The chemical manufacturing industry is a crucial sector of the United States economy, contributing to a wide range of industries, including pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and energy.
According to the American Chemistry Council, the industry generated over $553 billion in revenue and employed over 870,000 workers in 2020, with an average salary of over $87,000. However, chemical manufacturers face several challenges, including rising costs and the need to optimize production processes to remain competitive.

One critical aspect of chemical manufacturing that directly affects costs is the production process's efficiency. Chemical production involves several stages: raw material procurement, reaction, separation, and purification.
Each step involves different costs, and inefficiencies in any of these stages can lead to higher costs and lower profits. Therefore, analyzing the costs associated with each stage of the production process is essential to optimize production efficiency and reduce costs.
This article will analyze the costs associated with chemical manufacturing and how they affect the industry's competitiveness.
Here's what we shall cover in this post:
- Introduction to Cost Analysis in Chemical Manufacturing
- Identifying Direct and Indirect Costs
- Understanding Fixed and Variable Costs
- Importance of Accurate Cost Estimation for Chemical Manufacturers
- Evaluating Cost-Effectiveness of Raw Materials
- Analyzing the Cost of Energy in Chemical Manufacturing
- Role of Automation in Cost Reduction in Chemical Manufacturing
- Incorporating Lean Manufacturing Principles to Reduce Costs
- Cost Management Best Practices
- Conclusion
- Key Takeaways
Introduction to Cost Analysis in Chemical Manufacturing
Cost analysis in chemical manufacturing is an essential tool used by chemical companies to determine the expenses associated with the production process. This analysis helps businesses identify the most cost-effective and efficient production methods and areas for potential cost savings.
- The cost analysis process involves examining all the factors involved in producing a chemical product, including raw material, labor, energy, and equipment costs.
- Cost analysis is also essential for making crucial business decisions. By understanding the costs associated with producing a product, companies can determine the profitability of introducing new products or expanding into new markets.
- Cost analysis can also be used to evaluate the effectiveness of cost-saving measures, such as switching to more energy-efficient production methods or reducing labor costs.
Identifying Direct and Indirect Costs
Cost analysis is an essential part of chemical production. It involves identifying, measuring, and evaluating the costs involved in producing a chemical product. In order to conduct a comprehensive cost analysis, it is essential to distinguish between direct and indirect costs.
Direct costs: These are costs that can be directly attributed to the production of a chemical product. They include:
- Raw materials: The cost of purchasing the necessary raw materials required for production.
- Labor: The wages and benefits paid to employees directly involved in production.
- Energy: The cost of energy required to power equipment and machinery involved in the production process.
- Equipment and machinery: The cost of purchasing, operating, and maintaining equipment and machinery used in production.
- Packaging and transportation: The cost of packaging and transporting the finished product to customers.
Indirect costs: These are costs that are not directly attributable to the production process but are necessary for the overall operation of the business. They include:
- Rent and utilities: The cost of renting or owning the production facility and paying for utilities such as electricity, water, and gas.
- Administrative expenses: The cost of administrative staff, office supplies, and other overhead expenses.
- Marketing and advertising: The cost of promoting the product and acquiring new customers.
- Taxes and insurance: The cost of paying taxes and insurance premiums.
Overhead costs: These are indirect costs that cannot be directly attributed to a specific product but are necessary for the overall operation of the business. They include:
- Depreciation: The decrease in the value of equipment and machinery over time.
- Interest: The cost of borrowing money to finance the business.
- Maintenance and repairs: The cost of maintaining and repairing equipment and machinery used in production.
Identifying direct and indirect costs is crucial for chemical manufacturers to determine the total cost of production, which in turn affects the product's pricing strategy. Understanding cost analysis also helps chemical manufacturers to:
- Identify areas where cost savings can be achieved.
- Determine the profitability of a particular product or production process.
- Evaluate the performance of the production process and make necessary improvements.
- Forecast future costs and make informed business decisions.
Understanding Fixed and Variable Costs
Fixed and variable costs are two essential concepts in cost analysis, particularly in chemical manufacturing, where the costs involved can be significant. Understanding the difference between these two types of costs is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions about pricing, production volumes, and profitability. Here are some key points to help understand fixed and variable costs in chemical manufacturing:
Fixed Costs
Fixed costs are expenses that remain constant over a given period, regardless of the level of production or sales. These costs are usually associated with investments in capital assets, such as buildings, equipment, and machinery.
