Imagine a world where manufacturing processes are seamlessly integrated, driven by data, and powered by automation—this is the promise of digital manufacturing. As industries continue to evolve, the global digital manufacturing market is on a significant growth trajectory.
Valued at USD 387.65 billion in 2022, it is expected to reach USD 456 billion by the end of 2023 and soar to an impressive USD 1,670.45 billion by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.5%. This rapid expansion underscores the growing reliance on digital technologies to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and boost scalability in modern manufacturing operations.
Digital manufacturing goes beyond just automation—it represents a shift toward a more connected, intelligent production environment. By leveraging technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and cloud computing, manufacturers can gain unprecedented control and visibility over their operations.
These advancements enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven decision-making, all of which contribute to greater efficiency and reduced downtime. As more companies embrace this digital transformation, the competitive landscape is evolving, with those adopting digital manufacturing positioned to lead in innovation and market growth.
One tool helping businesses streamline their production processes is Deskera MRP. With advanced features such as demand forecasting, production planning, and real-time reporting, Deskera MRP allows manufacturers to optimize their entire workflow.
Additionally, its AI-powered assistant, David, provides actionable insights, making it easier to meet customer demands and stay ahead of the competition. Whether managing raw materials or final products, Deskera’s comprehensive MRP solution helps businesses embrace the future of digital manufacturing.
What is Digital Manufacturing?
Digital manufacturing is the integration of digital technologies into manufacturing processes to enhance production efficiency, flexibility, and precision.
It involves the use of software, data analytics, automation, and advanced technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning to streamline the design, production, and supply chain management.
At its core, digital manufacturing enables manufacturers to create virtual models of products, optimize production workflows, and monitor processes in real-time.
This digital-first approach allows for better decision-making, predictive maintenance, and improved product quality, ultimately driving faster production times and reducing costs.
By harnessing data and automation, digital manufacturing transforms traditional production methods into highly efficient, data-driven operations.
The Role of Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
Digital transformation in manufacturing has revolutionized the way products are designed, produced, and delivered.
At the heart of this transformation is the adoption of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing, which enable manufacturers to optimize their operations.
This shift toward digital transformation in manufacturing is not just about automating tasks but about creating a more connected and intelligent production ecosystem.
For example, digital manufacturing harnesses real-time data to improve decision-making and enhance process efficiency. This means manufacturers can monitor production remotely, predict equipment failures through predictive maintenance, and adjust workflows on the go to avoid costly downtime.
As the manufacturing industry embraces digital tools, businesses are increasingly able to reduce costs, improve product quality, and boost their competitive edge in the market.
Furthermore, digital transformation in the manufacturing industry is reshaping supply chain management. By using integrated systems and real-time analytics, companies can better manage inventory, streamline logistics, and improve customer satisfaction.
The use of manufacturing software plays a key role in facilitating this transformation, allowing companies to manage everything from procurement to production through a single platform.
This level of integration and automation ensures that manufacturers are better equipped to meet evolving market demands and stay ahead in a rapidly changing landscape.
By embracing digital transformation in manufacturing, companies are not only future-proofing their operations but also setting the stage for long-term innovation and growth.
Key Benefits of Digital Manufacturing
Digital manufacturing offers numerous advantages that help businesses stay competitive in an increasingly connected world. By integrating advanced technologies like AI, IoT, and manufacturing software, companies can significantly improve their production processes.
Here are some key benefits:
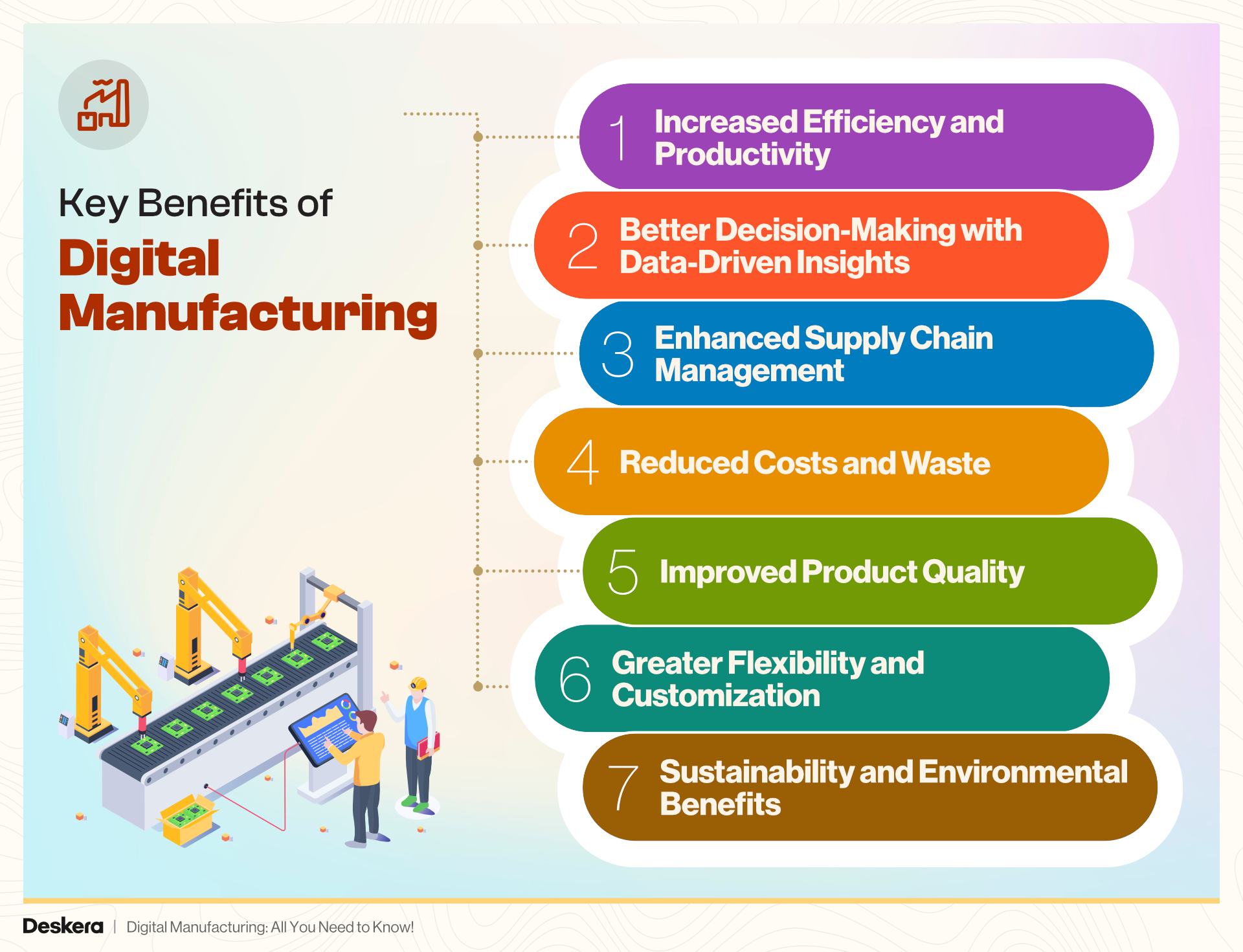
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
One of the primary benefits of digital manufacturing is its ability to enhance productivity. Automated systems and real-time data allow manufacturers to streamline workflows, minimize errors, and reduce downtime.
