In today’s fast-paced business landscape, organizations are increasingly turning to innovative solutions that offer flexibility and scalability. One such solution is composable ERP, an approach that enables businesses to assemble their enterprise resource planning systems using modular components tailored to their unique needs.
The global composable applications market is experiencing significant growth, projected to expand from $5.5 billion in 2023 to $27.71 billion by 2033. This burgeoning market reflects a growing recognition of the importance of adaptability in a digital-first world.
The anticipated growth rate of 17.60% between 2024 and 2033 further underscores the demand for composable ERP solutions among businesses striving for agility and responsiveness.
As organizations face increasing pressures to innovate and adapt to market changes, composable ERP systems offer a pathway to seamlessly integrate the best-of-breed applications that can meet evolving business needs. This dynamic approach empowers companies to customize their technology stacks without being locked into a single vendor.
A 2023 survey highlighted the rising awareness of composable ERP within the industry, revealing that 76% of IT decision-makers had heard of composable ERP. Even more compelling is the fact that 84% of these respondents planned to invest in composable ERP solutions in the near future. This momentum reflects a collective understanding that traditional ERP systems may no longer suffice in a landscape where speed and agility are critical for success.
Among the various options available, Deskera ERP stands out as a robust solution for businesses seeking to leverage composable principles. With its modular architecture and extensive suite of functionalities, Deskera ERP allows organizations to integrate multiple applications and tailor their operations to drive efficiency and innovation.
As we delve deeper into the world of composable ERP, this article will explore its benefits, implementation strategies, challenges, and real-world applications, providing you with everything you need to know to navigate this transformative landscape.
What is Composable ERP?
Composable ERP is a modern approach to enterprise resource planning (ERP) that allows organizations to build their ERP systems using a flexible and modular framework. Unlike traditional ERP systems, which are typically monolithic and require extensive customization to adapt to specific business needs, composable ERP enables companies to select and integrate best-of-breed applications and services tailored to their unique requirements.
Key Characteristics of Composable ERP
- Modularity: Composable ERP systems consist of independent modules or components, each focusing on specific functionalities, such as finance, human resources, supply chain management, and customer relationship management. This modularity allows organizations to customize their ERP solutions by choosing only the components that fit their needs.
- Integration Capabilities: Composable ERP emphasizes seamless integration between various applications and services. Organizations can connect different modules using APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) or integration platforms, ensuring that data flows smoothly across the entire system.
- Flexibility and Scalability: With composable ERP, businesses can easily adapt to changing market conditions or operational demands. They can add, remove, or modify modules as needed, allowing for rapid scalability and innovation without the constraints of traditional ERP systems.
- Focus on Best-of-Breed Solutions: Composable ERP encourages organizations to adopt best-of-breed applications that excel in specific areas rather than relying on a single vendor's suite of tools. This enables companies to leverage cutting-edge technologies and functionalities that best suit their operational needs.
- User-Centric Design: Composable ERP systems prioritize user experience by providing intuitive interfaces and personalized dashboards. This focus on usability can lead to higher adoption rates among employees and improved overall efficiency.
Composable ERP represents a significant shift in how organizations approach their enterprise resource planning needs. By embracing modularity, integration, and flexibility, companies can build a system that evolves alongside their business, ensuring they remain agile and responsive in an ever-changing landscape.
Composable ERP vs. Traditional ERP
When comparing composable ERP to traditional ERP, it’s essential to understand the fundamental differences in architecture, flexibility, scalability, and overall approach to enterprise resource planning. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the two systems:
1. Architecture
- Composable ERP:
- Modular Design: Composable ERP is built on a modular architecture that allows organizations to select specific components or applications based on their needs. Each module can function independently while still being part of a larger integrated system.
- Microservices: Many composable ERP systems use microservices architecture, enabling different components to be developed, updated, and scaled independently, promoting flexibility and innovation.
- Traditional ERP:
- Monolithic Structure: Traditional ERP systems are often monolithic, meaning that they are designed as a single, unified system where all functionalities are tightly integrated. Customizing or changing one part of the system typically affects the entire application.
