Chemical manufacturing is a complex and dynamic industry that plays a vital role in modern society, producing a wide range of products that are used in everything from medicines to plastics to food. While chemical manufacturing can be highly profitable, it also presents a number of significant challenges, particularly when it comes to safety and efficiency.
Optimizing safety and efficiency in chemical manufacturing is essential to the success of any operation in this industry. Safety is a top priority in chemical manufacturing, given the potential for hazardous materials, exposure risks, and the potential consequences of accidents or failures. At the same time, efficiency is critical to staying competitive in the global marketplace, given the high capital costs, energy demands, and production rates required in chemical manufacturing.
Achieving safety and efficiency in chemical manufacturing requires a multifaceted approach that involves a commitment to safety culture, the use of technology and automation, maintaining a skilled workforce, and pursuing continuous improvement. By prioritizing safety and efficiency, chemical manufacturers can reduce risk, increase profitability, and achieve long-term success in this challenging and dynamic industry.
In today’s guide, we’ll learn in-depth explanations of the problems affecting the chemical production industry as well as suggested solutions to increase effectiveness and safety. Before we dive in, let’s take a look at the table of content below:
- About Chemical Industry
- Different Types of Chemical Industries
- Top Operational Challenges Faced by Chemical Industries & its Solutions
- Wrapping Up
- How Deskera Can Assist You?
Let's get started!
About Chemical Industry
The chemical industry is a vast and complex industry that produces a wide range of chemicals and chemical-based products.
Chemicals are utilized in many different products, including polymers, medications, fertilizers, textiles, and electronics. The chemical industry includes a broad range of companies that produce chemicals, chemical products, and chemical raw materials.

One of the biggest and most influential industries in the world, the chemical industry has a big impact on the world economy.
Furthermore, it plays a crucial role in the development of new products, the improvement of existing products, and the advancement of many different fields, including healthcare, agriculture, energy, and technology.
However, the chemical industry also poses various risks, including environmental pollution, health hazards, and the potential for accidents. Therefore, the industry is subject to stringent regulations and safety standards.
Overall, the chemical industry is a dynamic and vital sector, and its products and innovations are essential for modern life.
Different Types of Chemical Industries
One of the world's most important economic sectors is the chemical industry, which produces roughly $4 trillion in chemical output annually and accounts for 96% of all goods produced (global revenue of the chemical industry).
With so many various products available on the market, it is an extremely competitive sector. It can be classified into various distinct categories, such as:
Agrochemicals and Fertilizers
For safety, growth, and health, fertilizers and agrochemicals are chemical substances used in agriculture and gardening (pesticides).

Petrochemicals
Petrochemicals are by-products of chemical reactions using petroleum, other fossil fuels (like gas and coal), or renewable fuels (like maize and palm oil), which are obtained during the refining process.

Commodity Chemicals (or Bulk Chemicals)
Commodity chemicals include, for instance, rubber, plastics, chemical fibres, detergents, solvents, adhesives, or cleaning agents (also known as bulk chemicals). The industrial sector is where most of these things are used.
Pharmaceuticals
Pharmaceuticals are a distinct segment of industry because of the specifics of the completed product and the demanding standards. The Supply Chain Management (SCM) for medicines has different possibilities and issues than the chemical industry. You may get more details on the medicine supply chain here.
For companies like chemical manufacture and its downstream processing industries, chemical supply chains work as a source of raw materials, completed goods, and processing facilities. The supply chain's main focus is on cutting costs while simultaneously delivering the right number of commodities to the places where they are needed at any given time.
Specialty Chemicals
Chemicals used in paints, coatings, colors, cosmetic additives, flavors, food additives, smells, and other items that are referred to as specialty chemicals have a specific use or industry.
Top Operational Challenges Faced by Chemical Industries & its Solutions
Following, we've discussed some crucial top operational challenges that are faced by chemical industries and also their solutions. Let's learn:
1. Lack of Inventory Visibility
Lack of inventory visibility can be a significant challenge for the chemical industry. The chemical industry typically deals with a large number of raw materials and finished goods, and the movement of these materials can be complex and difficult to track.
This can lead to inventory discrepancies, stockouts, overstocks, and other issues that can impact the efficiency and profitability of chemical companies.
The term "inventory visibility" describes the capacity to precisely trace inventory along the whole supply chain, from the initial order to the last delivery.
