
4. Automatic Updates and Maintenance
- SaaS providers handle all software updates, security patches, and system maintenance, ensuring manufacturers always have access to the latest features and improvements without needing to worry about manual updates or system downtime.
- Regular updates also ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations without disrupting day-to-day operations.
5. Enhanced Data Security
- SaaS providers offer robust data security protocols, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and secure data centers. This ensures that sensitive manufacturing data is protected from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber threats.
- Most SaaS solutions are compliant with industry regulations, providing manufacturers with tools to manage regulatory requirements like GDPR or ISO certifications.
6. Real-Time Data and Analytics
- SaaS solutions provide real-time access to data and advanced analytics, enabling manufacturers to monitor production processes, track key performance indicators (KPIs), and make informed, data-driven decisions.
- Real-time data insights help improve production efficiency, optimize inventory levels, and reduce downtime by identifying issues early.
7. Faster Implementation and Deployment
- SaaS solutions can be deployed much faster than traditional on-premise software. Manufacturers can start using the software within days or weeks rather than months, allowing for quicker integration into existing operations.
- SaaS platforms come with built-in templates, tools, and user-friendly interfaces, which reduce the learning curve and speed up adoption across the organization.
8. Mobility and Remote Access
- Many SaaS applications are mobile-friendly, allowing managers, engineers, and technicians to access important data and manage operations on the go. This mobility is crucial for plant managers and executives who need real-time updates while not being physically present on the shop floor.
- Remote access helps improve operational continuity, especially in cases where remote work is necessary, such as during global disruptions or natural disasters.
9. Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
- SaaS providers offer automatic backups and disaster recovery plans, ensuring that manufacturers' data and systems are protected in case of unexpected events like server crashes, power outages, or natural disasters.
- Cloud-based infrastructure ensures that data remains accessible and secure, even if on-site systems are compromised.
10. Streamlined Supply Chain and Inventory Management
- SaaS solutions for supply chain management (SCM) and inventory control allow manufacturers to manage and optimize their supply chain and inventory levels with real-time tracking and demand forecasting. This minimizes stockouts, reduces excess inventory, and improves supply chain efficiency.
- These tools enable manufacturers to work closely with suppliers, automate orders, and optimize just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing processes.
11. Customization and Integration
- SaaS platforms often offer customizable modules and tools, allowing manufacturers to tailor solutions to their specific needs. This includes adding integrations with existing ERP systems, CRM tools, and other business applications.
- Open APIs make it easier to integrate SaaS solutions into existing workflows without causing disruptions or requiring major overhauls of existing systems.
12. Compliance and Regulatory Management
- Many SaaS solutions come pre-configured to comply with industry-specific standards and regulations, including safety protocols, environmental regulations, and quality certifications.
- Manufacturers can track compliance activities, maintain audit trails, and manage certifications through the platform, ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements with minimal manual effort.
13. Continuous Innovation
- SaaS providers are constantly innovating and improving their software to meet the evolving needs of the manufacturing industry. Manufacturers can benefit from these innovations, such as AI-driven analytics, predictive maintenance, and smart factory integrations, without needing to invest in new technology or infrastructure.
- Staying updated with the latest advancements helps manufacturers maintain a competitive edge in the market.
14. Reduced Downtime and Enhanced Efficiency
- By leveraging real-time data, predictive maintenance tools, and automated workflows, SaaS helps reduce equipment downtime, optimize production schedules, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
- Manufacturers can identify bottlenecks, forecast demand, and plan production in a more efficient manner, improving productivity and profitability.
In summary, SaaS in manufacturing delivers numerous benefits, including cost savings, scalability, real-time data insights, enhanced security, and faster deployment.
These advantages enable manufacturers to optimize operations, improve collaboration, and ensure business continuity in a dynamic, fast-paced environment.
How SaaS Improves Key Manufacturing Areas
SaaS (Software as a Service) significantly improves various key areas of manufacturing by enhancing productivity, streamlining operations, and enabling real-time collaboration.
Here's how SaaS impacts different core aspects of manufacturing:
1. Production Planning and Scheduling
- Improvement: SaaS solutions optimize production planning and scheduling by using real-time data and demand forecasting. These tools help manufacturers align production schedules with current demand, ensuring better resource utilization and minimizing bottlenecks.
- Benefit: Enhanced production efficiency and reduced lead times, leading to improved order fulfillment and cost savings.
2. Inventory Management
- Improvement: SaaS-based inventory management systems provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, automate stock replenishment, and optimize order quantities through demand forecasting algorithms.
- Benefit: Reduced stockouts and overstock situations, improved cash flow, and enhanced inventory turnover.
3. Supply Chain Management
- Improvement: SaaS platforms improve supply chain visibility by tracking materials, parts, and finished goods throughout the supply chain. They also enable better communication with suppliers and logistics partners, making it easier to manage orders, shipments, and deliveries.
- Benefit: Enhanced coordination between suppliers and manufacturers, reduced lead times, and better risk management in the supply chain.
4. Quality Control
- Improvement: SaaS solutions for Quality Management Systems (QMS) automate quality control processes, such as inspection, compliance checks, and corrective actions. These tools can also analyze production data to identify quality trends and reduce defects.
- Benefit: Improved product quality, reduced rework costs, and compliance with industry standards and regulations.
5. Maintenance and Equipment Management
- Improvement: SaaS-based Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) and predictive maintenance tools monitor equipment performance in real-time, scheduling maintenance before a breakdown occurs. These systems can also track spare parts inventory and manage work orders.
- Benefit: Reduced equipment downtime, extended asset life, and lower maintenance costs through preventive maintenance.
6. Collaboration and Communication
- Improvement: SaaS platforms allow teams across different locations to collaborate on projects in real-time, sharing data, documents, and progress updates seamlessly. Cloud-based tools integrate workflows across departments, such as production, procurement, and sales.
