In 2024, businesses are increasingly turning to Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software to bolster their operations and stay competitive in the ever-evolving landscape.
With the promise of enhanced efficiency, productivity, and decision-making capabilities, ERP systems have become indispensable tools for modern enterprises.
Among the myriad benefits they offer, two statistics stand out:
Over 57% of businesses are confident that ERP software will enable them to achieve greater agility, adapting swiftly to changing market demands and emerging opportunities.
Moreover, a staggering 53% of organizations have reported experiencing a positive return on investment (ROI) following the implementation of ERP systems, underscoring the tangible benefits these solutions bring to businesses.
Deskera ERP is a leading player in the ERP market, offering comprehensive solutions tailored to meet the diverse needs of businesses across various industries.
With its user-friendly interface, robust features, and scalability, Deskera ERP empowers organizations to streamline processes, optimize resources, and drive growth in today's dynamic business environment.
What are ERP Systems?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are comprehensive software platforms designed to integrate and manage all the essential functions of a business.
These systems provide a centralized framework that supports various business processes and operations, allowing for streamlined data flow and improved efficiency.
Here’s a deeper look into ERP systems:
Key Components of ERP Systems
- Centralized Database: ERP systems use a single database to store data from various business functions, ensuring that information is consistent and accessible across the organization.
- Modular Design: ERP systems are often modular, meaning they consist of different modules that can be tailored to specific business needs. Common modules include finance, human resources, supply chain management, customer relationship management (CRM), and manufacturing.
- Integration: ERP systems integrate various business processes, such as accounting, procurement, project management, and inventory management, into a cohesive system.
ERP systems play a critical role in modern business operations, providing a unified platform that enhances efficiency, productivity, and decision-making. By integrating various business processes into a single system, ERP systems enable organizations to operate more cohesively and respond more agilely to market changes.
Evolving ERP Landscape in 2024
The ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) landscape in 2024 is characterized by several evolving trends and advancements that are shaping the way businesses implement and utilize these systems.
Here are the key aspects of the evolving ERP landscape in 2024:
1. Cloud-Based ERP Solutions
- Increased Adoption: More businesses are transitioning from on-premise ERP systems to cloud-based solutions due to their flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
- Hybrid Models: Companies are also exploring hybrid ERP models that combine on-premise and cloud-based systems, offering a balanced approach to data management and accessibility.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
- Enhanced Automation: AI and ML technologies are being integrated into ERP systems to automate complex tasks, such as predictive analytics, demand forecasting, and anomaly detection.
- Intelligent Insights: These technologies provide deeper insights through advanced data analysis, helping businesses make more informed decisions.
3. Increased Focus on User Experience (UX)
- Intuitive Interfaces: ERP vendors are prioritizing user-friendly interfaces and improved UX design to enhance user adoption and productivity.
- Personalization: Systems are becoming more customizable to individual user preferences and roles, making the software more accessible and efficient for end-users.
4. Advanced Data Analytics and Business Intelligence
- Real-Time Analytics: Real-time data processing and analytics capabilities are becoming standard, allowing businesses to access up-to-the-minute information and insights.
- Embedded BI Tools: ERP systems are increasingly embedding business intelligence tools that provide comprehensive reporting and visualization capabilities.
5. Enhanced Integration Capabilities
- APIs and Connectors: ERP systems are improving their integration capabilities through advanced APIs and connectors, enabling seamless data exchange with other business applications and third-party services.
- IoT Integration: Integration with Internet of Things (IoT) devices is becoming more common, allowing ERP systems to collect and analyze data from connected devices for better operational insights.
6. Greater Emphasis on Cybersecurity
- Robust Security Measures: As cyber threats become more sophisticated, ERP vendors are enhancing security measures, including advanced encryption, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring.
- Compliance Management: ERP systems are incorporating more robust compliance management tools to help businesses adhere to regulatory standards and protect sensitive data.
7. Industry-Specific Solutions
- Vertical ERP Solutions: There is a growing trend towards industry-specific ERP solutions tailored to the unique needs of sectors such as manufacturing, healthcare, retail, and finance.
- Customization and Flexibility: These solutions offer greater customization and flexibility, allowing businesses to implement ERP systems that align closely with their operational requirements.
8. Mobile Accessibility
- Mobile-First Design: ERP systems are being designed with mobile accessibility in mind, enabling users to access critical business functions from smartphones and tablets.
- Remote Work Support: Enhanced mobile capabilities support the increasing trend of remote work, allowing employees to perform tasks and access data from anywhere.
9. Sustainability and Green ERP
- Environmental Tracking: ERP systems are incorporating features that help businesses track and manage their environmental impact, such as carbon footprint analysis and resource usage monitoring.
- Sustainable Practices: These systems support sustainable business practices by optimizing resource management and reducing waste.
10. Increased Adoption of ERP by SMEs
- Affordable Solutions: The availability of affordable, scalable cloud-based ERP solutions is encouraging more small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to adopt ERP systems.
- Simplified Implementations: Vendors are offering simplified implementation processes and user-friendly solutions tailored to the needs and budgets of SMEs.
11. Continuous Updates and Improvements
- Agile Development: ERP vendors are adopting agile development methodologies, releasing continuous updates and improvements to their systems.
- Customer Feedback Integration: Vendors are increasingly incorporating customer feedback into their development processes to ensure their solutions meet evolving business needs.
17 Key Benefits of ERP in 2024
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems continue to evolve, offering numerous benefits that help businesses stay competitive and efficient in 2024.
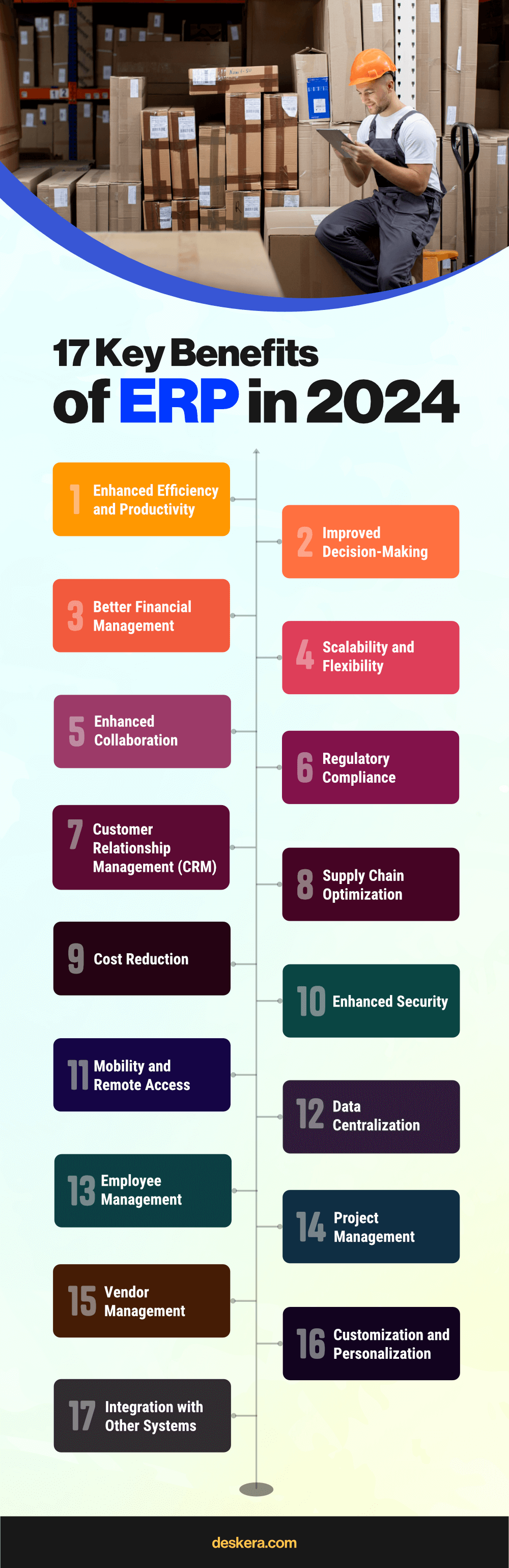
Here are the key benefits:
1. Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity
ERP systems significantly enhance efficiency and productivity in modern businesses by streamlining processes, automating routine tasks, and reducing manual errors.