This leads to faster production cycles and more efficient use of resources, enabling manufacturers to meet increasing demand without compromising quality.
Better Decision-Making with Data-Driven Insights
Digital manufacturing harnesses the power of real-time data analytics to improve decision-making.
By using manufacturing software, manufacturers can access valuable insights into their operations, allowing them to identify inefficiencies and optimize processes.
This data-driven approach also enables predictive maintenance, which helps prevent costly equipment failures and ensures smooth operations.
Enhanced Supply Chain Management
Digital transformation in the manufacturing industry also brings improvements to supply chain management. Manufacturers can use digital tools to track inventory, manage procurement, and monitor logistics in real-time.
This leads to better coordination between suppliers and manufacturers, resulting in more reliable delivery schedules and reduced operational delays.
Reduced Costs and Waste
By adopting digital manufacturing technologies, businesses can significantly reduce operating costs. Automated systems lower the need for manual labor, while advanced analytics help optimize resource use, cutting down on material waste. As a result, manufacturers can achieve cost savings without sacrificing quality or output.
Improved Product Quality
Digital transformation in manufacturing allows for greater control over the production process, leading to higher-quality products. Technologies like AI and IoT enable real-time monitoring and quality checks at various stages of production. This reduces the likelihood of defects and ensures that products consistently meet quality standards.
Greater Flexibility and Customization
One of the standout features of digital manufacturing is its ability to provide flexibility. Manufacturers can quickly adjust production lines to accommodate different product designs or variations, making it easier to offer customized solutions for customers. This flexibility is especially beneficial in industries where consumer preferences change frequently.
Sustainability and Environmental Benefits
Digital manufacturing promotes more sustainable practices by optimizing resource use and reducing waste. By integrating manufacturing software and leveraging IoT, manufacturers can track energy consumption, monitor emissions, and minimize their environmental footprint. This not only helps businesses comply with regulatory standards but also enhances their reputation as eco-friendly organizations.
Examples of Digital Manufacturing in Action
Digital manufacturing is being adopted by various industries, transforming how products are designed, manufactured, and delivered. From automotive giants to aerospace companies, digital manufacturing is revolutionizing production processes.
Here are some notable examples of digital manufacturing in action:
1. Automotive Industry: Smart Factories
In the automotive industry, companies like Tesla and BMW are leveraging digital manufacturing to create smart factories. These factories use IoT and manufacturing software to monitor production in real-time, automate tasks, and ensure higher precision in the assembly process.
For example, Tesla's Gigafactory utilizes advanced robotics and machine learning algorithms to streamline battery production, reducing costs and improving output efficiency.
2. Aerospace: 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
The aerospace industry has embraced digital manufacturing through technologies like 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing. Companies like Boeing and Airbus are using 3D printing to produce lightweight yet durable parts.
This method not only reduces production time but also allows for customized parts that meet specific design requirements, improving fuel efficiency and performance. The use of digital manufacturing software enables the precise design and simulation of these components before production.
3. Consumer Electronics: Automation and Customization
Consumer electronics manufacturers, such as Apple, have integrated digital transformation in manufacturing to automate their production lines. By using manufacturing software, these companies manage supply chains, track inventory, and optimize production scheduling.
This integration allows for the mass production of electronics while maintaining flexibility to accommodate product variations and customization, as seen in Apple’s iPhone assembly process.
4. Healthcare: Personalized Medical Devices
In healthcare, digital manufacturing plays a crucial role in the production of personalized medical devices. Companies use advanced manufacturing software and 3D printing to create patient-specific prosthetics, implants, and surgical tools.
The ability to manufacture customized devices based on individual patient data has revolutionized patient care, providing better-fitting, more effective medical solutions.
5. Consumer Goods: Data-Driven Production
Brands in the consumer goods industry are embracing digital manufacturing to better respond to consumer demands. Companies like Nike use real-time data and manufacturing software to optimize production, reduce waste, and improve the sustainability of their operations.
