If you own a business or are about to kickstart your business in Australia, or you want to understand more about how Australia's GST and BAS reporting and compliance work, this article is for you.
Australia is the world's 6th largest country, with a population of nearly 26 million and it's ranked as the world's 12th largest economy. The major cities are Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth, and Adelaide.

This guide will give you a complete rundown on how the GST and BAS works in Australia, the tax report you need to submit to the ATO, tax filing dues, and the penalty for failing to lodge or pay your tax obligations.
What is GST in Australia?
The GST (Goods and Service Tax Rate) in Australia is at 10% on most goods, services, or other items sold, consumed, or imported to Australia.
As a business owner, you will have to collect the additional 1/11th of the sales price from your customers if they purchase goods and services from you.
If you have just started using Deskera Books in Australia, you can refer to the article below to guide you.

What products are GST-free sales in Australia?
Not all products are subject to GST in Australia.
GST-free products are products that are exempted from Goods and Services Tax (GST).
Hence, it means that there is no tax collection if you purchase these GST-free goods and services.

Stated below are some of the products that are GST-free in Australia:
- Basic food such as bread, bread rolls, cooking ingredients, milk, cream, cheese, spices, and sauces
- Some educations courses, course materials, or related field trips
- Some medical, health, and care services such as services from a medical practitioner or pathologist and hospital treatment
- Some menstrual products such as tampons, sanitary pads, and panty liner
- Some medical aids and appliances
- Some medicine such as aspirin and paracetamol as per the GST-free Supply ( Drugs and Medicinal Preparations) Determination 2000 (No.2)
- Some childcare services, religious activities, and charitable activities
- Exported goods from Australia within 60 days of one of the following conditions; the vendor receives any payment for the goods or sends an invoice for the goods.
- Other exports other than supply of goods for consultation outside of Australia such as services, various rights, or professional services
- Any sale of a business as a going concern basis
What are input-taxed sales?
Any sales of goods and services which don't include GST in the price are known as input-taxed sales.
Input-taxed sales are financial supplies( lending money, providing credit for a fee, buying or selling securities ) and selling or renting out residential premises.
However, please note that if your residential premise is considered 'New", then taxable sale and GST are applicable.
If there is no GST on the price, it means that you cannot can't GST credit for the price of your inputs.
** For exceptional cases, you may be entitled to a GST credit for a purchase relating to making financial supplies.
Deskera Books allow you to create different types of goods. Read more here.
What is GST credit?
GST credits (input tax credit) are the credits that business owners can claim for their business purchases.
Also, this means that you cannot claim GST credits for personal expenses such as food, entertainment, and items for private use.

You will need to satisfy all of the following conditions mentioned below to apply for GST credit successfully:
- You have registered for a GST account
- Purchases for business use and the purchase exclude items for making input-taxed supplies
- The purchase price is inclusive of GST
- You have a record of the payment for the items purchases
- You can provide a tax invoice from your suppliers for purchases exceeding AUD 82.50 (inclusive GST)
What are the items excluded from the GST credit claim?
Although you may think that you can claim a GST credit for items purchased for business use, that's not always true.
Here are some of the exemptions:
- Any purchases of real property under the margin scheme
- Any purchases that cannot claim as income tax deductions, such as entertainment expenses
- Purchase price of a car that has exceeded the car limit amount for the relevant financial year
- Waged that you paid your employees (there is no GST on wages)
- Any purchases that do not have GST in the price, such as GST free goods, imputed-tax, and suppliers not registered for GST
When do you need to charge GST?
A sale is considered as taxable if:
- You are registered for GST
- Merchants selling low-value goods sold to a customer
- An electronic distributor platform operator such as an online marketplace through which merchants sell goods
- A re-deliverer that helps bring goods to Australia
- The goods sold aren't GST-free
- The exception rule for multiple goods over $1,000 doesn't apply
Do you know that you can customize your tax rate using Deskera Books? If wish to find out more, check on the link below.

What are the requirements to register for a GST account in Australia?
It’s your obligation to check whether you have reached the maximum threshold to register for GST.
As a business owner, you must register for GST if you have fulfilled one of the following conditions within 21 days after your GST turnover exceeding the stated threshold:
- You have hit a GST turnover of $75,000 or more, or if your non-profit organization has a GST turnover of $150,000 and more.