Here’s a detailed look at how these benefits of ERP systems manifest in practice:
Streamlined Business Processes
One of the core benefits of ERP systems is the integration and optimization of business processes across various departments. By consolidating functions such as finance, HR, supply chain, and sales into a single platform, ERP systems eliminate redundant activities and create seamless workflows.
This streamlining leads to:
- Improved Coordination: Departments can communicate and collaborate more effectively, ensuring that all parts of the organization are aligned.
- Faster Processes: By eliminating bottlenecks and inefficiencies, businesses can operate more swiftly, reducing the time taken to complete tasks.
- Consistency: Standardized processes across the organization ensure consistency in operations and output.
Automation of Routine Tasks
Automation is one of the significant advantages of ERP systems. By automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, ERP systems free up valuable employee time for more strategic activities.
This automation includes:
- Invoice Processing: Automatically generating and sending invoices, which reduces the workload on finance teams.
- Order Management: Streamlining order processing and fulfillment, which improves customer satisfaction and reduces errors.
- Payroll: Automating payroll calculations and payments, ensuring accuracy and compliance.
Reduction in Manual Errors
Manual data entry and paper-based processes are prone to errors, which can lead to significant inefficiencies and even financial losses. ERP systems mitigate these risks by:
- Data Accuracy: Automated data entry reduces the likelihood of human errors, ensuring that information is accurate and up-to-date.
- Real-Time Updates: Changes in one part of the system automatically update related data across the entire platform, maintaining consistency.
- Error Tracking: ERP systems often include error-checking and validation features, which help identify and correct errors quickly.
Free Tip: Implement Workflow Automation Tools
To maximize the benefits of ERP systems, businesses should consider implementing workflow automation tools. These tools can further enhance productivity by:
- Streamlining Approvals: Automating approval processes for expenses, purchase orders, and other requests speeds up decision-making and reduces delays.
- Task Management: Automating task assignments and tracking ensures that employees are always working on high-priority activities.
- Notifications and Alerts: Automated alerts and notifications keep employees informed of critical tasks and deadlines, reducing the risk of missed opportunities.
2. Improved Decision-Making
The advantages of ERP systems in 2024 extend significantly into the realm of decision-making, providing businesses with tools and insights that drive better outcomes.
Here’s how ERP systems improve decision-making capabilities:
Real-Time Data Analytics
One of the paramount benefits of ERP systems is their ability to provide real-time data analytics. In a rapidly changing business environment, having access to up-to-the-minute data is crucial.
Real-time data analytics offers:
- Immediate Insights: With real-time data, decision-makers can respond swiftly to emerging trends and issues.
- Enhanced Accuracy: Continuous data updates ensure that the information is always current and accurate, reducing the risk of decisions based on outdated data.
- Proactive Management: Real-time analytics enable proactive rather than reactive management, allowing businesses to anticipate and mitigate potential problems before they escalate.
Comprehensive Reporting Capabilities
ERP systems come equipped with comprehensive reporting tools that compile data from various business functions into coherent, detailed reports.
The benefits of these advanced reporting capabilities include:
- In-Depth Analysis: Detailed reports allow for in-depth analysis of business performance across different areas such as finance, sales, and operations.
- Customizable Reports: Users can create custom reports tailored to specific needs, ensuring that decision-makers have the precise information they require.
- Automated Reporting: Automation of reporting processes saves time and reduces the likelihood of human error, providing consistent and reliable reports on a scheduled basis.
Access to Actionable Insights
The integration of advanced analytics tools within ERP systems transforms raw data into actionable insights.
The advantages of ERP systems in providing actionable insights include:
- Data-Driven Decisions: ERP systems turn vast amounts of data into meaningful insights, helping managers make data-driven decisions that are backed by solid evidence.
- Identifying Trends: Analytical tools help identify trends and patterns in data, which can be critical for strategic planning and forecasting.
- Performance Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of key performance indicators (KPIs) allows businesses to track their progress towards goals and make adjustments as necessary.
Free Tip: Leverage Built-In Analytics Dashboards
To maximize the benefits of ERP systems in decision-making, businesses should leverage the built-in analytics dashboards that most modern ERP solutions offer.
Here’s how to do it effectively:
- Customizable Dashboards: Tailor dashboards to display key metrics and KPIs relevant to specific roles within the organization, ensuring that each user has access to the most pertinent data.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Use dashboards to monitor real-time data and track performance against goals, facilitating quick adjustments and timely interventions.
- Visualization Tools: Take advantage of visualization tools within dashboards to present data in a clear and understandable format, making it easier to interpret and act upon.
3. Better Financial Management
By integrating financial processes and providing accurate reporting and forecasting tools, ERP systems offer a comprehensive solution to manage a company’s finances effectively.
Here’s a detailed look at the benefits of ERP systems in financial management:
Integrated Financial Modules
One of the major benefits of ERP systems is the integration of various financial modules into a single cohesive platform.
This integration facilitates:
- Unified Financial Processes: Combining accounts payable, accounts receivable, general ledger, and other financial functions into one system streamlines financial management and reduces redundancy.
- Consistent Data Flow: Ensures that financial data flows seamlessly across departments, improving data consistency and reducing errors.
- Improved Financial Oversight: Provides a holistic view of the company’s financial health, allowing for better oversight and control.
Accurate Financial Reporting
Accurate financial reporting is a significant advantage of ERP systems. By automating data collection and processing, ERP systems ensure the precision and reliability of financial reports.
Benefits include:
- Regulatory Compliance: Automated and accurate reporting helps businesses comply with financial regulations and standards, reducing the risk of non-compliance penalties.
- Transparency: Provides clear and transparent financial statements, which are crucial for stakeholders and investors.
- Timely Reports: Automated report generation ensures that financial reports are produced quickly, allowing timely decision-making.
Budgeting and Forecasting Capabilities
ERP systems enhance budgeting and forecasting by providing tools that allow businesses to plan and project their financial future accurately.
These capabilities offer:
- Real-Time Budget Tracking: ERP systems allow for real-time tracking of budgets against actual performance, helping businesses stay within their financial limits.
- Dynamic Forecasting: Advanced forecasting tools in ERP systems use historical data and predictive analytics to create accurate financial forecasts.
- Scenario Analysis: Businesses can perform scenario analysis to understand the financial impact of various strategic decisions, aiding in risk management and planning.