Digital tools allow for on-demand manufacturing, enabling brands to create personalized products such as custom shoes with shorter lead times and reduced inventory.
These digital manufacturing examples showcase how industries are using cutting-edge technologies to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance product quality. As digital transformation continues to evolve, more companies are adopting these innovations to stay competitive in a rapidly changing landscape.
The Role of Manufacturing Software in Digital Manufacturing
Manufacturing software plays a pivotal role in enabling the successful implementation of digital manufacturing. As industries embrace digital transformation in manufacturing, software solutions provide the necessary tools to automate processes, manage data, and enhance operational efficiency.
Here are key ways manufacturing software is transforming the industry:
1. Streamlining Production Processes
One of the primary benefits of manufacturing software is its ability to streamline production workflows. From scheduling to machine operation, the software enables manufacturers to automate repetitive tasks, reducing manual labor and increasing production speed.
It integrates with manufacturing software systems, such as ERP and MRP platforms, to provide a cohesive production management experience. By automating these processes, companies can optimize resource utilization and minimize production downtime.
2. Real-Time Data Collection and Analytics
In the era of digital manufacturing, access to real-time data is critical. Manufacturing software collects data from IoT-enabled machines and systems, providing valuable insights into every stage of production.
This allows manufacturers to monitor performance, detect potential bottlenecks, and make data-driven decisions to improve efficiency. With advanced analytics, companies can predict equipment failures and schedule predictive maintenance, ultimately minimizing downtime and reducing operational costs.
3. Enhancing Supply Chain Visibility
The integration of manufacturing software with supply chain management systems is essential for modern manufacturers. By using real-time data, companies can track inventory, monitor suppliers, and manage logistics more effectively.
This enhanced visibility ensures that materials are available when needed and that production schedules remain on track. It also allows manufacturers to respond quickly to changes in demand, improving overall supply chain efficiency.
4. Facilitating Customization and Flexibility
Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on customization to meet specific customer demands. Manufacturing software allows for flexible production schedules and easy adjustments to design or production processes.
This is particularly valuable for industries like consumer goods and electronics, where personalized products are in high demand. By leveraging software solutions, companies can offer tailored solutions without compromising on production speed or efficiency.
5. Supporting Sustainability Efforts
Digital transformation in the manufacturing industry also emphasizes sustainability, and manufacturing software plays a crucial role in achieving this.
By optimizing energy consumption, reducing waste, and improving resource management, the software helps manufacturers meet environmental standards.
The ability to monitor and track energy usage in real-time allows companies to reduce their carbon footprint while still maintaining production efficiency.
6. Improving Collaboration and Communication
Collaboration across different departments is essential in digital manufacturing. Manufacturing software enables seamless communication between teams, from engineering and design to production and logistics.
By providing a centralized platform for data sharing and project management, the software fosters collaboration, leading to more coordinated efforts and faster problem-solving across the organization.
The Integration of AI and Machine Learning in Digital Manufacturing
The integration of AI (Artificial Intelligence) and machine learning into digital manufacturing is revolutionizing how companies design, produce, and deliver products.
By harnessing the power of these advanced technologies, manufacturers can optimize processes, reduce errors, and improve decision-making in ways that were previously unimaginable.
1. Predictive Maintenance and Downtime Reduction
AI and machine learning enable predictive maintenance, allowing manufacturers to monitor equipment performance in real-time.
By analyzing data collected from IoT devices, AI algorithms can predict when machinery is likely to fail, enabling timely repairs and reducing unplanned downtime.
This proactive approach helps companies avoid costly breakdowns, ensuring continuous production and minimizing disruption.
2. Process Optimization with AI-Driven Insights
AI provides manufacturers with actionable insights into production processes, identifying inefficiencies and bottlenecks. Machine learning models can analyze vast amounts of data to suggest optimizations, such as adjusting machine settings or reallocating resources.
This results in smoother workflows, reduced waste, and faster production cycles. AI-driven process optimization plays a significant role in digital manufacturing by maximizing operational efficiency.
3. Quality Control and Defect Detection
In traditional manufacturing, quality control is often manual and time-consuming. However, with the integration of AI, manufacturers can automate quality checks and defect detection.
AI-powered visual inspection systems can analyze products in real-time, detecting defects that may be missed by the human eye. This ensures consistent quality, reduces rework, and minimizes waste, contributing to overall efficiency in digital manufacturing.
4. Enhanced Supply Chain Management
AI and machine learning are also transforming supply chain management. By analyzing historical data and market trends, AI can forecast demand more accurately, helping manufacturers adjust production schedules and optimize inventory levels.
Machine learning models can also optimize logistics, reducing lead times and improving delivery efficiency. This level of precision ensures that companies can better meet customer demands and avoid costly overproduction or shortages.
5. Advanced Robotics and Automation
Digital manufacturing is increasingly incorporating AI-powered robotics to automate complex tasks. These robots are equipped with machine learning capabilities, allowing them to learn and adapt to new tasks over time.
From assembly line automation to material handling, AI-driven robotics enhances productivity while reducing the need for human intervention in repetitive tasks. This leads to increased efficiency, scalability, and flexibility in manufacturing operations.
6. Personalization and Customization
AI and machine learning also enable manufacturers to offer more personalized and customized products. By analyzing customer data and preferences, AI systems can automatically adjust production settings to create tailored products.
This flexibility is essential in industries such as consumer goods, electronics, and healthcare, where demand for personalized products is growing rapidly.
Challenges and Solutions in Digital Manufacturing
Digital manufacturing represents a transformative leap forward for industries worldwide, but it also comes with its own set of challenges. Addressing these challenges effectively is crucial for realizing the full potential of digital transformation.