- Benefit: Improved coordination across teams and departments, faster decision-making, and enhanced productivity.
7. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Improvement: SaaS-based CRM tools help manufacturers manage customer interactions, track sales, handle customer service requests, and manage after-sales processes. These tools integrate with production and supply chain systems for seamless order processing and delivery.
- Benefit: Enhanced customer satisfaction, better sales performance, and improved customer retention rates.
8. Data Analytics and Business Intelligence
- Improvement: SaaS platforms provide advanced data analytics and business intelligence (BI) tools that collect and analyze real-time production, sales, and supply chain data. These analytics offer valuable insights into key performance indicators (KPIs) such as production efficiency, quality control, and profitability.
- Benefit: Informed, data-driven decision-making, identification of areas for improvement, and continuous operational optimization.
9. Compliance and Regulatory Adherence
- Improvement: SaaS systems automatically track and manage compliance with industry regulations, safety standards, and environmental laws. They maintain audit trails and provide real-time documentation to ensure that manufacturers meet regulatory requirements.
- Benefit: Simplified compliance management, reduced risk of non-compliance, and cost savings from avoiding fines or penalties.
10. Customer Order Management and Fulfillment
- Improvement: SaaS solutions streamline the order management process by automating sales orders, tracking order status in real-time, and coordinating with production and logistics teams for faster fulfillment.
- Benefit: Shortened order processing times, improved order accuracy, and better customer satisfaction.
11. Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)
- Improvement: SaaS-based PLM systems manage every stage of a product’s lifecycle, from design and engineering to manufacturing and disposal. These systems provide tools for collaboration between product development teams, suppliers, and manufacturers.
- Benefit: Accelerated product development cycles, reduced design errors, and faster time-to-market.
12. Energy and Resource Management
- Improvement: SaaS platforms monitor energy consumption, water usage, and raw material waste in real-time. They also help identify opportunities to reduce energy costs and optimize resource allocation.
- Benefit: Lower operational costs, reduced environmental impact, and improved sustainability practices.
13. Workforce Management
- Improvement: SaaS-based Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS) manage employee schedules, track labor costs, and monitor employee performance. These systems also handle payroll, training, and compliance with labor regulations.
- Benefit: Improved workforce productivity, reduced labor costs, and better employee engagement.
14. R&D and Innovation
- Improvement: SaaS solutions for R&D allow manufacturers to collaborate on new product designs and innovations using cloud-based tools. Data from production and customer feedback can be used to guide future product development.
- Benefit: Accelerated innovation cycles and more effective alignment between market needs and product development.
In conclusion, SaaS dramatically improves key areas of manufacturing by increasing operational efficiency, reducing costs, and enabling data-driven decision-making. The flexibility, scalability, and accessibility offered by SaaS allow manufacturers to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving industry.
SaaS vs. Traditional On-Premise Solutions
Here’s a comparison between SaaS (Software as a Service) and Traditional On-Premise Solutions in the context of manufacturing:
1. Deployment and Installation
- SaaS:
- SaaS solutions are cloud-based and hosted by the service provider. They require no physical installation of hardware or software at the user’s location. Manufacturers simply access the software through a web browser or app.
- Benefit: Faster setup and minimal upfront effort.
- Traditional On-Premise:
- On-premise solutions are hosted on local servers within the manufacturing facility. This requires purchasing hardware, setting up servers, and installing software manually.
- Drawback: Time-consuming deployment with significant upfront investment.
2. Cost Structure
- SaaS:
- SaaS operates on a subscription-based pricing model, with regular payments (monthly or annually) for access to the software. The subscription includes maintenance, updates, and customer support.
- Benefit: Lower upfront costs, more predictable pricing, and no hardware investment.
- Traditional On-Premise:
- On-premise solutions require a substantial initial investment in hardware, software licenses, and IT infrastructure. Ongoing costs include system maintenance, support, and updates.
- Drawback: Higher upfront costs with unpredictable future maintenance expenses.
3. Scalability
- SaaS:
- SaaS is highly scalable. Manufacturers can easily upgrade or downgrade services based on changing business needs without investing in additional hardware or IT resources.
- Benefit: Flexible and cost-effective scalability.
- Traditional On-Premise:
- Scaling on-premise solutions is more complex. It often involves purchasing new hardware, upgrading servers, or installing new software licenses.
- Drawback: Limited scalability with increased complexity and costs.
4. Maintenance and Updates
- SaaS:
- Maintenance, security patches, and software updates are handled by the SaaS provider, meaning manufacturers automatically receive the latest features without manual intervention.
- Benefit: Zero maintenance burden and access to continuous innovation.
- Traditional On-Premise:
- Maintenance and updates must be managed by in-house IT teams. Installing updates or performing upgrades can result in downtime and disruptions to operations.
- Drawback: Increased IT resource demand and potential operational interruptions.
5. Accessibility and Mobility
- SaaS:
- SaaS solutions are accessible from any device with an internet connection. This allows manufacturing teams, executives, and managers to monitor operations remotely or collaborate across locations.
- Benefit: Enhanced accessibility and support for remote work.
- Traditional On-Premise:
- On-premise software is typically only accessible on-site or through local networks, limiting the ability to work remotely or access data from different locations.
- Drawback: Restricted access and mobility.
6. Customization
- SaaS:
- SaaS platforms often provide limited customization compared to on-premise solutions, but they do offer configurable modules. Providers continuously release updates to meet industry needs.
- Benefit: Easier setup, but with limited deep customization.
- Traditional On-Premise:
- On-premise solutions offer extensive customization, allowing manufacturers to tailor the software to their specific operational needs and workflows.
- Benefit: Deep customization capabilities to meet unique business requirements.
7. Security
- SaaS:
- SaaS providers offer enterprise-level security measures, such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and secure data centers. However, some manufacturers may be concerned about storing sensitive data off-site in the cloud.