Some examples of fixed costs in chemical manufacturing include rent or lease payments, property taxes, and insurance premiums. Fixed costs are usually incurred regardless of the level of production and cannot be avoided in the short term.
Variable Costs
Variable costs are expenses that vary in proportion to the level of production or sales. These costs change as production volumes increase or decrease. Examples of variable costs in chemical manufacturing include raw materials, labor, energy, and transportation costs.
Variable costs are directly related to the level of production and can be reduced by decreasing production levels or negotiating better prices for raw materials.
Importance of Fixed and Variable Costs
Understanding fixed, and variable costs is vital for chemical manufacturing businesses because it helps them determine their break-even point, which is the production level at which the total production costs equal the total revenue generated.
By identifying fixed and variable costs, businesses can determine how much they need to sell at a given price to cover their costs and make a profit. This information is also helpful in making decisions about pricing, production volumes, and cost-saving measures.
Break-Even Analysis
Break-even analysis is a tool used to determine the minimum level of sales required to cover all fixed and variable costs. This calculation helps businesses set prices, determine production levels, and identify the minimum amount of sales needed to generate a profit.
Companies can decide if they are operating at a profit or loss by comparing the break-even point to actual sales.
Cost Reduction Strategies
Identifying fixed and variable costs can help businesses develop cost reduction strategies. For example, by reducing the use of energy or raw materials, companies can decrease variable costs.
Businesses can reduce fixed costs by negotiating better prices for raw materials or equipment. Implementing cost-reduction strategies can help companies to operate more efficiently and increase profitability.
Importance of Accurate Cost Estimation for Chemical Manufacturers
The accurate estimation of costs enables manufacturers to make informed decisions, evaluate their profitability, and improve their competitive position. The following are the importance of accurate cost estimation for chemical manufacturers:
- Budgeting and Planning: Cost estimation provides an accurate estimate of the cost of producing a particular chemical product, enabling manufacturers to create a budget and plan their production accordingly. Manufacturers can also identify the most cost-effective methods of production and evaluate the impact of different production volumes on their bottom line.
- Pricing: Accurate cost estimation allows chemical manufacturers to set competitive prices while ensuring that they make a profit. Manufacturers can evaluate the price sensitivity of their products and adjust prices accordingly.
- Profitability: Chemical manufacturers need to make a profit to stay in business, and accurate cost estimation plays a vital role in ensuring that the profitability of the manufacturing process is maintained. Manufacturers can identify opportunities to reduce costs and increase profitability by accurately estimating costs.
- Evaluation of Investments: Chemical manufacturers often invest in new technology, machinery, and equipment to improve their manufacturing process. Accurate cost estimation allows manufacturers to evaluate the financial feasibility of such investments, ensuring that they are cost-effective and can generate a return on investment.
- Resource Allocation: Accurate cost estimation helps manufacturers allocate their resources efficiently. By understanding the costs of producing different chemical products, manufacturers can allocate their resources to products that generate the highest profit margins.
- Decision-Making: Chemical manufacturers often make critical decisions that impact the future of their business. Accurate cost estimation provides the data required to make informed decisions and evaluate the potential impact of different scenarios.
Evaluating Cost-Effectiveness of Raw Materials
Chemical production involves using a wide range of raw materials that can significantly impact the overall cost of production. Therefore, chemical manufacturers must evaluate the cost-effectiveness of raw materials to ensure that they are using the most cost-effective options.
Here are some key points to consider when evaluating the cost-effectiveness of raw materials in chemical production:
- Analyze the price and availability of raw materials: One of the first steps in evaluating the cost-effectiveness of raw materials is to analyze their price and availability. This can help chemical manufacturers identify any potential cost savings or risks associated with using specific materials.
- Consider the quality and performance of raw materials: While the price of raw materials is essential, chemical manufacturers must also consider the quality and performance of the materials. Using high-quality materials can result in more efficient production and higher-quality products, ultimately increasing profitability.
- Evaluate the impact of raw materials on the production process: Different raw materials can have varying impacts on the production process. For example, some materials may require additional processing steps, increasing production costs. Chemical manufacturers must evaluate the impact of raw materials on the production process to ensure that they are not adding unnecessary costs.
- Factor in the environmental impact of raw materials: In addition to cost considerations, chemical manufacturers must also consider the environmental impact of their raw materials. Choosing more sustainable materials can reduce the overall environmental impact of the production process.