Free Tip: Use Financial Forecasting Tools for Better Planning
To maximize the benefits of ERP systems, businesses should leverage financial forecasting tools for better planning.
Here’s how to do it effectively:
- Regular Updates: Continuously update forecasting models with real-time data to ensure accuracy and relevance.
- Integrated Analytics: Use integrated analytics within the ERP system to enhance forecasting accuracy and gain deeper insights.
- Collaboration: Engage various departments in the forecasting process to gather comprehensive input and improve the reliability of forecasts.
4. Scalability and Flexibility
Scalability and flexibility are among the core benefits of ERP systems, allowing businesses to adapt and grow without being hindered by their software infrastructure.
Here’s how ERP systems provide these crucial advantages:
Adaptability to Business Growth
One of the significant benefits of ERP systems is their ability to scale with the business.
This adaptability includes:
- Seamless Expansion: As businesses grow, whether through increased production, expanded services, or geographic expansion, ERP systems can easily accommodate additional data, users, and transactions.
- Support for New Business Models: ERP systems can adapt to new business models and operational changes, ensuring continued efficiency and effectiveness.
- Resource Management: Helps manage resources effectively as the business scales, ensuring that all parts of the organization can keep pace with growth.
Modular Architecture
The modular architecture of ERP systems is a key advantage that enhances both scalability and flexibility:
- Tailored Implementation: Businesses can implement only the modules they need initially and add more as their requirements grow. This phased approach makes the adoption process more manageable and cost-effective.
- Functional Independence: Each module can operate independently, allowing businesses to customize their ERP system according to specific needs without disrupting other functions.
- Easy Upgrades: Modular systems make it easier to upgrade specific functionalities without affecting the entire system, reducing downtime and improving overall efficiency.
Customizable Solutions
ERP systems offer a high degree of customization, which is a significant advantage for businesses with unique processes and requirements:
- Personalized Features: Businesses can customize the ERP system to fit their specific workflows, processes, and industry requirements, ensuring that the software works exactly as needed.
- User-Specific Interfaces: Customizable user interfaces and dashboards can be tailored to different roles within the organization, enhancing usability and productivity.
- Flexibility in Integration: Customization extends to integration capabilities, allowing businesses to connect their ERP system with other software solutions seamlessly.
Free Tip: Choose ERP Systems That Offer Scalable Modules
To fully leverage the scalability and flexibility benefits of ERP systems, businesses should choose solutions that offer scalable modules.
Here’s how to make the best choice:
- Assess Current and Future Needs: Consider both current operational needs and future growth plans to select an ERP system with the right modules and scalability options.
- Evaluate Vendor Support: Ensure that the ERP vendor offers robust support for adding and upgrading modules as needed, including training and technical assistance.
- Focus on Interoperability: Choose an ERP system that integrates well with existing software and can easily incorporate new tools and technologies as the business evolves.
5. Enhanced Collaboration
In the contemporary business landscape, collaboration is key to success, and ERP systems play a pivotal role in facilitating seamless collaboration across departments.
Here’s how ERP systems enhance collaboration within organizations:
Centralized Data Repository
One of the primary benefits of ERP systems is the establishment of a centralized data repository, which serves as a single source of truth for all organizational data:
- Data Accessibility: By storing data in a centralized location, ERP systems ensure that information is readily accessible to all authorized users.
- Data Consistency: Centralizing data reduces the risk of discrepancies or conflicting information, ensuring consistency across departments.
- Efficient Information Retrieval: Employees can quickly locate the data they need, streamlining processes and eliminating time wasted searching for information.
Improved Interdepartmental Communication
ERP systems facilitate improved communication and collaboration between different departments within an organization:
- Shared Information: ERP systems enable departments to share data and insights, fostering a collaborative environment where teams can work together towards common goals.
- Cross-Functional Workflows: Integrated workflows allow for seamless handoffs between departments, reducing delays and improving efficiency.
- Task Assignment and Tracking: ERP systems include features for assigning tasks and tracking their progress, ensuring accountability and transparency across teams.
Real-Time Collaboration Tools
ERP systems incorporate real-time collaboration tools that enable employees to work together effectively regardless of their physical location:
- Instant Messaging: Built-in chat functionalities allow for real-time communication between team members, facilitating quick decision-making and problem-solving.
- Document Sharing: ERP systems often include document sharing capabilities, enabling teams to collaborate on projects and share files securely.
- Project Management Tools: Integrated project management tools within ERP systems help teams organize tasks, set deadlines, and track project progress collaboratively.
Free Tip: Utilize ERP’s Collaboration Features for Team Projects
To maximize the benefits of ERP systems in collaboration, businesses should actively utilize the collaboration features built into their ERP solution.
Here’s how to make the most of these features:
- Encourage Adoption: Provide training and support to ensure that employees are comfortable using the collaboration tools within the ERP system.
- Establish Communication Protocols: Define clear communication protocols and guidelines to ensure that collaboration remains effective and productive.
- Promote Cross-Functional Collaboration: Encourage collaboration between departments by facilitating cross-functional projects and initiatives that require collaboration across different teams.
6. Regulatory Compliance
In today's complex regulatory landscape, compliance is non-negotiable for businesses.
Here's how ERP systems ensure regulatory compliance:
Built-in Compliance Management Tools
ERP systems come equipped with built-in compliance management tools that help businesses stay abreast of regulatory requirements:
- Regulatory Updates: ERP systems are designed to monitor changes in regulations and automatically update compliance settings accordingly, ensuring that businesses remain compliant with the latest standards.
- Policy Implementation: Compliance management tools facilitate the implementation of internal policies and procedures to align with regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of non-compliance.
- Risk Assessment: ERP systems include features for conducting risk assessments and identifying potential compliance risks, allowing businesses to proactively address issues before they escalate.
Automatic Updates to Regulations
One of the significant advantages of ERP systems is their ability to automatically update to reflect changes in regulations:
- Real-Time Compliance: ERP systems continuously monitor regulatory changes and update compliance settings in real-time, ensuring that businesses are always compliant with the latest standards.
- Reduced Manual Effort: Automatic updates eliminate the need for manual tracking of regulatory changes, saving time and resources while minimizing the risk of oversight.
- Timely Adaptation: By automatically updating to reflect regulatory changes, ERP systems enable businesses to adapt quickly to evolving compliance requirements without disruption to operations.
Audit Trails and Documentation
ERP systems provide comprehensive audit trails and documentation capabilities, which are essential for demonstrating compliance:
- Traceability: Audit trails track changes made to data and transactions within the ERP system, providing a clear trail of accountability and ensuring transparency.
- Documentation Management: ERP systems include features for storing and managing compliance-related documents, such as policies, procedures, and certifications, ensuring easy access and retrieval during audits.
- Comprehensive Reporting: ERP systems generate detailed compliance reports, documenting adherence to regulatory requirements and providing evidence of compliance to auditors and regulatory authorities.
Free Tip: Regularly Update Compliance Settings to Match Current Standards
To ensure ongoing compliance, businesses should regularly update compliance settings within their ERP system to match current standards.
Here’s how to do it effectively:
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of changes in regulations and standards relevant to your industry and geographic location.
- Schedule Regular Updates: Establish a schedule for reviewing and updating compliance settings within the ERP system to ensure that they remain aligned with current requirements.
