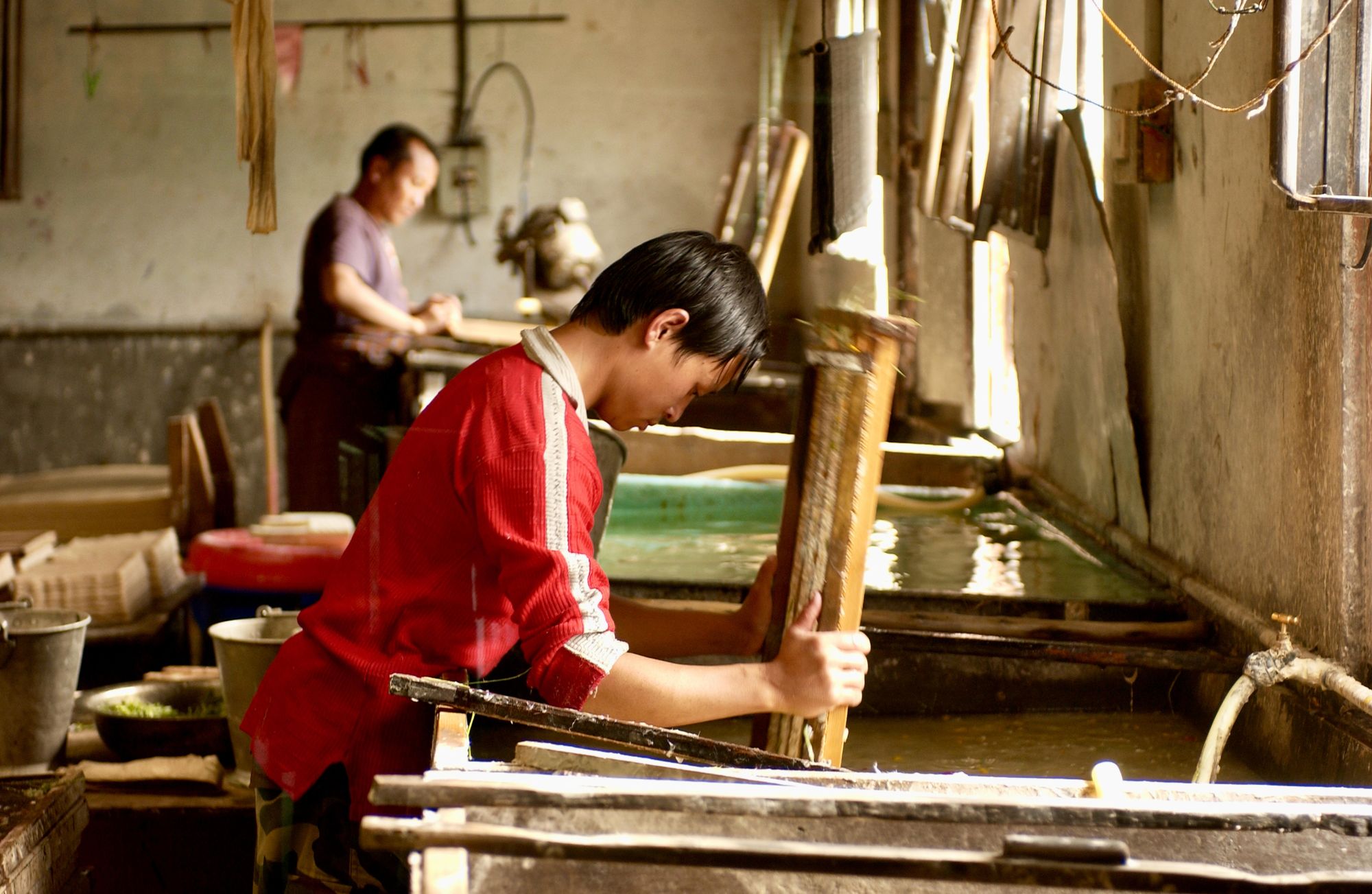
Paper is an essential product that we use in our daily lives, from writing and printing to packaging and sanitation. However, have you ever stopped to think about the quality of the paper you use?
