Have you ever struggled with maintaining the right level of inventory—either facing stockouts that disrupt operations or excess stock that ties up capital? Customer Managed Inventory (CMI) offers a smarter approach, giving customers more control over their stock while improving supply chain efficiency.
Unlike traditional inventory models where suppliers dictate stock levels, CMI shifts the responsibility to customers, allowing them to replenish inventory based on real-time demand data. This shift leads to improved accuracy, reduced waste, and stronger supplier-customer collaboration.
CMI is becoming a game-changer for businesses looking to enhance supply chain agility. By empowering customers to manage their own inventory, companies can reduce lead times, optimize order fulfillment, and minimize excess inventory costs.
This proactive approach not only streamlines operations but also strengthens relationships between suppliers and buyers, fostering a more responsive and efficient supply chain. Industries such as manufacturing, retail, and healthcare are already leveraging CMI to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
However, successful implementation of CMI requires robust inventory management technology, seamless data exchange, and a well-integrated ERP system. This is where Deskera ERP comes in.
Deskera provides real-time inventory tracking, automated stock updates, and AI-driven demand forecasting, making CMI execution smooth and efficient. With features like mobile accessibility and AI-powered assistance, businesses can gain complete visibility over inventory movements, enabling smarter decision-making.
As companies continue to seek cost-effective and efficient supply chain solutions, CMI is emerging as a key strategy to enhance operational flexibility. But how does it work in practice, and what are the challenges involved? In this blog, we’ll dive deep into the workings of CMI, its benefits, challenges, and the best practices for successful implementation.
What is Customer Managed Inventory (CMI)?
Customer Managed Inventory (CMI) is a supply chain strategy where businesses take full control of their inventory management instead of relying on suppliers to monitor and replenish stock. This means that companies are responsible for tracking stock levels, forecasting demand, and placing orders as needed. By doing so, businesses can ensure they always have the right amount of inventory—minimizing stockouts, reducing excess stock, and improving overall efficiency.
Unlike Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI)—where the supplier oversees inventory replenishment—CMI gives customers greater autonomy and flexibility over their stock. Companies use advanced inventory management systems, barcodes, RFID tracking, and real-time data analytics to monitor stock movements. This enables them to make data-driven decisions, optimize inventory levels, and quickly respond to fluctuations in demand.
CMI can be applied to various types of inventory, including raw materials, work-in-progress goods, and finished products. Businesses set predefined inventory thresholds, and when stock levels drop below a minimum point, automated replenishment orders are triggered. This helps in avoiding disruptions in supply chains while reducing carrying costs and preventing obsolete stock buildup.
To successfully implement CMI, businesses need a robust ERP system like Deskera ERP that provides real-time inventory tracking, demand forecasting, and seamless data exchange between customers and suppliers.
Deskera’s AI-driven tools and mobile accessibility help businesses manage inventory efficiently, ensuring they have full visibility and control over stock movements. By leveraging such technology, companies can enhance supply chain collaboration, improve operational efficiency, and drive cost savings.
CMI vs. VMI: Key Differences and Which One is Right for Your Business?
Customer Managed Inventory (CMI) and Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI) are two distinct inventory management strategies, each with its own advantages and challenges. Understanding their differences can help businesses determine the most suitable approach for their supply chain operations.
1. Definition and Control
- Customer Managed Inventory (CMI): The customer takes full responsibility for tracking inventory levels, placing replenishment orders, and managing stock flow. Suppliers provide stock based on customer requests.
- Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI): The supplier monitors the customer’s inventory levels and takes responsibility for restocking, ensuring optimal stock levels without requiring customer intervention.
2. Inventory Ownership and Decision-Making
- CMI: The customer controls the ordering process and decides when and how much stock to replenish.
- VMI: The supplier determines replenishment schedules based on real-time inventory data, reducing the customer’s administrative workload.
3. Data Sharing and Communication
- CMI: Customers track their own inventory using internal systems and communicate order requirements to suppliers.
- VMI: Suppliers have direct access to customer inventory data, enabling automated replenishment and minimizing stockouts.
4. Responsibility for Stock Availability
- CMI: The customer is responsible for avoiding shortages and overstocking by actively managing inventory levels.
- VMI: The supplier ensures inventory availability, reducing the risk of stockouts and optimizing order fulfillment.
5. Suitability for Businesses
- CMI Works Best For:
- Companies with strong internal inventory management capabilities.
- Businesses that want full control over their inventory decisions.
- Organizations that prefer to manage supplier relationships directly.
- VMI Works Best For:
- Businesses looking to reduce inventory management workload.
- Companies with fluctuating demand that require supplier-driven restocking.
- Organizations seeking to improve supplier collaboration and reduce stockouts.
6. Key Benefits of Each Model
How Does Customer Managed Inventory (CMI) Work?
Customer Managed Inventory (CMI) is a supply chain management approach that shifts the responsibility of inventory control from suppliers to customers. This model allows businesses to independently track inventory levels, place replenishment orders, and manage supplier relationships while leveraging real-time data and automation for improved efficiency.