- Limited Flexibility: Customization usually requires extensive configuration or programming, making it more challenging to adapt to new business needs or technologies.
2. Flexibility and Customization
- Composable ERP:
- High Flexibility: Organizations can rapidly adapt their ERP solutions by adding or removing modules according to changing requirements. This flexibility allows businesses to keep pace with market dynamics and emerging technologies.
- Best-of-Breed Approach: Companies can choose best-of-breed applications for specific functions, ensuring they leverage the most effective tools for their unique operational needs.
- Traditional ERP:
- Limited Customization: Customizing traditional ERP systems can be complex and costly, often requiring significant time and resources. Organizations are frequently locked into their vendor's ecosystem, making it harder to switch applications or add new functionalities.
- Slow to Adapt: Changes to the system may take considerable time to implement, making it challenging for organizations to respond swiftly to new business challenges.
3. Scalability
- Composable ERP:
- Easily Scalable: Composable ERP allows organizations to scale up or down by adding or removing modules as needed. This scalability is particularly beneficial for growing companies or those facing fluctuating demands.
- On-Demand Growth: Businesses can enhance their capabilities gradually, incorporating new technologies or applications as their needs evolve.
- Traditional ERP:
- Challenging Scalability: Scaling a traditional ERP system can be cumbersome and costly, often requiring a complete overhaul or significant upgrades to the existing system.
- Rigid Growth: Organizations may find themselves constrained by their ERP system, limiting their ability to expand or innovate.
4. Implementation and Upgrades
- Composable ERP:
- Faster Implementation: Since composable ERP systems consist of independent modules, implementation can be quicker, allowing businesses to realize value sooner.
- Continuous Upgrades: Organizations can update individual components without affecting the entire system, ensuring they always have access to the latest features and technologies.
- Traditional ERP:
- Lengthy Implementation: Traditional ERP implementations can take months or even years, requiring significant planning and resources to deploy effectively.
- Complex Upgrade Processes: Upgrading a traditional ERP system often necessitates significant downtime and may require a complete system upgrade, impacting business operations.
5. Cost Structure
- Composable ERP:
- Cost-Effective: Organizations can choose only the modules they need, potentially lowering initial costs and ongoing maintenance expenses. This pay-as-you-go model allows for more predictable budgeting.
- Reduced Total Cost of Ownership: By leveraging modular solutions, companies can avoid the high costs associated with comprehensive traditional ERP systems.
- Traditional ERP:
- High Initial Investment: The costs associated with traditional ERP systems can be substantial due to licensing fees, hardware requirements, and implementation expenses.
- Ongoing Maintenance Costs: The complexity of traditional systems can lead to higher long-term maintenance costs, including the need for specialized IT staff.
Key Benefits of Composable ERP
Composable ERP offers numerous advantages for organizations seeking to enhance their enterprise resource planning capabilities. Here are some key benefits:
1. Flexibility and Customization
- Tailored Solutions: Composable ERP allows businesses to select and assemble modules that best fit their unique processes and requirements, leading to highly customized solutions.
- Adapting to Change: Companies can easily modify their ERP systems by adding or removing components as their needs evolve, ensuring they stay relevant in a rapidly changing market.
2. Scalability
- On-Demand Growth: Organizations can scale their ERP solutions seamlessly by integrating additional modules or applications as they grow or as market demands change.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Businesses can allocate resources more effectively by only implementing necessary components, optimizing their operational capabilities without over-investing in unused functionalities.
3. Cost-Effectiveness
- Reduced Upfront Costs: Composable ERP systems typically require lower initial investments compared to traditional ERP systems, as businesses can choose only the components they need.
- Lower Total Cost of Ownership: Ongoing maintenance and upgrade costs are often reduced because businesses can update or replace specific modules without overhauling the entire system.
4. Enhanced Integration Capabilities
- Seamless Data Flow: Composable ERP systems promote easier integration with other best-of-breed applications, ensuring a smooth exchange of data across various platforms.
- API-Driven Connectivity: Organizations can leverage APIs to connect modules and third-party applications, enabling a more cohesive and efficient digital ecosystem.
