Did you know that the global contract manufacturing market is expected to grow at a robust CAGR of 6.2% from 2023 to 2030, according to Data Bridge Market Research? This statistic underscores the increasing reliance on contract manufacturing by businesses worldwide. But why is it so crucial for your business?
Contract manufacturing offers companies the flexibility to scale operations, reduce overhead costs, and access specialized production capabilities without the need for significant capital investment.
In this landscape, leveraging the right tools to manage your manufacturing processes is essential. Deskera MRP provides an integrated solution that simplifies demand forecasting, production planning, and inventory management. With Deskera, you can seamlessly coordinate with contract manufacturers, ensuring efficiency and consistency in your supply chain.
By partnering with a contract manufacturer, you can also focus more on your core business activities—whether that’s innovation, marketing, or customer service—while leaving the complexities of production to experts.
This approach not only enhances your operational efficiency but also allows you to respond more quickly to market changes, giving you a competitive edge in your industry.
In this blog, we’ll delve into the many reasons why contract manufacturing is crucial for your business’s success.
What is Contract Manufacturing?
Contract manufacturing is a business arrangement where a company outsources the production of its goods to a third-party manufacturer. Instead of investing in its own production facilities, the company partners with a specialized manufacturer to produce its products according to specific requirements.
This approach allows businesses to leverage the expertise, equipment, and production capabilities of the contract manufacturer, often leading to cost savings and increased efficiency.
In contract manufacturing, the hiring company typically provides the design, specifications, and branding, while the contract manufacturer handles the actual production process.
This can include anything from sourcing raw materials to assembly, packaging, and even distribution. The relationship is built on a mutual agreement that ensures the contract manufacturer adheres to the quality standards and timelines set by the hiring company.
One of the key advantages of contract manufacturing is the ability to scale production quickly without the need for substantial capital investment. This is particularly beneficial for companies that experience seasonal demand fluctuations or those entering new markets.
Additionally, contract manufacturing allows companies to focus on their core competencies, such as research and development, marketing, and sales, while relying on the manufacturer to handle the complexities of production.
By utilizing contract manufacturing, companies can also benefit from the specialized expertise of manufacturers who are often more adept at producing specific types of products or components.
This can lead to better quality products and potentially faster time-to-market. Overall, contract manufacturing offers a strategic advantage by enabling businesses to operate more flexibly and efficiently in a competitive market.
What Occurs in Contract Manufacturing?
In contract manufacturing, a series of coordinated activities take place between the hiring company (often referred to as the client) and the contract manufacturer. Here's what typically occurs in the process:
Initial Agreement
The relationship begins with the client identifying the need to outsource certain manufacturing activities. The two parties negotiate and establish a contract that outlines the scope of work, product specifications, quality standards, costs, timelines, and any other pertinent details. This agreement forms the foundation of the partnership.
Design and Specifications
The client provides the contract manufacturer with detailed product designs, specifications, and any other relevant requirements. This may include technical drawings, material lists, and performance criteria. The contract manufacturer may also offer input to optimize the design for manufacturing efficiency or cost-effectiveness.
Sourcing of Materials
Depending on the agreement, the contract manufacturer may be responsible for sourcing the raw materials needed for production. They may leverage their established supplier networks to procure materials at competitive prices, ensuring that they meet the specified quality standards.
Manufacturing Process
The core of contract manufacturing is the actual production process. The contract manufacturer uses its facilities, equipment, and labor to produce the goods according to the agreed-upon specifications. This can involve various stages such as machining, assembly, testing, and quality control.
Quality Control
Throughout the manufacturing process, quality control measures are implemented to ensure that the products meet the client’s standards. This may involve inspections, testing, and adherence to regulatory requirements. The contract manufacturer is responsible for maintaining consistency and quality across all produced units.
Packaging and Labeling
After production, the products are packaged and labeled according to the client’s instructions. This step is crucial, especially in industries like consumer goods, pharmaceuticals, and electronics, where packaging plays a key role in branding and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Logistics and Distribution
Depending on the contract, the manufacturer may also handle logistics, including warehousing, shipping, and distribution of the finished products. This can involve delivering the products directly to the client or to the client’s customers.
Final Delivery
The finished products are delivered to the client or as otherwise specified in the contract. The client then takes over the responsibility of selling or distributing the products under their brand.
Ongoing Collaboration and Feedback
The relationship between the client and the contract manufacturer is often ongoing. They continue to collaborate on production runs, make improvements, and address any issues that arise. Regular communication ensures that both parties remain aligned on expectations, timelines, and any potential changes in the manufacturing process.