Below is a step-by-step breakdown of how CMI functions.
1. Inventory Tracking and Real-Time Monitoring
Effective inventory tracking is the foundation of a successful CMI system. Businesses utilize advanced tracking methods to monitor stock levels, movements, and usage in real time.
Key Inventory Tracking Methods
- Barcode Scanners: Customers use barcode scanners to log product movements during stocking and sales.
- RFID Tags and IoT Sensors: These tools automatically track inventory without manual scanning, reducing human error.
- Weighing Bins and Automated Scales: Useful for managing small, frequently used items like screws or fasteners.
Data Collection and Synchronization
- Each inventory transaction (stock receipt, usage, and replenishment) is recorded instantly.
- Inventory data is transmitted to a central system, ensuring transparency for all stakeholders.
- Automated alerts notify businesses when stock levels reach predefined thresholds.
2. Centralized Inventory Visibility
A CMI system consolidates inventory data from multiple locations, ensuring accurate, real-time insights into stock availability.
Features of Centralized Visibility
- Inventory management software updates stock levels instantly across warehouses, retail locations, and distribution centers.
- Cloud-based ERP systems provide a single, real-time view of inventory for better decision-making.
- Automated alerts help prevent stock imbalances by notifying businesses when inventory needs replenishment.
Advantages
- Eliminates manual stock reconciliation across different locations.
- Prevents overstocking or stock shortages by maintaining optimal inventory levels.
- Enhances coordination between different departments, suppliers, and distribution centers.
3. Demand Forecasting and Data-Driven Inventory Planning
Predicting future inventory needs is critical for maintaining the right stock levels. Businesses rely on analytics tools and historical data to forecast demand accurately.
Demand Forecasting Techniques
- AI-Powered Analytics: Machine learning algorithms analyze past sales data to predict future demand.
- Seasonal Trend Analysis: Businesses track seasonal demand fluctuations to plan inventory accordingly.
- Market Trend Monitoring: External factors, such as market conditions and customer preferences, influence forecasting.
Benefits of Accurate Forecasting
- Reduces the risk of stockouts and overstocking.
- Supports just-in-time (JIT) replenishment strategies to minimize inventory holding costs.
- Improves order fulfillment rates by ensuring stock availability when needed.
4. Automated Replenishment Triggers and Order Processing
Automation is a key component of CMI, ensuring seamless replenishment when inventory reaches critical levels.
How Automated Replenishment Works
- Establishing Inventory Thresholds: Customers set minimum and maximum inventory levels for each item.
- Real-Time Stock Monitoring: The system continuously tracks stock levels.
- Automatic Order Generation: When inventory falls below the reorder point, the system automatically generates a purchase order.
- Supplier Notification: Orders are sent electronically to suppliers without manual intervention.
- Order Confirmation and Processing: Suppliers process and ship replenishment stock based on automated triggers.
Advantages
- Eliminates the need for manual order placement.
- Reduces delays and ensures a steady supply of critical items.
- Enhances operational efficiency by preventing disruptions due to stock shortages.
5. Seamless Integration with Supplier Systems
For CMI to function efficiently, it must be integrated with supplier systems, enabling smooth data exchange and collaboration.
Integration Technologies
- Electronic Data Interchange (EDI): Automates the sharing of inventory data and purchase orders with suppliers.
- Supplier Portals: Suppliers can access real-time customer inventory levels, improving coordination.
- Cloud-Based ERP Systems: Allows seamless communication between customers and suppliers for better inventory planning.
Benefits of Supplier Integration
- Improves supplier response times for replenishment.
- Enhances order accuracy, reducing supply chain disruptions.
- Strengthens supplier-customer relationships by enabling data-driven collaboration.
6. Inventory Receipt, Verification, and Stock Updates
Once replenishment stock arrives, businesses must verify its accuracy and update their inventory records.
Steps in Inventory Receipt and Update
- Verification: Barcode or RFID scanning ensures that the delivered products match the purchase order.
- Quality Check: Businesses inspect goods for damages or discrepancies before accepting stock.
- Stock Entry: Approved inventory is logged into the system and updated in real time.
- Replenishment Confirmation: The system marks the order as complete, updating stock levels accordingly.
Importance of Accurate Inventory Updates
- Ensures correct stock levels, preventing discrepancies.
- Enhances inventory visibility for future demand planning.
- Reduces losses due to miscounts or incorrect shipments.
7. Continuous Performance Monitoring and Optimization
A well-managed CMI system requires ongoing evaluation to maintain efficiency and identify areas for improvement.
Key Metrics for Performance Evaluation
- Inventory Turnover Rate: Measures how frequently inventory is sold and replaced.
- Order Fulfillment Speed: Tracks how quickly replenishment orders are processed and delivered.
- Stock Accuracy: Assesses discrepancies between recorded and actual inventory levels.
Strategies for Continuous Improvement
- Adjust Replenishment Triggers: Modify reorder points based on changing demand.
- Improve Supplier Lead Times: Work with suppliers to reduce delivery times.