With accurate inventory visibility, chemical companies can better manage their inventory levels, reduce stockouts and overstocks, improve customer service, and optimize their production schedules.
They need to track and keep an eye on inventory in a number of different categories, such as:
- Shelf life
- Grade
- Disposition (tracks whether a product can be used for sale or isn’t usable)
- Lot number
- Container for bulk products in their final receptacle (drum, pallet, bag, railcar)
- Serial numbers
Yet, in the chemical sector, achieving inventory visibility might be difficult because the complex nature of the supply chain. There may be multiple intermediaries, distributors, and suppliers involved in the movement of materials, which can make it difficult to track inventory levels accurately.
To address this challenge, chemical companies can implement advanced supply chain management systems that provide real-time visibility into inventory levels and movement.
Furthermore, these systems use technologies such as barcode scanning, RFID tracking, and GPS tracking to monitor inventory and provide accurate, up-to-date information on inventory levels.
By improving inventory visibility, chemical companies can improve their supply chain operations, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction, all of which can contribute to increased profitability and growth.
2. Compliance
Compliance in the chemical industry refers to the adherence to laws, regulations, and standards that are established to ensure the safety of people, the environment, and property.
Moreover, it is crucial for chemical companies to comply with all relevant laws and regulations in order to protect their workers, the communities in which they operate, and the environment.
There are many different aspects of compliance in the chemical industry, including:
- Environmental compliance: This involves compliance with laws and regulations related to air emissions, water discharges, waste disposal, and other environmental impacts.
- Occupational health and safety compliance: This includes compliance with regulations related to workplace safety, chemical exposure, and employee health.
- Product compliance: This involves compliance with regulations related to the production and sale of chemical products, such as labeling, testing, and certification requirements.
- Transportation compliance: This involves compliance with regulations related to the transportation of chemicals, including labeling, packaging, and documentation requirements.
To achieve compliance with all relevant laws and regulations, chemical businesses must have a strong compliance program in place that consists of policies and processes, training and education, internal audits, and ongoing monitoring.
Depending on the goods your company produces, you can be subject to regulations from one or more of the following organizations:
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
- Dope Control Agency (FDA)
- Office of Occupational Safety and Health (OSHA) optimum manufacturing procedures (GMP)
Consider sending products to the European Union. In that case, REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulations may also apply to you.
Remember: Non-compliance can lead to significant penalties, fines, and reputational damage, so it is essential for chemical companies to take compliance seriously.
3. Formula Management
Formula management in the chemical industry refers to the process of creating, storing, and managing chemical formulas for products. The sorts of atoms and their numbers in each molecule are listed in a chemical formula, which is a symbolic representation of a chemical complex.
Furthermore, it is essential for chemical companies to manage their formulas effectively to ensure that the products they produce are safe, of high quality, and meet customer specifications.
Effective formula management in the chemical industry involves the following steps:
Formula creation: This involves creating a new formula for a product. The formula must be carefully crafted to ensure that it meets the desired product specifications, is safe, and can be produced efficiently.
Formula storage: The formula must be stored in a safe place that is easily accessible after it has been prepared. This is typically done using a computerized system that allows for easy retrieval and updating of the formula.
Formula revision: Chemical formulas are frequently updated as new knowledge becomes available or as client requirements shift over time. It is essential to have a system in place to manage revisions to ensure that all changes are properly documented and tracked.
Formula control: Chemical companies must have robust controls in place to ensure that the formulas they use are accurate, up-to-date, and comply with all relevant laws and regulations.
Formula sharing: In some cases, chemical companies may need to share formulas with customers, suppliers, or regulatory agencies. It is important to have a secure system in place for sharing formulas that protects the company's intellectual property and ensures that confidential information is not shared improperly.
Furthermore, to ensure the uniformity of their completed items, chemical enterprises must utilize formulas to measure their material use and maintain thorough records. Formula management includes:
- Keeping track of different metrics
- Formula integration with inventory
- Ordering from inventory
- Increasing production to meet demand
With the right software, managing formulas will be simpler for you. You'll be able to monitor your formulations in connection to your supply chain and production schedules. If you want to use more expensive or less expensive chemicals to get the same results, you can specify your cost distributions.