Paper quality plays a crucial role in determining its performance and durability, and it is directly related to the quality control measures in place during the manufacturing process. That's why implementing the best practices for paper manufacturing quality control is critical to ensuring that the paper you use is of high quality and meets your needs.
The quality control process starts with raw material inspection and continues through in-process quality control, testing and analysis, record-keeping, and continuous improvement and training. By adopting these best practices, paper manufacturers can not only ensure consistent paper quality but also reduce waste, improve efficiency, and increase customer satisfaction.

In this article, we will explore the essential best practices for paper manufacturing quality control and their importance in the paper-making industry.
- Best Practices for Paper Manufacturing Quality Control
- Significance of Raw Material Inspection in Paper Manufacturing Quality Control
- Significance of Testing and Analysis
- Record Keeping and Documentation in Quality Control
- Continuous Improvement and Training
- How can MRP and ERP Systems be Beneficial in Paper Manufacturing?
- How can Deskera Help You?
- Key Takeaways
- Related Articles
Best Practices for Paper Manufacturing Quality Control
Paper manufacturing is a complex process that requires strict quality control measures to ensure the final product meets customer expectations and regulatory requirements. Effective quality control is critical in paper manufacturing to minimize defects, reduce waste, and enhance customer satisfaction.
In this response, we shall be looking at an overview of best practices for paper manufacturing quality control, including monitoring key parameters, implementing statistical process control, using advanced analytical tools, and conducting regular audits and inspections.
Monitor Key Parameters
Paper manufacturing involves a series of processes, from pulp production to papermaking, coating, and finishing. Each process has specific parameters that affect the quality of the final product, such as pulp consistency, refining intensity, retention aid dosage, sheet formation, caliper, moisture content, coating weight, and gloss.
Key parameters refer to the critical factors that affect the quality of the final paper product. These parameters may vary depending on the type of paper being produced, the raw materials used, and the manufacturing process. Examples of key parameters in paper manufacturing include:
- Pulp consistency: The concentration of fiber in the pulp slurry affects the strength and stiffness of the paper. Paper manufacturers must monitor the consistency of the pulp throughout the manufacturing process to ensure it meets the target value.
- Refining intensity: The degree of refining affects the fiber length and strength. Paper manufacturers must monitor the refining intensity to ensure the fibers are properly treated and the paper meets the desired properties.
- Retention aid dosage: Retention aids are used to improve the retention of fibers and fillers in the papermaking process. Paper manufacturers must monitor the dosage of retention aids to ensure the optimal amount is used and the paper quality is not compromised.
- Sheet formation: The uniformity and formation of the paper sheet affect its appearance and printability. Paper manufacturers must monitor the sheet formation to detect any variations and adjust the process accordingly.
- Caliper: The thickness of the paper sheet affects its bulk, stiffness, and opacity. Paper manufacturers must monitor the caliper to ensure it meets the target value and the paper properties are consistent.
- Moisture content: The moisture content of the paper affects its strength, dimensional stability, and printability. Paper manufacturers must monitor the moisture content throughout the process to ensure it is within the target range.
- Coating weight: Coating weight refers to the amount of coating applied to the paper sheet. Paper manufacturers must monitor the coating weight to ensure it meets the target value and the paper properties are consistent.
- Gloss: Gloss refers to the reflective properties of the paper surface. Paper manufacturers must monitor the gloss to ensure it meets the desired level and the paper appearance is consistent.
Implement Statistical Process Control
Statistical process control (SPC) is a methodology used in manufacturing to monitor and control a process by using statistical techniques. SPC involves measuring the process output and comparing it to a set of control limits to determine whether the process is stable and predictable. If the process output falls outside the control limits, the operator takes corrective actions to bring it back on target.
In paper manufacturing, SPC can be used to monitor key parameters that affect the quality of the final product, such as pulp consistency, refining intensity, retention aid dosage, sheet formation, caliper, moisture content, coating weight, and gloss. SPC involves collecting data on these parameters and using statistical tools to analyze the data and identify trends or patterns. SPC charts are used to graphically display the data and control limits, making it easier for operators to identify any deviations from the target values.
There are several types of SPC charts that can be used in paper manufacturing, including:
- X-bar and R charts: These charts are used to monitor the average value (X-bar) and the range (R) of a process parameter. They are useful for detecting shifts or trends in the process mean or variability.