- Leverage Predictive Analytics: Use AI tools to refine inventory planning strategies.
8. The Role of Technology in Customer Managed Inventory
Technology plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficiency of CMI systems, automating tasks, and improving accuracy.
Essential Technologies for CMI
- Cloud-Based Inventory Management Software: Provides real-time inventory visibility and tracking.
- AI-Driven Demand Forecasting: Uses machine learning to predict stock needs accurately.
- EDI and Supplier Portals: Enable automated order processing and supplier communication.
- Barcode, RFID, and IoT Sensors: Enhance tracking and reduce manual errors.
- Mobile Inventory Apps: Allow instant stock updates and monitoring from any location.
Benefits of Customer Managed Inventory (CMI) in Supply Chain Management
Customer Managed Inventory (CMI) offers several advantages for businesses seeking greater control over their supply chain operations. By allowing customers to manage their own inventory replenishment, CMI helps optimize stock levels, reduce operational inefficiencies, and improve supplier collaboration.
1. Enhanced Inventory Control
CMI empowers businesses to take full control of their inventory management processes. Customers can set optimal stock levels, determine reorder points, and adjust replenishment schedules based on their specific needs. This reduces the risk of stockouts or overstocking.
2. Improved Demand Forecasting
With CMI, businesses analyze historical sales data, market trends, and customer behavior to forecast demand more accurately. This allows for better planning and helps companies maintain just the right amount of inventory, supporting efficient supply chain operations.
3. Increased Supply Chain Agility
CMI enables businesses to respond quickly to market fluctuations and changing customer demands. By directly managing their inventory levels, companies can adapt to shifts in demand without waiting for suppliers to intervene.
4. Reduced Lead Times
Since customers manage their own inventory and place replenishment orders proactively, they can reduce reliance on suppliers' schedules. This minimizes delays and ensures products are available when needed, improving overall supply chain efficiency.
5. Lower Holding Costs
CMI helps businesses avoid excessive inventory storage costs by maintaining lean inventory levels. This leads to reduced warehousing expenses, lower carrying costs, and optimized cash flow.
6. Minimized Stockouts and Overstocking
With real-time inventory tracking and automated alerts, customers can replenish stock before running out. At the same time, CMI prevents excessive stock accumulation, reducing waste and ensuring a balanced supply-demand ratio.
7. Stronger Supplier Relationships
Although customers take responsibility for inventory management, suppliers benefit from more predictable and stable demand patterns. This fosters better collaboration, leading to more efficient supply chain operations and long-term partnerships.
8. Customization and Flexibility
Businesses can tailor CMI processes to suit their specific operational requirements. Unlike Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI), which follows supplier-driven replenishment, CMI allows customers to adjust their inventory strategies based on internal goals.
9. Reduced Administrative Workload
By leveraging automated inventory tracking tools, businesses can streamline order placement and stock monitoring. This reduces manual work, minimizes human errors, and enhances overall operational efficiency.
10. Better Cost Management and Profitability
With optimized inventory levels, reduced carrying costs, and fewer stock-related losses, businesses can improve cost efficiency and maximize profitability. CMI ensures resources are allocated effectively, reducing waste and increasing return on investment (ROI).
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing Customer Managed Inventory (CMI)
While Customer Managed Inventory (CMI) offers several advantages, its successful implementation comes with challenges and key considerations. Businesses must assess their internal capabilities, technological infrastructure, and supplier relationships before adopting a CMI model.
1. Increased Responsibility on Customers
Unlike Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI), where suppliers handle stock replenishment, CMI shifts the responsibility to the customer. This requires businesses to have the necessary expertise, resources, and personnel to manage inventory effectively.
2. Need for Accurate Data and Forecasting
CMI relies heavily on accurate inventory data and demand forecasting. Errors in data entry, miscalculations, or poor forecasting models can lead to stockouts, overstocking, or inefficiencies in order placement. Businesses must invest in robust analytics tools and real-time inventory tracking systems.
3. Initial Setup and Integration Challenges
Implementing a CMI system requires integrating inventory tracking tools, barcode scanners, RFID systems, and inventory management software. Ensuring seamless connectivity between these systems and the supplier's infrastructure can be complex and time-consuming.
4. Dependence on Reliable Technology
Automated inventory tracking and electronic data interchange (EDI) systems are critical for CMI success. Any technical issues, system failures, or cybersecurity risks can disrupt inventory management and delay replenishment processes.
5. Supplier Collaboration and Communication
For CMI to work effectively, businesses must maintain strong communication with suppliers. Misalignment in order processing, lead times, or pricing agreements can create inefficiencies and affect supply chain performance.
6. Cost of Implementation and Maintenance
While CMI can reduce long-term inventory costs, initial setup expenses can be significant. Investing in inventory tracking devices, software, and employee training may require substantial upfront costs. Additionally, businesses must allocate resources for ongoing maintenance and system upgrades.
7. Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Certain industries, such as pharmaceuticals and food manufacturing, require strict compliance with inventory management regulations. Businesses implementing CMI must ensure they meet industry standards and maintain accurate records to comply with legal requirements.