5. Improved Agility
- Faster Time to Market: The ability to quickly adapt and implement new functionalities allows organizations to respond faster to market opportunities or challenges, enhancing their competitive edge.
- Rapid Innovation: Businesses can incorporate the latest technologies and innovations without lengthy overhaul processes, ensuring they remain at the forefront of their industries.
6. User-Centric Design
- Enhanced User Experience: Many composable ERP solutions prioritize user experience with intuitive interfaces and personalized dashboards, leading to higher adoption rates and better user satisfaction.
- Empowered Employees: By providing tools tailored to specific roles, organizations can enhance employee productivity and collaboration.
7. Continuous Upgrades and Improvements
- Real-Time Updates: Composable ERP allows for ongoing updates to individual modules, ensuring organizations always benefit from the latest features and improvements.
- Reduced Downtime: Since only specific components need to be updated, businesses can minimize disruptions during the upgrade process, maintaining operational efficiency.
8. Focus on Core Competencies
- Strategic Resource Allocation: With composable ERP, organizations can focus their resources on areas that drive the most value for their business while leveraging specialized applications for other functions.
- Streamlined Operations: By integrating best-of-breed applications, businesses can streamline their operations and enhance overall efficiency without being tied to a single vendor's limitations.
Components of a Composable ERP System
A composable ERP system is designed to be modular and flexible, allowing organizations to tailor their enterprise resource planning solutions to meet their unique needs.
Here are the key components typically found in a composable ERP system:
1. Core ERP Functions
- Finance and Accounting: Modules for managing financial transactions, budgeting, forecasting, and reporting.
- Human Resources Management (HRM): Tools for managing employee records, payroll, recruitment, performance evaluation, and talent management.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM): Components for inventory management, procurement, logistics, and supplier relationship management.
2. Industry-Specific Applications
- Manufacturing: Modules designed for production planning, quality control, and manufacturing execution.
- Retail: Applications for point-of-sale systems, customer relationship management, and omnichannel operations.
- Healthcare: Tools for patient management, billing, compliance, and resource allocation.
3. Best-of-Breed Applications
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Systems for managing customer interactions, sales tracking, and marketing automation.
- Project Management Tools: Applications for planning, executing, and monitoring projects, including resource allocation and timeline tracking.
- Business Intelligence (BI) and Analytics: Tools that provide insights through data analysis, reporting, and dashboards, aiding in data-driven decision-making.
4. Integration Layer
- APIs (Application Programming Interfaces): Enable communication and data exchange between different modules and third-party applications, facilitating seamless integration.
- Middleware Solutions: Software that connects disparate systems, ensuring data consistency and interoperability across the composable ERP ecosystem.
5. User Interface and Experience
- Dashboards: Customizable dashboards that provide users with relevant insights, metrics, and KPIs in real-time.
- Mobile Applications: Solutions that enable access to ERP functionalities on mobile devices, enhancing usability and accessibility for remote workforces.
6. Automation and Workflow Management
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Tools that automate repetitive tasks and processes, increasing efficiency and reducing manual effort.
- Workflow Management: Systems that allow organizations to design, execute, and monitor business processes across different departments.
7. Data Management and Security
- Data Governance Tools: Solutions for ensuring data quality, compliance, and security across the organization.
- Cloud Storage and Management: Services that facilitate secure data storage, backup, and retrieval, often with scalability options to accommodate growing data needs.
8. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- Predictive Analytics: AI-driven tools that analyze historical data to forecast trends and provide actionable insights.
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: AI applications that enhance customer service and internal operations by automating inquiries and support tasks.
9. Collaboration Tools
- Communication Platforms: Integrated tools for team communication and collaboration, such as messaging apps, video conferencing, and project collaboration spaces.
- Document Management: Systems for storing, sharing, and managing documents and files within the organization.
How to Implement a Composable ERP Strategy
Implementing a composable ERP strategy requires careful planning, a clear understanding of business needs, and a focus on integration and adaptability. Here are the key steps to successfully implement a composable ERP strategy:
1. Define Business Objectives and Requirements
- Identify Goals: Determine the specific business goals you want to achieve with a composable ERP system, such as improving efficiency, reducing costs, or enhancing customer experience.