Throughout the entire contract manufacturing process, the client maintains control over the product's design and branding, while the contract manufacturer focuses on efficiently producing the product to meet the client's needs. This arrangement allows businesses to leverage external expertise and resources while focusing on their core competencies.
Process of Contract Manufacturing
The process of contract manufacturing involves several key steps, each crucial to ensuring that the partnership between the hiring company (client) and the contract manufacturer runs smoothly and delivers the desired results.
Here’s an overview of the typical process:
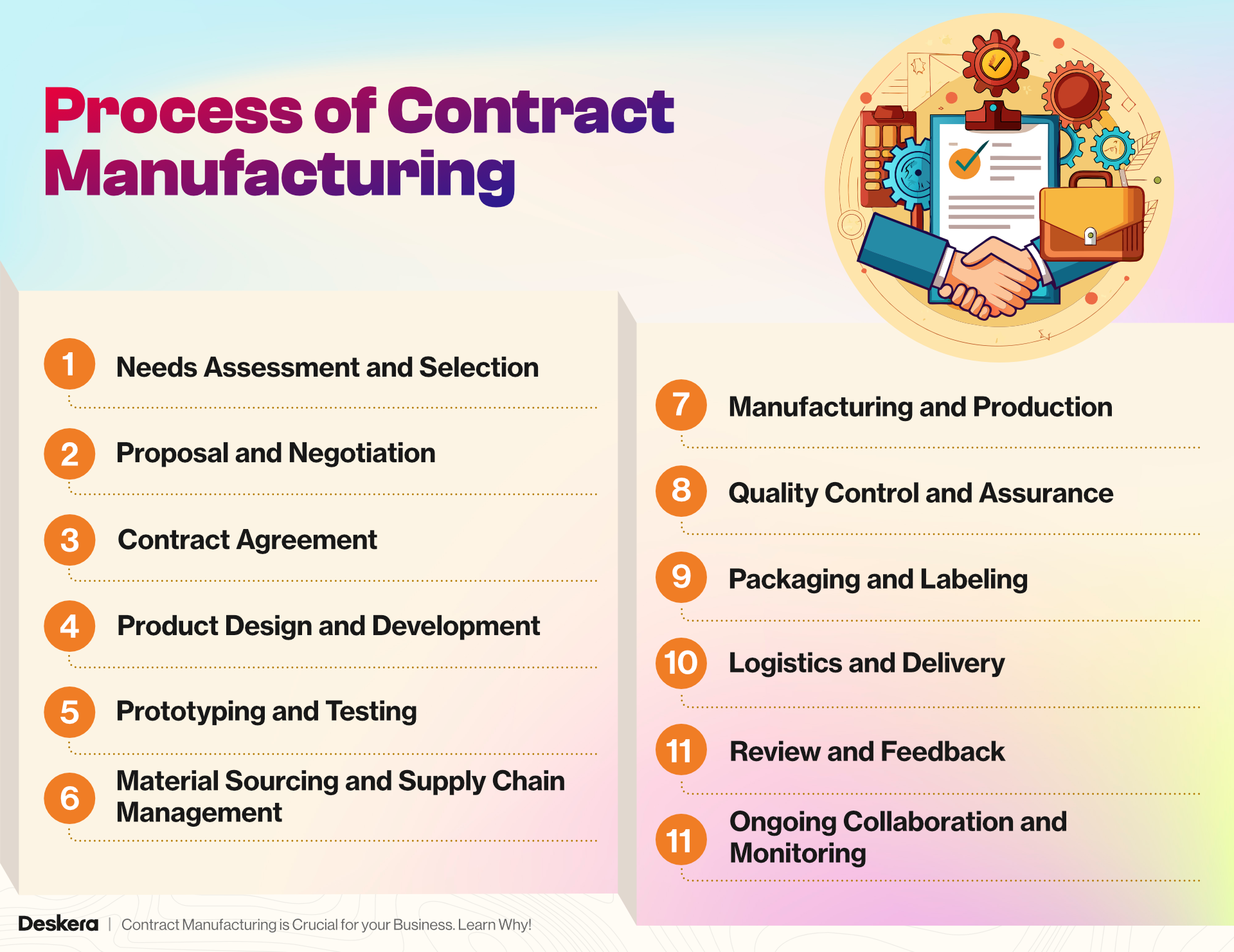
Needs Assessment and Selection
The client begins by assessing the need for contract manufacturing. This involves identifying which products or components would benefit from outsourcing. The client then conducts research to select a suitable contract manufacturer based on factors such as expertise, capacity, reputation, and cost.