- Benefit: Strong security protocols, but concerns over data ownership and control may arise.
- Traditional On-Premise:
- With on-premise systems, manufacturers have full control over security measures, data storage, and access. However, ensuring adequate security requires a dedicated in-house IT team and resources.
- Benefit: Complete control over security, but with significant internal effort and expense.
8. Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
- SaaS:
- SaaS providers offer automatic backups and disaster recovery plans as part of the service. Data is stored in multiple secure locations, ensuring business continuity in the event of a disaster.
- Benefit: Built-in disaster recovery without the need for manual intervention.
- Traditional On-Premise:
- Backup and disaster recovery for on-premise solutions must be managed internally. This requires additional resources and careful planning to ensure data is protected.
- Drawback: Increased complexity and risk of data loss if not properly managed.
9. Integration
- SaaS:
- SaaS solutions offer easy integration with other cloud-based systems, including CRM, ERP, and supply chain management platforms. Many SaaS tools provide APIs for seamless connectivity across applications.
- Benefit: Streamlined integration with cloud services and third-party applications.
- Traditional On-Premise:
- Integrating on-premise systems with other software can be complex and may require custom development, especially when connecting to newer cloud-based platforms.
- Drawback: Challenging and costly integration processes.
10. Performance and Reliability
- SaaS:
- SaaS platforms are hosted in distributed cloud environments, ensuring high availability and uptime. Downtime risks are mitigated by the provider’s robust infrastructure.
- Benefit: Greater reliability with guaranteed service levels.
- Traditional On-Premise:
- Performance and reliability depend on the in-house infrastructure. Downtime can occur due to hardware failures, power outages, or insufficient IT support.
- Drawback: Higher risks of downtime and service interruptions.
11. Compliance
- SaaS:
- Many SaaS providers adhere to industry standards and regulatory requirements, such as GDPR, ISO, or HIPAA, ensuring compliance for manufacturers without requiring internal audits.
- Benefit: Built-in compliance management.
- Traditional On-Premise:
- Compliance management in on-premise systems must be handled internally, often requiring audits, certifications, and continual monitoring by the manufacturer’s IT team.
- Drawback: Increased burden for maintaining regulatory compliance.
12. Ownership and Control
- SaaS:
- With SaaS, the service provider retains control over the software and infrastructure, and manufacturers don’t own the software itself. This may raise concerns over data control and long-term reliance on a third party.
- Drawback: Less control over software customization and data ownership.
- Traditional On-Premise:
- On-premise solutions are owned and fully controlled by the manufacturer, allowing complete autonomy over software usage, updates, and data storage.
- Benefit: Full ownership and control over software and data.
Integrating SaaS with Legacy Systems in Manufacturing
Integrating SaaS solutions with existing legacy systems in manufacturing can be a powerful way to modernize operations without completely replacing traditional infrastructure. However, it requires careful planning and execution to ensure smooth data flow and minimal disruptions.
Here’s an overview of the key considerations, benefits, and challenges in integrating SaaS with legacy systems:
1. Understanding Legacy Systems
- Legacy Systems: These are older software or hardware systems that are still in use but may no longer be fully supported or easily upgradable. In manufacturing, this often includes ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems), or SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems.
- Challenge: Legacy systems may not have modern APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) or integration capabilities, making it difficult to connect them with new cloud-based SaaS solutions.
2. Integration Approaches
- API Development: For some legacy systems, custom APIs can be developed to enable communication with SaaS platforms. This can involve modifying legacy system code or using third-party API services.
- Benefit: Allows tailored integration based on the specific needs of the manufacturing process.
- Data Synchronization: In cases where real-time integration is not feasible, manufacturers can use batch processing to sync data at regular intervals. Data from the legacy system is uploaded to the cloud and processed by the SaaS application.
- Benefit: Simplifies integration but may result in delayed data updates.
3. Key Benefits of SaaS-Legacy Integration
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Integrating SaaS with legacy systems allows manufacturers to optimize and automate various processes without fully replacing existing infrastructure. For example, integrating a SaaS-based inventory management tool with a legacy ERP can streamline supply chain operations.
- Enhanced Data Visibility: SaaS solutions provide advanced analytics and real-time data dashboards, offering enhanced visibility into manufacturing operations. When integrated with legacy systems, this data can provide a more complete view of production metrics, inventory, and machine performance.
- Cost-Effective Modernization: Instead of undertaking a costly full-scale system overhaul, integrating SaaS with legacy systems provides a more cost-effective solution, allowing manufacturers to leverage modern technologies incrementally.
- Scalability and Flexibility: SaaS platforms are highly scalable, and when integrated with legacy systems, they provide manufacturers the flexibility to expand operations without heavily investing in new hardware or on-premise software.
4. Challenges in SaaS-Legacy Integration
- Data Silos: Legacy systems often operate in silos, meaning data is not easily accessible or shareable across different platforms. Integrating these with SaaS can require significant effort to break down these silos and ensure smooth data exchange.
- Compatibility Issues: Legacy systems may use outdated technologies, programming languages, or data formats that are incompatible with modern SaaS applications. Overcoming these technical challenges may require custom development or middleware solutions.
- Security Risks: Integrating cloud-based SaaS solutions with legacy systems can introduce new security vulnerabilities. It’s critical to ensure that data is encrypted during transmission and that both legacy and SaaS systems comply with relevant security standards.
- Downtime Risk: Integration projects can sometimes cause temporary disruptions to operations, particularly if legacy systems are not designed for easy integration. Careful planning and testing are required to minimize downtime.
5. Best Practices for Successful Integration
- Assessment of Existing Infrastructure: Before integrating SaaS with legacy systems, manufacturers should assess their existing IT infrastructure to understand the potential integration points, data flow requirements, and compatibility issues.
- Use of APIs and iPaaS: Where possible, manufacturers should leverage APIs or iPaaS solutions to simplify the integration process. Many modern SaaS solutions offer robust APIs that facilitate smooth integration with older systems.