Here’s a look at some of the key challenges and the solutions that can overcome them:
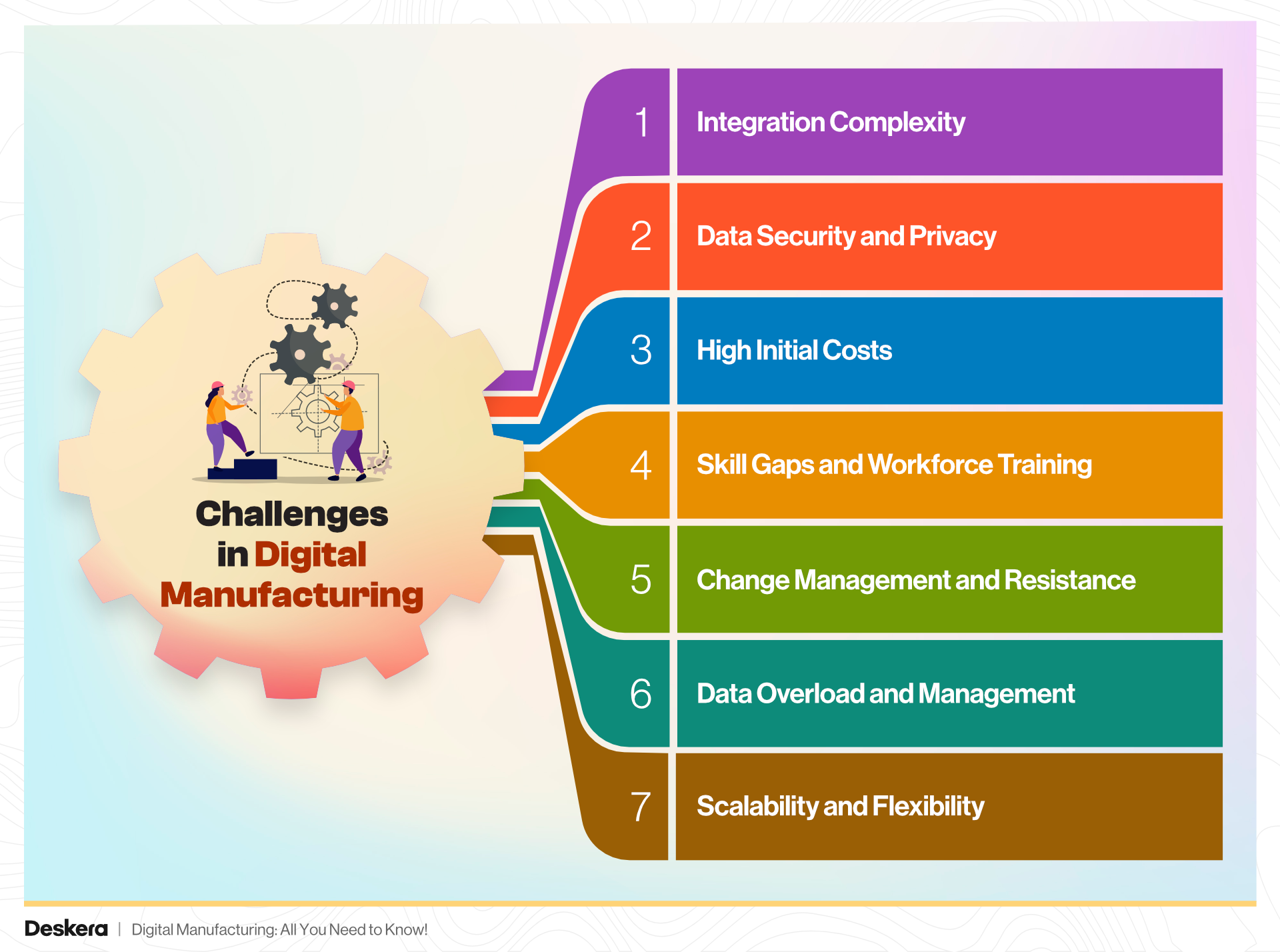
1. Integration Complexity
Challenge: Integrating new digital technologies with existing systems can be complex and costly. Legacy systems may not be compatible with modern software, creating obstacles in data exchange and process integration.
Solution: Adopting a phased integration approach can help ease the transition. Start by implementing manufacturing software that supports interoperability with existing systems.
Additionally, investing in middleware solutions can bridge gaps between old and new systems, facilitating smoother integration. It’s also beneficial to work with vendors who offer robust support for integration.
2. Data Security and Privacy
Challenge: As manufacturing processes become more digital, the amount of data generated and shared increases. This creates concerns about data security and privacy, particularly with sensitive operational and customer information.
Solution: Implementing strong cybersecurity measures is essential. Use encryption for data transmission, regularly update software to protect against vulnerabilities, and enforce strict access controls.
Additionally, educate employees on data security best practices and develop a comprehensive data protection policy to safeguard against potential breaches.
3. High Initial Costs
Challenge: The initial investment required for digital manufacturing technologies, such as AI, IoT, and advanced robotics, can be significant. This includes costs for new equipment, software, and training.
Solution: Consider a strategic approach to investment. Start with pilot projects to demonstrate the ROI of digital technologies before scaling up.
Look for funding options such as grants, incentives, or partnerships with technology providers that offer flexible financing plans. Additionally, prioritize investments based on potential impact and return on investment.
4. Skill Gaps and Workforce Training
Challenge: The shift to digital manufacturing often requires new skill sets that current employees may not possess. This creates a challenge in terms of workforce training and development.