Proposal and Negotiation
Once potential manufacturers are identified, the client issues a request for proposal (RFP) or directly engages with manufacturers to discuss the project. The contract manufacturer provides a proposal that includes details such as cost estimates, timelines, production capabilities, and quality assurance processes. Negotiations follow to finalize terms, including pricing, delivery schedules, and other contractual obligations.
Contract Agreement
After negotiations, both parties sign a formal contract. This document outlines all aspects of the partnership, including the scope of work, responsibilities, product specifications, confidentiality agreements, intellectual property rights, payment terms, and penalties for non-compliance. The contract serves as a legal framework for the relationship.
Product Design and Development
The client provides the contract manufacturer with detailed product designs, blueprints, specifications, and any required materials or components. In some cases, the contract manufacturer may assist with product development, offering suggestions to improve manufacturability, reduce costs, or enhance product performance.
Prototyping and Testing
Before full-scale production begins, the contract manufacturer may produce prototypes or initial samples. These prototypes are thoroughly tested to ensure they meet the client’s specifications and quality standards. The client reviews the prototypes and provides feedback, leading to any necessary adjustments in the design or production process.
Material Sourcing and Supply Chain Management
Once the product design is finalized, the contract manufacturer sources the required raw materials, components, and other inputs needed for production. The manufacturer may have established relationships with suppliers, allowing for cost-effective and reliable procurement. Effective supply chain management ensures that materials are available when needed, preventing production delays.
Manufacturing and Production
With materials in hand, the contract manufacturer begins the production process. This involves setting up production lines, calibrating machinery, and training personnel as needed. The manufacturing process follows the specifications provided by the client, with a focus on maintaining consistency and quality.
Quality Control and Assurance
Throughout the production process, the contract manufacturer implements quality control measures to ensure that the products meet the client’s standards. This may include regular inspections, testing, and adherence to regulatory requirements. Any defects or issues identified are addressed immediately to prevent them from affecting the final product.
Packaging and Labeling
Once production is complete, the products are packaged and labeled according to the client’s instructions. Packaging may include protective materials, branding elements, and compliance with industry regulations. Proper packaging ensures that the products are safe during transportation and visually appealing to end consumers.
Logistics and Delivery
The finished products are then prepared for shipment. Depending on the agreement, the contract manufacturer may handle logistics, including warehousing, shipping, and distribution. The products are delivered to the client or directly to the client’s customers, as specified in the contract.
Review and Feedback
After delivery, the client reviews the products and provides feedback to the contract manufacturer. This feedback is essential for continuous improvement and maintaining a strong working relationship. Any issues or suggestions are discussed, and adjustments are made for future production runs.
Ongoing Collaboration and Monitoring
The relationship between the client and the contract manufacturer is often ongoing, with repeated production runs, updates to product designs, and evolving needs. Regular communication, performance monitoring, and periodic reviews help both parties stay aligned and ensure long-term success.
The process of contract manufacturing is a collaborative effort that requires clear communication, detailed planning, and mutual trust between the client and the manufacturer. When executed effectively, it allows companies to produce high-quality products efficiently and cost-effectively while focusing on their core business activities.
Types of Contract Manufacturing
There are several types of contract manufacturing, each serving different needs and industries. Here’s an overview of the main types:
Component Manufacturing
In this type, a company outsources the production of specific components or parts of a product. The company then assembles these components in-house or sends them to another manufacturer for final assembly. This approach is common in industries like automotive, electronics, and aerospace, where specialized parts are needed.
Private Label Manufacturing
Here, a manufacturer produces goods that are then branded and sold by another company as their own. The hiring company typically provides the design and branding, while the manufacturer handles the production. This type is prevalent in consumer goods industries, including cosmetics, food, and clothing.
OEM Manufacturing (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEMs produce products or components that are purchased by another company and retailed under that company’s brand name. For example, a tech company may design a product and outsource the manufacturing to an OEM, who produces the product to the specified design.
Turnkey Manufacturing
In turnkey manufacturing, the contract manufacturer handles the entire production process from start to finish. This includes everything from sourcing raw materials to final assembly and packaging.
The hiring company simply receives the finished product, ready for distribution. This type is often used in complex industries like pharmaceuticals, electronics, and industrial equipment.
Subcontracting
Subcontracting involves a company outsourcing specific tasks or processes within the manufacturing cycle to a contract manufacturer. Unlike turnkey manufacturing, the hiring company may still handle other parts of the production process. This is common in industries that require specialized expertise, such as machining, welding, or coating services.
Full-Service Manufacturing
Full-service contract manufacturers provide a complete suite of services, including design, prototyping, manufacturing, and logistics. This allows the hiring company to rely on a single partner for all aspects of production, from concept to delivery. This type is advantageous for companies looking to streamline their supply chain and reduce the number of suppliers they work with.