8. Balancing Inventory Levels
Maintaining the right balance between sufficient stock availability and lean inventory levels can be challenging. Businesses must continuously monitor consumption rates and adjust replenishment strategies to prevent shortages or excess stock.
9. Training and Employee Readiness
Transitioning to a CMI model requires training employees to use new systems, understand inventory management best practices, and collaborate effectively with suppliers. Resistance to change or a lack of expertise can slow down implementation.
10. Scalability and Business Growth Considerations
As businesses expand, their inventory needs evolve. A CMI system must be flexible enough to scale with growing product lines, new market demands, and changing supply chain dynamics. Companies must ensure their inventory management strategy can adapt to future business growth.
Best Practices for Successful Customer Managed Inventory (CMI) Implementation
Implementing Customer Managed Inventory (CMI) effectively requires a well-structured approach, the right technology, and strong collaboration between stakeholders. By following best practices, businesses can optimize inventory control, improve efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction.
1. Choose the Right Technology Partner
The success of a CMI system heavily depends on the technology supporting it. Businesses should invest in an advanced inventory management system that offers:
- Real-time inventory visibility to track stock across multiple locations
- Automated tracking tools such as RFID, barcode scanners, and IoT-enabled sensors
- Seamless integration with enterprise resource planning (ERP) and order management systems. Reliable technology ensures accurate data collection and minimizes errors, preventing issues such as overstocking or stockouts.
2. Train Employees and Support Your Team
A well-trained workforce is essential for accurate inventory management. Employees should be equipped with the knowledge to:
- Use barcode scanners and RFID technology effectively
- Interpret real-time inventory data and respond proactively
- Follow best practices for stock handling and replenishment. Regular training reduces human errors and ensures smooth implementation of the CMI system.
3. Collaborate with Your Fulfillment and Logistics Partners
CMI requires close coordination with suppliers, fulfillment centers, and logistics providers. A strong partnership ensures:
- Faster replenishment cycles and timely delivery of stock
- Strategic inventory distribution across multiple warehouses for improved efficiency
- Consistent order fulfillment to maintain service levels. By working closely with fulfillment partners, businesses can optimize inventory allocation and minimize lead times.
4. Leverage Automation and Predictive Analytics
Automation and data-driven decision-making enhance the effectiveness of CMI by:
- Automating reorder triggers to prevent stockouts and ensure continuous supply
- Analyzing demand patterns to anticipate future inventory needs
- Reducing manual intervention through self-regulating inventory systems. Predictive analytics enables businesses to refine demand forecasting and align replenishment with actual consumption trends.
5. Establish Clear Communication Protocols
A successful CMI model depends on seamless communication between customers and suppliers. Businesses should:
- Define roles and responsibilities for inventory tracking and order placement
- Set up automated alerts for low stock levels and replenishment requirements
- Regularly review performance metrics to identify areas for improvement. Strong communication ensures alignment between all parties and prevents disruptions in inventory flow.
6. Implement Robust Inventory Auditing and Compliance Measures
Maintaining data accuracy and compliance with industry standards is critical in CMI implementation. Businesses should:
- Perform regular inventory audits to validate system-generated data
- Ensure compliance with industry regulations (especially in pharmaceuticals, food, and healthcare industries)
- Use advanced security measures to protect inventory data from cyber threats. A well-structured auditing process enhances accountability and prevents discrepancies in stock levels.
7. Optimize Inventory Placement for Faster Replenishment
Strategic inventory placement ensures quicker restocking and lower transportation costs. Businesses should:
- Store fast-moving items closer to fulfillment centers
- Maintain safety stock levels for critical SKUs
- Use demand-based stocking strategies to balance supply and demand efficiently
8. Continuously Monitor and Improve CMI Performance
CMI implementation should be an ongoing process of optimization. Businesses must:
- Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as stock accuracy, fulfillment rates, and order cycle times
- Adjust replenishment strategies based on changing customer demand and seasonal trends
- Seek continuous feedback from stakeholders to enhance system efficiency
When to Consider Customer Managed Inventory (CMI)
Customer Managed Inventory (CMI) is a supply chain strategy where the responsibility for managing inventory shifts from the supplier to the customer.
While this model offers several advantages, it is not suitable for every business. Companies must evaluate various factors, such as business size, product type, customer base, and internal capabilities, to determine whether CMI is the right choice for their supply chain needs.
1. Business Size and Scalability
Small and Medium-Sized Businesses (SMBs)
- CMI can be a cost-effective solution for SMBs by reducing reliance on external inventory management systems.
- It simplifies operations, allowing businesses to maintain control without significant investment in specialized inventory software or personnel.
Large Enterprises
- Large businesses with complex supply chains may benefit from the increased visibility and control that CMI provides.
- However, they must have robust systems and resources in place to manage high-volume inventory efficiently.
2. Suitability Based on Product Type
High-Volume, Predictable Demand Products
- CMI is most effective for products with consistent demand patterns.
- It enables businesses to automate replenishment and maintain optimal stock levels, reducing the risk of overstocking or stockouts.