Solution: Invest in ongoing training and development programs to upskill employees. Partner with educational institutions or training providers to offer specialized courses in digital manufacturing technologies.
Encourage a culture of continuous learning and provide opportunities for employees to gain hands-on experience with new systems and tools.
5. Change Management and Resistance
Challenge: Implementing digital transformation in manufacturing can face resistance from employees who are accustomed to traditional processes. Change management is crucial to ensure a smooth transition.
Solution: Develop a comprehensive change management strategy that includes clear communication about the benefits of digital transformation. Involve employees early in the process and address their concerns through workshops and feedback sessions. Provide support and resources to help them adapt to new technologies and processes.
6. Data Overload and Management
Challenge: The vast amount of data generated by digital manufacturing technologies can be overwhelming. Managing and analyzing this data effectively is crucial for making informed decisions.
Solution: Utilize advanced manufacturing software with robust data analytics capabilities to handle large volumes of data. Implement data management systems that can filter, analyze, and visualize data in actionable formats.
Leveraging AI and machine learning can also enhance data analysis, helping to extract valuable insights and improve decision-making.
7. Scalability and Flexibility
Challenge: As businesses grow, their digital manufacturing systems must scale accordingly. Ensuring that systems remain flexible and adaptable to changing needs can be challenging.
Solution: Choose modular and scalable manufacturing software that can grow with your business. Implement cloud-based solutions to provide the flexibility and scalability needed to adapt to new demands. Regularly review and update your systems to ensure they meet evolving business requirements.
The Future of Digital Manufacturing
The future of digital manufacturing promises to be dynamic and transformative, driven by ongoing advancements in technology and evolving industry demands.
As companies continue to embrace digital transformation in manufacturing, several key trends and innovations are expected to shape the landscape.
Here’s a look at what the future holds for digital manufacturing:
1. Advanced AI and Machine Learning Integration
AI and machine learning will become increasingly integral to digital manufacturing, enhancing automation, predictive analytics, and decision-making. Future developments will see more sophisticated AI algorithms capable of optimizing complex production processes in real-time.
Machine learning will enable continuous improvement by analyzing vast amounts of data to uncover insights and refine manufacturing strategies. This integration will lead to even greater efficiency, accuracy, and innovation in manufacturing operations.
2. Expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) will expand further in digital manufacturing, with more devices and machines becoming interconnected. IoT sensors and devices will provide real-time data on equipment performance, environmental conditions, and product quality.
This enhanced connectivity will enable manufacturers to monitor and control their operations from anywhere, leading to improved responsiveness, reduced downtime, and optimized resource management.
3. Growth of Additive Manufacturing and 3D Printing
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, will continue to evolve, offering new possibilities for product design and production. Future advancements will enhance the speed, precision, and material options available for 3D printing.
This technology will enable the production of highly customized and complex parts, reducing lead times and costs. It will also support more sustainable practices by minimizing material waste and enabling localized production.
4. Development of Digital Twins
Digital twins—virtual replicas of physical assets—will become more prevalent in digital manufacturing. These digital models will simulate the performance and behavior of physical systems, allowing manufacturers to test and optimize processes in a virtual environment before implementation.
The use of digital twins will enhance product development, predictive maintenance, and overall operational efficiency by providing valuable insights into system behavior and potential issues.
5. Enhanced Cybersecurity Measures
As digital manufacturing systems become more interconnected, cybersecurity will be a critical focus. Future developments will include more robust cybersecurity measures to protect against cyber threats and data breaches.
Advanced encryption, threat detection, and response technologies will ensure the security of sensitive manufacturing data and systems, safeguarding against potential vulnerabilities.
6. Integration of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) will play a significant role in the future of digital manufacturing. These technologies will enhance training, maintenance, and design processes by providing immersive and interactive experiences.
AR will assist technicians with real-time, on-site information and guidance, while VR will enable detailed simulation and design review, improving accuracy and reducing errors.
7. Increased Focus on Sustainability
Sustainability will become a central theme in the future of digital manufacturing. Companies will increasingly adopt technologies and practices that minimize environmental impact and enhance resource efficiency.
This includes the use of manufacturing software to optimize energy consumption, reduce waste, and support circular economy initiatives. The push for greener manufacturing practices will drive innovation and contribute to more sustainable production processes.
8. Rise of Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Collaborative robots, or cobots, will become more common in digital manufacturing environments. Unlike traditional robots, cobots are designed to work alongside human operators, enhancing productivity and flexibility.
These robots will handle repetitive or hazardous tasks, allowing human workers to focus on more complex and creative aspects of production. The integration of cobots will improve safety and efficiency in manufacturing operations.
The Impact of Digital Manufacturing on Supply Chains
Digital manufacturing is revolutionizing supply chains, driving efficiencies, and transforming how companies manage production and distribution. By integrating advanced technologies into manufacturing processes, businesses are achieving greater visibility, agility, and coordination across their supply chains.
Here’s a look at the significant impacts of digital manufacturing on supply chains:
1. Enhanced Visibility and Transparency
Digital manufacturing provides real-time data and insights that improve supply chain visibility. Advanced manufacturing software and IoT technologies enable companies to track the status of raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods throughout the supply chain.
This transparency allows for better monitoring of inventory levels, production progress, and potential disruptions, leading to more informed decision-making and proactive management.
2. Improved Demand Forecasting and Planning
The integration of AI and machine learning into digital manufacturing enhances demand forecasting accuracy. By analyzing historical data, market trends, and consumer behavior, these technologies can predict future demand with greater precision.
Improved forecasting allows companies to align production schedules with actual demand, reducing excess inventory and minimizing stockouts. This leads to more efficient inventory management and optimized supply chain planning.