- Assess Current Processes: Conduct a thorough analysis of your existing processes and systems to identify pain points, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement.
- Gather Stakeholder Input: Involve key stakeholders from various departments (e.g., finance, HR, operations) to gather insights on their needs and expectations for the new system.
2. Choose the Right Components
- Evaluate Modules and Applications: Research and select modules that align with your business requirements, including core ERP functions, best-of-breed applications, and industry-specific solutions.
- Consider Scalability: Ensure that the selected components can grow with your business, allowing for future additions or modifications as needs change.
- Focus on Integration: Choose components that offer strong integration capabilities to facilitate seamless data flow and communication across different applications.
3. Develop a Roadmap
- Create a Detailed Implementation Plan: Outline the timeline, key milestones, and resources needed for the implementation process.
- Prioritize Phases: Consider implementing the composable ERP strategy in phases, starting with critical components and gradually expanding to additional modules.
- Set Measurable KPIs: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to evaluate the success of the implementation and measure progress against business objectives.
4. Engage with Technology Partners
- Select Trusted Vendors: Identify technology partners and vendors with expertise in composable ERP solutions and a proven track record of successful implementations.
- Negotiate Contracts: Ensure that contracts include support and maintenance services to address any potential issues that may arise during and after implementation.
- Leverage Professional Services: Consider engaging consultants or specialists who can provide guidance and support throughout the implementation process.
5. Focus on Change Management
- Communicate Changes: Clearly communicate the benefits and changes associated with the new composable ERP strategy to all employees.
- Provide Training: Offer comprehensive training programs for users to ensure they understand how to effectively use the new system and its components.
- Encourage Feedback: Foster an open environment for feedback and questions, allowing employees to share their experiences and challenges with the new system.
6. Ensure Data Migration and Integration
- Plan Data Migration: Develop a strategy for migrating existing data into the new composable ERP system, ensuring data accuracy and integrity.
- Test Integration: Conduct thorough testing of integration between different modules and applications to ensure seamless data exchange and functionality.
- Monitor Data Quality: Implement data governance practices to maintain high data quality and consistency across the organization.
7. Evaluate and Optimize Post-Implementation
- Monitor Performance: Continuously track the performance of the composable ERP system against established KPIs and business objectives.
- Solicit User Feedback: Regularly gather feedback from users to identify areas for improvement and address any challenges they may encounter.
- Iterate and Enhance: Be prepared to make iterative improvements and updates to the system, adding new modules or functionalities as business needs evolve.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing a Composable ERP Strategy
Implementing a composable ERP strategy comes with its own set of challenges and considerations that organizations must address to ensure a successful transition. Here are some of the key challenges and considerations:
1. Complexity of Integration
- Multiple Systems: Composable ERP involves integrating various components and applications, which can lead to complexities in ensuring smooth data flow and interoperability.
- Technical Skills Requirement: Organizations may need specialized technical skills to manage integrations effectively, which could necessitate additional training or hiring.
2. Data Management and Quality
- Data Silos: Different modules might create data silos, leading to inconsistencies and difficulties in accessing unified data for decision-making.
- Data Migration Challenges: Migrating existing data into the new system can be complicated, especially if data formats vary across legacy systems.
3. Change Management
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist transitioning to a new system, particularly if they are accustomed to existing workflows and tools.
- Training Needs: Comprehensive training is necessary to ensure users are proficient in using the new components, which can require significant time and resources.
4. Cost Management
- Unexpected Costs: While composable ERP can be cost-effective, organizations may encounter unforeseen expenses related to integration, training, and ongoing maintenance.
- Budget Constraints: Allocating sufficient budget for multiple components can be challenging, particularly for smaller organizations with limited resources.
5. Vendor Management
- Dependence on Multiple Vendors: Working with several vendors for different components can complicate vendor management and increase the risk of miscommunication or misalignment.
- Vendor Reliability: Ensuring that chosen vendors have a strong track record and reliable support can be challenging, particularly in a rapidly evolving technology landscape.