- Use cost modeling tools: Cost modeling tools can help chemical manufacturers evaluate the cost-effectiveness of different raw materials. These tools allow manufacturers to simulate different scenarios and analyze the impact of different variables on production costs.
Analyzing the Cost of Energy in Chemical Manufacturing
The cost of energy can account for a significant portion of the overall production cost of chemicals. Therefore, chemical manufacturers must analyze the cost of energy to identify opportunities for cost savings and increase their profitability. In this section, we will discuss the importance of analyzing the cost of energy in chemical manufacturing and how it can be done.
Energy Cost Breakdown
- The first step in analyzing the energy cost in chemical manufacturing is to break it down into its different components, such as fuel, electricity, and steam.
- Each component may have different cost drivers and can be analyzed separately to identify opportunities for cost savings.
Energy Efficiency Assessment
- Conducting an energy efficiency assessment can help identify areas where energy consumption can be reduced, such as optimizing equipment usage and process control, upgrading or retrofitting equipment, or implementing energy-efficient technologies.
- This assessment can also help prioritize energy efficiency projects based on their potential cost savings.
Renewable Energy
- Using renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, can significantly reduce energy costs for chemical manufacturers.
- Installing renewable energy sources on-site or purchasing renewable energy certificates (RECs) can also help companies achieve their sustainability goals and increase their competitive advantage.
Energy Procurement Strategies
- Chemical manufacturers can also analyze their energy procurement strategies to identify cost-saving opportunities.
- This can include negotiating better energy prices with suppliers, purchasing energy on the spot market, or implementing a hedging strategy to protect against price volatility.
Benchmarking
- Benchmarking energy consumption against industry standards can provide chemical manufacturers with insights into their energy performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Comparing energy consumption against similar companies can also help identify best practices and opportunities for cost savings.
Role of Automation in Cost Reduction in Chemical Manufacturing
Automation has been playing an increasingly important role in the chemical manufacturing industry, especially in terms of cost reduction. Here are some key points on the topic:
- Automation can help reduce labor costs: One of the most significant benefits of automation is that it can help reduce the amount of labor required to produce chemicals. This is because automated systems can perform tasks that would otherwise require manual labor, which can be time-consuming and expensive.
- Automation can increase efficiency: Automated systems can work faster and more consistently than human workers, which can help to improve overall production efficiency. This can help reduce costs associated with downtime, errors, and delays.
- Automation can reduce waste: By controlling processes more precisely, automation can help reduce the amount of waste generated during chemical production. This can reduce costs associated with waste disposal and improve sustainability.
- Automation can improve safety: Automated systems can help reduce the risk of accidents and injuries associated with chemical manufacturing. This can help reduce costs associated with lost productivity, medical expenses, and legal liabilities.
- Automation can provide better data for cost analysis: Automated systems can provide more accurate and detailed data on the production process, which can be used for cost analysis. This can help manufacturers identify areas where costs can be reduced and optimize their operations for greater efficiency.
- Automation can help manufacturers remain competitive: With rising labor costs and increasing competition in the chemical manufacturing industry, automation can help manufacturers remain competitive by reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Incorporating Lean Manufacturing Principles to Reduce Costs
Lean manufacturing principles are widely used in various industries to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and increase profitability. Chemical manufacturers can also benefit from incorporating these principles into their operations.
Here are some points on how incorporating lean manufacturing principles can help reduce costs in chemical production:
- Streamlining processes: Lean manufacturing principles focus on identifying and eliminating process waste. By simplifying processes, chemical manufacturers can reduce the time and resources required to produce a product. This can result in significant cost savings.
- Improving inventory management: Chemical manufacturers often have to deal with large quantities of raw materials and finished products. Effective inventory management is critical to reducing costs. Lean manufacturing principles can help in reducing inventory levels, thus reducing inventory carrying costs.
- Eliminating overproduction: Overproduction is a common problem in chemical manufacturing. Overproduction leads to excess inventory, increased costs, and decreased profitability. Lean manufacturing principles focus on producing only what is required, when it is required, and in the required quantity.
- Reducing defects: Defects in chemical production can lead to significant costs. Lean manufacturing principles focus on identifying and eliminating the root causes of defects. By reducing defects, chemical manufacturers can improve product quality and reduce costs.
- Maximizing equipment utilization: Equipment utilization is critical to profitability in chemical manufacturing. Lean manufacturing principles maximize equipment utilization by reducing downtime and increasing efficiency.