In addition, effective formula management is critical for the success of chemical companies. By managing their formulas effectively, companies can ensure that their products are safe, of high quality, and meet customer needs, while also complying with all relevant laws and regulations.
4. Hazard Analysis
Hazard analysis in the chemical industry is a systematic process that identifies and assesses the potential hazards associated with the handling, storage, processing, and transportation of chemicals. The goal of hazard analysis is to identify potential risks and implement measures to prevent accidents and minimize the impact of hazards on people, property, and the environment.

Information must be obtained at many stages of the manufacturing process, including production, finished goods, and supplier purchase orders. Data from hazard analyses are necessary to satisfy the EPA and other regulatory bodies, as well as to monitor the chemical industry's carbon impact.
The procedures that producers employ to create waste, rubbish, and byproducts can be tracked. If they are aware of this, CEOs can contact the EPA to stay in compliance.
By moving labor-intensive work to off-peak hours, chemical businesses can also optimize their resource use. The action will result in lower energy prices.
The following are some common methods of hazard analysis used in the chemical industry:
- Hazard and Operability (HAZOP) Studies: A HAZOP study is a structured process used to identify potential hazards and operability problems in a system or process. It involves a team of experts who systematically analyze the system and identify deviations from normal operation, and then assess the potential consequences of those deviations.
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA): FMEA is a technique for locating and evaluating probable failure modes in a system or process. It involves identifying potential failure modes, evaluating the effects of those failures, and developing mitigation strategies to reduce the likelihood or impact of failures.
- Quantitative Risk Analysis: Quantitative risk analysis involves assessing the probability and consequences of potential hazards and using this information to make decisions about risk management. This method typically involves modeling the potential outcomes of various scenarios and assessing the risk associated with each scenario.
- Job Safety Analysis (JSA): JSA is a technique for finding potential risks connected to a certain work or operation. The job or task must be broken down into its component phases, and each step's potential hazards must be identified.
Overall, hazard analysis is an essential part of managing risks in the chemical industry. It helps ensure that appropriate measures are in place to prevent accidents and protect workers, the public, and the environment.
5. Quality Control
An important component of the works performed in the chemical industry is quality control. Businesses must ensure that their products are trustworthy and secure.
Quality control is a critical aspect of the chemical industry, which involves the production and distribution of various chemicals, including pharmaceuticals, polymers, fertilizers, and other industrial chemicals. To guarantee that the chemicals produced satisfy the required criteria for safety, efficacy, and purity, quality control is crucial.
Here are some of the key aspects of quality control in the chemical industry:
Raw material inspection: The quality control process starts with the inspection of raw materials used in the production process. The raw materials should meet the desired standards for purity and quality.
In-process inspection: During the production process, the quality of the product is monitored at various stages to ensure that it meets the desired specifications. To make sure the product is of the desired quality, regular testing and analysis are required.
Final product inspection: Once the production process is complete, the final product undergoes a series of tests to ensure that it meets the desired quality standards. These tests may include chemical analysis, physical tests, and performance tests.
Quality control documentation: All the quality control tests and results are documented, and this documentation is used to ensure that the product meets the desired quality standards.
Quality assurance: Quality control is part of a broader quality assurance process that includes the development and implementation of quality systems, procedures, and protocols. This ensures that the quality control process is consistent and reliable.
From inspecting batches of finished goods to keeping track of standing inventory, quality control is practiced throughout the manufacturing process. The business must also be prepared to act promptly in the event of a recall in order to find and remove all batches of the afflicted products from its premises.
Chemical companies conduct research and development (R&D) during the formulation process to provide the best formulae with the lowest possible cost.
Since their compositions must frequently be modified, R&D is a continual process. Chemical firms require the proper tools to monitor and compare the results of their research, changes to formulations, and results.
6. Scrapping or Reworking of Batch
In the chemical industry, it is not uncommon to encounter batches that do not meet the desired specifications. In such situations, the decision to scrap or rework a batch depends on various factors, including the extent of the deviation, the cost of the materials, and the time required to rework the batch.
Scraping a batch involves discarding the entire batch due to a significant deviation from the desired quality or performance. This decision may be made if the deviation is too severe and cannot be corrected through rework. In such cases, the batch is usually destroyed, and the material is disposed of in a safe and environmentally responsible manner.