- Train Employees: Provide training to employees on updated compliance procedures and requirements to ensure awareness and adherence.
7. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRM functionality integrated into ERP systems offers businesses a comprehensive solution for managing customer relationships effectively.
Let’s explore how ERP systems enhance CRM capabilities:
Integrated CRM Functionalities
ERP systems with integrated CRM functionalities provide a unified platform for managing customer interactions and data:
- Single Source of Truth: Having CRM functionality integrated into the ERP system ensures that customer data is centralized and easily accessible across departments.
- Seamless Data Integration: Integration between CRM and other modules such as sales, marketing, and finance enables seamless data flow and improves collaboration between teams.
- 360-Degree View of Customers: ERP systems provide a holistic view of customer interactions, including sales history, support tickets, and communication logs, empowering businesses to deliver personalized experiences.
Better Customer Insights
ERP systems generate valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences, enabling businesses to make data-driven decisions:
- Data Analysis Tools: ERP systems offer robust analytics tools that allow businesses to analyze customer data, identify trends, and predict future behavior.
- Segmentation Capabilities: ERP systems enable businesses to segment customers based on various criteria such as demographics, purchase history, and engagement level, facilitating targeted marketing campaigns.
- Predictive Analytics: Advanced analytics functionalities within ERP systems help businesses anticipate customer needs and preferences, allowing for proactive engagement and personalized recommendations.
Improved Customer Service
Enhanced CRM capabilities within ERP systems contribute to improved customer service and satisfaction:
- Efficient Issue Resolution: ERP systems streamline customer support processes by providing customer service representatives with access to comprehensive customer data and historical interactions, enabling quicker issue resolution.
- Automated Communication: ERP systems include features for automating communication with customers, such as email notifications and follow-up reminders, ensuring timely responses and proactive engagement.
- Feedback Management: ERP systems facilitate the collection and analysis of customer feedback, enabling businesses to identify areas for improvement and address customer concerns effectively.
Free Tip: Use CRM Data to Personalize Customer Interactions
To maximize the benefits of CRM within ERP systems, businesses should leverage CRM data to personalize customer interactions effectively:
- Segmentation and Targeting: Use CRM data insights to segment customers into distinct groups based on their preferences, behavior, and demographics, and tailor marketing messages and offers accordingly.
- Personalized Communication: Utilize CRM data to personalize communication with customers across various channels, such as email, social media, and phone calls, ensuring relevance and engagement.
- Feedback Analysis: Analyze CRM data to gather feedback from customers and identify areas for improvement in products, services, and processes, demonstrating responsiveness and commitment to customer satisfaction.
8. Supply Chain Optimization
Supply chain optimization is crucial for businesses to maintain efficiency, reduce costs, and meet customer demands.
Let’s delve into how ERP systems optimize supply chains:
Real-Time Supply Chain Visibility
ERP systems provide real-time visibility into the entire supply chain, from procurement to delivery:
- End-to-End Tracking: ERP systems track inventory, orders, and shipments in real-time, providing businesses with a comprehensive view of their supply chain processes.
- Demand Forecasting: By analyzing historical data and market trends, ERP systems help businesses predict future demand more accurately, enabling proactive planning and inventory management.
- Supply Chain Analytics: ERP systems offer advanced analytics tools that allow businesses to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) and identify areas for optimization within the supply chain.
Improved Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is a key benefit of ERP systems, ensuring that businesses maintain optimal inventory levels while minimizing costs:
- Inventory Optimization: ERP systems use algorithms and forecasting models to optimize inventory levels, preventing stockouts and overstock situations.
- Automated Replenishment: ERP systems automate the replenishment process by generating purchase orders and reorder points based on predefined rules and inventory thresholds.
- Inventory Traceability: ERP systems enable traceability of inventory movements, allowing businesses to track the movement of goods throughout the supply chain and comply with regulatory requirements.
Supplier Management Tools
ERP systems include robust supplier management tools that facilitate collaboration and communication with suppliers:
- Supplier Performance Tracking: ERP systems track supplier performance metrics such as delivery times, quality, and compliance, enabling businesses to evaluate supplier performance objectively.
- Supplier Collaboration Portals: ERP systems offer supplier collaboration portals where businesses and suppliers can exchange information, collaborate on orders, and resolve issues efficiently.
- Vendor Scorecards: ERP systems generate vendor scorecards that provide insights into supplier performance and help businesses make informed decisions when selecting and managing suppliers.
Free Tip: Implement Just-in-Time Inventory Practices
To optimize inventory management further, businesses can implement just-in-time (JIT) inventory practices using ERP systems:
- Demand Forecasting: Use ERP systems to analyze demand patterns and forecast customer demand accurately, allowing for JIT inventory replenishment.
- Supplier Collaboration: Collaborate closely with suppliers and use ERP systems to automate order processing and streamline supplier relationships, ensuring timely delivery of materials and components.
- Continuous Improvement: Continuously monitor and optimize supply chain processes using ERP systems, identifying opportunities for JIT inventory practices and cost savings.
9. Cost Reduction
Cost reduction is a significant advantage of implementing ERP systems in businesses, offering various avenues for lowering operational expenses and optimizing resource allocation.
Here's how ERP systems contribute to cost reduction:
Lower Operational Costs
ERP systems streamline business processes, eliminate inefficiencies, and reduce manual labor, leading to lower operational costs:
- Process Automation: ERP systems automate repetitive tasks and workflows, reducing the need for manual intervention and minimizing labor costs.
- Efficiency Gains: By standardizing and optimizing processes across departments, ERP systems improve operational efficiency, reducing waste and lowering production costs.
- Inventory Optimization: ERP systems optimize inventory levels, preventing overstock and stockouts, and minimizing carrying costs associated with excess inventory.
Reduction in IT Expenses
Cloud-based ERP solutions offer cost savings opportunities by reducing IT infrastructure and maintenance expenses:
- Infrastructure Cost Savings: Cloud ERP eliminates the need for on-premises hardware and infrastructure, reducing upfront capital expenditures and ongoing maintenance costs.
- Automatic Updates and Maintenance: Cloud ERP providers handle software updates and maintenance tasks, reducing IT staff workload and eliminating the need for dedicated IT resources.
- Scalability: Cloud ERP solutions scale dynamically with business needs, ensuring that businesses only pay for the resources they use, thereby avoiding over-provisioning and associated costs.
Improved Resource Allocation
ERP systems provide insights into resource utilization and enable better allocation of resources, leading to cost savings:
- Resource Optimization: ERP systems track resource usage and performance metrics, allowing businesses to identify underutilized resources and reallocate them more efficiently.
- Project Management: ERP systems facilitate project planning and resource allocation, ensuring that resources are allocated effectively to meet project deadlines and budget constraints.
- Strategic Planning: ERP systems offer reporting and analytics tools that enable businesses to conduct scenario analysis and make data-driven decisions about resource allocation, optimizing costs and maximizing returns on investment.
Free Tip: Conduct Regular Cost-Benefit Analysis of ERP Features
To maximize cost reduction benefits, businesses should conduct regular cost-benefit analysis of ERP features:
- Identify Cost Drivers: Evaluate the cost drivers within your organization and assess how ERP features can help mitigate these costs.
- Quantify Savings: Estimate the potential cost savings associated with implementing specific ERP features, such as process automation, inventory optimization, or IT infrastructure reduction.