- P charts: These charts are used to monitor the proportion of defects in a sample of paper. They are useful for detecting changes in the defect rate and identifying the source of the defects.
- C charts: These charts are used to monitor the count of defects in a sample of paper. They are useful for detecting changes in the defect rate and identifying the source of the defects.
- Control charts for individual measurements: These charts are used to monitor the individual measurements of a process parameter. They are useful for detecting out-of-control conditions and identifying the source of the variation.
By using SPC, paper manufacturers can identify trends, detect variations, and prevent defects. SPC can help operators identify when a process is out of control and take corrective actions before defects occur. SPC also provides a framework for continuous improvement, as it allows operators to analyze the data and identify areas for improvement in the process.
Use Advanced Analytical Tools
Advanced analytical tools, such as machine vision, spectroscopy, and chromatography, can provide valuable insights into the quality of the paper product. These tools can help improve the efficiency and quality of the process, reduce waste and downtime, and increase profitability. Here are some examples of advanced analytical tools used in paper manufacturing:
- Multivariate analysis: Multivariate analysis is a statistical technique used to analyze multiple variables simultaneously. In paper manufacturing, multivariate analysis can be used to identify the key process parameters that affect the quality of the final product. By analyzing the relationships between these parameters, operators can identify the optimal settings for each parameter to achieve the desired quality and efficiency.
- Predictive modeling: Predictive modeling is a technique used to predict the behavior of a system based on historical data. In paper manufacturing, predictive modeling can be used to forecast the performance of the manufacturing process, identify potential problems, and optimize process parameters to achieve the desired outcomes.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning: Artificial intelligence and machine learning are techniques used to develop algorithms that can learn from data and make predictions or decisions based on that data. In paper manufacturing, AI and machine learning can be used to optimize process parameters, predict equipment failures, and identify opportunities for process improvement.
- Process simulation: Process simulation is a technique used to create a virtual model of a manufacturing process. In paper manufacturing, process simulation can be used to test different scenarios and identify the optimal process parameters to achieve the desired quality and efficiency.
- Image analysis: Image analysis is a technique used to analyze images of the final product to identify defects or inconsistencies. In paper manufacturing, image analysis can be used to detect variations in paper thickness, identify defects in the paper surface, and optimize the coating process.
Conduct Regular Audits and Inspections
Audits and inspections are conducted to ensure that the manufacturing process is operating in compliance with regulatory requirements, industry standards, and internal quality control procedures. Here are some key benefits of conducting regular audits and inspections:
- Ensure compliance with regulations: Paper manufacturing is subject to various regulations related to environmental, health and safety, and product quality. Conducting regular audits and inspections can help ensure that the manufacturing process is operating in compliance with these regulations.
- Identify areas for improvement: Audits and inspections can help identify areas for improvement in the manufacturing process. By reviewing process documentation, equipment performance, and product quality data, operators can identify opportunities to optimize process parameters, reduce waste, and improve efficiency.
- Prevent quality issues: Regular audits and inspections can help identify potential quality issues before they become major problems. By monitoring process parameters and inspecting the final product, operators can identify deviations from the target quality and take corrective actions to prevent defects.
- Build customer trust: Audits and inspections can help build customer trust by demonstrating a commitment to quality and compliance. Customers are more likely to trust a paper manufacturer that has a proven track record of quality and compliance.
- Maintain brand reputation: Paper manufacturers rely on their brand reputation to differentiate themselves from competitors. Regular audits and inspections can help ensure that the manufacturing process is operating in compliance with quality control procedures, which can help maintain brand reputation.
Thus, effective quality control is critical in paper manufacturing to minimize defects, reduce waste, and enhance customer satisfaction. To achieve this goal, paper manufacturers must adopt best practices, including monitoring key parameters, implementing statistical process control, using advanced analytical tools, and conducting regular audits and inspections.
By following these best practices, paper manufacturers can produce high-quality paper products that meet customer expectations and regulatory requirements.