- Incremental Integration: Rather than attempting to integrate all systems at once, manufacturers can take an incremental approach. For example, they could start with integrating specific areas like inventory management, production scheduling, or customer relationship management (CRM) and then expand to other areas over time.
- Testing and Validation: Rigorous testing is crucial to ensure that data flows seamlessly between systems and that the integration does not introduce errors or inefficiencies. Manufacturers should validate the integration by testing various scenarios and ensuring the system performs as expected.
- Security and Compliance: Security measures such as encryption, authentication protocols, and access controls should be implemented to protect sensitive data. Additionally, manufacturers must ensure that the integration complies with relevant regulations, such as GDPR or ISO 27001.
Security and Data Privacy in SaaS Manufacturing Solutions
In today's digital age, where manufacturing operations increasingly rely on cloud-based SaaS (Software as a Service) platforms, ensuring security and data privacy has become a top priority.
As manufacturers transition to cloud solutions for functions such as inventory management, production planning, and customer relationship management, the risks associated with data breaches, cyber-attacks, and regulatory non-compliance have escalated.
Here’s an in-depth look at key security and data privacy considerations for manufacturers adopting SaaS solutions:
1. Understanding the Security Risks in SaaS Manufacturing
- Data Breaches: The cloud is a target for hackers, who seek to gain unauthorized access to sensitive manufacturing data, such as intellectual property, customer details, and production schedules.
- Cyber Attacks: SaaS applications may be vulnerable to cyber-attacks such as DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks, ransomware, and malware. Manufacturing disruptions from such attacks can halt production and damage reputation.
- Insider Threats: Employees or third-party contractors with access to SaaS platforms may unintentionally or maliciously expose sensitive data, especially if security protocols are weak or not properly enforced.
2. Key Security Features of SaaS Solutions
- Encryption: Data should be encrypted both at rest (stored data) and in transit (data being transmitted between systems). This ensures that sensitive information remains unreadable to unauthorized users.
- Example: AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) with 256-bit encryption is commonly used for securing sensitive data in SaaS platforms.
- Access Control and Authentication: Implementing strict user access control through role-based access control (RBAC) ensures that only authorized personnel can access specific data. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security to prevent unauthorized access.
- Benefit: Reduces the risk of unauthorized data access by enforcing stricter control over who can access what data within the SaaS platform.
- Data Backups: Regular data backups are crucial for minimizing downtime and data loss in case of a cyber-attack, system failure, or accidental data deletion. Most SaaS providers offer automatic backup features that securely store backup copies in geographically dispersed locations.
- Network Security: SaaS providers use firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to monitor network traffic for suspicious activity. These systems detect and prevent potential attacks before they reach critical manufacturing operations.
3. Data Privacy in SaaS Manufacturing
- Compliance with Regulations: Manufacturers using SaaS must comply with local and international data privacy regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and industry-specific regulations like ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations).
- Example: Under GDPR, manufacturers must ensure that any data collected or processed via a SaaS platform is handled in accordance with data protection laws, including obtaining user consent and enabling data deletion upon request.
- Data Residency and Sovereignty: Manufacturers need to be aware of where their data is physically stored and processed. Some countries have strict rules regarding data sovereignty, requiring data to be stored within national borders.
- Best Practice: Ensure that your SaaS provider offers data residency options that align with local regulations, particularly if you operate in multiple countries.
- Data Minimization: Only the necessary data should be collected, processed, and stored. SaaS providers can help implement data minimization practices by ensuring that unnecessary data points are not retained, reducing the exposure to privacy risks.
4. Third-Party Vendor Security
- Vendor Risk Assessment: Before adopting a SaaS solution, manufacturers should conduct a vendor risk assessment to evaluate the security measures that the SaaS provider has in place. This includes reviewing their certifications (e.g., ISO 27001, SOC 2 compliance), security policies, and data handling practices.
- Security Audits and Penetration Testing: SaaS providers should conduct regular security audits and penetration tests to identify vulnerabilities in their systems. Manufacturers should ask for audit reports and confirm that any security gaps are promptly addressed.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Manufacturers must ensure that their SaaS provider includes robust security and privacy clauses in the SLA. This includes uptime guarantees, data breach notification timelines, and liability for data loss or breach incidents.
5. Data Ownership and Control
- Data Ownership: One common concern in SaaS is the issue of data ownership. Manufacturers need to clarify in their agreements that they retain full ownership of their data, and the SaaS provider serves only as a processor.
- Data Portability: Manufacturers must ensure that their data can be easily exported or migrated if they decide to switch SaaS providers. The right to data portability allows manufacturers to retain control over their operational data without being locked into one provider.
6. Security Best Practices for Manufacturers Using SaaS
- Regular Security Training: Manufacturers should provide regular cybersecurity training for their staff to raise awareness about phishing attacks, password security, and safe data practices. Employees are often the weakest link in cybersecurity, so continuous education is key to minimizing insider threats.
- Secure API Integration: Many manufacturers use APIs to connect SaaS applications with other software systems, such as ERP or MES. It's important to secure these API connections to prevent unauthorized access or data leaks during data exchange.
- Incident Response Plan: In the event of a data breach or cyber-attack, manufacturers should have an incident response plan in place that outlines steps for isolating the threat, notifying stakeholders, and restoring data from backups.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning in SaaS Solutions
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) have become transformative forces in SaaS solutions across industries, including manufacturing.
By integrating AI and ML into SaaS platforms, manufacturers are able to automate processes, gain predictive insights, and improve decision-making.
These technologies enable SaaS platforms to not only process vast amounts of data but also continuously learn and adapt to new patterns, driving greater efficiency and competitiveness.