Each type of contract manufacturing offers different benefits, depending on the specific needs and goals of the hiring company. Whether it's reducing costs, accessing specialized expertise, or accelerating time-to-market, selecting the right type of contract manufacturing can be a key strategic decision for many businesses.
Key Sectors Leveraging Contract Manufacturing
Contract manufacturing is utilized across a diverse range of sectors, each benefiting from the specialized services and efficiencies provided by contract manufacturers.
Here are some of the primary sectors that extensively use contract manufacturing:
Pharmaceuticals and Biotechnology
In this sector, contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) handle the production of drugs, vaccines, and biologics. They offer expertise in complying with stringent regulatory standards, ensuring high-quality and consistent manufacturing processes essential for the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products.
Electronics
The electronics industry relies heavily on contract manufacturing for the production of components such as circuit boards, semiconductors, and consumer electronics.
Contract manufacturers in this sector offer advanced technology and specialized capabilities, enabling companies to bring innovative electronic products to market efficiently.
Automotive
Contract manufacturing in the automotive sector includes the production of parts, components, and assemblies for vehicles. Automotive manufacturers partner with contract manufacturers to achieve cost efficiencies, meet high production standards, and scale operations according to market demand.
Consumer Goods
This sector encompasses a broad range of products, including apparel, household goods, and personal care items. Contract manufacturers help companies manage production volumes, ensure product quality, and adapt to changing consumer trends.
Food and Beverage
In the food and beverage industry, contract manufacturing involves the production of packaged foods, beverages, and dietary supplements. Contract manufacturers in this sector ensure compliance with health and safety regulations, manage ingredient sourcing, and maintain quality control.
Medical Devices
Contract manufacturing for medical devices involves the production of equipment and instruments used in healthcare settings. Manufacturers in this sector provide specialized production capabilities, including precision engineering and regulatory compliance, crucial for developing safe and effective medical devices.
Cosmetics and Personal Care
The cosmetics and personal care industry leverages contract manufacturing for the production of skincare products, cosmetics, and hair care items. Contract manufacturers in this sector offer expertise in formulation, packaging, and quality assurance, helping brands meet consumer demands and regulatory requirements.
Aerospace and Defense
In the aerospace and defense sector, contract manufacturing involves the production of components and systems for aircraft, spacecraft, and defense equipment. These manufacturers provide high levels of precision and adherence to strict industry standards, essential for the safety and reliability of aerospace and defense products.
In summary, contract manufacturing serves a variety of sectors by providing specialized production capabilities, cost efficiencies, and scalability. Each sector benefits from the tailored services offered by contract manufacturers, enabling companies to focus on their core competencies and market strategies.
Exploring Contract Manufacturing Opportunities for Business Growth
Contract manufacturing presents numerous opportunities for businesses seeking to expand their production capabilities, enter new markets, or optimize their operations.
By leveraging contract manufacturing opportunities, companies can tap into a range of strategic benefits that contribute to their overall growth and competitiveness.
One of the primary opportunities lies in cost reduction. Companies can take advantage of contract manufacturers' established infrastructure, expertise, and economies of scale.
This allows businesses to produce goods at a lower cost than if they were to handle production in-house, especially in industries where large-scale production is necessary to achieve profitability.
Another significant opportunity is market expansion. Contract manufacturing enables companies to quickly scale production and enter new markets without the need to invest heavily in new facilities or workforce. This flexibility is particularly valuable for businesses looking to test the waters in foreign markets or introduce new products with minimal risk.
Additionally, contract manufacturing provides access to specialized expertise and advanced technology. Many contract manufacturers specialize in specific types of production, offering cutting-edge processes and technologies that may not be available in-house.
This access to expertise allows companies to produce high-quality products that meet stringent market demands without needing to develop these capabilities internally.
Contract manufacturing opportunities also include the ability to focus on core business functions. By outsourcing production, companies can allocate more resources to research and development, marketing, and customer engagement. This strategic focus can lead to innovation, better customer experiences, and stronger market positioning.
Moreover, contract manufacturing can facilitate innovation. Companies can collaborate with manufacturers who have experience in producing complex or innovative products, leading to faster development cycles and quicker time-to-market. This collaboration can also spur new ideas and improvements in product design and manufacturing processes.
In summary, exploring contract manufacturing opportunities allows businesses to reduce costs, expand into new markets, access specialized expertise, and focus on core activities. By strategically leveraging these opportunities, companies can achieve sustainable growth and maintain a competitive edge in their respective industries.