3. Streamlined Production and Inventory Management
Digital manufacturing technologies, such as ERP and MRP systems, streamline production and inventory management processes. These systems automate tasks such as order processing, inventory tracking, and production scheduling, reducing manual effort and errors.
By integrating these systems with supply chain management tools, companies can synchronize production with supply chain activities, ensuring that materials and products are available when needed and improving overall efficiency.
4. Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
The adoption of digital technologies fosters better collaboration and communication across the supply chain. Manufacturing software and collaborative platforms facilitate real-time sharing of information between suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors.
This improved communication helps to coordinate activities, resolve issues quickly, and align efforts across the supply chain. Enhanced collaboration leads to more cohesive operations and a more responsive supply chain.
5. Increased Agility and Flexibility
Digital manufacturing enables greater agility and flexibility in supply chain operations. Technologies like 3D printing and additive manufacturing allow for rapid prototyping and production of customized parts.
This flexibility helps companies adapt to changing market conditions, customer preferences, and supply chain disruptions. Additionally, digital tools enable faster response times to changes in demand, allowing for more agile and adaptable supply chain management.
6. Optimization of Logistics and Distribution
Advanced manufacturing software and IoT solutions optimize logistics and distribution processes. Real-time tracking and data analytics provide insights into transportation routes, delivery times, and potential bottlenecks.
This optimization improves route planning, reduces transportation costs, and enhances delivery reliability. Efficient logistics and distribution contribute to faster order fulfillment and improved customer satisfaction.
7. Enhanced Quality Control and Compliance
Digital manufacturing technologies improve quality control and ensure compliance with industry standards. Automated inspection systems powered by AI can detect defects and deviations in real-time, leading to higher product quality and fewer recalls.
Additionally, digital tools help track and document compliance with regulatory requirements, ensuring that products meet necessary standards and certifications.
8. Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Digital manufacturing supports sustainability initiatives within the supply chain. Manufacturing software helps optimize resource usage, reduce waste, and lower energy consumption.
Technologies like IoT and data analytics enable better management of environmental impact by monitoring and controlling emissions, energy use, and waste production. Sustainable practices contribute to a greener supply chain and align with corporate social responsibility goals.
9. Cost Reduction and Efficiency Gains
Overall, the integration of digital manufacturing technologies leads to cost reduction and efficiency gains across the supply chain. Automation, improved forecasting, and optimized processes reduce operational costs and waste.
Enhanced visibility and communication also help prevent costly disruptions and delays. By leveraging these benefits, companies can achieve a more cost-effective and efficient supply chain.
How to Implement Digital Manufacturing in Your Business
Implementing digital manufacturing can transform your business by enhancing efficiency, agility, and innovation. However, successfully integrating digital technologies into your manufacturing operations requires careful planning and execution.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you implement digital manufacturing effectively:
1. Assess Your Current Capabilities and Needs
Conduct a thorough assessment of your current manufacturing processes, systems, and technologies. Identify existing strengths and weaknesses, and determine the specific needs of your business.
Evaluate your current manufacturing software, equipment, and data management practices. Understanding your baseline will help you identify areas where digital manufacturing technologies can provide the most value.
2. Define Your Objectives and Goals
Set clear objectives for implementing digital manufacturing. These goals could include improving efficiency, reducing costs, enhancing product quality, or increasing flexibility.
Establishing specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals will guide your implementation strategy and help you track progress.
3. Develop a Comprehensive Digital Transformation Strategy
Create a digital transformation strategy that outlines the technologies and solutions you plan to implement. This strategy should include:
- Technology Selection: Choose the appropriate digital manufacturing technologies, such as IoT, AI, machine learning, 3D printing, or ERP systems, based on your objectives and needs.
- Integration Plan: Develop a plan for integrating new technologies with existing systems. Consider how to address potential compatibility issues and ensure smooth data flow between systems.
- Timeline and Milestones: Establish a timeline for implementation with key milestones to track progress and make adjustments as needed.
4. Invest in the Right Technologies and Solutions
Select and invest in the manufacturing software and hardware that align with your digital transformation goals. Consider factors such as scalability, ease of integration, and vendor support. Some key technologies to explore include:
- ERP Systems: For streamlined resource planning and management.
- IoT Sensors: For real-time monitoring and data collection.
- AI and Machine Learning Tools: For predictive analytics and process optimization.
- 3D Printing Solutions: For rapid prototyping and customization.
5. Train Your Workforce
Employee training is crucial for successful digital manufacturing implementation. Provide comprehensive training on new technologies, tools, and processes. This includes:
- Technical Training: Ensure employees understand how to operate and maintain new systems and equipment.
- Change Management: Educate staff on the benefits of digital transformation and how it will impact their roles. Address any concerns and foster a culture of continuous learning.
6. Implement Pilot Projects
Start with pilot projects to test new technologies and processes on a smaller scale before full-scale implementation. Pilot projects allow you to:
- Evaluate Performance: Assess the effectiveness of new technologies and processes.
- Identify Issues: Detect and address any challenges or issues before broader deployment.
- Refine Processes: Make necessary adjustments based on pilot results to optimize implementation.
7. Monitor and Evaluate Performance
Once digital manufacturing technologies are implemented, continuously monitor and evaluate their performance. Use key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress towards your objectives. Common KPIs include:
- Operational Efficiency: Assess improvements in production speed and resource utilization.
- Quality Metrics: Track changes in product quality and defect rates.
- Cost Savings: Measure reductions in operational costs and waste.