Low-Volume, Variable Demand Products
- If demand is unpredictable, Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI) may be a better alternative, as suppliers can adjust inventory levels based on fluctuating customer needs.
- Businesses should assess demand variability before choosing CMI over VMI.
3. Customer Base and Market Stability
Stable, Established Customer Base
- CMI works well for businesses with a consistent customer base and predictable demand trends.
- Regular purchasing patterns ensure accurate forecasting and efficient inventory management.
Volatile Customer Base
- If customer demand is highly variable or subject to seasonal fluctuations, VMI may be a better fit.
- A supplier-managed approach can help mitigate stock shortages and prevent excess inventory buildup.
4. Internal Capabilities and Readiness
Inventory Management Expertise
- CMI requires businesses to have strong internal inventory management capabilities.
- Companies must be able to track stock levels, forecast demand accurately, and place timely orders.
Data Accuracy and Real-Time Visibility
- Accurate inventory data is crucial for successful CMI implementation.
- Businesses should have reliable inventory tracking systems to ensure data integrity.
Communication and Collaboration
- Effective coordination between customers and suppliers is essential.
- Businesses must establish clear communication channels to facilitate inventory updates, order fulfillment, and issue resolution.
5. Supply Chain Goals and Strategic Objectives
Businesses considering CMI should align their inventory management approach with their broader supply chain objectives, such as:
- Improving inventory accuracy and reducing discrepancies in stock levels.
- Lowering inventory holding costs by optimizing stock replenishment.
- Enhancing supply chain control through better oversight and planning.
6. Additional Considerations for Implementing CMI
Supplier Relationships
- CMI depends on strong partnerships with suppliers to ensure seamless order fulfillment and data exchange.
- Businesses must establish clear expectations and maintain trust with suppliers.
Technology Integration
- A successful CMI system should integrate seamlessly with existing Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and inventory management systems.
- This integration ensures data consistency and streamlined processes across the supply chain.
Employee Training and Readiness
- Employees involved in inventory management should receive proper training to handle CMI responsibilities effectively.
- Training programs should cover order placement, inventory tracking, and demand forecasting.
Continuous Monitoring and Optimization
- Businesses must regularly assess CMI performance to identify areas for improvement.
- Implementing key performance indicators (KPIs) can help measure inventory accuracy, stock turnover, and fulfillment efficiency.
Key Considerations When Choosing Between CMI and VMI
Selecting the right inventory management approach—Customer Managed Inventory (CMI) or Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI)—requires a thorough evaluation of a company’s operational capabilities, supply chain structure, and business goals.
While both models aim to enhance inventory efficiency, they offer distinct advantages and challenges based on how responsibilities are distributed between the customer and supplier.
By assessing the following key factors, businesses can make an informed decision that aligns with their long-term strategy and resource availability.
1. Control and Ownership
A fundamental distinction between CMI and VMI is who retains control over inventory management.
- CMI allows businesses to maintain full ownership and control over stock levels, which is crucial for industries with strict regulatory compliance or quality control needs.
- VMI, on the other hand, shifts the responsibility to the supplier, making it a suitable option for companies that lack inventory expertise or need to scale operations without investing heavily in inventory management.
2. Responsibilities and Workload
- CMI places the burden of inventory tracking, demand forecasting, and order placement on the customer. This is ideal for businesses with well-established internal inventory management capabilities.
- VMI reduces this workload, as suppliers take over stock replenishment decisions, making it a more hands-off approach for businesses with limited resources.
3. Collaboration and Supplier Relationships
A company’s relationship with its suppliers plays a pivotal role in determining the success of either approach.
- CMI requires active collaboration, ensuring that inventory data is shared accurately between the customer and the supplier.
- VMI demands an even higher level of trust, as the supplier takes on decision-making responsibilities. Long-standing, reliable partnerships are critical to avoiding disruptions.
4. Industry and Market Dynamics
The nature of the industry and its demand variability greatly influence the choice between CMI and VMI.
- CMI works best in industries with stable, predictable demand and long product lifecycles, such as manufacturing and wholesale distribution.
- VMI is better suited for markets with fluctuating demand, short product cycles, and frequent updates, such as fashion retail and consumer electronics.
5. Technology and Infrastructure Readiness
The level of technological integration required varies significantly between the two models.
- CMI often necessitates investment in inventory tracking software, ERP systems, and real-time analytics to optimize inventory levels efficiently.
- VMI shifts the technological burden to the supplier, making it a better choice for companies with limited IT resources or outdated infrastructure.
6. Risk Management and Flexibility
Companies must assess their risk tolerance and need for flexibility when choosing between CMI and VMI.
- CMI provides greater flexibility, as businesses can adjust inventory levels based on real-time insights and market conditions.
- VMI transfers risk to the supplier, but customers may have less direct control over inventory adjustments, potentially leading to mismatches in stock levels during demand fluctuations.
7. Inventory Visibility and Transparency
- CMI allows businesses to track inventory in real time, offering deeper transparency into stock movements, which is crucial for companies managing complex supply chains.