The Role of Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs) and Companies
Contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) and contract manufacturing companies play a vital role in the production landscape, offering specialized services that enable businesses to outsource their manufacturing needs efficiently and effectively.
Contract manufacturing organizations are specialized entities that focus on providing end-to-end production services for companies that prefer to outsource their manufacturing.
These organizations typically offer a wide range of services, including product design, material procurement, production, quality control, and sometimes even packaging and distribution.
By partnering with a CMO, companies can leverage the expertise and infrastructure of these organizations to produce high-quality products without investing in their own manufacturing facilities.
Contract manufacturing companies vary in size and specialization, from large multinational corporations to smaller niche manufacturers. These companies offer their clients flexibility in scaling production, ensuring that businesses can meet varying levels of demand without the burden of maintaining extensive in-house production capabilities.
Contract manufacturing companies often specialize in specific industries, such as pharmaceuticals, electronics, automotive, or consumer goods, providing tailored solutions that meet the unique requirements of each sector.
The partnership between businesses and contract manufacturing organizations or companies can significantly reduce time-to-market for new products. These organizations bring extensive industry knowledge, regulatory expertise, and established supply chains, allowing businesses to focus on innovation and market expansion rather than the complexities of production.
In summary, working with contract manufacturing organizations and companies offers businesses a strategic advantage, enabling them to produce goods at scale, ensure high quality, and maintain flexibility in a competitive market.
Benefits of Contract Manufacturing
Contract manufacturing offers a range of benefits that can significantly enhance a company’s operational efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and overall business strategy.
Here are some of the key advantages:
Cost Savings
One of the most significant benefits of contract manufacturing is the reduction in capital expenditures. Companies can avoid the high costs associated with building and maintaining production facilities, purchasing equipment, and managing a workforce. Instead, they leverage the existing infrastructure and expertise of the contract manufacturer, which often leads to lower production costs.
Access to Expertise and Advanced Technology
Contract manufacturers often specialize in specific types of production and have extensive experience and expertise in those areas. This specialization means they are likely to use the latest technologies, processes, and quality control measures.
By partnering with a contract manufacturer, companies can benefit from this advanced knowledge and technology without having to invest in it themselves.
Scalability and Flexibility
Contract manufacturing allows companies to scale their production up or down based on demand without the need for significant investments in capacity.
This flexibility is particularly valuable for businesses with seasonal products or those entering new markets where demand may fluctuate. It also enables companies to respond quickly to changes in market conditions or consumer preferences.
Focus on Core Competencies
By outsourcing production, companies can focus their resources and attention on their core competencies, such as research and development, marketing, and customer service.
This focus can lead to innovation and a stronger competitive position in the market, as the company can devote more time and energy to activities that directly impact its growth and success.
Reduced Time-to-Market
Contract manufacturers typically have established production processes and supply chains, which can significantly reduce the time it takes to bring a product to market. This speed is crucial in industries where product life cycles are short or where being first to market can provide a competitive advantage.
Risk Mitigation
Contract manufacturing allows companies to mitigate various risks associated with production. These include the risks of investment in capital-intensive assets, labor management issues, and the complexities of regulatory compliance.
The contract manufacturer assumes many of these risks, allowing the client company to focus on other aspects of its business.
Quality Assurance
Reputable contract manufacturers have robust quality control systems in place to ensure that the products they produce meet the required standards. This can result in higher product quality and consistency, which is essential for maintaining brand reputation and customer satisfaction.
Access to Global Markets
Contract manufacturers often have a global presence, which can help companies expand into new markets more easily. By leveraging the manufacturer’s existing supply chains, distribution networks, and local knowledge, companies can enter and operate in international markets without the complexities of setting up their own facilities abroad.
Resource Optimization
Companies can better allocate their internal resources by outsourcing production. For instance, financial resources that would have been used for manufacturing can be redirected toward marketing, product development, or expanding into new business areas. Human resources can also be optimized, as employees can focus on strategic tasks rather than day-to-day production issues.
Innovation and Collaboration
Contract manufacturers often work with multiple clients across various industries, which exposes them to a wide range of innovations and best practices.
This experience can lead to valuable insights and collaborative opportunities, where the contract manufacturer can offer suggestions for product improvement, cost reduction, or enhanced manufacturing processes.
In summary, contract manufacturing provides companies with a strategic advantage by offering cost savings, access to specialized expertise, flexibility, and the ability to focus on core business activities.
These benefits make contract manufacturing an attractive option for companies looking to optimize their operations and compete more effectively in their respective markets.
Limitations of Contract Manufacturing
While contract manufacturing offers numerous advantages, it also comes with certain limitations that companies need to consider when deciding whether to outsource their production.