8. Scale and Expand
After successful pilot projects and initial implementation, scale and expand your digital manufacturing efforts. Gradually roll out new technologies and processes across other areas of your business. Ensure that you continue to:
- Optimize Processes: Continuously refine and improve digital manufacturing processes based on performance data.
- Incorporate Feedback: Gather feedback from employees and stakeholders to make ongoing adjustments and improvements.
9. Foster a Culture of Innovation
Encourage a culture of innovation within your organization. Promote the adoption of new technologies and support employees in exploring innovative solutions. Stay informed about emerging trends and advancements in digital manufacturing to remain competitive and continue evolving.
10. Review and Update Your Strategy
Regularly review and update your digital manufacturing strategy to ensure it aligns with your business goals and market changes. Stay adaptable and open to integrating new technologies and processes as they become available.
The Role of Digital Manufacturing Marketing Agencies
Digital manufacturing is a rapidly evolving field, and effectively marketing its innovations and benefits requires specialized expertise. Digital manufacturing marketing agencies play a crucial role in bridging the gap between manufacturers and their target audiences.
Here’s a look at how these agencies contribute to the growth and visibility of digital manufacturing solutions:
1. Crafting Targeted Marketing Strategies
Digital manufacturing marketing agencies develop targeted marketing strategies tailored to the unique needs of the manufacturing sector. They use data-driven insights to identify key industry trends, target audiences, and market opportunities.
By creating customized strategies, these agencies ensure that digital manufacturing solutions are effectively promoted to the right stakeholders, such as manufacturing executives, engineers, and technology buyers.
2. Enhancing Brand Visibility and Recognition
One of the primary roles of digital manufacturing marketing agencies is to enhance brand visibility and recognition.
They leverage various marketing channels—such as digital advertising, social media, content marketing, and public relations—to build and maintain a strong brand presence.
This increased visibility helps digital manufacturing companies establish themselves as leaders in the industry and attract potential clients and partners.
3. Creating Compelling Content
Content creation is a key function of digital manufacturing marketing agencies. They produce a range of content types, including:
- Educational Articles and Blogs: Informative content that explains the benefits and applications of digital manufacturing technologies.
- Case Studies and White Papers: Detailed reports showcasing successful implementations and real-world examples of digital manufacturing solutions.
- Infographics and Videos: Visual content that simplifies complex concepts and engages audiences with compelling storytelling.
This content not only educates potential customers but also positions digital manufacturing companies as thought leaders in the industry.
4. Driving Lead Generation and Conversion
Digital manufacturing marketing agencies implement strategies to drive lead generation and conversion.
They use tactics such as targeted advertising, email marketing, and search engine optimization (SEO) to attract potential leads and guide them through the sales funnel.
By optimizing landing pages, call-to-actions, and lead capture forms, these agencies help convert prospects into customers, ultimately boosting sales and growth.
5. Managing Online Reputation
Online reputation management is crucial in the digital age. Marketing agencies monitor and manage the online presence of digital manufacturing companies, addressing any negative reviews or feedback and highlighting positive customer experiences.
They work to build a strong, positive reputation through proactive engagement and transparent communication, ensuring that the company’s brand is perceived favorably in the marketplace.
6. Utilizing Data Analytics
Data analytics is a powerful tool used by digital manufacturing marketing agencies to track the effectiveness of marketing campaigns. Agencies analyze metrics such as website traffic, engagement rates, lead conversion rates, and return on investment (ROI) to assess performance and make data-driven decisions. This approach allows them to refine strategies, optimize campaigns, and maximize the impact of marketing efforts.
7. Facilitating Industry Networking and Partnerships
Marketing agencies play a role in facilitating industry networking and partnerships. They organize and manage events, webinars, and conferences that bring together key players in the digital manufacturing sector.
These events provide opportunities for networking, collaboration, and knowledge sharing, helping companies build valuable relationships and expand their industry connections.
8. Navigating Market Trends and Innovations
Digital manufacturing is a field characterized by rapid technological advancements and shifting market trends.
Marketing agencies stay abreast of these changes, helping companies navigate new developments and adapt their marketing strategies accordingly.
By keeping clients informed about emerging trends and innovations, agencies ensure that their marketing efforts remain relevant and effective.
9. Providing Expertise in Digital Marketing Channels
Digital manufacturing marketing agencies are experts in leveraging various digital marketing channels, including:
- Social Media: Using platforms like LinkedIn, Twitter, and Facebook to engage with industry professionals and share valuable content.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Enhancing online visibility through keyword optimization and improved search engine rankings.
- Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising: Running targeted ad campaigns to attract and convert potential leads.
Their expertise in these channels ensures that digital manufacturing companies can reach their audience effectively and achieve their marketing goals.
10. Supporting Product Launches and Campaigns
Finally, marketing agencies assist with product launches and campaigns, helping digital manufacturing companies introduce new technologies and solutions to the market.
They coordinate promotional activities, create launch materials, and execute marketing campaigns that generate excitement and drive interest in new offerings.
How Deskera MRP Can Help You with Digital Manufacturing?
Deskera MRP (Material Requirements Planning) is a powerful tool designed to enhance manufacturing processes and streamline operations. When integrated into digital manufacturing environments, Deskera MRP offers several advantages that can significantly improve efficiency, accuracy, and productivity.
Here’s how Deskera MRP can support your digital manufacturing efforts:
1. Streamlined Production Planning
Deskera MRP facilitates streamlined production planning by providing real-time insights into inventory levels, production schedules, and material requirements. This enables manufacturers to plan and execute production activities with greater precision, reducing lead times and ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently. With Deskera MRP, you can:
- Create accurate production schedules based on demand forecasts and inventory levels.
- Optimize resource utilization and minimize downtime.