- Monitor Performance: Continuously monitor the performance of ERP systems and track cost savings metrics to ensure that the expected benefits are being realized.
10. Enhanced Security
Security is a paramount concern for businesses, especially when it comes to managing sensitive data and ensuring the integrity of their operations.
Let’s explore how ERP systems enhance security:
Robust Security Features
ERP systems are equipped with a wide range of security features designed to mitigate risks and protect against unauthorized access:
- Authentication Protocols: ERP systems utilize strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), to verify user identities and prevent unauthorized access.
- Data Encryption: ERP systems employ encryption techniques to secure data both in transit and at rest, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected from unauthorized interception or tampering.
- Firewall Protection: ERP systems incorporate firewall protection to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic, preventing unauthorized access to the system.
Data Encryption and Protection
Data security is a top priority for ERP systems, and they employ various encryption and protection mechanisms to safeguard sensitive information:
- End-to-End Encryption: ERP systems encrypt data from the point of entry to storage and transmission, ensuring that it remains secure throughout its lifecycle.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): ERP systems implement RBAC mechanisms to restrict access to sensitive data based on users’ roles and responsibilities, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Data Masking: ERP systems employ data masking techniques to conceal sensitive information, such as personally identifiable information (PII), from unauthorized users while still allowing authorized users to access the data they need.
Access Control Mechanisms
ERP systems provide granular access control mechanisms to regulate user permissions and limit access to sensitive functionalities:
- User Access Policies: ERP systems allow administrators to define user access policies based on roles, departments, or specific criteria, ensuring that users only have access to the data and functionalities necessary to perform their duties.
- Audit Trails: ERP systems maintain detailed audit trails that track user activities and changes made to the system, enabling administrators to monitor user behavior and detect potential security breaches.
- Session Management: ERP systems manage user sessions securely, automatically logging out inactive users and enforcing session timeouts to prevent unauthorized access.
Free Tip: Regularly Update Security Protocols and Conduct Audits
To maintain enhanced security, businesses should follow best practices such as regularly updating security protocols and conducting security audits:
- Patch Management: Keep ERP systems up-to-date by installing security patches and updates released by the vendor to address known vulnerabilities and security weaknesses.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Conduct regular vulnerability scans and penetration tests to identify potential security vulnerabilities in ERP systems and remediate them promptly.
- Employee Training: Provide employees with security awareness training to educate them about common security threats and best practices for safeguarding sensitive information.
11. Mobility and Remote Access
In today's dynamic work environment, mobility and remote access have become essential for businesses to stay competitive and agile.
Let's explore how ERP systems enhance mobility and remote access:
Mobile-Friendly ERP Solutions
ERP systems are designed with mobile-friendly interfaces and applications that enable users to access essential features and data on smartphones and tablets:
- Responsive Design: ERP systems incorporate responsive design principles to ensure that user interfaces adapt seamlessly to various screen sizes and resolutions, providing an optimal viewing experience on mobile devices.
- Native Mobile Apps: Many ERP vendors offer native mobile applications that provide access to core ERP functionalities, such as inventory management, sales tracking, and task management, while on the go.
- Offline Access: Some mobile ERP solutions offer offline access capabilities, allowing users to continue working even when they are not connected to the internet, and sync data automatically once a connection is restored.
Access from Anywhere
ERP systems enable users to access critical business data and functionalities from anywhere with an internet connection, fostering flexibility and productivity:
- Cloud-Based Accessibility: Cloud ERP solutions enable users to access ERP systems via web browsers from any location, eliminating the need for on-premises infrastructure and enabling remote access.
- Remote Work Support: ERP systems support remote work initiatives by providing employees with access to essential tools and resources, enabling them to collaborate effectively with colleagues and customers regardless of their physical location.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: ERP systems are compatible with various operating systems and devices, including Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android, ensuring seamless access across different platforms and devices.
Support for Remote Work
ERP systems facilitate remote work by offering a range of features and functionalities that support collaboration and productivity:
- Virtual Collaboration Tools: ERP systems include virtual collaboration tools such as chat, video conferencing, and document sharing, enabling remote teams to communicate and collaborate effectively in real-time.
- Task Management: ERP systems provide task management functionalities that enable remote teams to organize and track tasks, assign responsibilities, and monitor progress, ensuring that projects stay on track regardless of team members' locations.
- Security and Compliance: ERP systems implement robust security measures and compliance protocols to protect data and ensure that remote access is secure and compliant with regulatory requirements.
Free Tip: Ensure ERP System is Optimized for Mobile Devices
To maximize the benefits of mobility and remote access, businesses should ensure that their ERP system is optimized for mobile devices:
- User Training: Provide employees with training and support to familiarize them with mobile ERP applications and best practices for remote access and collaboration.
- Performance Testing: Conduct performance testing to ensure that the ERP system performs optimally on various mobile devices and network conditions, providing a seamless user experience.
- Security Measures: Implement robust security measures, such as encryption, authentication, and access controls, to protect sensitive data and ensure that remote access is secure and compliant with regulatory requirements.
12. Data Centralization
Data centralization is a fundamental advantage of ERP systems, offering businesses a single source of truth for all their data.
Let’s explore how ERP systems enhance data centralization:
Single Source of Truth for Data
ERP systems serve as a centralized repository for all critical business data, providing a single source of truth that ensures data accuracy and integrity:
- Unified Data Model: ERP systems integrate data from various departments, functions, and processes into a unified data model, enabling businesses to access comprehensive and up-to-date information across the organization.
- Real-Time Data Updates: ERP systems update data in real-time, ensuring that users have access to the most current information for making informed decisions and driving business processes.
- Data Governance Policies: ERP systems enforce data governance policies and standards to maintain data quality, consistency, and security, ensuring that data remains reliable and trustworthy.
Eliminates Data Silos
ERP systems break down data silos by centralizing data from disparate systems and applications, enabling seamless data integration and sharing:
- Cross-Functional Integration: ERP systems integrate data from different functional areas such as finance, sales, marketing, inventory management, and human resources, eliminating the need for separate systems and databases.
- Interdepartmental Collaboration: ERP systems facilitate collaboration and communication between departments by providing a shared platform for accessing and sharing data, fostering transparency and alignment across the organization.
- Streamlined Processes: By eliminating data silos, ERP systems streamline business processes and workflows, reducing duplication of effort and improving operational efficiency.
Improved Data Consistency
ERP systems ensure data consistency by enforcing standardized processes and data validation rules:
- Standardized Data Formats: ERP systems enforce standardized data formats and structures, ensuring consistency and compatibility across different data sources and applications.
- Data Validation Rules: ERP systems validate data entered into the system against predefined rules and criteria, reducing errors and inconsistencies and maintaining data accuracy.
- Data Quality Management: ERP systems include tools and functionalities for monitoring and improving data quality, such as data cleansing, deduplication, and error detection, ensuring that data remains clean and reliable over time.
Free Tip: Regularly Back Up Centralized Data
To ensure data integrity and resilience, businesses should regularly back up centralized data using ERP systems:
- Automated Backup Processes: Configure ERP systems to automatically back up centralized data at regular intervals, ensuring that data is protected against loss or corruption.
- Offsite Storage: Store backup copies of centralized data in secure offsite locations or cloud-based storage platforms to mitigate the risk of data loss due to disasters or hardware failures.