Here are some of the key limitations:
Loss of Control
One of the most significant drawbacks of contract manufacturing is the reduced control over the production process.
Since manufacturing is outsourced to a third party, the hiring company may have less oversight and influence over how products are made, including quality control, production schedules, and labor practices.
This loss of control can lead to issues if the contract manufacturer does not meet the client’s expectations or standards.
Quality Risks
Although reputable contract manufacturers usually have robust quality control processes, there is still a risk that the products may not meet the required quality standards.
Any defects or inconsistencies can damage the hiring company’s reputation and lead to customer dissatisfaction. Ensuring that the contract manufacturer adheres to strict quality standards is crucial, but it can be challenging to monitor from a distance.
Dependency on the Manufacturer
Relying heavily on a contract manufacturer can create a dependency that may be risky for the hiring company.
If the manufacturer faces issues such as supply chain disruptions, labor strikes, or financial instability, it could impact the production and availability of the hiring company’s products.
This dependency can also lead to challenges if the relationship between the two parties deteriorates.
Intellectual Property Risks
Outsourcing production can expose a company to intellectual property (IP) risks. Sharing designs, proprietary processes, and other confidential information with a contract manufacturer increases the risk of IP theft or unauthorized use.
Protecting intellectual property through well-drafted contracts and legal safeguards is essential, but the risk cannot be entirely eliminated.
Communication Challenges
Effective communication is vital in any business relationship, and it becomes even more critical in contract manufacturing. Differences in language, culture, and time zones can create barriers to clear and timely communication.
Miscommunication or delays in information exchange can lead to errors, production delays, and misunderstandings that may impact the final product.
Supply Chain Vulnerability
Contract manufacturing often involves global supply chains, which can be vulnerable to disruptions caused by political instability, natural disasters, transportation issues, or changes in trade policies.
Such disruptions can affect the availability of raw materials, production timelines, and overall supply chain efficiency, leading to delays and increased costs.
Hidden Costs
While contract manufacturing can lead to cost savings, there may be hidden costs associated with the arrangement. These can include costs related to shipping, tariffs, customs, and regulatory compliance in different countries.
Additionally, the need for frequent travel, audits, and quality inspections can add to the overall expenses of the partnership.
Loss of Flexibility
Once a contract is in place, making changes to the product design, production process, or order quantities can be more difficult and costly. The contract manufacturer may not be as agile or responsive as an in-house team, leading to delays or increased costs when changes are required. This lack of flexibility can be a significant limitation in fast-paced industries where adaptability is key.
Brand Risk
The quality and reliability of the products produced by the contract manufacturer directly reflect on the hiring company’s brand. Any issues with product quality, ethical practices, or labor conditions at the manufacturing facility can negatively impact the hiring company’s reputation. Customers often hold the brand responsible for any shortcomings, even if the production was outsourced.
Regulatory Compliance
Different countries and regions have varying regulations regarding manufacturing, labor practices, environmental standards, and product safety.
Ensuring that the contract manufacturer complies with all relevant regulations can be complex and challenging, particularly when dealing with multiple jurisdictions. Non-compliance can lead to legal issues, fines, and damage to the company’s reputation.
In conclusion, while contract manufacturing can offer significant benefits, companies must carefully weigh these advantages against the potential limitations.
Thorough due diligence, strong contracts, ongoing monitoring, and effective communication are essential to mitigating the risks associated with contract manufacturing.
How MRP Systems Optimize Contract Manufacturing Processes
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) systems are essential tools for optimizing contract manufacturing processes.
Here’s how MRP systems specifically enhance contract manufacturing:
Accurate Demand Forecasting
MRP systems enable companies to forecast demand more accurately by analyzing historical data, sales trends, and market conditions. This precision ensures that contract manufacturing in MRP is aligned with actual production needs, reducing the risk of overproduction or stockouts.
Efficient Inventory Management
MRP systems track inventory levels in real-time, ensuring that the necessary raw materials and components are available when needed. This is crucial for contract manufacturing in MRP, as it minimizes production delays and helps maintain smooth operations without excess inventory or material shortages.
Streamlined Production Scheduling
MRP systems optimize production schedules by considering factors such as lead times, capacity constraints, and material availability. This efficiency is vital for contract manufacturing in MRP, leading to better resource utilization, reduced downtime, and adherence to delivery timelines.
Cost Control and Optimization
MRP systems provide detailed insights into material costs, labor, and overhead, allowing for better cost management in contract manufacturing. By optimizing processes and reducing waste, contract manufacturing in MRP becomes more cost-effective, benefiting both the manufacturer and the client.