6. Scalability and Future-Proofing
- Long-Term Viability: Organizations need to assess whether the chosen components will remain relevant and scalable as business needs change over time.
- Integration of New Technologies: As new technologies emerge, organizations must be prepared to integrate them into their existing composable ERP system, which could require ongoing adjustments.
7. Regulatory Compliance and Security
- Data Privacy Regulations: Complying with regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA can complicate data management across different components, especially when using cloud-based solutions.
- Security Concerns: Ensuring data security across multiple applications and integrations can be challenging, necessitating robust security measures and protocols.
8. Performance Monitoring and Optimization
- Continuous Evaluation: Organizations must consistently monitor the performance of various components and integrations to ensure they meet business objectives.
- Resource Allocation: Determining where to allocate resources for maintenance, updates, and optimizations can be complex, requiring ongoing attention and strategic planning.
9. User Experience
- Fragmented User Experience: Users may face a disjointed experience if different components have varying user interfaces or functionalities.
- Adoption Rates: Ensuring high adoption rates across all departments can be challenging, especially if some users find certain components less intuitive or beneficial.
Future Trends in Composable ERP
The landscape of composable ERP is continually evolving, driven by advancements in technology, changing business needs, and emerging market trends. Here are some key future trends in composable ERP to watch:
1. Increased Adoption of Cloud-Native Solutions
- Shift to Cloud Infrastructure: More organizations are moving to cloud-native ERP solutions that offer scalability, flexibility, and cost efficiency.
- Hybrid Deployments: Businesses will increasingly adopt hybrid deployments, utilizing both cloud and on-premises solutions to leverage the benefits of each.
2. Enhanced Integration Capabilities
- API-First Architectures: As composable ERP relies on integrating various applications, the use of API-first architectures will become more prevalent, allowing for seamless connectivity between systems.
- Low-Code/No-Code Platforms: The rise of low-code and no-code development platforms will empower non-technical users to create integrations and customize applications easily.
3. Focus on Data-Driven Decision Making
- Advanced Analytics: Organizations will increasingly use advanced analytics and business intelligence tools within their composable ERP systems to gain insights and drive data-driven decisions.
- Real-Time Data Access: Real-time data access will be prioritized, allowing businesses to respond quickly to changes in market conditions and customer needs.
4. Emphasis on User Experience
- Personalized Interfaces: Composable ERP solutions will focus on delivering personalized user experiences, allowing users to customize their dashboards and workflows based on individual preferences.
- Mobile Accessibility: As remote work continues to rise, mobile accessibility of composable ERP applications will become essential, enabling users to access critical information on-the-go.
5. Greater Emphasis on Security and Compliance
- Robust Security Measures: With the growing concern over data breaches and cyber threats, composable ERP solutions will incorporate advanced security features to protect sensitive information.
- Compliance Automation: Organizations will increasingly adopt compliance automation tools within their composable ERP systems to streamline adherence to regulations and standards.
6. Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- AI-Driven Insights: The integration of AI and machine learning capabilities will enhance the analytical power of composable ERP systems, providing predictive insights and recommendations.
- Automation of Routine Tasks: AI will automate repetitive tasks within the ERP system, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic initiatives.
7. Sustainability and Social Responsibility
- Green Initiatives: As sustainability becomes a priority, composable ERP solutions will incorporate features that help organizations track and manage their environmental impact.
- Social Responsibility Features: Organizations will increasingly look for ERP systems that support social responsibility initiatives, such as diversity and inclusion tracking.
8. Collaborative Ecosystems
- Partnerships and Ecosystems: Composable ERP will foster collaborative ecosystems where businesses can partner with third-party vendors, startups, and industry experts to enhance their ERP capabilities.
- Marketplace Models: Organizations will leverage marketplace models to discover and integrate new applications and services into their composable ERP systems easily.
9. Continuous Improvement and Evolution
- Agile Development Practices: Organizations will adopt agile development practices for their composable ERP systems, allowing for rapid updates and iterative improvements based on user feedback.
- Focus on Innovation: As technology continues to evolve, businesses will prioritize innovation, regularly updating their composable ERP solutions to stay competitive in the market.