- Testing and Verification: Periodically test and verify backup copies of centralized data to ensure that they can be restored successfully in the event of a data loss incident, minimizing downtime and disruption to business operations.
13. Employee Management
Employee management is a critical aspect of business operations, encompassing various HR functions such as recruitment, payroll, benefits management, and performance tracking.
Let's explore how ERP systems enhance employee management:
Integrated HR Functionalities
ERP systems integrate HR functionalities into a single platform, providing a centralized solution for managing all aspects of employee lifecycle management:
- Recruitment and Onboarding: ERP systems facilitate the recruitment process by automating job postings, candidate screening, and interview scheduling, streamlining onboarding processes for new hires.
- Employee Records Management: ERP systems maintain comprehensive employee records, including personal information, employment history, training records, and performance evaluations, ensuring data accuracy and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Time and Attendance Tracking: ERP systems track employee attendance, hours worked, and time-off requests, automating timekeeping processes and ensuring compliance with labor regulations.
Streamlined Payroll and Benefits Management
ERP systems streamline payroll and benefits management processes, automating calculations, deductions, and disbursements:
- Payroll Processing: ERP systems automate payroll calculations, tax withholdings, and direct deposits, reducing errors and ensuring timely and accurate payment of wages to employees.
- Benefits Administration: ERP systems manage employee benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and leave entitlements, enabling employees to enroll in benefits programs, view coverage options, and make changes as needed.
- Compliance Management: ERP systems ensure compliance with labor laws, tax regulations, and benefits administration rules, generating reports and documentation for audits and regulatory reporting.
Employee Performance Tracking
ERP systems track employee performance metrics and provide insights for talent management and development:
- Performance Reviews: ERP systems facilitate performance evaluations, goal setting, and feedback collection, enabling managers to assess employee performance objectively and identify areas for improvement.
- Skills Management: ERP systems track employee skills, certifications, and training requirements, identifying skill gaps and training needs to support career development and succession planning.
- Recognition and Rewards: ERP systems recognize employee achievements and milestones, such as performance bonuses, awards, and promotions, fostering a culture of appreciation and motivation.
Free Tip: Use ERP Tools for Employee Development Programs
To maximize the benefits of employee management, businesses should leverage ERP tools for employee development programs:
- Skills Assessments: Use ERP systems to conduct skills assessments and identify training needs for employees, aligning training programs with business goals and objectives.
- Training Management: Use ERP systems to manage employee training programs, including course registration, scheduling, and tracking of completion certificates, ensuring that employees receive the necessary training to enhance their skills and competencies.
- Career Planning: Use ERP systems to track employee career progression, identify potential career paths, and provide opportunities for advancement and development, fostering employee engagement and retention.
14. Project Management
Efficient project management is essential for businesses to deliver projects on time, within budget, and with the desired quality.
Let's delve into how ERP systems enhance project management:
Project Tracking and Management Tools
ERP systems provide project tracking and management tools that enable businesses to plan, execute, and monitor projects effectively:
- Task Management: ERP systems facilitate task assignment, tracking, and prioritization, ensuring that project tasks are completed on time and according to specifications.
- Budget Management: ERP systems track project budgets, expenses, and resource costs, providing real-time visibility into project financials and enabling project managers to control costs and mitigate risks.
- Document Management: ERP systems centralize project documentation, including plans, specifications, and deliverables, ensuring that project teams have access to the latest information and collaborate effectively.
Resource Allocation
ERP systems facilitate resource allocation by providing insights into resource availability, utilization, and allocation:
- Resource Planning: ERP systems forecast resource requirements based on project schedules and workload, enabling project managers to allocate resources effectively and prevent overallocation or underutilization.
- Skills Matching: ERP systems match project tasks with available resources based on skills, qualifications, and availability, ensuring that the right resources are assigned to the right projects at the right time.
- Capacity Planning: ERP systems optimize resource utilization by balancing workload across teams and departments, maximizing productivity and minimizing bottlenecks.
Timeline and Milestone Tracking
ERP systems enable businesses to track project timelines and milestones, ensuring that projects are completed on schedule:
- Gantt Charts: ERP systems visualize project schedules and timelines using Gantt charts, enabling project managers to monitor progress, identify dependencies, and adjust schedules as needed.
- Milestone Tracking: ERP systems track project milestones and critical path activities, alerting project managers to potential delays or issues that may impact project timelines.
- Progress Reporting: ERP systems generate progress reports and status updates for stakeholders, providing transparency and accountability throughout the project lifecycle.
Free Tip: Utilize ERP Project Templates for Standardization
To streamline project management processes and ensure consistency, businesses should utilize ERP project templates:
- Standardized Processes: Use ERP project templates to define standardized processes, workflows, and deliverables for different types of projects, ensuring consistency and efficiency across projects.
- Best Practices: Incorporate industry best practices and lessons learned from past projects into ERP project templates, enabling project teams to leverage proven methodologies and approaches for project success.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and update ERP project templates based on feedback, lessons learned, and changing business needs, ensuring that project management practices remain relevant and effective over time.
15. Vendor Management
Vendor management is crucial for businesses to maintain strong relationships with suppliers, ensure efficient procurement processes, and monitor vendor performance effectively.
Let's explore how ERP systems enhance vendor management:
Enhanced Vendor Relationship Management
ERP systems facilitate vendor relationship management by providing centralized tools for communication, collaboration, and documentation:
- Vendor Database: ERP systems maintain a centralized vendor database that stores vendor information, contact details, contracts, and agreements, enabling easy access and retrieval of vendor-related information.
- Communication Tools: ERP systems include communication tools such as email integration, messaging platforms, and document sharing, facilitating communication and collaboration with vendors throughout the procurement process.
- Contract Management: ERP systems automate contract creation, negotiation, and approval processes, ensuring compliance with contract terms and conditions and minimizing disputes with vendors.
Efficient Procurement Processes
ERP systems optimize procurement processes by automating purchasing, ordering, and payment workflows:
- Purchase Order Management: ERP systems generate purchase orders automatically based on inventory levels, reorder points, and demand forecasts, ensuring timely replenishment of stock and materials.
- Supplier Portal: ERP systems provide supplier portals where vendors can submit quotes, invoices, and payment requests electronically, streamlining procurement processes and reducing manual paperwork.
- Inventory Control: ERP systems track inventory levels, stock movements, and lead times, enabling businesses to optimize inventory management and reduce stockouts and overstock situations.
Performance Monitoring
ERP systems enable businesses to monitor vendor performance using key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics:
- Quality Metrics: ERP systems track vendor performance metrics such as product quality, delivery accuracy, and lead times, enabling businesses to assess vendor reliability and consistency.
- Cost Metrics: ERP systems analyze vendor pricing, discounts, and payment terms to evaluate cost-effectiveness and identify opportunities for cost savings and negotiation.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): ERP systems monitor vendor compliance with SLAs, contract terms, and service level commitments, enabling businesses to hold vendors accountable and address performance issues promptly.
Free Tip: Regularly Evaluate Vendor Performance Using ERP Metrics
To maximize the benefits of vendor management, businesses should regularly evaluate vendor performance using ERP metrics:
- Performance Reviews: Conduct regular performance reviews with vendors to discuss KPIs, metrics, and service level agreements, identify areas for improvement, and set performance targets.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establish feedback mechanisms for soliciting input from stakeholders, including employees, customers, and partners, regarding vendor performance and satisfaction.