- You provide taxi, limousine service, ride-sourcing services such as Uber, GoCatch, Didi, etc. This applies to both driver owners and also, those that lease or rent a car.
- If you want to claim the fuel tax credit for your business
For non-resident business, a special rule may apply to you. Otherwise, the GST registration is optional if you didn’t fulfill any of the conditions mentioned above.
GST turnover computation
One reminder that when computing the GST turnover is that you are using your gross business income as the parameter and not your profit.
Your gross income is calculated using the total business income deduct from the following categories:
- GST in sales
- Sales that aren’t for payment and aren’t taxable
- Sales not related to your enterprise
- Input-taxed sales
- Sales not connected with Australia
What is the GST number in Australia?
The GST number is your tax identification number, which establishes your relationship with the Australian tax system.
Your GST number is crucial for your business as it tracks your business tax dealings, such as the tax you pay, the tax you have collected from your customers, and your tax credit application.
How can you register for a GST account?
You need to have an Australian Business Number (ABN) before registering for a GST account. When you register for your business name, you will be given the Australian Business Number (ABN).
Once you have your ABN ready, you can register for GST once you exceed the GST threshold.

There are a few methods you can register for a GST account:
- Using online services
- Make a call to 13 28 66
- Apply via your registered tax agent BAS agent
- Complete the NAT 2954 form. Order a form using the online publication ordering service
The Australian Tax Officer (ATO) will reach out to you in writing once they have received your GST registration details.
What is Australian Business Number (ABN)?
The ABN is a special 11 digit number issued by the Australian Business Register, the ATO.
The special number is issued to all entities registered in Australia, that helps identify your business from other entities.
Not everyone needs an ABN. To get one, you need to have your business up and running in Australia.
Generally, you can use the ABN to:
- Distinguish your business to others when ordering or invoicing
- Avoid pay as you go (PAYG) tax on payment you receive
- Claim GST credits
- Claim energy grant credits
- Register an Australian domain name
If you already have your Australian Business Number (ABN), you can look-up your existing ABN here, which is also available to the rest of the public.
Reporting your GST Return to the ATO
Your GST Return Report is also known as the Business Activity Statement in Australia.
Once you have registered for GTS, you have the obligation to issue tax invoices to your customers, collect GST and send the GST collection to the Australia Tax Officer with your business activity statement.
In the BAS, you will have to include the pay as you go withholding tax, pay as you go instalments, fringe benefits tax, wine equalisation tax and luxury car tax in this report.
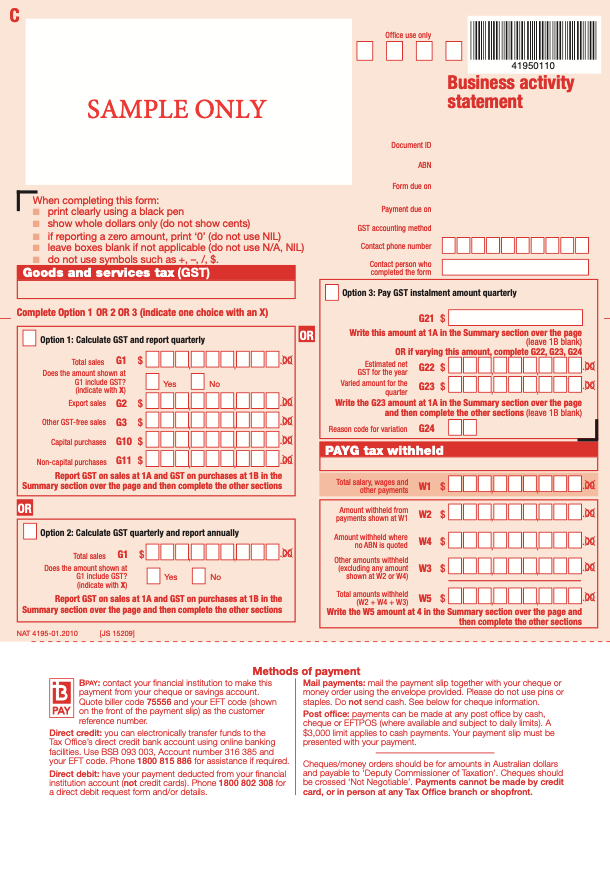
Example of Business Activity Statement
Below is an example of the business activity statement in Australia.