Below are key areas where AI and ML enhance SaaS solutions in manufacturing:
1. Automation of Routine Tasks
- AI-driven SaaS platforms can automate mundane and repetitive tasks such as data entry, inventory tracking, and work order management. By automating these processes, manufacturers reduce manual errors and improve operational speed.
- Example: AI-enabled SaaS systems can automatically reorder inventory when stock levels are low, eliminating the need for human intervention.
2. Predictive Maintenance
- AI and ML are essential for predictive maintenance in manufacturing. By analyzing data from IoT sensors and machines, AI-powered SaaS systems can predict equipment failures before they happen, allowing manufacturers to schedule maintenance during downtime rather than in the middle of production.
- Benefit: Reduces unplanned downtime, lowers maintenance costs, and extends the lifespan of machinery.
3. Enhanced Decision-Making with Data Insights
- SaaS solutions with AI and ML capabilities can analyze vast amounts of manufacturing data to provide actionable insights. Machine learning algorithms sift through historical and real-time data to identify trends and anomalies, helping manufacturers make more informed decisions.
- Example: AI-based SaaS can recommend the most cost-effective production schedules based on historical demand patterns and real-time market data.
- Benefit: Increases agility by providing data-driven insights into production optimization and cost reduction.
4. Demand Forecasting
- AI and ML algorithms can accurately predict customer demand by analyzing historical data, market trends, and external factors like economic changes or seasonality. This helps manufacturers optimize their production schedules and manage inventory more efficiently.
- Example: ML model deployment can be used to predict a surge in demand for specific products and adjust production plans accordingly to avoid stockouts or overproduction.
- Benefit: Minimizes inventory costs and ensures manufacturers are prepared to meet market demand.
5. Supply Chain Optimization
- AI-driven SaaS platforms enhance supply chain management by offering end-to-end visibility and automating procurement processes. Machine learning algorithms can optimize supplier selection, reduce lead times, and improve inventory management through real-time data analysis.
- Example: AI can analyze shipping routes and suggest optimal routes for deliveries, reducing transit times and logistics costs.
- Benefit: Ensures timely delivery of materials and products, leading to greater operational efficiency.
6. Personalization and Customization
- AI-driven SaaS solutions offer a personalized experience to manufacturers by tailoring the platform’s functionality to specific business needs. Adaptive learning algorithms allow SaaS platforms to understand user behavior and preferences, customizing dashboards, workflows, and reports accordingly.
- Benefit: Improves user satisfaction and productivity by delivering a solution that fits the manufacturer’s exact requirements.
7. Real-Time Data Processing
- AI and ML enable SaaS platforms to process and analyze data in real-time, providing manufacturers with immediate insights. This is particularly useful for monitoring production lines, quality control, and machine performance.
- Example: In a manufacturing environment, AI-based systems can monitor product quality in real-time, immediately flagging defects and halting production to avoid costly errors.
- Benefit: Ensures higher product quality and faster response times to production issues.
8. Cost Optimization
- AI-based SaaS solutions can analyze costs across various departments and suggest areas for optimization. From raw material procurement to energy consumption, machine learning models identify inefficiencies and suggest ways to minimize costs while maintaining or improving productivity.
- Example: AI algorithms can recommend using cheaper materials without compromising product quality, or suggest energy-saving measures for production processes.
- Benefit: Reduces overall operational costs and improves the manufacturer’s bottom line.
9. Supply Chain Risk Mitigation
- AI and ML algorithms can analyze global market conditions, political events, and weather patterns to anticipate supply chain disruptions. SaaS solutions with AI capabilities help manufacturers proactively adjust supply chains to mitigate risks before they impact production.
- Example: Predicting potential supply chain disruptions due to natural disasters or geopolitical issues and suggesting alternative suppliers or routes.
- Benefit: Reduces the risk of production delays due to unforeseen supply chain issues.
10. AI-Driven Quality Control
- AI and machine learning are increasingly used for quality assurance in manufacturing. AI-powered image recognition algorithms in SaaS platforms can detect defects on production lines faster and more accurately than human inspectors.
- Example: AI can identify microscopic defects in products that are invisible to the human eye, ensuring higher product quality and reducing recalls.
- Benefit: Ensures consistent product quality, minimizes waste, and enhances customer satisfaction.
11. AI-Powered Customer Service
- SaaS platforms that integrate AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants improve customer service for manufacturers. These tools provide real-time support, resolving issues related to order tracking, product availability, or technical difficulties with machinery.
- Example: AI-powered assistants can answer common customer questions about product specifications or order statuses without human intervention.
- Benefit: Enhances customer experience and frees up staff for higher-level tasks.
12. AI for Sustainable Manufacturing
- AI in SaaS platforms can also support sustainability goals by optimizing resource usage. Machine learning models can suggest ways to reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and lower emissions based on real-time data from production processes.
- Example: AI algorithms can identify the most energy-efficient settings for machines, helping to reduce the carbon footprint of manufacturing plants.
- Benefit: Supports sustainability initiatives while reducing operational costs.
13. AI and ML in SaaS for Continuous Improvement
- AI-powered SaaS platforms can evolve and improve over time. Machine learning models continue to learn from the data they process, becoming more accurate and effective as they gain more information. This ensures that the SaaS solutions keep pace with the changing needs of the manufacturer and the market.
- Example: An AI-driven SaaS system can suggest process improvements as it learns from production data, leading to continuous efficiency gains.
- Benefit: Encourages a culture of continuous improvement and innovation in manufacturing.
Challenges in Implementing SaaS Solutions
While the benefits of implementing SaaS solutions in manufacturing are substantial, there are several challenges that companies may face during the adoption process. Overcoming these challenges requires careful planning, strategic execution, and a focus on aligning new technologies with existing processes and business goals.
Here are some common challenges manufacturers face when implementing SaaS solutions:
1. Integration with Legacy Systems
- Challenge: Many manufacturing companies still rely on older, on-premise systems such as ERP or MRP systems. Integrating these legacy systems with modern SaaS solutions can be complex and may require significant customization to ensure data flow and process alignment.