- Continuous Improvement: Collaborate with vendors to implement corrective actions, process improvements, and performance enhancements based on feedback and performance evaluations, driving continuous improvement in vendor management practices.
16. Customization and Personalization
Customization and personalization are essential aspects of ERP systems, allowing businesses to tailor the software to their specific requirements, preferences, and workflows.
Let's explore how customization and personalization enhance the benefits of ERP:
Tailored ERP Solutions
ERP systems offer flexibility and configurability to meet the unique needs and preferences of businesses across industries and sectors:
- Module Customization: ERP systems allow businesses to customize modules and functionalities to align with their specific business processes, workflows, and industry requirements.
- Data Configuration: ERP systems enable businesses to configure data fields, forms, and templates according to their data management needs and reporting preferences, ensuring data consistency and relevance.
- Workflow Automation: ERP systems support workflow customization and automation, allowing businesses to streamline processes, eliminate manual tasks, and improve operational efficiency.
User-Specific Dashboards and Reports
ERP systems provide personalized dashboards and reports tailored to individual user roles, responsibilities, and preferences:
- Role-Based Access: ERP systems offer role-based access controls that restrict user access to specific functionalities, data, and reports based on their job responsibilities and permissions.
- Customizable Dashboards: ERP systems allow users to create personalized dashboards with relevant KPIs, metrics, and reports, enabling quick access to critical information and insights.
- Ad Hoc Reporting: ERP systems enable users to generate ad hoc reports and queries to analyze data, identify trends, and make informed decisions, without requiring IT support or programming skills.
Adaptation to Unique Business Needs
ERP systems adapt to evolving business needs, changes in market conditions, and emerging trends, ensuring long-term viability and relevance:
- Scalable Architecture: ERP systems feature scalable architecture that accommodates growth, expansion, and changes in business requirements, ensuring that the software remains effective and efficient over time.
- Modular Design: ERP systems adopt a modular design approach that allows businesses to add, remove, or customize modules and functionalities as needed, enabling agility and flexibility in adapting to changing business needs.
- Continuous Innovation: ERP vendors continuously update and enhance their software with new features, functionalities, and capabilities based on customer feedback, industry trends, and technological advancements, ensuring that businesses have access to the latest tools and technologies.
Free Tip: Regularly Review and Update ERP Customizations
To maximize the benefits of customization and personalization, businesses should regularly review and update ERP customizations:
- Business Process Reviews: Conduct regular business process reviews to identify areas for improvement, optimization, and customization within the ERP system, ensuring that the software aligns with evolving business needs and objectives.
- User Feedback: Solicit feedback from users regarding their experiences, preferences, and pain points with the ERP system, incorporating user input into customization and personalization efforts to enhance user satisfaction and adoption.
- Vendor Updates: Stay informed about updates, patches, and new releases from the ERP vendor, evaluating new features, functionalities, and customization options for their potential impact on business operations and performance.
17. Integration with Other Systems
Integration with other systems is a critical feature of ERP systems, enabling businesses to achieve seamless data exchange, enhanced interoperability, and connectivity across various applications and platforms.
Let's explore how integration with other systems enhances the benefits of ERP:
Seamless Integration with Third-Party Applications
ERP systems offer seamless integration with a wide range of third-party applications, allowing businesses to connect ERP functionality with other systems, tools, and services:
- APIs and Connectors: ERP systems provide application programming interfaces (APIs) and connectors that enable integration with popular business applications, such as CRM, e-commerce, supply chain management, and HR software.
- Pre-built Integrations: ERP vendors offer pre-built integrations and connectors for commonly used third-party applications, simplifying the integration process and reducing development time and effort.
- Custom Integration: ERP systems support custom integration projects for connecting with proprietary or legacy systems, enabling businesses to tailor integration solutions to their specific needs and requirements.
Enhanced Interoperability
ERP systems enhance interoperability by enabling seamless data exchange and communication between different systems and platforms:
- Data Mapping and Transformation: ERP systems facilitate data mapping and transformation to ensure compatibility and consistency between data formats, structures, and schemas across integrated systems.
- Real-time Data Synchronization: ERP systems support real-time data synchronization between integrated systems, ensuring that information is accurate, up-to-date, and consistent across all applications and platforms.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: ERP systems are designed to be compatible with various operating systems, databases, and technologies, enabling seamless integration with diverse IT environments and infrastructures.
Data Exchange Across Platforms
ERP systems facilitate data exchange across platforms by providing robust data integration and exchange capabilities:
- Data Import and Export: ERP systems support data import and export functionalities that enable businesses to exchange data between ERP modules, external systems, and data warehouses.
- Batch Processing: ERP systems support batch processing for large volumes of data, enabling businesses to schedule and automate data imports, exports, and synchronization tasks to minimize manual effort and ensure data accuracy and completeness.
- Data Transformation: ERP systems offer data transformation tools and capabilities that enable businesses to convert data formats, clean and normalize data, and perform data enrichment to ensure data quality and consistency across integrated systems.
Free Tip: Regularly Update Integration Points to Ensure Compatibility
To maximize the benefits of integration with other systems, businesses should regularly update integration points to ensure compatibility:
- Version Control: Maintain version control for integrated systems, applications, and APIs to ensure that updates and changes do not disrupt integration functionality or data exchange processes.
- Compatibility Testing: Conduct compatibility testing and validation when implementing updates, patches, or new releases for integrated systems to ensure seamless integration and data exchange without any errors or disruptions.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Monitor integration points and data exchange processes regularly to identify and address any issues, errors, or performance bottlenecks, ensuring optimal functionality and reliability of integrated systems.
How Can Deskera ERP Help Businesses?
Deskera ERP offers a wide array of features and functionalities designed to address the complex needs of modern businesses across various industries.