Improved Collaboration and Communication
MRP systems offer a centralized platform for sharing production plans, updates, and inventory data. This transparency is key to successful contract manufacturing in MRP, fostering better collaboration, reducing misunderstandings, and ensuring alignment on production goals.
Enhanced Quality Control
MRP systems integrate quality control measures throughout the supply chain, ensuring that contract manufacturing in MRP adheres to required standards. This reduces the risk of defects and ensures consistent product quality.
Scalability and Flexibility
MRP systems support the scalability of contract manufacturing by allowing quick adjustments to production plans based on demand changes. This flexibility is crucial for contract manufacturing in MRP, enabling manufacturers to respond efficiently to client needs without compromising quality or delivery times.
Incorporating contract manufacturing in MRP systems significantly enhances efficiency, reduces costs, and improves overall production quality, making them indispensable tools for businesses optimizing their outsourcing strategies.
The Role of Contract Manufacturing in International Business
Contract manufacturing plays a pivotal role in the landscape of international business, providing companies with the ability to produce goods across borders while leveraging global resources and expertise. This approach allows businesses to remain competitive in diverse markets without the need to establish their own production facilities abroad.
In international business, contract manufacturing offers several strategic advantages. First, it enables companies to reduce costs by taking advantage of lower labor and production expenses in different countries. By partnering with local manufacturers, businesses can minimize their overhead while maintaining high-quality standards.
Moreover, contract manufacturing in international business facilitates market entry. Companies can quickly and efficiently introduce products to new regions without the delays and complexities associated with setting up operations in foreign territories. This is particularly beneficial in regions with stringent regulations or where establishing a physical presence is challenging.
Another significant benefit is the ability to focus on core competencies. By outsourcing production, companies can concentrate on activities that drive innovation and growth, such as research and development, marketing, and customer relations. This focus not only enhances product development but also strengthens a company’s global brand presence.
Furthermore, contract manufacturing supports supply chain efficiency in international business. It allows for the integration of global supply chains, enabling companies to source materials from various regions and produce products closer to their target markets. This reduces lead times, lowers transportation costs, and improves responsiveness to local demand.
However, businesses must carefully manage the challenges associated with contract manufacturing in an international context. These include navigating different regulatory environments, ensuring consistent quality across borders, and managing risks related to intellectual property and supply chain disruptions.
In summary, contract manufacturing is a crucial component of international business strategy, offering cost savings, market agility, and enhanced focus on core activities. When effectively managed, it enables companies to capitalize on global opportunities and remain competitive in the increasingly interconnected world economy.
How to Choose the Right Contract Manufacturer
Selecting the right contract manufacturer is crucial for ensuring that your production needs are met efficiently and effectively.
Here are key factors to consider when choosing a contract manufacturer:
Experience and Expertise
Evaluate the manufacturer’s experience in your industry and their expertise with the specific type of product you need. A manufacturer with a proven track record in your sector will be better equipped to handle your requirements and adhere to industry standards.
Quality Control
Assess the manufacturer’s quality control processes to ensure they align with your quality standards. Look for certifications such as ISO, FDA, or other relevant industry standards that indicate a commitment to maintaining high-quality production practices.
Production Capabilities
Review the manufacturer’s production capabilities, including their technology, equipment, and scalability. Ensure they can meet your production volume requirements and have the flexibility to adjust to changes in demand.
Cost and Pricing Structure
Compare the pricing structures of different manufacturers to find a balance between cost and quality. Consider not only the unit price but also any additional costs such as setup fees, tooling, and shipping.
Lead Times and Delivery Performance
Evaluate the manufacturer’s lead times and track record for on-time delivery. Reliable and timely delivery is essential to meet your market deadlines and maintain customer satisfaction.
Communication and Responsiveness
Effective communication is key to a successful partnership. Choose a manufacturer that is responsive, transparent, and willing to collaborate closely with you throughout the production process.
Location and Logistics
Consider the manufacturer’s location and how it affects logistics, including shipping costs and delivery times. Domestic manufacturers may offer quicker turnaround times, while international manufacturers might provide cost advantages.
Compliance and Regulatory Adherence
Ensure the manufacturer complies with relevant regulations and standards for your industry. This is particularly important for sectors such as pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and food and beverages, where regulatory adherence is critical.
Reputation and References
Research the manufacturer’s reputation by checking references and reading customer reviews. Feedback from other companies can provide valuable insights into the manufacturer’s reliability, quality, and overall performance.
Flexibility and Innovation
Choose a manufacturer that demonstrates flexibility and a willingness to innovate. This can be beneficial if you need to make changes to product designs, processes, or materials during the production cycle.