The first page
The second page
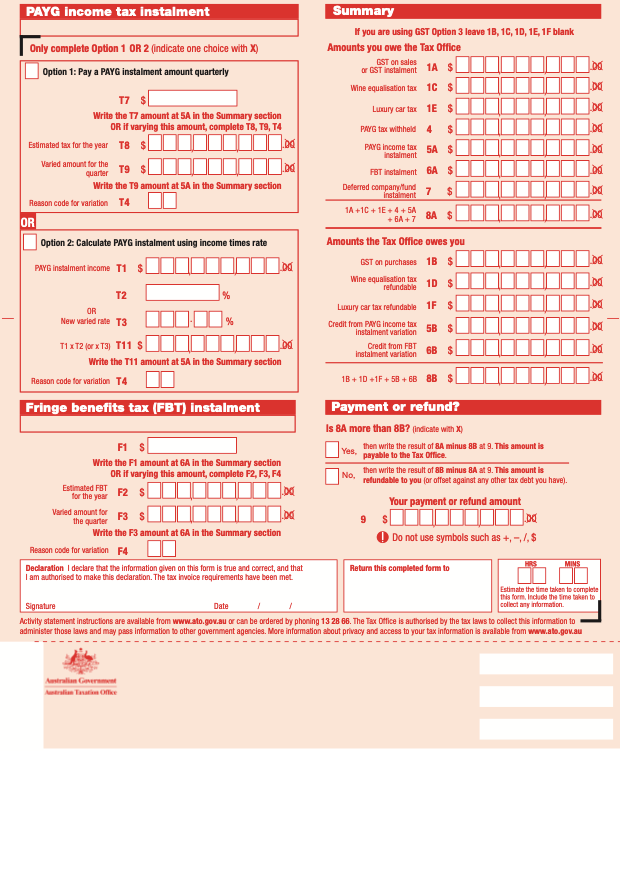
There are a few sections in the Business Activity Statement that you need to complete.
We will explain in great detail the different parts and sections in the Business Activity Statement (BAS) so that you can complete the form with accurate information.
A) Goods and Service Tax (GST)
The first section in the BAS is the Goods and Service Tax section.
There are five boxes here. Enter the amount in each box, if relevant.
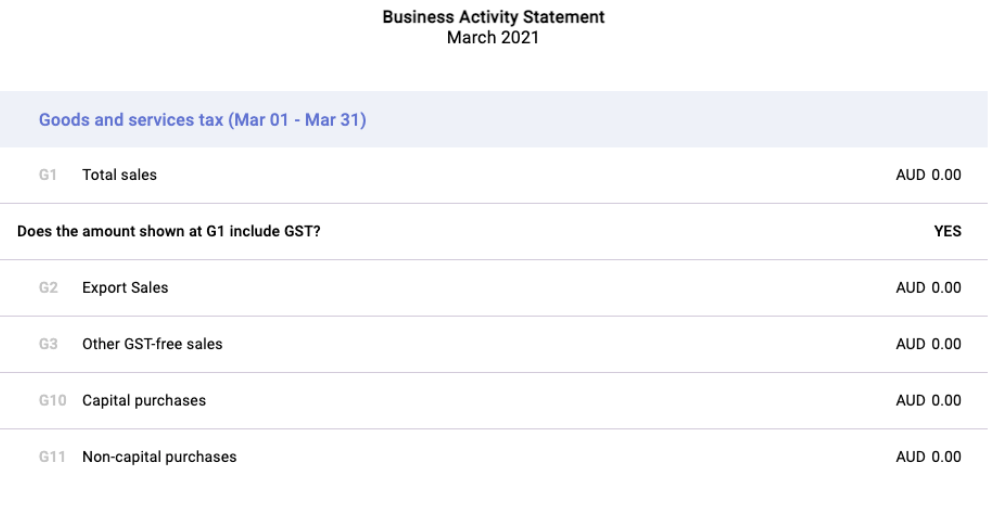
B) Pay as You Go (PAYG) Withheld
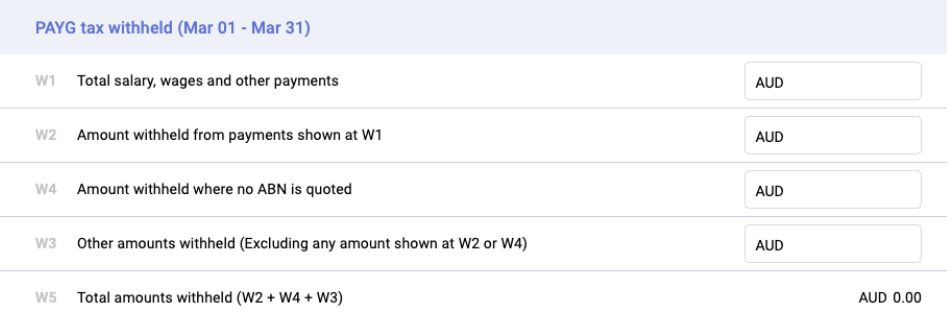
C) i. PAYG income tax instalment (option 1)
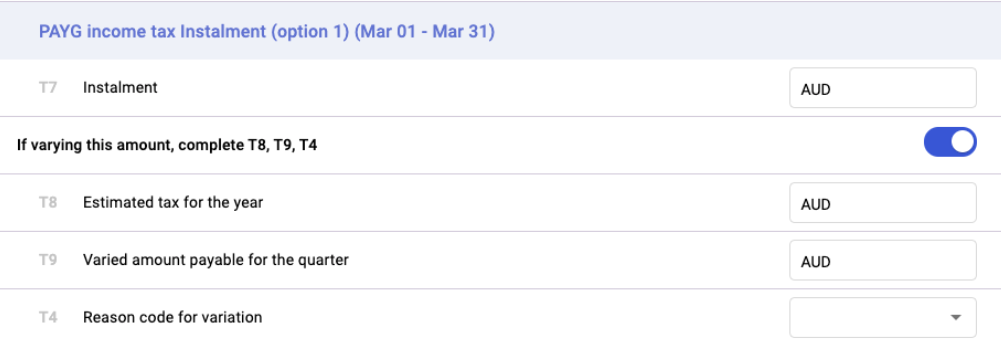
C) ii. PAYG income tax instalment (option 2)
D) Fringe benefits tax (FBT) installment
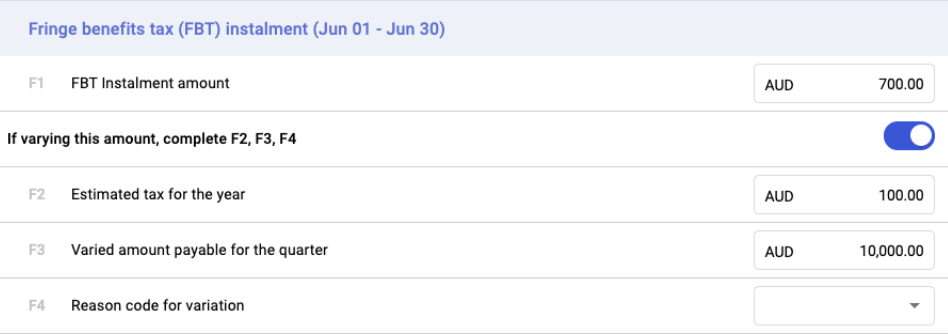
E) Amounts you owe to ATO
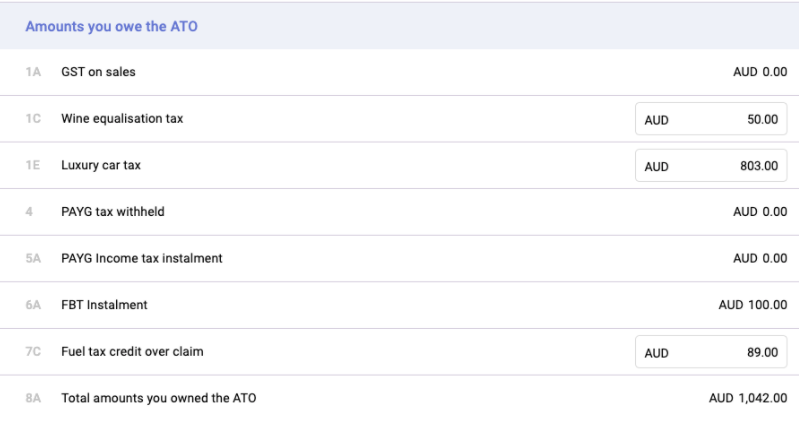
F) The amounts ATO owes you
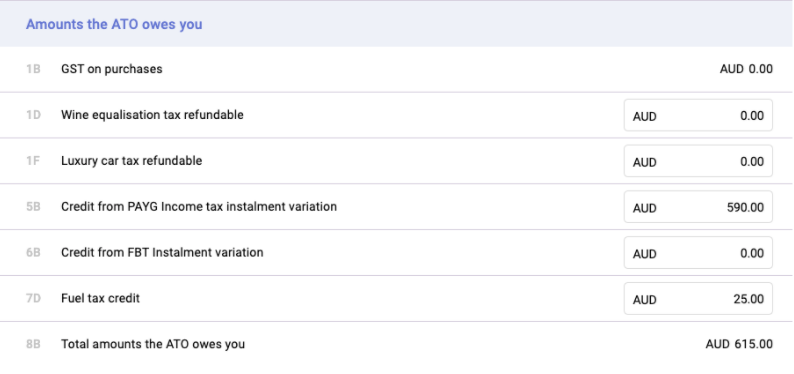
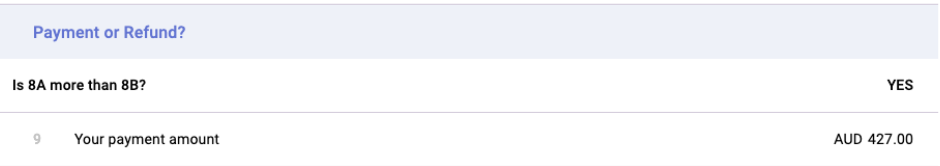
G) Payment or Refund
Do you know that you can generate your Business Activity Statement using Deskera Books?

When is the due date of lodging BAS?
One of the essential things that you need to note is the due date of filing your BAS.
Your business GST turnover is the factor that determines your GST reporting and payment cycle. For example;
- Quarterly, your GST turnover is less than $20 million.
- Monthly, your GST turnover is $20 million or more.
- Annually, if you are voluntarily registered for GST and your GST turnover is less than $75,000 or $150,000 for non-profit bodies.