- VMI provides visibility but may lack the same level of granularity, as customers rely on suppliers for inventory reporting.
8. Cost and Resource Allocation
Both CMI and VMI come with unique cost implications:
- CMI requires investment in technology, personnel, and infrastructure, but it provides greater cost control and the ability to negotiate better pricing with suppliers.
- VMI reduces the internal burden of inventory management but may lead to higher dependency on suppliers and less flexibility in negotiating inventory costs.
The decision between CMI and VMI ultimately depends on a company’s internal capabilities, industry dynamics, and strategic priorities. Businesses that prioritize control, visibility, and flexibility may find CMI the better fit, while those looking to reduce workload, scale efficiently, and leverage supplier expertise may benefit from VMI.
By carefully weighing these considerations, companies can select the inventory management strategy that best aligns with their operational goals and supply chain efficiency.
How to Maximize Results With Customer Managed Inventory (CMI)
Customer Managed Inventory (CMI) offers businesses greater control over their inventory, reduces stockouts, and improves operational efficiency. However, to fully maximize its benefits, companies must implement best practices, leverage the right technology, and ensure seamless collaboration with suppliers and logistics partners.
Below are key strategies to optimize CMI and achieve maximum results.
1. Leverage Advanced Inventory Management Technology
A robust inventory management system is essential for maximizing CMI efficiency. Businesses should:
- Use real-time tracking tools: Implement RFID, barcode scanning, and IoT sensors to maintain accurate inventory data.
- Adopt AI-driven forecasting: Machine learning algorithms can predict demand patterns and adjust stock levels accordingly.
- Integrate cloud-based platforms: Cloud solutions enable businesses to access inventory data from anywhere, ensuring seamless coordination across multiple locations.
2. Establish Clear Inventory Policies and Guidelines
To avoid mismanagement and inefficiencies, businesses should set clear inventory control policies, including:
- Reorder thresholds and replenishment cycles: Define stock levels that trigger reordering to prevent shortages or overstocking.
- Inventory classification: Use ABC analysis to prioritize inventory based on value and demand frequency.
- Quality control checks: Implement regular audits to maintain inventory accuracy and reduce shrinkage.
3. Strengthen Collaboration With Suppliers and Logistics Partners
A strong relationship with suppliers and third-party logistics (3PL) providers is crucial for effective CMI implementation. To improve coordination:
- Establish clear communication channels: Use centralized dashboards to share real-time inventory insights with suppliers.
- Align inventory goals: Work with suppliers to set common objectives, such as minimizing lead times and improving order accuracy.
- Negotiate flexible agreements: Develop dynamic supplier contracts that allow adjustments based on changing demand patterns.
4. Utilize Data Analytics for Continuous Improvement
Data-driven decision-making is key to optimizing CMI performance. Businesses should:
- Monitor key inventory metrics: Track stock turnover rates, order fulfillment speed, and carrying costs.
- Identify demand trends: Use historical sales data to anticipate seasonal fluctuations and adjust inventory accordingly.
- Optimize warehouse efficiency: Analyze picking and packing times to streamline warehouse operations.
5. Automate Replenishment and Ordering Processes
Automation reduces manual errors and ensures timely inventory restocking. Companies can:
- Implement automated reorder triggers: Set up inventory thresholds that automatically generate purchase orders.
- Use smart algorithms for supplier selection: AI can identify the best supplier based on price, delivery speed, and reliability.
- Integrate CMI with ERP systems: Synchronize inventory data with enterprise resource planning (ERP) software for better resource allocation.
6. Train Employees for Effective Inventory Management
A well-trained workforce ensures smooth CMI operations. Businesses should:
- Provide inventory management training: Educate employees on best practices for stock tracking, handling, and reporting.
- Encourage cross-functional collaboration: Train teams from procurement, sales, and logistics to align CMI goals.
- Use simulation tools for practice: Implement training modules that replicate real-world inventory scenarios.
7. Implement Sustainable Inventory Practices
Sustainability in CMI not only reduces environmental impact but also improves cost efficiency. Companies should:
- Reduce excess inventory: Implement just-in-time (JIT) strategies to minimize waste and storage costs.
- Optimize reverse logistics: Develop processes for handling returns, refurbishments, and product recycling.
- Source from eco-friendly suppliers: Work with vendors that prioritize sustainable materials and ethical sourcing.
8. Continuously Evaluate and Improve CMI Performance
CMI is not a one-time setup—it requires ongoing monitoring and optimization. To ensure continued success:
- Conduct regular performance reviews: Assess the effectiveness of CMI policies and make necessary adjustments.
- Stay updated with industry trends: Keep pace with advancements in inventory management technology.
- Gather customer and supplier feedback: Use insights from partners and customers to refine inventory strategies.
Future of Customer Managed Inventory (CMI) in Supply Chain Management
Customer Managed Inventory (CMI) is evolving as businesses seek greater control, efficiency, and agility in their supply chain operations.
With technological advancements, shifting consumer expectations, and increased global competition, CMI is set to play an even more significant role in modern supply chain management.