Intellectual Property Protection
Assess the manufacturer’s policies and practices regarding intellectual property protection. Ensure they have measures in place to safeguard your proprietary information and designs.
Cultural Fit
Consider the cultural and organizational fit between your company and the manufacturer. A good cultural match can enhance collaboration, reduce misunderstandings, and foster a more effective working relationship.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can select a contract manufacturer that aligns with your business needs, supports your quality and production goals, and contributes to your overall success.
How Deskera MRP Enhances Contract Manufacturing
Deskera’s Material Requirements Planning (MRP) system provides comprehensive solutions that can significantly enhance contract manufacturing processes. Here’s how Deskera MRP helps streamline and optimize contract manufacturing:
Accurate Demand Forecasting
Deskera MRP leverages historical data and advanced analytics to provide precise demand forecasting. This capability ensures that contract manufacturers receive accurate production schedules and material requirements, reducing the risk of overproduction or stockouts.
Real-Time Inventory Management
Deskera MRP offers real-time inventory tracking, helping businesses manage their inventory levels effectively. This feature ensures that contract manufacturers have the necessary raw materials and components on hand, minimizing production delays and reducing excess inventory.
Optimized Production Scheduling
Deskera MRP helps in creating efficient production schedules by considering factors such as lead times, resource availability, and order priorities. This optimization improves resource utilization, reduces downtime, and ensures that contract manufacturers adhere to production timelines.
Cost Management and Control
Deskera MRP provides detailed insights into material costs, labor, and overhead. By analyzing these costs, businesses can better manage their expenses and optimize their contract manufacturing processes, leading to cost savings and improved profitability.
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
Deskera MRP facilitates better communication between businesses and contract manufacturers through a centralized platform. This transparency allows for seamless sharing of production plans, updates, and inventory data, fostering stronger collaboration and reducing the risk of misunderstandings.
Quality Assurance and Compliance
Deskera MRP integrates quality control measures into the production process by tracking materials and components throughout the supply chain. This ensures that contract manufacturing meets the required quality standards and regulatory compliance.
Scalability and Flexibility
Deskera MRP supports the scalability of contract manufacturing by allowing businesses to adjust production plans based on demand changes. This flexibility enables contract manufacturers to respond quickly to shifts in market conditions without compromising on quality or delivery times.
Streamlined Workflow and Efficiency
Deskera MRP enhances overall workflow efficiency by automating various aspects of the manufacturing process, from inventory management to order processing. This automation reduces manual errors, speeds up production, and improves operational efficiency.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Deskera MRP provides comprehensive reporting and analytics tools that help businesses make informed decisions about their contract manufacturing strategies. By analyzing production data, businesses can identify trends, optimize processes, and improve overall performance.
Key Takeaways
Contract manufacturing is a critical component of modern business strategy, offering numerous benefits that contribute to growth and efficiency. These benefits include:
- Strategic Advantage: Contract manufacturing offers businesses a strategic advantage by allowing them to focus on core activities while outsourcing production to specialized partners. This approach can lead to cost savings, increased efficiency, and faster time-to-market.
- Cost Efficiency: Partnering with contract manufacturers can significantly reduce production costs by leveraging their established infrastructure, economies of scale, and expertise. This cost efficiency is particularly beneficial for scaling production and entering new markets.
- Access to Expertise: Contract manufacturers bring specialized knowledge and advanced technologies that may not be available in-house. This expertise ensures high-quality production and adherence to industry standards.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Contract manufacturing provides the flexibility to adjust production volumes based on demand fluctuations, allowing businesses to respond quickly to market changes without the need for extensive investments in new facilities.
- Market Expansion: Utilizing contract manufacturing facilitates market entry and expansion by enabling companies to introduce products to new regions without the complexities and costs associated with setting up operations in foreign markets.
- Enhanced Focus: By outsourcing production, businesses can allocate more resources to innovation, research and development, and customer engagement, leading to better product development and a stronger market presence.
- Risk Management: Contract manufacturing helps mitigate risks related to production, such as equipment failures and supply chain disruptions, by relying on experienced partners with robust risk management practices.
As businesses navigate the complexities of production and global markets, contract manufacturing stands out as a valuable solution for achieving competitive advantage and sustaining long-term success.
Embracing contract manufacturing allows companies to streamline operations, reduce costs, and respond agilely to market demands, ultimately driving their growth and maintaining their position in the competitive landscape.
Deskera MRP offers a range of features that enhance contract manufacturing by improving demand forecasting, inventory management, production scheduling, and cost control.
These capabilities contribute to more efficient and effective contract manufacturing processes, supporting businesses in achieving their production and operational goals.
Related Articles