Significance of Raw Material Inspection in Paper Manufacturing Quality Control
The raw materials used in paper manufacturing, such as pulp, chemicals, and additives, have a significant impact on the quality of the final product. Raw material inspection involves testing and evaluating the quality of these materials before they are used in the manufacturing process. Here are some key reasons why raw material inspection is significant in paper manufacturing:
- Ensuring quality of final product: The quality of raw materials used in paper manufacturing directly impacts the quality of the final product. Raw material inspection helps ensure that only high-quality materials are used in the manufacturing process, which helps improve the quality of the final product.
- Reducing waste and cost: Raw material inspection can help reduce waste and cost by identifying and rejecting low-quality materials before they are used in the manufacturing process. Using low-quality raw materials can result in defects, which can lead to waste and increased costs.
- Compliance with regulations: Raw material inspection helps ensure compliance with regulatory requirements related to product quality. The use of low-quality or non-compliant raw materials can result in non-compliance with regulations, which can lead to fines, penalties, and damage to the reputation of the paper manufacturer.
- Consistency of product quality: Raw material inspection helps ensure consistency of product quality. By using only high-quality raw materials, paper manufacturers can produce consistent quality products that meet or exceed customer expectations.
- Customer satisfaction: Raw material inspection helps ensure customer satisfaction by producing high-quality products that meet customer requirements. Consistent quality products help build customer trust and loyalty, which can lead to repeat business and increased profitability.
Significance of Testing and Analysis
Testing and analysis play a critical role in ensuring the quality of paper manufacturing processes and products. Paper products are used in various industries and applications, including packaging, printing, writing, and hygiene products. Therefore, it is essential to produce high-quality paper that meets the required specifications and standards.
Here are some of the key reasons why testing and analysis are significant in paper manufacturing quality control:
- Quality assurance: Testing and analysis help to verify that the paper produced meets the required quality standards. This ensures that customers receive products that meet their expectations in terms of physical, chemical, and mechanical properties.
- Process optimization: Testing and analysis provide feedback on the paper manufacturing process, identifying areas for improvement and optimization. This can help reduce production costs, improve efficiency, and increase yield.
- Compliance: The paper industry is subject to various regulations and standards related to quality, safety, and environmental impact. Testing and analysis ensure that the paper products comply with these regulations, protecting the health and safety of workers and consumers.
- Product development: Testing and analysis are critical in developing new paper products or improving existing ones. They provide insight into the properties of the paper and its performance under different conditions, helping to optimize the product for specific applications.
- Root cause analysis: When problems occur during the manufacturing process, testing and analysis can help identify the root cause. This enables manufacturers to take corrective actions, prevent future issues, and improve overall quality control.
Record Keeping and Documentation in Quality Control
Record keeping and documentation are essential aspects of paper manufacturing quality control. They involve the systematic and accurate documentation of all aspects of the production process, including raw materials, equipment, testing, and analysis.
Here are some of the key reasons why record keeping and documentation are significant in paper manufacturing quality control:
- Traceability: Record keeping and documentation enable the traceability of paper products throughout the manufacturing process. This ensures that any issues or defects can be identified and traced back to their source, allowing for corrective actions to be taken.
- Compliance: The paper industry is subject to various regulations and standards related to quality, safety, and environmental impact. Record keeping and documentation ensure that the paper products comply with these regulations, providing evidence of compliance in case of an audit or inspection.
- Quality assurance: Record keeping and documentation enable the monitoring and tracking of the quality of paper products. This helps to identify any issues or trends, allowing for corrective actions to be taken to ensure consistent product quality.
- Process optimization: Record keeping and documentation provide valuable data for analyzing and optimizing the paper manufacturing process. This enables manufacturers to identify areas for improvement, reduce waste, and increase efficiency.
- Historical data: Record keeping and documentation provide a historical record of the paper manufacturing process. This enables manufacturers to analyze trends and patterns over time, providing valuable insights for future process improvements.
Continuous Improvement and Training
Continuous improvement involves the ongoing identification and implementation of process improvements, while training involves ensuring that employees have the knowledge and skills necessary to carry out their roles effectively.
Here are some of the key reasons why continuous improvement and training are significant in paper manufacturing quality control:
- Quality assurance: Continuous improvement and training are essential for maintaining consistent product quality. Continuous improvement enables manufacturers to identify and address quality issues, while training ensures that employees have the necessary knowledge and skills to produce high-quality paper products.