- Solution: A phased integration approach can help. Manufacturers can begin by integrating critical modules while gradually transitioning other components over time, ensuring minimal disruption to operations.
2. Data Migration
- Challenge: Migrating vast amounts of data from legacy systems to a cloud-based SaaS platform can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Ensuring data accuracy and consistency is critical to avoid operational issues post-implementation.
- Solution: Careful data mapping, thorough testing, and using specialized migration tools can ease the transition. Engaging experienced IT professionals and SaaS vendors during the migration process can also mitigate risks.
3. Security and Data Privacy Concerns
- Challenge: Cloud-based systems are inherently more exposed to security risks than on-premise systems, raising concerns about data breaches, intellectual property theft, and compliance with industry regulations such as GDPR and FERPA.
- Solution: Manufacturers should work with SaaS providers that have strong data security measures, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and compliance with relevant regulations. Additionally, conducting regular security audits and implementing access controls can help protect sensitive data.
4. Internet Dependency
- Challenge: SaaS solutions depend on reliable internet connectivity, which can be a challenge for manufacturing facilities in remote or industrial locations where internet access is limited or unstable.
- Solution: To mitigate this, manufacturers can implement redundant internet connections or use hybrid SaaS models that offer offline functionality, ensuring that key processes can continue even during connectivity issues.
5. Change Management and Workforce Training
- Challenge: Employees may resist new technologies, particularly if they are unfamiliar with cloud-based platforms or have used traditional systems for many years. Resistance to change can slow adoption and reduce the overall effectiveness of SaaS solutions.
- Solution: Comprehensive training programs and change management initiatives should be rolled out to help employees adapt to the new system. Providing clear communication about the benefits of SaaS and offering ongoing support can foster acceptance and ease the transition.
6. Customization and Flexibility Limitations
- Challenge: While SaaS solutions offer scalability and ease of use, they may not be as customizable as traditional on-premise systems. Manufacturers with highly specific workflows or unique business processes may find it difficult to tailor SaaS platforms to their needs.
- Solution: Choosing a SaaS provider that offers modular customization or application programming interfaces (APIs) can allow for greater flexibility. Manufacturers may also consider using a combination of SaaS and custom-built solutions for highly specialized operations.
7. Vendor Lock-In
- Challenge: SaaS platforms often create a dependency on the provider, making it difficult for manufacturers to switch vendors if they are dissatisfied with service or pricing. This is known as "vendor lock-in," where businesses face high switching costs when moving to a new platform.
- Solution: To mitigate this, manufacturers should thoroughly assess vendors before committing, ensuring that the SaaS provider offers contract flexibility, data portability, and clear service-level agreements (SLAs) to avoid being locked into unfavorable conditions.
8. Compliance and Regulatory Issues
- Challenge: Manufacturing companies must adhere to various industry-specific regulations, such as ISO, FDA, or OSHA standards. Ensuring that SaaS solutions comply with these regulations can be challenging, especially in highly regulated industries like pharmaceuticals or automotive manufacturing.
- Solution: Manufacturers should select SaaS providers that understand industry regulations and offer platforms that meet compliance requirements. Conducting thorough due diligence before implementation ensures that the chosen platform supports regulatory adherence.
9. Cost Management and ROI Concerns
- Challenge: Although SaaS is often more cost-effective upfront compared to traditional on-premise solutions, ongoing subscription fees can add up, especially for larger organizations. Additionally, manufacturers may be concerned about whether the investment in SaaS will deliver the expected return on investment (ROI).
- Solution: Conducting a detailed cost-benefit analysis before implementation is essential. Manufacturers should compare the total cost of ownership (TCO) between SaaS and traditional systems and monitor ROI through key performance indicators (KPIs) after deployment.
10. Downtime and System Reliability
- Challenge: While SaaS providers generally offer high levels of uptime, any service interruptions or outages can lead to significant operational disruptions for manufacturers. Relying on external vendors for maintenance and uptime can be a concern for manufacturers with strict production schedules.
- Solution: Selecting SaaS providers with strong uptime guarantees (ideally 99.9% or above) and robust disaster recovery plans can mitigate the risks. Additionally, ensuring the availability of backup systems or offline functionalities can help reduce the impact of potential downtime.
11. Lack of Internal Expertise
- Challenge: Implementing and managing SaaS platforms require a certain level of IT expertise, which may be lacking in some manufacturing companies, particularly smaller businesses. Without the necessary technical skills, implementation may be delayed, or the platform may not be utilized effectively.
- Solution: Manufacturers can address this challenge by partnering with a SaaS vendor that offers comprehensive support services or by hiring external consultants for implementation. Upskilling internal teams through training programs can also be a long-term solution.
12. Scalability Concerns
- Challenge: While SaaS platforms are designed to scale with business growth, manufacturers with highly complex or large-scale operations may encounter challenges as they expand. The platform’s ability to handle large volumes of data or an increased number of users may become a concern.
- Solution: Manufacturers should choose SaaS platforms that are built for scalability, with modular features that allow the system to grow with the business. Working closely with the vendor to assess future needs and potential limitations can ensure long-term scalability.
Key Metrics for Measuring SaaS Performance in Manufacturing
To evaluate the effectiveness of a SaaS solution in manufacturing, it’s essential to track key performance indicators (KPIs) that measure efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and overall impact on operations.
These metrics provide insight into how well the SaaS platform is supporting manufacturing processes and driving business goals.
Here are the key metrics for measuring SaaS performance in manufacturing:
System Uptime and Availability
- What it measures: The percentage of time the SaaS solution is operational and available to users.
- Why it matters: High system uptime is critical for ensuring smooth, uninterrupted production processes. Downtime can result in production delays, missed deadlines, and increased operational costs. A typical benchmark for SaaS solutions is an uptime of 99.9% or higher.