The due date for quarterly reporting
Note: If you choose to lodge your BAS online, you may be eligible for additional two weeks to lodge and pay your quarterly BAS.
The due date for monthly reporting
If your reporting period falls monthly, you will have to lodge and pay your monthly BAS on the 21st of the month following the taxable period.
For example, an August monthly BAS is due on 21 September.
The due date for annual reporting
The due date and pay your GST for annual reporting falls on 31 October.
If you are not required to lodge a tax return, the due date will be on 28 February, following the annual tax period.
One way to remember your reporting period is by setting calendar reminders on your phone for the critical date of lodging your report. Then, you wouldn't miss out on this crucial task.
How to lodge BAS?
After completing your Business Activity Statement and verified all the amount declared, you will have to lodge this form within the due date.
You can use a few methods to lodge your BAS:
- Through your tax or BAS agent
- Online using the SBR-enabled software,
- If you are filing for a NIL statement only, you can call ATO by phone. Dial 13 72 26 anytime
- By mail. Mail to;
Australian Taxation Office
Locked Bag 1936
ALBURY NSW 2640
- Government portal through your myGov account linked to the ATO (only if you're a sole trader)
Quick Tips when Filing Your BAS
Listed below are a few tips you need to note when filing, completing, and lodging your business activity statement correctly.
Please ensure that:
- You fill in the PAYG installment and other information that is relevant for your business
- Verify the amount in each section is true and accurate
- No decimal numbers are allowed. You can round down to whole dollars.
- Lodge and pay your tax liability by the due date
- Update your business details within 28 days
How can I update my business details?
You must update the Registrar of the Australian Business Register (ABR) in the scenarios where:
- You change your postal, email, or business address
- Changes in business associates
- Changes in main business activity
- Changes in Australian Company Number or Australian Registered Body Number (ARBN)
- Update in the name of trustees
You can follow the steps suggested below:
- Do it online via the Australian Business Register
- External link or online services for business
- Make a call to ATO
- Through your tax agent or BAS agent
How can I make a payment to ATO?
Once you have collected GST from your customers, you need to remit the GST collection to the Australian Tax Officer within the due dates.

Here are the few steps to make payment:
- Pay via BPAY- Biller Code is 75556
- Ensure that you indicate the correct payment reference number (EFT code) to ensure that your money goes to the correct account
- Use a credit card or debit card that can be a Visa, MasterCard, or American Express card
- Pay online
- Pay by phone - make a call the Government EasyPay service on 1300 898 089
Penalty for late payment
Due to a busy schedule, as humans, sometimes we missed the due date of filing our tax return or forgetting to make payment, even though we have no intention of doing so.