Reworking a batch involves taking corrective action to bring the batch back to the desired specifications. The decision to rework a batch is usually made if the deviation is minor and can be corrected without affecting the quality or performance of the final product. The rework process may involve additional processing steps or adjustments to the formulation or processing parameters.
When deciding whether to scrap or rework a batch, several factors should be considered. These include the cost of the materials, the impact on production schedules, the potential impact on the quality of the final product, and the time required to complete the rework. In some cases, it may be more cost-effective to scrap the batch and start over, while in other cases, reworking the batch may be a more viable option.
Overall, the decision to scrap or rework a batch should be based on a careful evaluation of the situation, with a focus on minimizing waste, ensuring product quality, and maintaining efficient production processes.
7. Managing Inventory for Cost Efficiency
Maintaining correct inventory levels that are neither too high nor too low is essential for a successful supply chain. Before new chemicals can be manufactured, a chemical factory just needs to have enough base materials and intermediate (inactive) compounds on hand.
A corporation won't be able to meet customer demand for its product if it has insufficient chemical inventory, and an excess could lead to chemical waste or spoilage.
Unmanaged inventories not only cost a lot of money, but they also cause capital restrictions that restrict alternatives for expansion and prolong production delays, which lower profitability.
To enable successful processes while still adhering to safety and environmental regulations, inventory management within a complex supply chain with a range of items demands flexibility, scalability, agility, and reactivity.
Warehouse specifications should be adjusted for chemical manufacture in order to prevent excess inventory, which is typically expensive for chemical industry.
Calculating the ideal amount of chemical raw materials or intermediate chemicals required at any particular stage of the process can be done using machine learning algorithms that combine data collected in close to real-time from production lines.
When there is understanding of what inventory must appear like at any given time point throughout a complex supplier network who supply goods to numerous customers across various markets regions around the world, inventory optimization for both completed goods and raw materials can be completed with much greater accuracy.
Furthermore, AI's ability to instantly communicate information across all levels of a business allows chemical firms to make better judgements on their production schedules by synchronizing chemical production with consumer demand.
8. Environment Regulations
Environmental regulations are a challenge for the chemical industry. Chemical makers and consumers alike must abide by environmental standards that govern how they create their products and get rid of them once they are no longer needed.
The chemical industry will reportedly have to spend more than $300 billion over the next five years on pollution prevention technology and compliance costs due to this legislation alone, according to estimates.
Chemical companies will increasingly rely on artificial intelligence (AI) as they strive to comply with environmental standards and lessen their carbon footprint. From reducing pollutants during chemical manufacture and product transportation to disposal when they are no longer required, AI can be utilized to optimize industrial processes.
Today, chemical companies can use AI for predictive analytics to identify issues before they arise, such as equipment breakdowns or the requirement for more products owing to escalating demand. Because to this proactive approach, chemical companies may now decrease waste, increase productivity, save costs, and still adhere to environmental standards.
Also, there is always a possibility of incurring significant fines or other penalties when creating the vast range of chemicals that chemical providers do nowadays. AI can help chemical suppliers minimize risks by anticipating compliance issues before they occur, which will save chemical enterprises a ton of time and money.
9. Load Optimization
Getting the most out of truck loadings is another challenge in the chemical supply chain. In the chemical industry, load optimization is difficult, if not impossible, because just-in-time (JIT) inventory systems are so common.
While deciding how to fill a truck with their product orders, chemical manufacturers must take into account the quantity of products needed for each customer as well as the weight limitations and regularly necessary ADRs by shipping carriers. Bulk shipments should always be planned ahead of time to save on transportation fees and boost chemical effectiveness.
Furthermore, ERP software or AI can help in freight loads and inventory management. AI can unearth new data that can enhance chemical supply chain manufacturing and logistics.
10. Planning Production
Given that creating chemicals is a multi-step, complex process, chemical suppliers must carefully plan production. They must be knowledgeable about the components they'll be using, such as the chemicals that will be used as reactants, solvents, or starting materials; which chemical products will be necessary for manufacturing processes downstream; in which these chemical products are placed throughout the supply chain (i.e., how far along is each product); what resources are available, how much of those chemicals should be employed in this specific plant.
Chemical firms heavily rely on information technology (IT) capabilities like enterprise resource planning to effectively handle all this complexity (ERP). Yet, in the absence of AI breakthroughs, ERPs find it difficult to keep up with the sometimes fast changing state of things in chemical manufacturing.