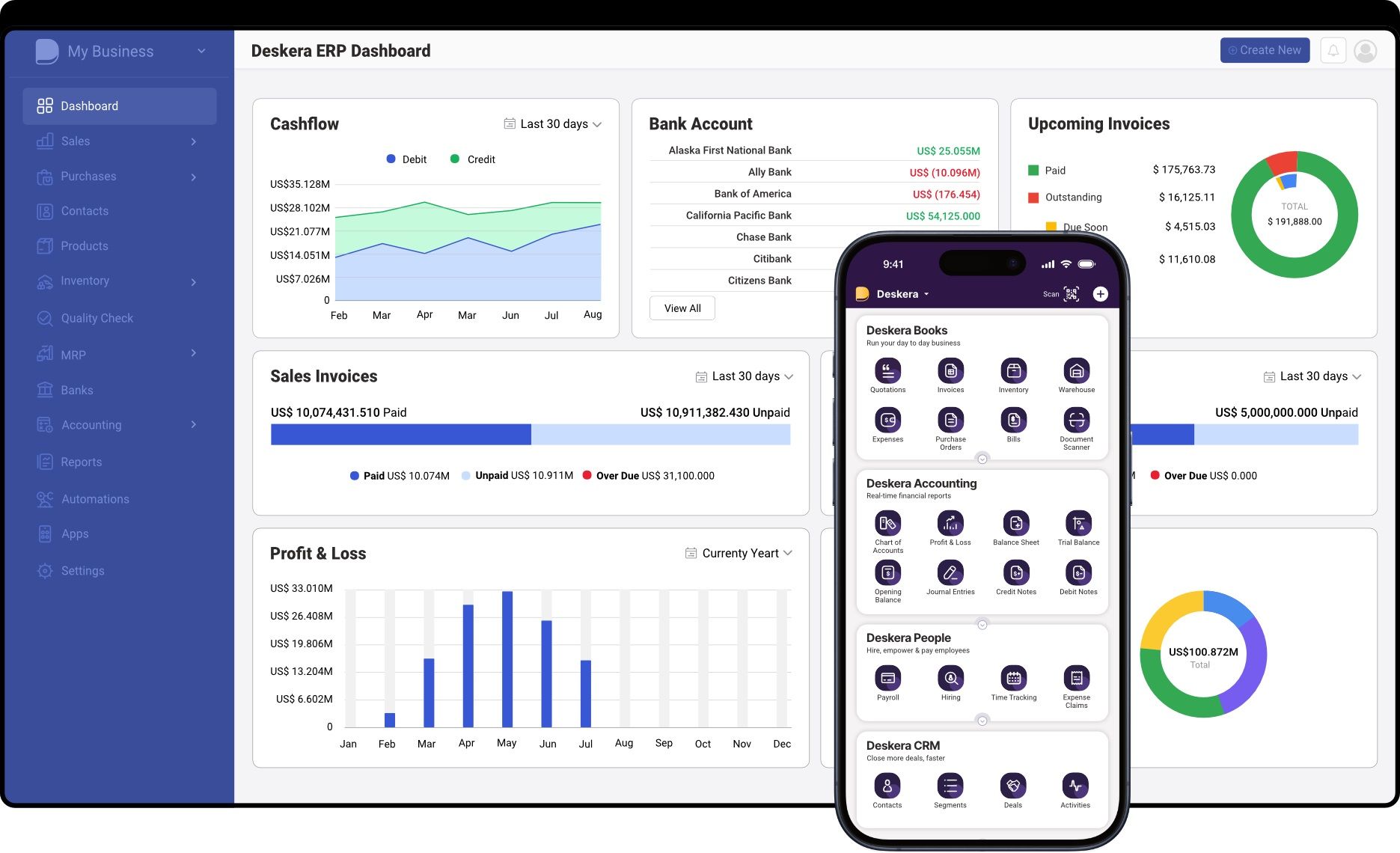
Here's how Deskera ERP can help your business:
- Streamlined Operations: Deskera ERP streamlines your business operations by integrating different functions such as finance, sales, inventory, procurement, and HR into a single platform. This integration eliminates silos, improves communication, and enhances collaboration among different departments, resulting in increased efficiency and productivity.
- Improved Decision-Making: With Deskera ERP, you gain access to real-time data and insights across all aspects of your business. Advanced reporting and analytics tools help you analyze trends, identify opportunities, and make informed decisions quickly. Whether it's monitoring sales performance, tracking inventory levels, or evaluating financial metrics, Deskera ERP provides the insights you need to steer your business in the right direction.
- Enhanced Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Deskera ERP includes robust CRM capabilities that enable you to manage customer interactions, track leads and opportunities, and provide personalized service to your clients. By centralizing customer data and automating key processes, Deskera ERP helps you build stronger relationships with your customers and drive customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Efficient Resource Management: Deskera ERP helps you optimize your resources, whether it's managing your workforce, tracking inventory, or allocating financial resources. With features such as payroll management, inventory optimization, and budgeting tools, Deskera ERP ensures that you're utilizing your resources effectively and maximizing your ROI.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Deskera ERP is highly scalable and customizable, allowing you to tailor the system to your specific business needs and scale it as your business grows. Whether you're a small startup or a large enterprise, Deskera ERP adapts to your requirements, providing the flexibility you need to stay agile in a rapidly changing business environment.
- Compliance and Security: Deskera ERP helps you stay compliant with industry regulations and standards by automating compliance processes and providing built-in security features. With Deskera ERP, you can ensure that your data is secure, your processes are compliant, and your business is protected from potential risks and threats.
Key Takeaways
In 2024, the benefits of ERP systems have never been more apparent. These benefits include:
1. Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity
- Streamlined business processes
- Automation of routine tasks
- Reduction in manual errors
- Free Tip: Implement workflow automation tools
2. Improved Decision-Making
- Real-time data analytics
- Comprehensive reporting capabilities
- Access to actionable insights
- Free Tip: Leverage built-in analytics dashboards
3. Better Financial Management
- Integrated financial modules
- Accurate financial reporting
- Budgeting and forecasting capabilities
- Free Tip: Use financial forecasting tools for better planning
4. Scalability and Flexibility
- Adaptability to business growth
- Modular architecture
- Customizable solutions
- Free Tip: Choose ERP systems that offer scalable modules
5. Enhanced Collaboration
- Centralized data repository
- Improved interdepartmental communication
- Real-time collaboration tools
- Free Tip: Utilize ERP’s collaboration features for team projects
6. Regulatory Compliance
- Built-in compliance management tools
- Automatic updates to regulations
- Audit trails and documentation
- Free Tip: Regularly update compliance settings to match current standards
7. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Integrated CRM functionalities
- Better customer insights
- Improved customer service
- Free Tip: Use CRM data to personalize customer interactions
8. Supply Chain Optimization
- Real-time supply chain visibility
- Improved inventory management
- Supplier management tools
- Free Tip: Implement just-in-time inventory practices
9. Cost Reduction
- Lower operational costs
- Reduction in IT expenses
- Improved resource allocation
- Free Tip: Conduct regular cost-benefit analysis of ERP features
10. Enhanced Security
- Robust security features
- Data encryption and protection
- Access control mechanisms
- Free Tip: Regularly update security protocols and conduct audits
11. Mobility and Remote Access
- Mobile-friendly ERP solutions
- Access from anywhere
- Support for remote work
- Free Tip: Ensure ERP system is optimized for mobile devices
12. Data Centralization
- Single source of truth for data
- Eliminates data silos
- Improved data consistency
- Free Tip: Regularly back up centralized data
13. Employee Management
- Integrated HR functionalities
- Streamlined payroll and benefits management
- Employee performance tracking
- Free Tip: Use ERP tools for employee development programs
14. Project Management
- Project tracking and management tools
- Resource allocation
- Timeline and milestone tracking
- Free Tip: Utilize ERP project templates for standardization
15. Vendor Management
- Enhanced vendor relationship management
- Efficient procurement processes
- Performance monitoring
- Free Tip: Regularly evaluate vendor performance using ERP metrics
16. Customization and Personalization
- Tailored ERP solutions
- User-specific dashboards and reports
- Adaptation to unique business needs
- Free Tip: Regularly review and update ERP customizations
17. Integration with Other Systems
- Seamless integration with third-party applications
- Enhanced interoperability
- Data exchange across platforms
- Free Tip: Regularly update integration points to ensure compatibility
Deskera ERP empowers your business with the tools and capabilities you need to streamline operations, improve decision-making, enhance customer relationships, optimize resources, and ensure compliance and security.
With Deskera ERP by your side, you can unlock your business's full potential and achieve sustainable growth in today's competitive landscape.
Related Articles