The future of CMI will be shaped by digital transformation, automation, data-driven decision-making, and strategic collaborations.
1. The Rise of Digital and AI-Driven Inventory Management
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are revolutionizing inventory management by providing predictive analytics, automation, and intelligent decision-making capabilities.
Future CMI systems will leverage these technologies to:
- Enhance demand forecasting: AI-driven algorithms will analyze historical data and market trends to predict demand fluctuations more accurately.
- Automate replenishment processes: Automated reordering systems will trigger inventory restocking without manual intervention, reducing human error and improving efficiency.
- Optimize stock levels in real-time: AI will enable businesses to adjust inventory dynamically based on real-time demand signals, minimizing overstocking and stockouts.
2. Integration of IoT for Real-Time Visibility
The Internet of Things (IoT) is expected to play a crucial role in CMI by providing real-time inventory tracking and monitoring. IoT-enabled sensors, RFID tags, and smart shelves will:
- Improve stock accuracy: Automated tracking systems will provide real-time insights into inventory levels, preventing discrepancies.
- Enable predictive maintenance: Sensors will detect issues in storage conditions (e.g., temperature-sensitive goods) and alert businesses before problems occur.
- Enhance supply chain transparency: IoT will facilitate end-to-end visibility, ensuring seamless coordination between customers and suppliers.
3. Blockchain for Secure and Transparent Transactions
Blockchain technology will enhance trust and transparency in CMI by ensuring secure, tamper-proof inventory data. Benefits include:
- Decentralized inventory tracking: Blockchain will create an immutable record of inventory transactions, reducing errors and fraud.
- Smart contracts for automated transactions: Contracts will automatically trigger orders and payments based on predefined inventory thresholds.
- Enhanced supplier collaboration: Blockchain will enable seamless and secure data sharing between customers and suppliers.
4. Increased Adoption of Cloud-Based Inventory Solutions
Cloud technology is making CMI more accessible and scalable by providing real-time access to inventory data across multiple locations. Key benefits include:
- Remote access and control: Businesses can manage inventory from anywhere, improving flexibility.
- Scalability: Cloud solutions can accommodate growing inventory needs without significant infrastructure investments.
- Seamless integration with ERP and fulfillment systems: Businesses can synchronize inventory data with their existing supply chain management software.
5. Shift Toward Sustainable and Circular Supply Chains
Sustainability will be a key driver in the future of CMI. Companies will implement eco-friendly practices by:
- Reducing excess inventory and waste: AI-driven demand forecasting will prevent overproduction and unsold stock.
- Implementing reverse logistics: Businesses will optimize returns and reusability of products through CMI-enabled tracking systems.
- Encouraging sustainable sourcing: CMI will enable businesses to make data-driven decisions about suppliers that align with sustainability goals.
6. Hybrid Models: CMI and VMI Working Together
In the future, businesses may adopt hybrid models combining elements of CMI and Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI) for greater flexibility. These models will allow:
- Better risk management: Companies can use CMI for core inventory control while allowing suppliers to manage slow-moving or high-risk stock through VMI.