How Can Deskera ERP Help You?
Deskera ERP offers a comprehensive suite of tools designed to help businesses streamline their operations, improve efficiency, and drive growth. Here are several ways Deskera ERP can benefit your organization:
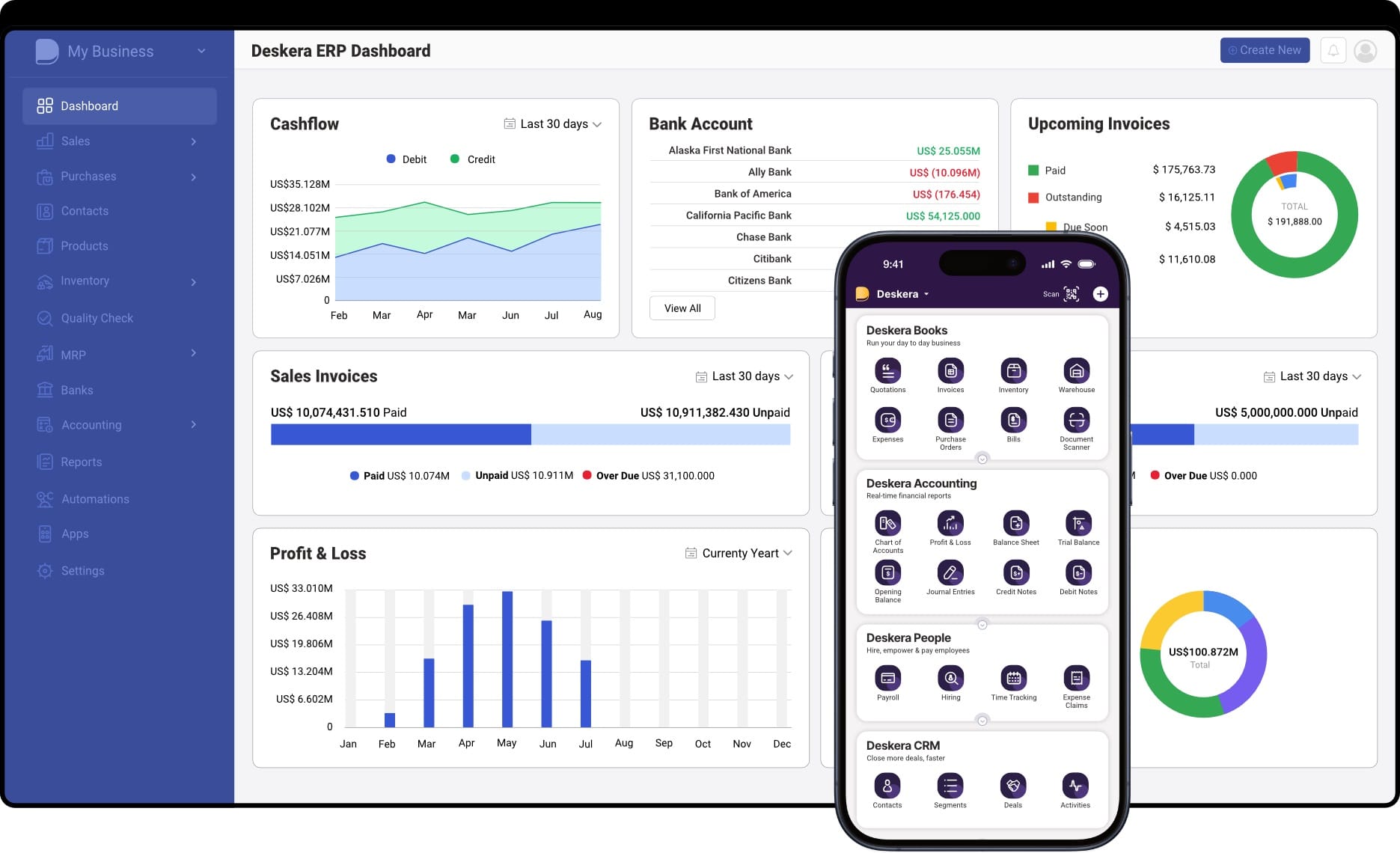
1. Integrated Business Management
- Unified Platform: Deskera ERP provides a single platform that integrates various business functions, including finance, HR, inventory, sales, and CRM, enabling seamless data flow and collaboration across departments.