Due to AI-enhanced chemical supply chain management with advanced analytics, chemical suppliers will be able to optimize planning production schedules, make informed decisions to identify market changes, and provide products that satisfy demand while optimizing performance across all stages of the supply chain.
Wrapping Up
The chemical industry has a variety of challenges that have proven challenging to overcome because their current processes can't keep up with their digital transition.
Optimizing safety and efficiency in chemical manufacturing requires a comprehensive and proactive approach that addresses the unique challenges of this industry.
By implementing effective safety protocols, leveraging technology and automation, maintaining a skilled workforce, and pursuing continuous improvement, chemical manufacturers can improve their safety record, enhance efficiency, and remain competitive in the global marketplace.
Chemical firms can do a lot of things, like enhance manufacturing processes, increase output, decrease the possibility of environmental violations or fines, look for opportunities to use recycled chemicals as raw materials when suitable, and much more. If you're interested in learning more about how ERP software or AI could benefit your company's chemical supply chain, schedule a meeting right away.
It is critical to prioritize safety in chemical manufacturing, given the risks involved and the potential consequences of accidents or failures. This requires a commitment to safety culture, regular safety training and drills, and the implementation of safety protocols that are tailored to the specific needs of each facility and operation.
Efficiency can be improved through the use of technology and automation, such as data analytics, predictive maintenance, and real-time monitoring and control. By leveraging these tools, manufacturers can reduce costs, increase production rates, and improve quality control.
Maintaining a skilled workforce is also critical to addressing the challenges of chemical manufacturing. This requires a focus on recruiting, training, and retaining employees with the necessary technical skills and experience, as well as promoting a culture of continuous learning and improvement.
Finally, continuous improvement is essential for addressing the challenges of chemical manufacturing, given the rapidly evolving nature of the industry and the need to remain competitive in the global marketplace. This requires a commitment to innovation, collaboration, and ongoing investment in research and development.
In conclusion, addressing the challenges of chemical manufacturing requires a multifaceted and dynamic approach that involves a commitment to safety, the use of technology and automation, a skilled workforce, and continuous improvement. By following these principles, chemical manufacturers can optimize safety and efficiency, enhance their reputation, and achieve long-term success.
How Deskera Can Assist You?
Deskera's integrated financial planning tools allow investors to better plan their investments and track their progress. It can help investors make decisions faster and more accurately.