Response Time and Performance
- What it measures: The speed at which the SaaS platform processes requests and performs functions such as generating reports, executing transactions, or managing inventory data.
- Why it matters: Fast response times ensure that users can work efficiently without experiencing lag, which can disrupt production scheduling, order fulfillment, and decision-making processes.
User Adoption Rate
- What it measures: The percentage of employees or departments actively using the SaaS solution compared to the total number of potential users.
- Why it matters: High adoption rates indicate that the platform is user-friendly and effectively integrated into daily workflows. Low adoption may point to a need for additional training or improvements in the platform’s functionality.
Return on Investment (ROI)
- What it measures: The financial return generated by the SaaS solution relative to its cost (implementation, subscription fees, and maintenance).
- Why it matters: Calculating ROI helps manufacturers determine whether the SaaS platform is delivering value by improving efficiency, reducing costs, and increasing productivity. A positive ROI justifies continued use and investment in the solution.
Customer Support Response Time
- What it measures: The average time it takes for the SaaS vendor to respond to support requests or resolve issues.
- Why it matters: Timely customer support ensures that any disruptions to the manufacturing process due to software issues are resolved quickly, minimizing downtime and operational delays.
Scalability and Flexibility
- What it measures: The system's ability to scale as the business grows or as operational needs increase, without sacrificing performance or requiring significant additional investment.
- Why it matters: A scalable SaaS solution supports business growth, whether it involves increased production volumes, new product lines, or geographic expansion. Scalability also reduces the need for costly upgrades or platform changes.
Operational Efficiency Improvement
- What it measures: The percentage of improvement in key operational areas, such as reduced lead times, optimized inventory levels, or improved production throughput, after implementing the SaaS solution.
- Why it matters: This metric shows how well the SaaS platform is driving process improvements and eliminating inefficiencies within the manufacturing operations.
Error Reduction Rate
- What it measures: The decrease in errors in production, inventory management, or order fulfillment after the SaaS solution is implemented.
- Why it matters: Reducing errors directly impacts product quality, customer satisfaction, and operational costs. A lower error rate means that the SaaS platform is improving data accuracy and automating manual processes effectively.
Compliance and Audit Readiness
- What it measures: The system's ability to meet regulatory and industry compliance standards, such as ISO or OSHA, and its readiness for audits.
- Why it matters: Compliance is critical in manufacturing, especially in highly regulated industries like pharmaceuticals or automotive. A SaaS platform that helps maintain compliance ensures smooth operations and reduces the risk of fines or legal issues.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
- What it measures: The overall cost of the SaaS solution, including subscription fees, implementation, maintenance, and training, compared to the cost of traditional on-premise solutions.
- Why it matters: Measuring TCO provides a full picture of the financial impact of the SaaS solution and helps determine if it offers cost savings compared to alternative systems.
User Satisfaction and Feedback
- What it measures: The level of satisfaction among users based on surveys, feedback, and usage patterns.
- Why it matters: High user satisfaction indicates that the SaaS platform is meeting the needs of the team and improving workflow efficiency. Continuous feedback allows for ongoing improvements and ensures that the system aligns with business goals.
Tracking these metrics enables manufacturers to assess the performance of their SaaS solutions effectively, ensuring that they are optimizing operations, achieving desired outcomes, and deriving maximum value from their technology investment.
How Deskera SaaS Solution Enhances Efficiency in Manufacturing
Deskera, as a leading SaaS solution, offers a comprehensive suite of tools designed to streamline and optimize key manufacturing processes. By leveraging its cloud-based platform, manufacturers can improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance decision-making.
Here’s how Deskera can help improve efficiency in manufacturing:
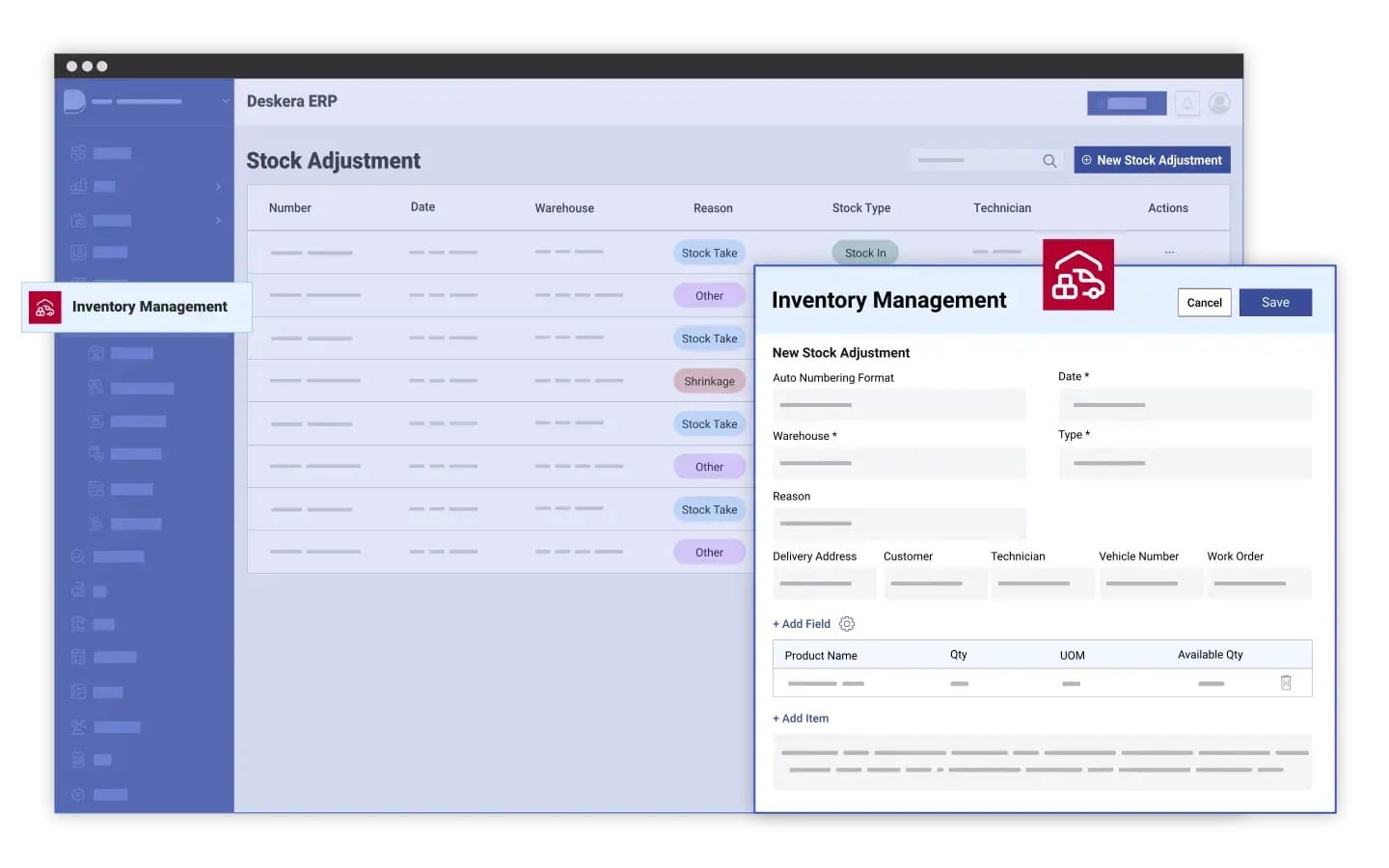
Real-Time Inventory Management
Deskera’s robust inventory management features allow manufacturers to track stock levels, monitor material usage, and automate reordering processes in real time. This helps prevent stockouts and overstocking, ensuring smooth production cycles and reducing waste.
Automated Production Planning and Scheduling