- Centralized Data Access: With all your data in one place, decision-makers can easily access real-time information, leading to more informed decisions.
2. Enhanced Financial Management
- Automated Accounting: Deskera simplifies accounting processes with automated features for invoicing, expense tracking, and financial reporting, reducing the risk of errors and saving time.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: The ERP system includes tools for budgeting and forecasting, allowing organizations to plan for future growth and manage resources more effectively.
3. Efficient Inventory Management
- Real-Time Inventory Tracking: Deskera’s inventory management module enables real-time tracking of stock levels, helping businesses prevent stockouts and overstock situations.
- Demand Forecasting: Advanced forecasting tools help predict inventory needs based on historical data and trends, improving supply chain efficiency.
4. Streamlined Operations
- Workflow Automation: Deskera automates repetitive tasks and workflows, freeing up employee time for more strategic activities and increasing overall productivity.
- Project Management Tools: The ERP includes project management features that allow teams to plan, execute, and monitor projects effectively, ensuring timely delivery and resource optimization.
5. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Comprehensive CRM Features: Deskera’s CRM tools help businesses manage customer relationships, track sales leads, and monitor customer interactions to enhance service delivery and satisfaction.
- Sales Pipeline Management: The platform offers tools to visualize and manage the sales pipeline, enabling sales teams to focus on high-priority leads and improve conversion rates.
6. User-Friendly Interface
- Intuitive Design: Deskera ERP features a user-friendly interface that simplifies navigation and reduces the learning curve for employees, facilitating quicker adoption across the organization.
- Mobile Accessibility: With mobile access to the ERP system, employees can manage tasks and access important information anytime, anywhere.
7. Robust Reporting and Analytics
- Customizable Dashboards: Deskera provides customizable dashboards that give users insight into key performance indicators (KPIs) and business metrics, enabling data-driven decision-making.
- Advanced Analytics: The system includes advanced analytics capabilities that help businesses identify trends, evaluate performance, and make strategic adjustments.
8. Scalability and Flexibility
- Adaptable to Business Needs: Deskera ERP is designed to grow with your business, allowing you to add new modules or features as your needs evolve without a complete overhaul of your system.
- Cloud-Based Solution: Being cloud-based, Deskera ensures that you can access your ERP system from anywhere, making it ideal for remote teams and businesses with multiple locations.
9. Compliance and Security
- Regulatory Compliance: Deskera ERP helps businesses stay compliant with industry regulations by automating processes and maintaining accurate records.
- Data Security: The platform prioritizes data security with robust measures in place to protect sensitive business information and ensure privacy.
Key Takeaways
- Composable ERP is a modular approach that allows businesses to create customized ERP solutions by selecting and integrating various applications and services tailored to their specific needs.
- Unlike traditional ERP systems that are monolithic and rigid, composable ERP offers flexibility, scalability, and adaptability, allowing organizations to respond quickly to changing business requirements.
- The main advantages of composable ERP include enhanced agility, improved integration capabilities, tailored solutions, reduced implementation times, and lower total cost of ownership.
- A composable ERP system typically consists of various components such as best-of-breed applications, integration tools, APIs, and data analytics solutions that work together to meet diverse business needs.
- Implementing a composable ERP strategy involves assessing business needs, selecting the right components, ensuring robust integration, training users, and continuously optimizing the system based on feedback and performance.
- Organizations may face challenges like data integration complexity, vendor management, and ensuring data security, which must be carefully considered when adopting a composable ERP approach.
- Future trends in composable ERP include increased cloud adoption, enhanced integration capabilities, AI and machine learning integration, a focus on user experience, and greater emphasis on security and compliance.
- Deskera ERP is a powerful tool that can significantly enhance your business operations. By integrating various functions into a single platform, automating processes, and providing real-time insights, Deskera ERP enables organizations to improve efficiency, drive growth, and stay competitive in today’s dynamic business environment.
Related Articles