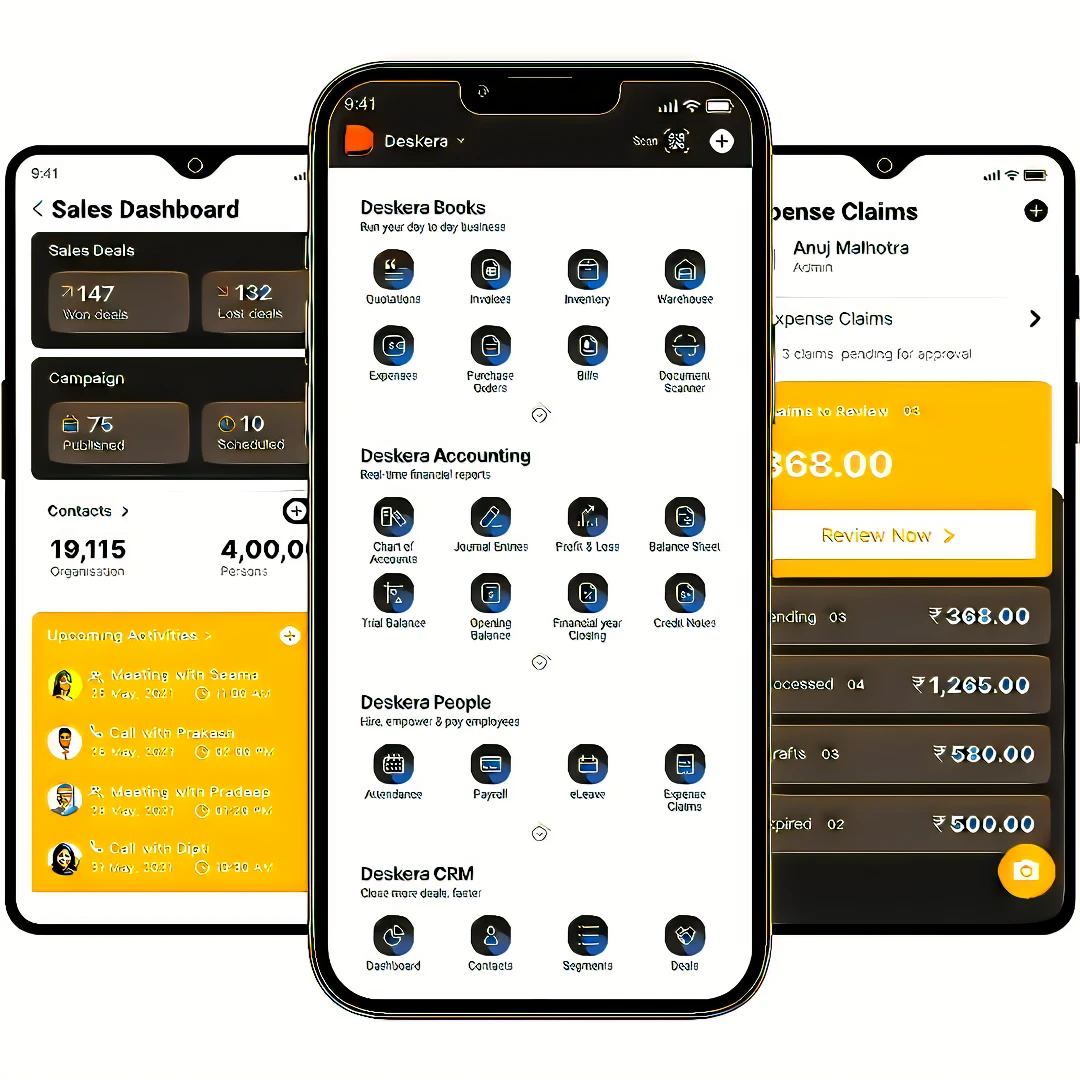
Deskera Books enables you to manage your accounts and finances more effectively. Maintain sound accounting practices by automating accounting operations such as billing, invoicing, and payment processing.
Deskera CRM is a strong solution that manages your sales and assists you in closing agreements quickly. It not only allows you to do critical duties such as lead generation via email, but it also provides you with a comprehensive view of your sales funnel.
Deskera People is a simple tool for taking control of your human resource management functions. The technology not only speeds up payroll processing but also allows you to manage all other activities such as overtime, benefits, bonuses, training programs, and much more. This is your chance to grow your business, increase earnings, and improve the efficiency of the entire production process.
Final Takeaways
We've arrived at the last section of this guide. Let's have a look at some of the most important points to remember:
- Chemicals are utilized in many different products, including polymers, medications, fertilizers, textiles, and electronics. The chemical industry includes a broad range of companies that produce chemicals, chemical products, and chemical raw materials.
- The term "inventory visibility" describes the capacity to precisely trace inventory along the whole supply chain, from the initial order to the last delivery.With accurate inventory visibility, chemical companies can better manage their inventory levels, reduce stockouts and overstocks, improve customer service, and optimize their production schedules.
- Formula management in the chemical industry refers to the process of creating, storing, and managing chemical formulas for products. The sorts of atoms and their numbers in each molecule are listed in a chemical formula, which is a symbolic representation of a chemical complex.
- Information must be obtained at many stages of the manufacturing process, including production, finished goods, and supplier purchase orders. Data from hazard analyses are necessary to satisfy the EPA and other regulatory bodies, as well as to monitor the chemical industry's carbon impact.
- Quality control is a critical aspect of the chemical industry, which involves the production and distribution of various chemicals, including pharmaceuticals, polymers, fertilizers, and other industrial chemicals.
- Scraping a batch involves discarding the entire batch due to a significant deviation from the desired quality or performance. This decision may be made if the deviation is too severe and cannot be corrected through rework. In such cases, the batch is usually destroyed, and the material is disposed of in a safe and environmentally responsible manner.
- Chemical firms heavily rely on information technology (IT) capabilities like enterprise resource planning to effectively handle all this complexity (ERP). Yet, in the absence of AI breakthroughs, ERPs find it difficult to keep up with the sometimes fast changing state of things in chemical manufacturing.
Related Articles