- Adaptive supply chain strategies: Businesses will dynamically switch between CMI and VMI based on market conditions, customer demand, and supplier capabilities.
How Deskera ERP Enhances Customer Managed Inventory (CMI) Efficiency
Deskera ERP provides a comprehensive suite of tools that streamline inventory management, making it an ideal solution for businesses implementing Customer Managed Inventory (CMI).
Here’s how Deskera ERP supports CMI:
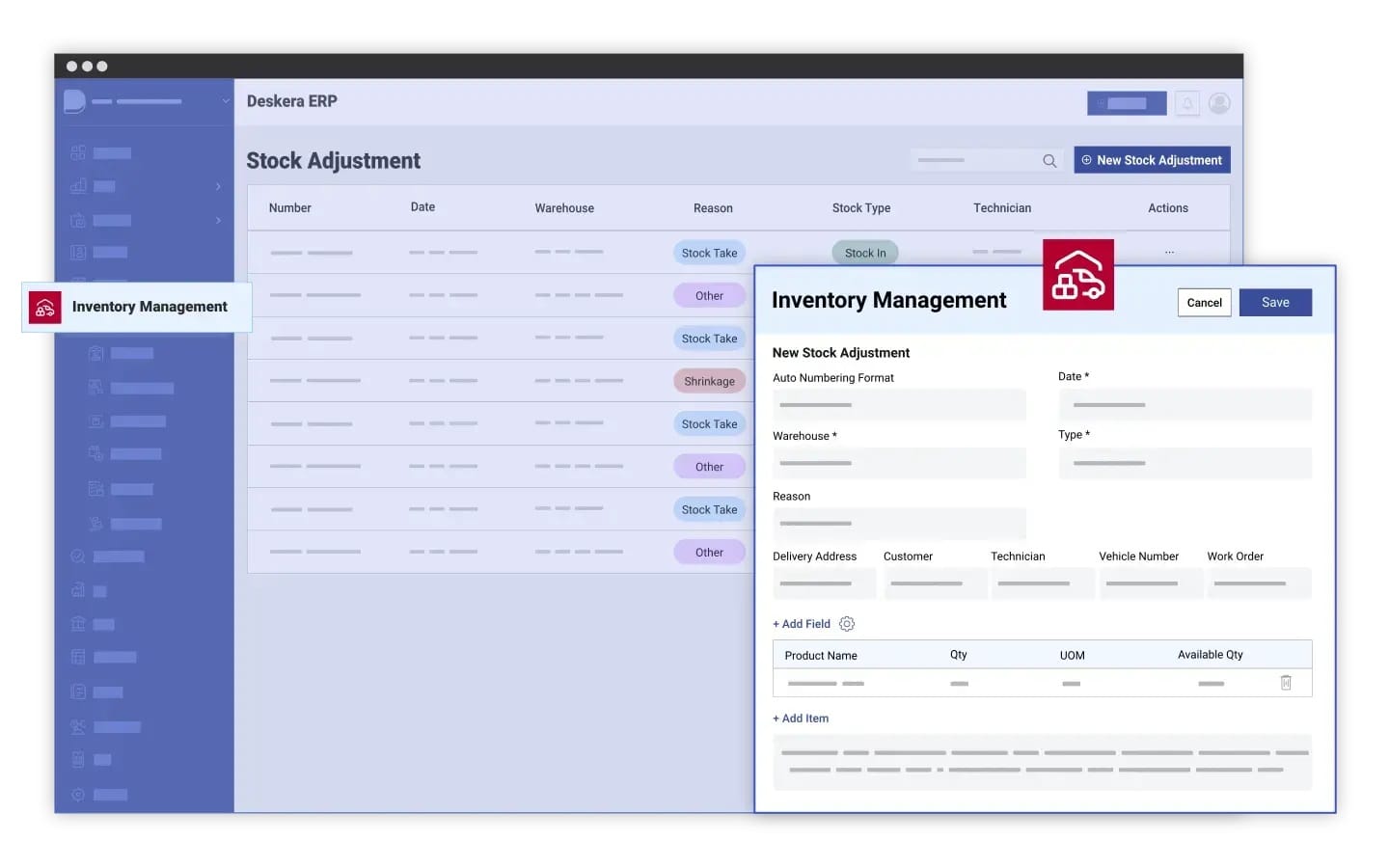
Real-Time Inventory Tracking
- Deskera ERP offers real-time visibility into inventory levels, ensuring businesses can accurately track stock across multiple locations.
- This prevents stockouts and overstocking, improving inventory control efficiency.
Automated Replenishment and Forecasting
- Advanced demand forecasting features help businesses predict inventory needs based on historical data.
- Automated alerts and replenishment options enable timely stock ordering, reducing manual effort.
Seamless Supplier Collaboration
- Deskera ERP facilitates smooth communication and data sharing between customers and suppliers, ensuring a well-coordinated supply chain.
- Businesses can set up automated workflows to streamline purchase orders and deliveries.
Integrated Accounting and Cost Management
- With built-in accounting features, businesses can track procurement costs, analyze spending, and manage supplier payments efficiently.
- Cost control mechanisms ensure optimized budget allocation for inventory procurement.
Mobile Accessibility for On-the-Go Management
- Deskera ERP’s mobile-friendly interface allows businesses to monitor and manage inventory from anywhere.
- Instant access to stock levels, sales data, and supplier updates enhances decision-making speed.
Scalability for Growing Businesses
- Whether for small businesses or large enterprises, Deskera ERP scales effortlessly, adapting to evolving inventory needs.
- Customizable dashboards provide tailored insights for different business requirements.
Key Takeaways
- CMI shifts inventory management responsibility from suppliers to customers, offering greater control, visibility, and efficiency in supply chain operations.
- CMI is best suited for businesses with stable demand patterns, strong inventory management capabilities, and the technological infrastructure to handle inventory tracking.
- CMI enhances inventory control, reduces carrying costs, improves order accuracy, and strengthens supplier-customer collaboration, leading to greater supply chain efficiency.
- Implementing CMI requires significant investment in technology, skilled personnel, and strong supplier relationships to ensure accurate inventory tracking and seamless coordination.
- Successful CMI implementation requires clear communication with suppliers, robust inventory tracking systems, employee training, seamless ERP integration, and continuous performance monitoring for ongoing optimization.
- Businesses must evaluate factors like control, workload, collaboration with suppliers, industry dynamics, technology requirements, risk management, visibility, and cost implications to determine the right approach.
- Effective CMI implementation requires real-time inventory tracking, accurate demand forecasting, seamless supplier collaboration, and continuous monitoring for process improvements.
- With advancements in AI, IoT, and automation, CMI is evolving toward more predictive and data-driven decision-making, enhancing supply chain resilience and agility.
- Deskera ERP simplifies CMI by providing real-time visibility, automated replenishment, seamless supplier collaboration, integrated accounting, and mobile accessibility, ensuring optimized inventory management.
Related Articles