- Adjust production plans dynamically in response to changes in demand or supply.
2. Enhanced Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is crucial in digital manufacturing. Deskera MRP helps you manage inventory levels more effectively by providing real-time data on stock availability, usage, and replenishment needs. Key benefits include:
- Automated inventory tracking and updates.
- Reduction of excess inventory and associated carrying costs.
- Improved accuracy in order fulfillment and stock replenishment.
3. Accurate Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting is essential for aligning production with market needs. Deskera MRP integrates advanced forecasting tools to predict future demand based on historical data, trends, and market conditions. This helps you:
- Plan production schedules that match expected demand.
- Minimize the risk of stockouts and overproduction.
- Make data-driven decisions to align production with customer needs.
4. Improved Supply Chain Coordination
Deskera MRP enhances supply chain coordination by integrating with various supply chain partners and stakeholders. This integration facilitates:
- Real-time sharing of data and updates across the supply chain.
- Better communication with suppliers and vendors.
- Improved visibility into supply chain operations and potential disruptions.
5. Optimized Material Requirements
One of the core functions of Deskera MRP is to optimize material requirements. It calculates the exact amount of raw materials and components needed for production based on current inventory and production plans. Benefits include:
- Reduction of material wastage and excess inventory.
- Timely procurement of materials to avoid production delays.
- Efficient management of procurement and supplier relationships.
6. Enhanced Data-Driven Decision Making
Deskera MRP provides valuable data-driven insights that support better decision-making. By analyzing data from various sources, including production, inventory, and sales, you can:
- Identify trends and patterns that inform strategic decisions.
- Evaluate the performance of production processes and supply chain activities.
- Make informed adjustments to improve overall efficiency and effectiveness.
7. Integration with Other Digital Manufacturing Tools
Deskera MRP integrates seamlessly with other digital manufacturing tools, such as ERP systems, IoT devices, and AI-driven analytics platforms. This integration ensures:
- Unified data management and process automation across systems.
- Enhanced visibility into production processes and supply chain activities.
- Streamlined operations and reduced manual intervention.
8. Advanced Reporting and Analytics
Advanced reporting and analytics capabilities in Deskera MRP provide in-depth insights into various aspects of manufacturing operations. You can:
- Generate detailed reports on production performance, inventory levels, and supply chain metrics.
- Use analytics to identify areas for improvement and optimize processes.
- Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress and achieve goals.
9. Scalability and Flexibility
Deskera MRP offers scalability and flexibility to adapt to changing business needs. Whether you’re scaling up production or adjusting to new market demands, Deskera MRP can:
- Support growth by handling increased production volumes and complexity.
- Provide flexible solutions that can be customized to fit your specific requirements.
- Ensure that your manufacturing processes remain efficient and effective as your business evolves.
10. Cost Reduction and Efficiency Gains
Ultimately, Deskera MRP helps you achieve cost reduction and efficiency gains by optimizing production planning, inventory management, and supply chain coordination. Key outcomes include:
- Lower operational costs through efficient resource management and reduced waste.
- Increased productivity and reduced lead times.
- Improved profitability and competitive advantage in the digital manufacturing landscape.
Key Takeaways
- The digital manufacturing market is expanding rapidly, with the global market size projected to grow from USD 387.65 billion in 2022 to USD 1,670.45 billion by 2031. Integrating digital manufacturing technologies can significantly enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and drive innovation in manufacturing processes.
- Digital manufacturing refers to the use of digital technologies such as IoT, AI, and advanced analytics to optimize and streamline manufacturing processes. It encompasses the entire lifecycle of production, from design to delivery, enhancing flexibility, precision, and efficiency.
- Digital transformation in manufacturing involves adopting technologies that improve operational efficiency, data management, and decision-making. It enables manufacturers to stay competitive by enhancing productivity, reducing downtime, and fostering innovation.
- Digital manufacturing offers several benefits, including increased operational efficiency, enhanced product quality, reduced time-to-market, and improved supply chain visibility. These advantages lead to cost savings and a stronger competitive edge in the industry.
- Real-world examples, such as the use of predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and digital twins, illustrate how digital manufacturing technologies are being applied to solve complex challenges, optimize production, and improve outcomes across various industries.
- Manufacturing software, including ERP and MRP systems, plays a crucial role in digital manufacturing by providing tools for managing production planning, inventory control, and supply chain coordination. These systems enhance efficiency and accuracy in manufacturing operations.
- AI and machine learning are transforming digital manufacturing by enabling predictive analytics, process automation, and real-time decision-making. These technologies help manufacturers optimize operations, reduce costs, and drive innovation.
- Common challenges in digital manufacturing include high implementation costs, data security concerns, and integration issues. Addressing these challenges through strategic planning, investment in cybersecurity, and seamless integration can lead to successful digital transformation.
- The future of digital manufacturing will be shaped by advancements in technologies such as AI, IoT, and advanced robotics. Embracing these innovations will drive further growth and transformation, offering new opportunities for efficiency and customization in manufacturing.
- Digital manufacturing enhances supply chain efficiency by providing real-time visibility, improving coordination, and enabling more accurate demand forecasting. This leads to reduced lead times, better inventory management, and a more agile supply chain.
- Implementing digital manufacturing involves assessing current capabilities, defining clear objectives, selecting the right technologies, and providing employee training. A structured approach ensures successful integration and maximizes the benefits of digital manufacturing.
- Digital manufacturing marketing agencies help companies effectively promote their technologies by crafting targeted marketing strategies, creating compelling content, and managing online reputation. Their expertise drives brand visibility, lead generation, and market growth.
Related Articles