- Continuous improvement: Lean manufacturing principles emphasize the importance of continuous improvement. Chemical manufacturers can reduce costs and increase profitability by continually improving processes and operations.
- Employee involvement: Employee involvement is critical to the success of lean manufacturing principles. Employees are encouraged to identify and eliminate waste in processes. By involving employees in the process of reducing costs, chemical manufacturers can improve morale, productivity, and profitability.
Cost Management Best Practices
To remain competitive in the market, chemical manufacturing companies must maintain an efficient cost management system. The following are some best practices for cost management in the chemical industry:
- Establish a robust cost accounting system: Companies should implement a cost accounting system that accurately tracks production costs and identifies inefficient areas.
- Monitor and control variable costs: Variable costs such as raw materials, energy, and labor costs are directly related to production volume. Implementing cost-saving measures such as energy-efficient technologies, waste reduction, and process optimization can help reduce variable costs.
- Monitor and control fixed costs: Fixed costs such as depreciation, insurance, and rent are incurred regardless of production volume. Companies should closely monitor these costs and implement cost-saving measures such as negotiating better vendor contracts or reducing unnecessary expenses.
- Implement cost-reduction programs: Chemical manufacturing companies can reduce costs by implementing lean manufacturing, Six Sigma, and Total Quality Management (TQM) programs. These programs aim to eliminate waste, improve efficiency, and reduce production costs.
- Invest in automation: Automation technology can help reduce labor costs and increase efficiency in chemical production. Automated systems can perform tasks faster and more accurately than manual labor, reducing the need for human intervention and increasing production output.
- Monitor and manage inventory levels: Companies should closely monitor their inventory levels to avoid overstocking or understocking. Overstocking can lead to unnecessary storage costs, and understocking can cause production delays and lost sales.
- Implement a cost-conscious culture: Cost management is not just the finance department's responsibility but should be a part of the company culture. Encouraging employees to identify and report cost-saving opportunities can lead to a more efficient and cost-effective operation.
- Regularly review and update cost management strategies: Companies should regularly review and update their cost management strategies to adapt to changing market conditions, technology advancements, and internal operations.
How Deskera Can Assist You?
Deskera MRP allows you to closely monitor the manufacturing process. From the bill of materials to the production planning features, the solution helps you stay on top of your game and keep your company's competitive edge.
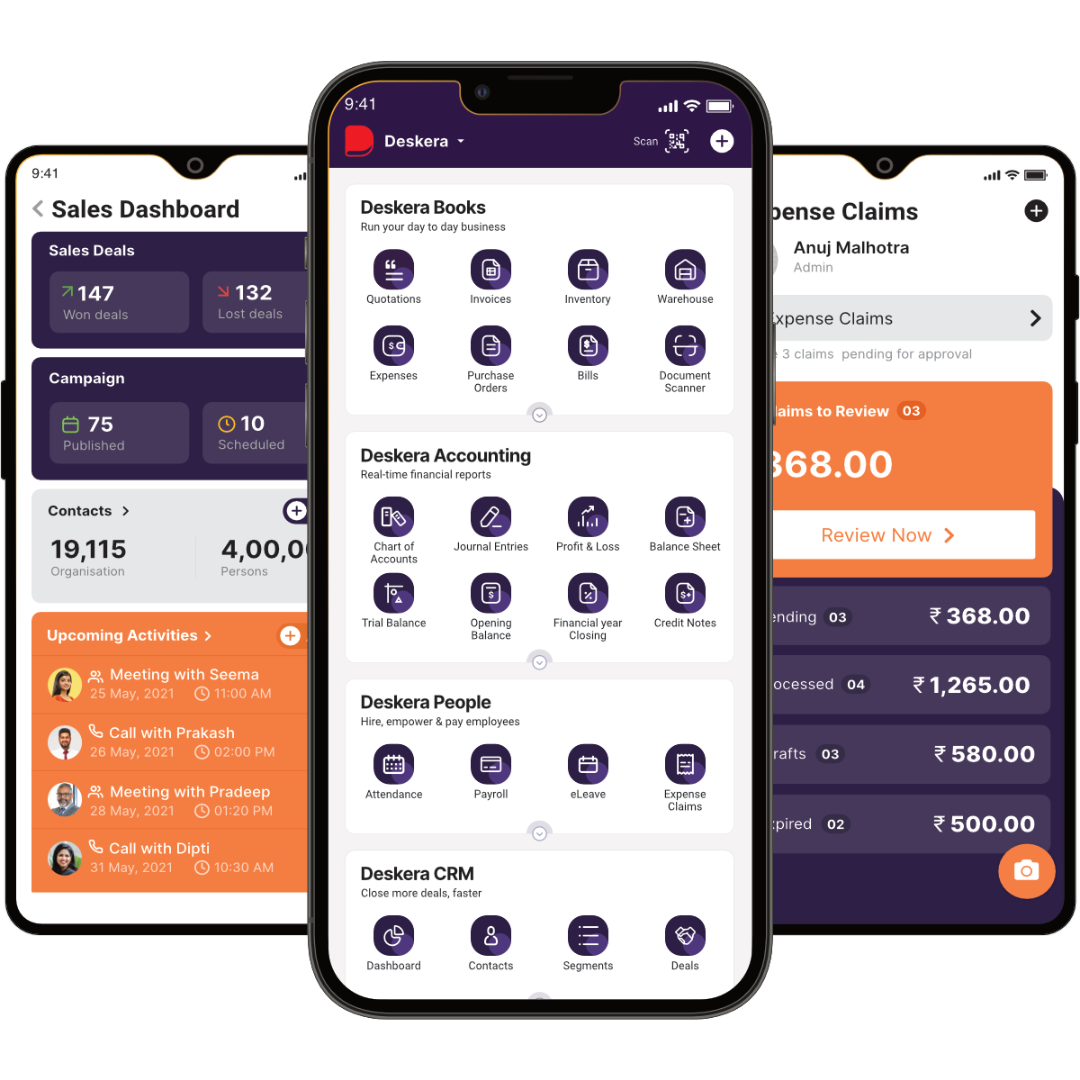
Deskera ERP and MRP system can help you:
- Manage production plans
- Maintain Bill of Materials
- Generate detailed reports
- Create a custom dashboard