However, that doesn't mean we are spared from our negligence. If you forget to lodge your BAS form or failed to make payment, you may be charged with a late penalty.
The ATO will still compute the penalty amount based on the following conditions:
- Using the statutory formula, based on your behavior and the amount of tax avoided
- Multiple penalty units based on the company size. You can refer to the table below for the penalty unit
Over the years, the penalty by unit amount has changed.
You can also check on the changes over the past few years below.
GST, BAS and Invoicing in Australia Using Deskera Books
Australia GST and BAS is a piece of cake with Deskera. You can setup an Australia company in minutes and start creating and sending invoices immediately.
With Deskera Books, you can generate beautiful invoice templates from the system without the need to design your template from scratch.
You can specify your customers' location and charge the correct tax rate using the tax configuration in the system.
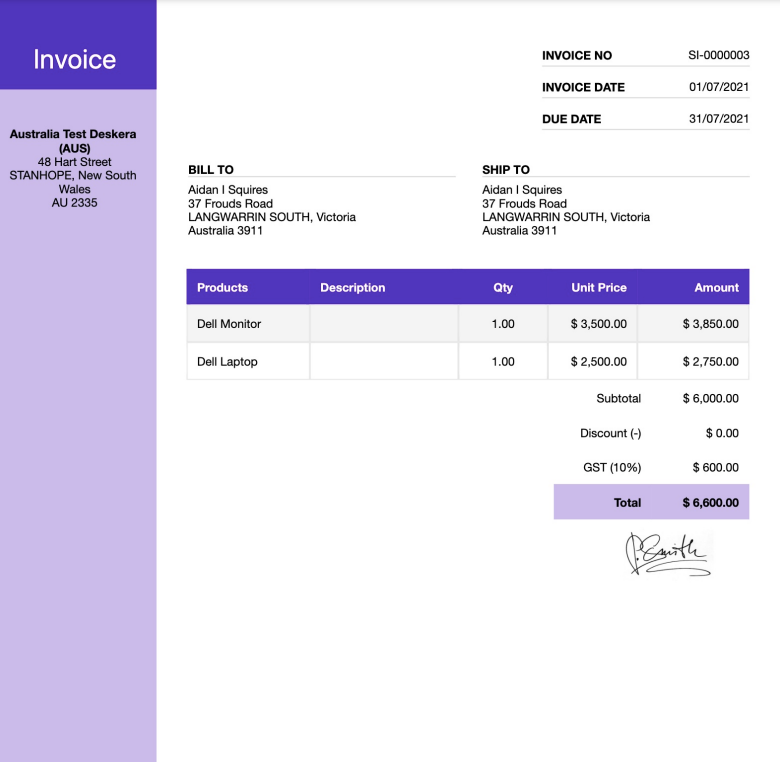
Here are the essential pieces of information that you can include in your invoice:
- Your company name and address
- The date when you issue the invoice
- Your business number (GST Registration Number)
- The purchaser's name and address
- Term of Payment
- The name of the products or services purchased and their description
- Cost of each product and quantity purchased
- Total amount payable
- Tax component
Learn more about the invoicing feature using Deskera Books.

Key Takeaways

And that is a wrap. From this article, you can take away the following points:
- What is the sales tax in Australia?
- What products are GST-free sales in Australia?
- What are input-taxed sales?
- What is GST credit?
- What are the items excluded from the GST credit claim?
- When do you need to charge GST?
- What are the requirements to register for a GST account in Australia?
- GST turnover computation
- What is the GST number in Australia?
- How can you register for a GST account?
- What is the Australian Business Number (ABN)?
- Reporting your GST Return to the ATO
- Example of Business Activity Statement
- When is the due date of lodging BAS?
- How to lodge BAS?
- Quick Tips when Filing Your BAS
- How can I update my business details?
- How can I make a payment to ATO?
- Penalty for late payment
With Deskera, you can easily apply the Australia GST tax rates to your transactions and generate a proper sales invoice.
You can rest assured as the software will do the work for your tax calculation. Instead of spending a tremendous amount of time on manual tasks, you can have more time for the things you love with Deskera.