The platform’s Material Requirements Planning (MRP) module enables manufacturers to automate production planning, scheduling, and demand forecasting. This ensures that resources are optimally allocated and production timelines are met, minimizing downtime and increasing productivity.
Seamless Collaboration Across Teams
Deskera’s cloud-based collaboration tools enable seamless communication between production, procurement, and finance teams. This ensures that everyone has access to real-time data, reducing miscommunication and fostering cross-functional coordination.
Cost Control and Financial Management
With built-in accounting and financial management tools, Deskera helps manufacturers keep track of production costs, monitor profit margins, and generate financial reports. By providing visibility into operational expenses, manufacturers can make data-driven decisions to optimize resource usage and reduce costs.
Mobile Accessibility and Remote Management
Deskera’s mobile app allows managers to monitor production, track inventory, and access key performance indicators (KPIs) from anywhere. This level of accessibility ensures that decision-makers can respond quickly to any issues, enhancing operational agility.
Advanced Reporting and Analytics
Deskera provides customizable reporting and advanced analytics that offer manufacturers insights into their production efficiency, resource utilization, and overall operational performance. These data-driven insights empower manufacturers to identify bottlenecks, optimize workflows, and drive continuous improvement.
Regulatory Compliance and Quality Control
With features that help manufacturers adhere to industry standards and regulatory requirements, Deskera ensures compliance with quality control processes. This reduces the risk of errors, recalls, or non-compliance issues, contributing to smoother operations and maintaining product quality.
By integrating Deskera into their operations, manufacturers can improve efficiency across various areas, from production and inventory management to financial oversight and collaboration, ultimately driving growth and operational excellence.
Key Takeaways
- SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) solutions provide manufacturers with cloud-based tools that streamline operations, improve collaboration, and offer real-time data access, enabling companies to operate more efficiently and stay competitive.
- SaaS solutions in manufacturing offer flexibility, scalability, cost-effectiveness, and automatic updates, allowing manufacturers to adapt quickly to changing demands without the burden of managing complex IT infrastructures.
- Popular SaaS applications for manufacturing include inventory management, production planning, ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), CRM (Customer Relationship Management), and accounting, all of which help automate and optimize different operational areas.
- SaaS solutions reduce operational costs, increase agility, and improve collaboration across departments, resulting in faster decision-making, better resource allocation, and enhanced overall productivity in manufacturing processes.
- SaaS improves key manufacturing areas such as inventory management, production scheduling, quality control, and supply chain visibility by providing real-time data and analytics that drive smarter and more informed decision-making.
- Unlike traditional on-premise software, SaaS solutions are more flexible, require lower upfront costs, and eliminate the need for complex maintenance, making them a more scalable and cost-effective option for manufacturers.
- Modern SaaS platforms are designed to integrate seamlessly with existing legacy systems, allowing manufacturers to gradually adopt new technologies without disrupting ongoing operations or requiring complete overhauls.
- SaaS providers prioritize robust security protocols and compliance standards, ensuring that manufacturers' sensitive data and intellectual property are protected from cyber threats and unauthorized access.
- SaaS solutions that incorporate AI and machine learning help manufacturers optimize processes, predict demand, and improve maintenance scheduling, leading to more efficient operations and reduced downtime.
- Cloud-based collaboration tools within SaaS platforms enable teams across different locations to work together in real-time, improving communication, reducing miscommunication, and fostering better decision-making.
- While SaaS offers numerous benefits, challenges such as data migration, employee training, and initial implementation costs can arise. However, these can be mitigated with proper planning and support from the SaaS provider.
- Deskera’s comprehensive SaaS solution helps manufacturers streamline processes like inventory management, production planning, and financial tracking, offering real-time insights and automation to boost operational efficiency.
- Key metrics such as system uptime, user adoption, ROI, and operational efficiency help manufacturers assess the effectiveness of their SaaS solution, ensuring it delivers value and supports long-term growth goals.
Related Articles