- Process optimization: Continuous improvement and training enable manufacturers to identify and implement process improvements that increase efficiency and reduce waste. This can lead to cost savings and improved overall manufacturing performance.
- Compliance: Continuous improvement and training are essential for maintaining compliance with regulations and standards related to quality, safety, and environmental impact. This helps to protect the health and safety of workers and consumers, while also ensuring that the paper products meet regulatory requirements.
- Innovation: Continuous improvement and training can foster innovation and creativity within the paper manufacturing industry. By encouraging employees to identify and implement new ideas, manufacturers can develop new products and processes that can provide a competitive advantage.
- Employee engagement: Continuous improvement and training can improve employee engagement and satisfaction. By involving employees in the improvement process and providing them with training opportunities, manufacturers can demonstrate that they value their employees and are committed to their development.
How can MRP and ERP Systems be Beneficial in Paper Manufacturing?
MRP (Material Requirements Planning) and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems can be highly beneficial in paper manufacturing in several ways:
- Inventory Management: MRP and ERP systems can help paper manufacturers to manage their inventory more efficiently. These systems provide real-time data on inventory levels, enabling manufacturers to avoid stockouts, reduce waste, and ensure that they have the necessary raw materials and finished products to meet customer demand.
- Production Planning: MRP and ERP systems can help paper manufacturers to plan their production more effectively. These systems can provide insights into demand forecasting, production capacity, and material availability, allowing manufacturers to optimize their production schedules and reduce lead times.
- Quality Control: MRP and ERP systems can support quality control efforts in paper manufacturing by enabling real-time monitoring of production processes and quality inspection results. This can help manufacturers to identify and address quality issues promptly, ensuring that the final products meet the required specifications and standards.
- Cost Control: MRP and ERP systems can help paper manufacturers to control costs by providing real-time data on production processes, inventory levels, and resource utilization. This information can help manufacturers to identify areas where costs can be reduced, optimize production processes, and improve supply chain management.
- Traceability: MRP and ERP systems can help paper manufacturers to maintain traceability throughout the production process. These systems can track raw materials and finished products, enabling manufacturers to identify the source of any issues or defects quickly and take corrective actions.
- Regulatory Compliance: MRP and ERP systems can help paper manufacturers to comply with regulatory requirements by ensuring that products meet the required specifications and standards. These systems can track and document all aspects of the production process, providing evidence of compliance in case of an audit or inspection.
How can Deskera Help You?
Deskera ERP and MRP systems help you to keep your business units organized. The system's primary functions are as follows:
- Keep track of your raw materials and final items inventories
- Control production schedules and routings
- Keep a bill of materials
- Produce thorough reports
- Make your own dashboards
Deskera's integrated financial planning tools enable investors to better plan and track their investments. It can assist investors in making faster and more accurate decisions.
Deskera Books allows you to better manage your accounts and finances. Maintain good accounting practices by automating tasks like billing, invoicing, and payment processing.
Deskera CRM is a powerful solution that manages your sales and helps you close deals quickly. It not only enables you to perform critical tasks like lead generation via email, but it also gives you a comprehensive view of your sales funnel.
Deskera People is a straightforward tool for centralizing your human resource management functions.
Key Takeaways
- Develop a comprehensive quality management system that covers all aspects of paper manufacturing.
- Implement rigorous testing and analysis procedures to ensure that the paper products meet the required specifications and standards.
- Keep accurate and comprehensive records and documentation to enable traceability, compliance, and process improvement.
- Train employees to ensure that they have the knowledge and skills necessary to carry out their roles effectively and contribute to process improvement.
- Foster a culture of continuous improvement, encouraging employees to identify and implement new ideas for process optimization and product development.
- Monitor and analyze key performance indicators to identify trends and areas for improvement, enabling manufacturers to make data-driven decisions.
- Establish a system for root cause analysis and corrective action, ensuring that any issues or defects are identified and addressed promptly.
- Maintain a focus on environmental sustainability, ensuring that the paper manufacturing process minimizes waste and has a minimal impact on the environment.
Related Articles