Deskera ERP is a comprehensive system that allows you to maintain inventory, manage suppliers, and track supply chain activity in real-time, as well as streamline a variety of other corporate operations.
Deskera Books enables you to manage your accounts and finances more effectively. Maintain sound accounting practices by automating accounting operations such as billing, invoicing, and payment processing.
Deskera CRM is a strong solution that manages your sales and assists you in closing agreements quickly. It not only allows you to do critical duties such as lead generation via email, but it also provides you with a comprehensive view of your sales funnel.
Deskera People is a simple tool for taking control of your human resource management functions. The technology not only speeds up payroll processing but also allows you to manage all other activities such as overtime, benefits, bonuses, training programs, and much more. This is your chance to grow your business, increase earnings, and improve the efficiency of the entire production process.
Conclusion
Analyzing costs associated with chemical manufacturing is crucial for the success of any chemical manufacturing operation. By identifying and tracking the costs associated with each stage of the manufacturing process, manufacturers can better understand their cost structure and identify areas where cost savings can be achieved.
Considering all costs associated with chemical manufacturing, including raw materials, labor, energy, equipment maintenance and depreciation, and regulatory compliance is essential.
By tracking these costs over time and comparing them to production output, manufacturers can gain insights into their overall cost structure and identify areas where efficiency improvements can be made.
It is also crucial for manufacturers to consider the environmental and social costs associated with chemical manufacturing. By adopting sustainable practices and minimizing the use of hazardous materials, manufacturers can reduce their environmental impact and protect workers' and communities' health and safety.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the cost structure of the manufacturing process helps manufacturers identify areas where cost savings can be achieved.
- Tracking all costs associated with chemical manufacturing, including raw materials, labor, energy, equipment maintenance and depreciation, and regulatory compliance, is essential.
- Manufacturers can use cost accounting software and value stream mapping tools to identify and reduce costs associated with the manufacturing process.
- Environmental and social costs associated with chemical manufacturing should also be considered for sustainability and responsible business practices.
- Understanding the lifecycle costs of chemicals and products can help manufacturers make informed decisions about production processes and materials.
- Strategic sourcing and procurement can help manufacturers secure materials and services at competitive prices.
- Using data analytics and performance metrics can help manufacturers track costs and make data-driven decisions to optimize performance.
- Collaboration with suppliers, customers, and other stakeholders can help manufacturers identify opportunities for cost reduction and sustainable practices.
Related Articles